最近又學到了很多新知識,感謝優銳課老師細緻地講解,這篇博客記錄下自己所學所想。 想更多地瞭解Spring Boot項目中的功能測試嗎?這篇文章帶你瞭解有關在測試中使用Docker容器的更多信息。 本文重點介紹在Spring Boot應用程式的功能測試期間應用一些最佳實踐。我們將演示一種高級方法,該方 ...
最近又學到了很多新知識,感謝優銳課老師細緻地講解,這篇博客記錄下自己所學所想。
想更多地瞭解Spring Boot項目中的功能測試嗎?這篇文章帶你瞭解有關在測試中使用Docker容器的更多信息。
本文重點介紹在Spring Boot應用程式的功能測試期間應用一些最佳實踐。我們將演示一種高級方法,該方法如何在不設置登臺環境的情況下將服務作為黑盒進行測試。
理論
讓我們從定義功能測試的含義開始:
功能測試是在軟體開發中使用的軟體測試過程,其中對軟體進行測試以確保其符合所有要求。功能測試是一種檢查軟體的方法,以確保軟體具有其功能要求中指定的所有必需功能。
儘管這有點令人困惑,但請不要擔心——以下定義提供了進一步的解釋:
功能測試主要用於驗證某個軟體所提供的輸出與最終用戶或企業所需的輸出相同。通常,功能測試涉及評估每個軟體功能並將其與業務需求進行比較。通過為軟體提供一些相關的輸入來對其進行測試,以便可以評估輸出以查看其與基本要求相比是否相符,相關或變化。此外,功能測試還檢查軟體的可用性,例如通過確保導航功能按要求工作。
在我們的案例中,我們將微服務作為軟體,應根據最終用戶的要求提供一些輸出。
目的
功能測試應涵蓋我們應用程式的以下方面:
- 上下文啟動-確保服務在上下文中沒有衝突,並且可以順利引導。
- 業務需求/用戶案例-這包括請求的功能。
基本上,每個(或大多數)用戶故事都應該有自己專用的功能測試。如果至少有一個功能測試,我們不需要編寫上下文啟動測試,因為它仍然會測試它。
實踐
為了演示如何應用最佳實踐,我們需要編寫一些示例服務。讓我們從頭開始。
任務
我們的新服務要求滿足以下要求:
- 用於存儲和檢索用戶詳細信息的REST API。
- REST API,用於通過REST從聯繫人服務獲取豐富的聯繫方式的用戶詳細信息。
架構設計
對於此任務,我們將使用Spring平臺作為框架,並使用Spring Boot作為應用程式引導程式。為了存儲用戶詳細信息,我們將使用MariaDB。
由於該服務應存儲和檢索用戶詳細信息,因此將其命名為“用戶詳細信息”服務是合乎邏輯的。
在實施之前,應製作組件圖以更好地瞭解系統的主要組件:

實操
以下示例代碼包含許多Lombok批註。你可以在網站上的docs文件中找到有關每個註釋的說明。
Models
用戶詳細信息模型:
1 @Value(staticConstructor = "of") 2 public class UserDetails { 3 String firstName; 4 String lastName; 5 public static UserDetails fromEntity(UserDetailsEntity entity) { 6 return UserDetails.of(entity.getFirstName(), entity.getLastName()); 7 } 8 public UserDetailsEntity toEntity(long userId) { 9 return new UserDetailsEntity(userId, firstName, lastName); 10 } 11 }
用戶聯繫人模型:
1 @Value 2 public class UserContacts { 3 String email; 4 String phone; 5 } 6
具有彙總信息的用戶:
1 @Value(staticConstructor = "of") 2 public class User { 3 UserDetails userDetails; 4 UserContacts userContacts; 5 }
REST API
1 @RestController 2 @RequestMapping("user") 3 @AllArgsConstructor 4 public class UserController { 5 private final UserService userService; 6 @GetMapping("/{userId}") //1 7 public User getUser(@PathVariable("userId") long userId) { 8 return userService.getUser(userId); 9 } 10 @PostMapping("/{userId}/details") //2 11 public void saveUserDetails(@PathVariable("userId") long userId, @RequestBody UserDetails userDetails) { 12 userService.saveDetails(userId, userDetails); 13 } 14 @GetMapping("/{userId}/details") //3 15 public UserDetails getUserDetails(@PathVariable("userId") long userId) { 16 return userService.getDetails(userId); 17 } 18 }
- 按ID獲取用戶彙總數據
- 按ID為用戶發佈用戶詳細信息
- 通過ID獲取用戶詳細信息
聯繫人服務客戶端
1 @Component 2 public class ContactsServiceClient { 3 private final RestTemplate restTemplate; 4 private final String contactsServiceUrl; 5 public ContactsServiceClient(final RestTemplateBuilder restTemplateBuilder, 6 @Value("${contacts.service.url}") final String contactsServiceUrl) { 7 this.restTemplate = restTemplateBuilder.build(); 8 this.contactsServiceUrl = contactsServiceUrl; 9 } 10 public UserContacts getUserContacts(long userId) { 11 URI uri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(contactsServiceUrl + "/contacts") 12 .queryParam("userId", userId).build().toUri(); 13 return restTemplate.getForObject(uri, UserContacts.class); 14 } 15 }
詳細信息實體及其存儲庫
1 @Entity 2 @Data 3 @NoArgsConstructor 4 @AllArgsConstructor 5 public class UserDetailsEntity { 6 @Id 7 private Long id; 8 @Column 9 private String firstName; 10 @Column 11 private String lastName; 12 } 13 @Repository 14 public interface UserDetailsRepository extends JpaRepository<UserDetailsEntity, Long> { 15 }
用戶服務
1 @Service 2 @AllArgsConstructor 3 public class UserService { 4 private final UserDetailsRepository userDetailsRepository; 5 private final ContactsServiceClient contactsServiceClient; 6 public User getUser(long userId) { 7 UserDetailsEntity userDetailsEntity = userDetailsRepository.getOne(userId); //1 8 UserDetails userDetails = UserDetails.fromEntity(userDetailsEntity); 9 UserContacts userContacts = contactsServiceClient.getUserContacts(userId); //2 10 return User.of(userDetails, userContacts); //3 11 } 12 public void saveDetails(long userId, UserDetails userDetails) { 13 UserDetailsEntity entity = userDetails.toEntity(userId); 14 userDetailsRepository.save(entity); 15 } 16 public UserDetails getDetails(long userId) { 17 UserDetailsEntity userDetailsEntity = userDetailsRepository.getOne(userId); 18 return UserDetails.fromEntity(userDetailsEntity); 19 } 20 }
- 從資料庫檢索用戶詳細信息
- 從通訊錄服務中檢索用戶通訊錄
- 向用戶返回彙總數據
應用及其屬性
UserDetailsServiceApplication.java
1 @SpringBootApplication 2 public class UserDetailsServiceApplication { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 SpringApplication.run(UserDetailsServiceApplication.class, args); 5 } 6 }
application.properties:
1 #contact service 2 contacts.service.url=http://www.prod.contact.service.com 3 #database 4 user.details.db.host=prod.maria.url.com 5 user.details.db.port=3306 6 user.details.db.schema=user_details 7 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mariadb://${user.details.db.host}:${user.details.db.port}/${user.details.db.schema} 8 spring.datasource.username=prod-username 9 spring.datasource.password=prod-password 10 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver
POM文件
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 5 <artifactId>user-details-service</artifactId> 6 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 7 <packaging>jar</packaging> 8 <name>User details service</name> 9 <parent> 10 <groupId>com.tdanylchuk</groupId> 11 <artifactId>functional-tests-best-practices</artifactId> 12 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 13 </parent> 14 <dependencies> 15 <dependency> 16 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 17 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> 18 </dependency> 19 <dependency> 20 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 21 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 22 </dependency> 23 <dependency> 24 <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> 25 <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> 26 <scope>provided</scope> 27 </dependency> 28 <dependency> 29 <groupId>org.mariadb.jdbc</groupId> 30 <artifactId>mariadb-java-client</artifactId> 31 <version>2.3.0</version> 32 </dependency> 33 </dependencies> 34 <build> 35 <plugins> 36 <plugin> 37 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 38 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> 39 </plugin> 40 </plugins> 41 </build> 42 </project>
註意:父級是自定義的功能測試最佳實踐項目,該項目繼承了spring-boot-starter-parent。稍後將介紹其目的。
Structure
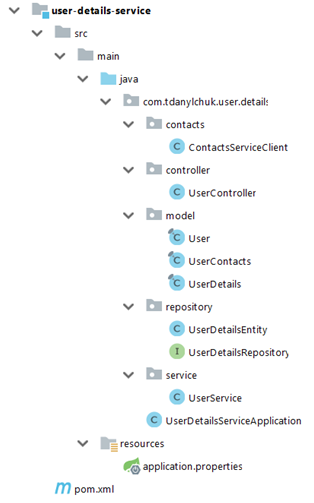
這幾乎是我們滿足初始需求所需的一切:保存和檢索用戶詳細信息以及檢索包含聯繫人的用戶詳細信息。
功能測試
是時候添加功能測試了!對於TDD,在實現之前需要閱讀本節。
地點
開始之前,我們需要選擇功能測試的位置;還有兩個更合適的地方:
- 與單元測試一起在單獨的文件夾中:
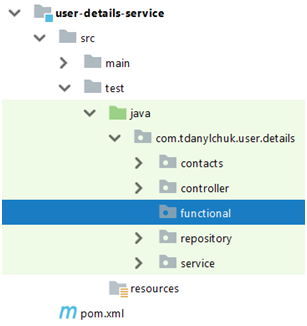
這是開始添加功能測試的最簡單,最快的方法,儘管它有一個很大的缺點:如果要單獨運行單元測試,則需要排除功能測試文件夾。為什麼每次應用較小的代碼修改後都不運行所有測試?因為在大多數情況下,功能測試與單元測試相比具有巨大的執行時間,因此應單獨進行修改以節省開發時間。
- 在一個單獨的項目以及一個公共父項下的服務項目中:
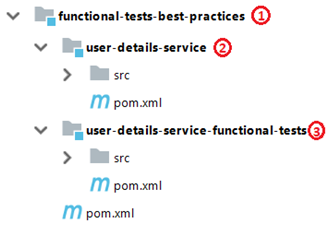
- Parent POM (aggregative project)
- Service project
- Functional tests project
這種方法比以前的方法有一個優勢——我們有一個與服務單元測試隔離的功能測試模塊,因此我們可以通過分別運行單元測試或功能測試輕鬆地驗證邏輯。另一方面,這種方法需要一個多模塊的項目結構,與單模塊的項目相比,難度更大。
你可能已經從服務pom.xml中猜到了,對於我們的情況,我們將選擇第二種方法。
父POM文件
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 5 <groupId>com.tdanylchuk</groupId> 6 <artifactId>functional-tests-best-practices</artifactId> 7 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 8 <packaging>pom</packaging> 9 <name>Functional tests best practices parent project</name> 10 <parent> <!--1--> 11 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 12 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 13 <version>2.0.4.RELEASE</version> 14 <relativePath/> 15 </parent> 16 <modules> <!--2--> 17 <module>user-details-service</module> 18 <module>user-details-service-functional-tests</module> 19 </modules> 20 <properties> 21 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 22 <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> 23 <java.version>1.8</java.version> 24 </properties> 25 </project>
- spring-boot-starter-parent是我們的父POM的父項目。這樣,我們就為Spring提供了依賴管理。
- 模塊聲明。註意:順序很重要,功能測試應始終排在最後。
案例
為了挑選功能測試涵蓋的案例,我們需要考慮兩個主要方面:
- 功能需求——基本上,每個請求的需求都應具有自己的功能測試。
- 較長的執行時間——專註於應用程式的關鍵部分,與單元測試相反,在單元測試中,應涵蓋每個較小的案例。否則,構建時間將是巨大的。
Architecture
是的,測試還需要架構,尤其是功能測試,在這些測試中執行時間很重要,邏輯可能會隨著時間變得過於複雜。而且,它們應該是可維護的。這意味著,如果發生功能轉移,功能測試對於開發人員而言將不會是頭痛的事情。
Steps
步驟(也稱為固定裝置)是一種封裝每個通信通道邏輯的方法。 每個通道應具有自己的步驟對象,該對象與其他步驟隔離。
就我們而言,我們有兩個溝通渠道:
- 用戶詳細信息服務REST API(在渠道中)
- 聯繫人服務REST API(渠道外)
對於通道中的REST,我們將使用名為REST Assured的庫。與我們使用MockMvc進行REST API驗證的集成測試相比,這裡我們使用更多的黑盒風格測試,以免將Spring上下文與測試模擬對象弄混。
至於REST out通道,將使用WireMock。我們不會指出Spring用模擬的模板替代REST模板。取而代之的是,WireMock在後臺使用的碼頭伺服器將與我們的服務一起被引導,以模擬真正的外部REST服務。
用戶詳細信息步驟
1 @Component 2 public class UserDetailsServiceSteps implements ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> { 3 private int servicePort; 4 public String getUser(long userId) { 5 return given().port(servicePort) 6 .when().get("user/" + userId) 7 .then().statusCode(200).contentType(ContentType.JSON).extract().asString(); 8 } 9 public void saveUserDetails(long userId, String body) { 10 given().port(servicePort).body(body).contentType(ContentType.JSON) 11 .when().post("user/" + userId + "/details") 12 .then().statusCode(200); 13 } 14 public String getUserDetails(long userId) { 15 return given().port(servicePort) 16 .when().get("user/" + userId + "/details") 17 .then().statusCode(200).contentType(ContentType.JSON).extract().asString(); 18 } 19 @Override 20 public void onApplicationEvent(@NotNull WebServerInitializedEvent webServerInitializedEvent) { 21 this.servicePort = webServerInitializedEvent.getWebServer().getPort(); 22 } 23 }
從步驟對象中可以看到,每個API端點都有自己的方法。
預設情況下,REST安全的將調用localhost,但是需要指定埠,因為我們的服務將使用隨機埠引導。為了區分它,應該偵聽WebServerInitializedEvent。
註意:這裡不能使用@LocalServerPor註釋,因為在Spring Boot嵌入式容器啟動之前已創建步驟bean。
聯絡人服務步驟
1 @Component 2 public class ContactsServiceSteps { 3 public void expectGetUserContacts(long userId, String body) { 4 stubFor(get(urlPathMatching("/contacts")).withQueryParam("userId", equalTo(String.valueOf(userId))) 5 .willReturn(okJson(body))); 6 } 7 }
在這裡,我們需要以與從應用程式調用遠程服務時完全相同的方式對伺服器進行模擬:端點,參數等。
資料庫
我們的服務是將數據存儲在Maria DB中,但是就功能測試而言,存儲數據的位置無關緊要,因此,如黑盒測試所要求的,在測試中不應提及任何內容。
在將來,如果我們考慮將Maria DB更改為某些NoSQL解決方案,則測試應保持不變。
但是,解決方案是什麼?
當然,我們可以像在集成測試中對H2資料庫那樣使用嵌入式解決方案,但是在生產中,我們的服務將使用Maria DB,這可能會導致出現問題。
例如,我們有一個名為MAXVALUE的列,並針對H2運行測試,一切正常。但是,在生產中,該服務失敗,因為這是MariaDB中的保留字,這意味著我們的測試不如預期的好,並且可能會浪費大量時間來解決問題,而該服務將保持不發佈狀態。
避免這種情況的唯一方法是在測試中使用真正的Maria DB。同時,我們需要確保我們的測試可以在本地執行,而無需在其中設置Maria DB的任何其他登臺環境中。
為瞭解決這個問題,我們將選擇testcontainers項目,該項目提供了常見資料庫,Selenium Web瀏覽器或可在Docker容器中運行的任何其他東西的輕量級,一次性的實例。
但是testcontainers庫不支持開箱即用的Spring Boot。因此,我們將使用另一個名為testcontainers-spring-boot的庫,而不是為MariaDB編寫自定義的通用容器並將其手動註入Spring Boot。它支持可能在你的服務中使用的最常見技術,例如:MariaDB,Couchbase,Kafka,Aerospike,MemSQL,Redis,neo4j,Zookeeper,PostgreSQL,ElasticSearch。
要將真正的Maria DB註入我們的測試中,我們只需要向我們的user-details-service-functional-tests項目pom.xml文件中添加適當的依賴項,如下所示:
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>com.playtika.testcontainers</groupId> 3 <artifactId>embedded-mariadb</artifactId> 4 <version>1.9</version> 5 <scope>test</scope> 6 </dependency>
如果你的服務不使用Spring Cloud,則應在上述依賴項的基礎上添加下一個依賴項:
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId> 4 <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> 5 <scope>test</scope> 6 </dependency>
在Spring Boot上下文啟動之前,它需要對dockerized資源進行引導。
這種方法顯然有很多優點。由於我們擁有“真實”資源,因此如果無法測試所需資源的真實連接,則無需在代碼中編寫變通辦法。 不幸的是,該解決方案帶來了一個巨大的缺點——測試只能在安裝了Docker的環境中運行。 這意味著你的工作站和CI工具應在板載Docker上。另外,你應該準備好測試將需要更多的時間來執行。
Parent Tests Class
由於執行時間很重要,因此我們需要避免為每個測試載入多個上下文,因此Docker容器將僅對所有測試啟動一次。Spring預設情況下啟用了上下文緩存功能,但是我們需要謹慎,因為通過僅添加簡單的註釋@MockBean,我們迫使Spring使用模擬的bean創建新的上下文,而不是重用現有的上下文。這個問題的解決方案是創建一個單一的父抽象類,該類將包含所有必需的Spring批註,以確保將單個上下文重用於所有測試套件:
1 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) 2 @SpringBootTest( 3 classes = UserDetailsServiceApplication.class, //1 4 webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) //2 5 @ActiveProfiles("test") //3 6 public abstract class BaseFunctionalTest { 7 @Rule 8 public WireMockRule contactsServiceMock = new WireMockRule(options().port(8777)); //4 9 @Autowired //5 10 protected UserDetailsServiceSteps userDetailsServiceSteps; 11 @Autowired 12 protected ContactsServiceSteps contactsServiceSteps; 13 @TestConfiguration //6 14 @ComponentScan("com.tdanylchuk.user.details.steps") 15 public static class StepsConfiguration { 16 } 17 }
- 指向Spring Boot測試註釋以載入我們服務的主要配置類。
- 在生產環境中使用Bootstraps Web環境(預設情況下使用模擬的環境)
- 需要測試配置文件來載入application-test.properties,其中將覆蓋生產屬性,例如URL,用戶,密碼等。
WireMockRule啟動碼頭伺服器以在提供的埠上存根。- 步驟的受保護的自動接線,因此在每次測試中都可以訪問它們。
-
@TestConfiguration通過掃描程式包將步驟載入到上下文中。
在這裡,我們試圖不修改上下文,將在生產環境中通過向其中添加一些util項來進一步使用該上下文,例如步驟和屬性覆蓋。
使用@MockBean註釋是不好的做法,該註釋將應用程式的一部分替換為模擬,並且該部分將保持未經測試的狀態。
不可避免的情況-即在邏輯中檢索當前時間,例如System.currentTimeMillis(),應重構此類代碼,因此將改用Clock對象:clock.millis()。並且,在功能測試中,應該模擬Clock對象,以便可以驗證結果。
測試性質
application-test.properties:
1 #contact service #1 2 contacts.service.url=http://localhost:8777 3 #database #2 4 user.details.db.host=${embedded.mariadb.host} 5 user.details.db.port=${embedded.mariadb.port} 6 user.details.db.schema=${embedded.mariadb.schema} 7 spring.datasource.username=${embedded.mariadb.user} 8 spring.datasource.password=${embedded.mariadb.password} 9 #3 10 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
- 使用WireMock碼頭伺服器端點而不是生產聯繫服務URL。
- 資料庫屬性的覆蓋。註意:這些屬性由spring-boo-test-containers庫提供。
- 在測試中,資料庫架構將由Hibernate創建。
自我測試
為了進行此測試,已經做了很多準備工作,所以讓我們看一下它的外觀:
1 public class RestUserDetailsTest extends BaseFunctionalTest { 2 private static final long USER_ID = 32343L; 3 private final String userContactsResponse = readFile("json/user-contacts.json"); 4 private final String userDetails = readFile("json/user-details.json"); 5 private final String expectedUserResponse = readFile("json/user.json"); 6 @Test 7 public void shouldSaveUserDetailsAndRetrieveUser() throws Exception { 8 //when 9 userDetailsServiceSteps.saveUserDetails(USER_ID, userDetails); 10 //and 11 contactsServiceSteps.expectGetUserContacts(USER_ID, userContactsResponse); 12 //then 13 String actualUserResponse = userDetailsServiceSteps.getUser(USER_ID); 14 //expect 15 JSONAssert.assertEquals(expectedUserResponse, actualUserResponse, false); 16 } 17 }
對於stubbing和asserting,使用先前通過JSON文件創建的。這樣,請求和響應格式都得到了驗證。最好不要在此處使用測試數據,而應使用生產請求/響應的副本。
由於整個邏輯都封裝在步驟,配置和JSON文件中,因此如果更改與功能無關,則此測試將保持不變。例如:
- 響應更改的格式-僅應修改測試JSON文件。
- 聯繫人服務端點更改-應該修改
ContactsServiceSteps對象。 - Maria DB被No SQL DB取代-pom.xml和測試屬性文件應被修改。
功能測試項目
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 5 <artifactId>user-details-service-functional-tests</artifactId> 6 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 7 <name>User details service functional tests</name> 8 <parent> 9 <groupId>com.tdanylchuk</groupId> 10 <artifactId>functional-tests-best-practices</artifactId> 11 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 12 </parent> 13 <dependencies> 14 <dependency> <!--1--> 15 <groupId>com.tdanylchuk</groupId> 16 <artifactId>user-details-service</artifactId> 17 <version>${project.version}</version> 18 <scope>test</scope> 19 </dependency> 20 <dependency> 21 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 22 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 23 <scope>test</scope> 24 </dependency> 25 <dependency> 26 <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> 27 <artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId> 28 <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> 29 <scope>test</scope> 30 </dependency> 31 <dependency> 32 <groupId>com.playtika.testcontainers</groupId> 33 <artifactId>embedded-mariadb</artifactId> 34 <version>1.9</version> 35 <scope>test</scope> 36 </dependency> 37 <dependency> 38 <groupId>com.github.tomakehurst</groupId> 39 <artifactId>wiremock</artifactId> 40 <version>2.18.0</version> 41 <scope>test</scope> 42 </dependency> 43 <dependency> 44 <groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId> 45 <artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId> 46 <scope>test</scope> 47 </dependency> 48 </dependencies> 49 </project>
- 添加了用戶詳細信息服務作為依賴項,因此可以由
SpringBootTest載入。
結構體
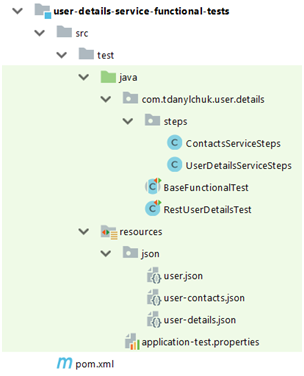
放在一起,我們就有了下一個結構。
向服務添加功能不會更改當前結構,只會擴展它。如果增加了更多的通信渠道,則可以通過其他步驟執行以下操作:使用常用方法添加utils文件夾;帶有測試數據的新文件;當然,還要針對每個功能要求進行額外的測試。
結論
在本文中,我們根據給定的需求構建了一個新的微服務,並通過功能測試涵蓋了這些需求。在測試中,我們使用了黑盒類型的測試,在這種測試中,我們嘗試不更改應用程式的內部部分,而是作為普通客戶端從外部與它進行通信,以儘可能地模擬生產行為。同時,我們奠定了功能測試體繫結構的基礎,因此將來的服務更改將不需要重構現有測試,並且添加新測試將儘可能地容易。



