背景 By 魯迅 By 高爾基 說明: 1. Kernel版本:4.14 2. ARM64處理器,Contex A53,雙核 3. 使用工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio 1. 概述 是一種物理地址反向映射虛擬地址的方法。 映射 頁表用於虛擬地址到物理地址映射,其中的 頁表項記 ...
背景
Read the fucking source code!--By 魯迅A picture is worth a thousand words.--By 高爾基
說明:
- Kernel版本:4.14
- ARM64處理器,Contex-A53,雙核
- 使用工具:Source Insight 3.5, Visio
1. 概述
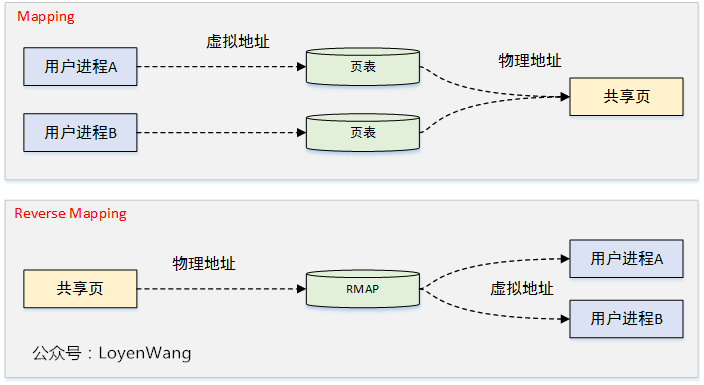
RMAP反向映射是一種物理地址反向映射虛擬地址的方法。
映射
頁表用於虛擬地址到物理地址映射,其中的PTE頁表項記錄了映射關係,同時struct page結構體中的mapcount欄位保存了有多少PTE頁表項映射了該物理頁。反向映射
當某個物理地址要進行回收或遷移時,此時需要去找到有多少虛擬地址射在該物理地址,並斷開映射處理。在沒有反向映射的機制時,需要去遍歷進程的頁表,這個效率顯然是很低下的。反向映射可以找到虛擬地址空間VMA,並僅從VMA使用的用戶頁表中取消映射,可以快速解決這個問題。
反向映射的典型應用場景:
kswapd進行頁面回收時,需要斷開所有映射了該匿名頁面的PTE表項;- 頁面遷移時,需要斷開所有映射了該匿名頁面的PTE表項;
2. 數據結構
反向映射有三個關鍵的結構體:
struct vm_area_struct,簡稱VMA;
VMA我們在之前的文章中介紹過,用於描述進程地址空間中的一段區域。與反向映射相關的欄位如下:
struct vm_area_struct {
...
/*
* A file's MAP_PRIVATE vma can be in both i_mmap tree and anon_vma
* list, after a COW of one of the file pages. A MAP_SHARED vma
* can only be in the i_mmap tree. An anonymous MAP_PRIVATE, stack
* or brk vma (with NULL file) can only be in an anon_vma list.
*/
struct list_head anon_vma_chain; /* Serialized by mmap_sem &
* page_table_lock */
struct anon_vma *anon_vma; /* Serialized by page_table_lock */
...
}struct anon_vma,簡稱AV;
AV結構用於管理匿名類型VMAs,當有匿名頁需要unmap處理時,可以先找到AV,然後再通過AV進行查找處理。結構如下:
/*
* The anon_vma heads a list of private "related" vmas, to scan if
* an anonymous page pointing to this anon_vma needs to be unmapped:
* the vmas on the list will be related by forking, or by splitting.
*
* Since vmas come and go as they are split and merged (particularly
* in mprotect), the mapping field of an anonymous page cannot point
* directly to a vma: instead it points to an anon_vma, on whose list
* the related vmas can be easily linked or unlinked.
*
* After unlinking the last vma on the list, we must garbage collect
* the anon_vma object itself: we're guaranteed no page can be
* pointing to this anon_vma once its vma list is empty.
*/
struct anon_vma {
struct anon_vma *root; /* Root of this anon_vma tree */
struct rw_semaphore rwsem; /* W: modification, R: walking the list */
/*
* The refcount is taken on an anon_vma when there is no
* guarantee that the vma of page tables will exist for
* the duration of the operation. A caller that takes
* the reference is responsible for clearing up the
* anon_vma if they are the last user on release
*/
atomic_t refcount;
/*
* Count of child anon_vmas and VMAs which points to this anon_vma.
*
* This counter is used for making decision about reusing anon_vma
* instead of forking new one. See comments in function anon_vma_clone.
*/
unsigned degree;
struct anon_vma *parent; /* Parent of this anon_vma */
/*
* NOTE: the LSB of the rb_root.rb_node is set by
* mm_take_all_locks() _after_ taking the above lock. So the
* rb_root must only be read/written after taking the above lock
* to be sure to see a valid next pointer. The LSB bit itself
* is serialized by a system wide lock only visible to
* mm_take_all_locks() (mm_all_locks_mutex).
*/
/* Interval tree of private "related" vmas */
struct rb_root_cached rb_root;
};struct anon_vma_chain,簡稱AVC;
AVC是連接VMA和AV之間的橋梁。
/*
* The copy-on-write semantics of fork mean that an anon_vma
* can become associated with multiple processes. Furthermore,
* each child process will have its own anon_vma, where new
* pages for that process are instantiated.
*
* This structure allows us to find the anon_vmas associated
* with a VMA, or the VMAs associated with an anon_vma.
* The "same_vma" list contains the anon_vma_chains linking
* all the anon_vmas associated with this VMA.
* The "rb" field indexes on an interval tree the anon_vma_chains
* which link all the VMAs associated with this anon_vma.
*/
struct anon_vma_chain {
struct vm_area_struct *vma;
struct anon_vma *anon_vma;
struct list_head same_vma; /* locked by mmap_sem & page_table_lock */
struct rb_node rb; /* locked by anon_vma->rwsem */
unsigned long rb_subtree_last;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_VM_RB
unsigned long cached_vma_start, cached_vma_last;
#endif
};來一張圖就清晰明瞭了:

- 通過
same_vma鏈表節點,將anon_vma_chain添加到vma->anon_vma_chain鏈表中; - 通過
rb紅黑樹節點,將anon_vma_chain添加到anon_vma->rb_root的紅黑樹中;
2. 流程分析
先看一下巨集觀的圖:
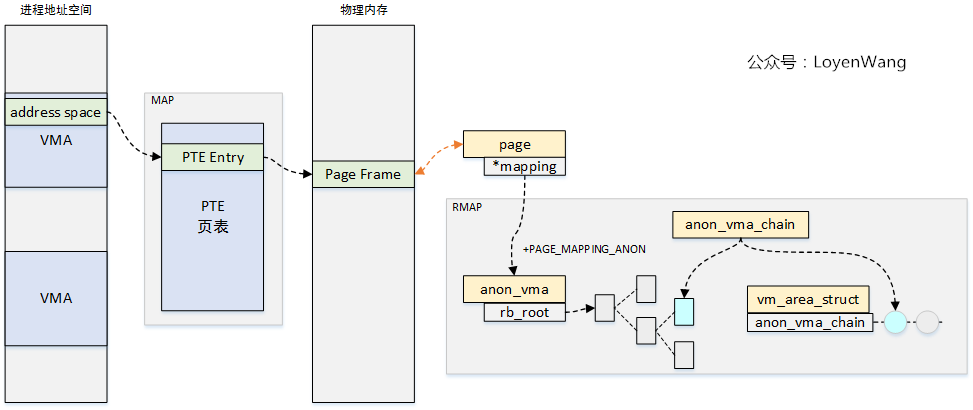
- 地址空間
VMA可以通過頁表完成虛擬地址到物理地址的映射; - 頁框與
page結構對應,page結構中的mapping欄位指向anon_vma,從而可以通過RMAP機制去找到與之關聯的VMA;
2.1 anon_vma_prepare
之前在page fault的文章中,提到過anon_vma_prepare函數,這個函數完成的工作就是為進程地址空間中的VMA準備struct anon_vma結構。
調用常式及函數流程如下圖所示:

至於VMA,AV,AVC三者之間的關聯關係,在上文的圖中已經有所描述。
當創建了與VMA關聯的AV後,還有關鍵的一步需要做完,才能算是真正的把RMAP通路打通,那就是讓page與AV關聯起來。只有這樣才能通過page找到AV,進而找到VMA,從而完成對應的PTE unmap操作。
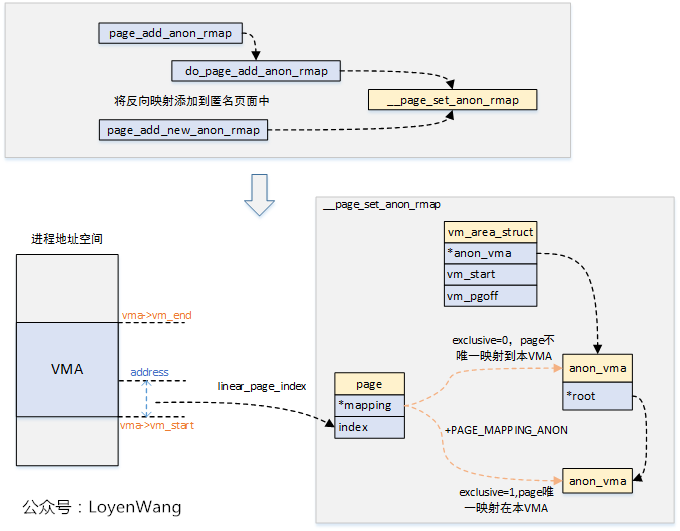
2.2 子進程創建anon_vma
父進程通過fork()來創建子進程,子進程會複製整個父進程的地址空間及頁表。子進程拷貝了父進程的VMA數據結構內容,而子進程創建相應的anon_vma結構,是通過anon_vma_fork()函數來實現的。
anon_vma_fork()效果圖如下:
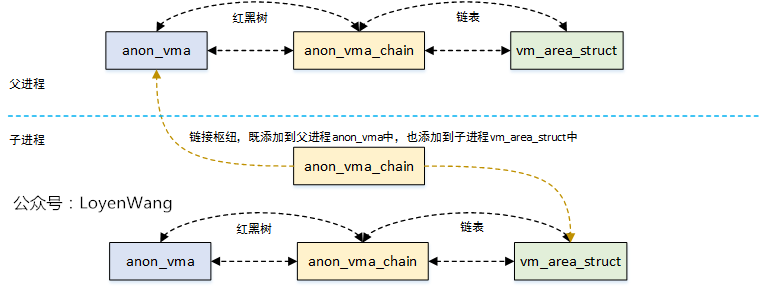
以實際fork()兩次為例,發生COW之後,看看三個進程的鏈接關係,如下圖:
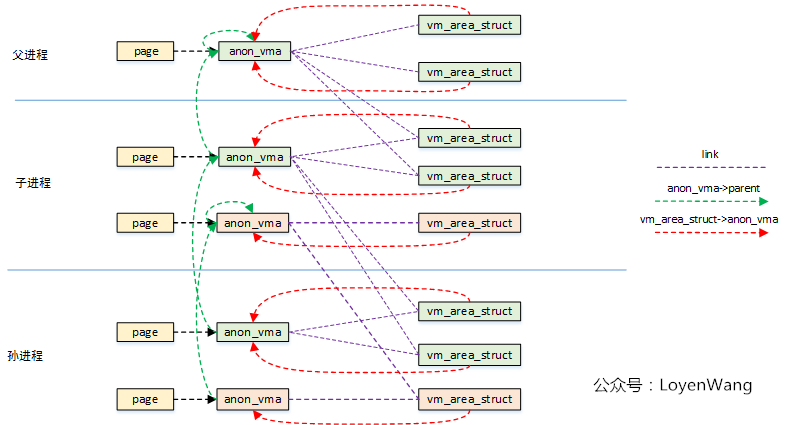
2.3 TTU(try to unmap)和Rmap Walk
如果有page被映射到多個虛擬地址,可以通過Rmap Walk機制來遍歷所有的VMA,並最終調用回調函數來取消映射。
與之相關的結構體為struct rmap_walk_control,如下:
/*
* rmap_walk_control: To control rmap traversing for specific needs
*
* arg: passed to rmap_one() and invalid_vma()
* rmap_one: executed on each vma where page is mapped
* done: for checking traversing termination condition
* anon_lock: for getting anon_lock by optimized way rather than default
* invalid_vma: for skipping uninterested vma
*/
struct rmap_walk_control {
void *arg;
/*
* Return false if page table scanning in rmap_walk should be stopped.
* Otherwise, return true.
*/
bool (*rmap_one)(struct page *page, struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr, void *arg);
int (*done)(struct page *page);
struct anon_vma *(*anon_lock)(struct page *page);
bool (*invalid_vma)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, void *arg);
};
取消映射的入口為try_to_unmap,流程如下圖所示:
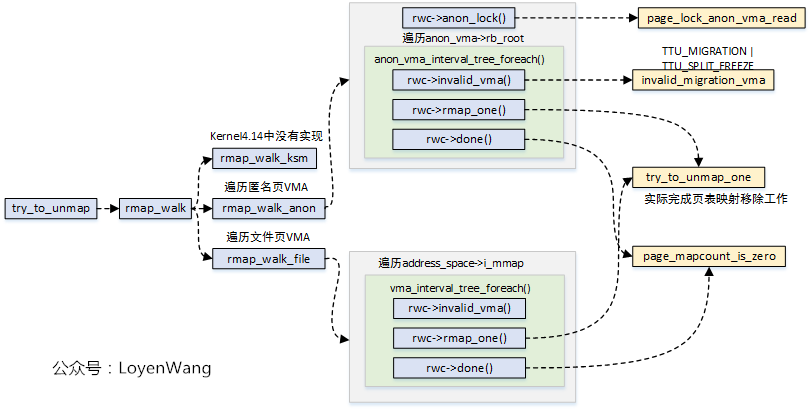
基本的套路就是圍繞著struct rmap_walk_control結構,初始化回調函數,以便在適當的時候能調用到。
關於取消映射try_to_unmap_one的詳細細節就不進一步深入了,把握好大體框架即可。




