1、算術運算: 2、比較運算: 3、賦值運算: 4、邏輯運算: 5、成員運算: 1、數字 int(整型) 在32位機器上,整數的位數為32位,取值範圍為-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647 在64位系統上,整數的位數為64位,取值範圍為-2**63~2**63 ...
| Python 運算符 |
1、算術運算:
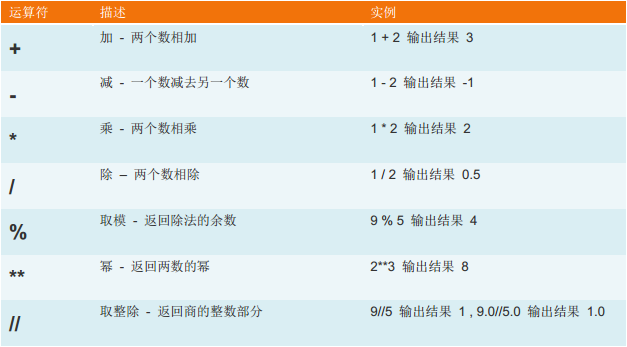
2、比較運算:
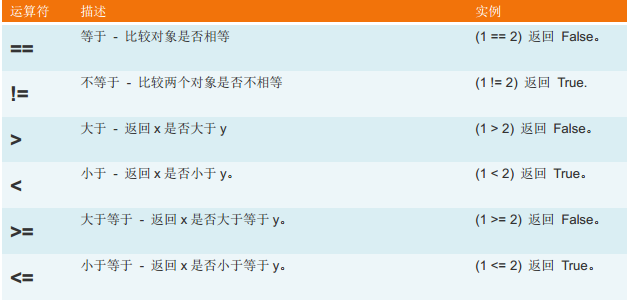
3、賦值運算:
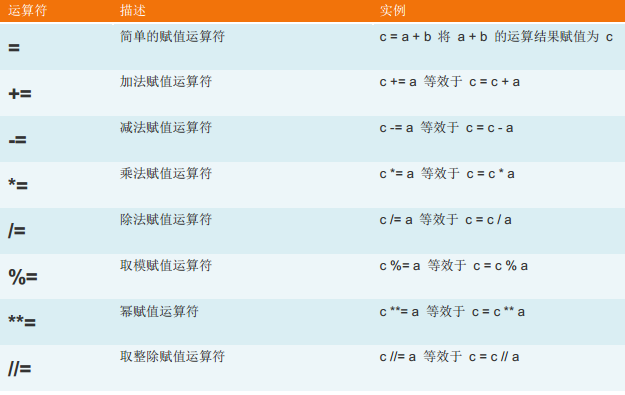
4、邏輯運算:
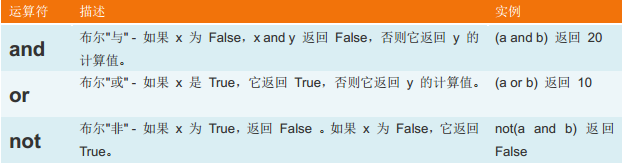
5、成員運算:

| 基本數據類型 |
1、數字
int(整型)
在32位機器上,整數的位數為32位,取值範圍為-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647在64位系統上,整數的位數為64位,取值範圍為-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
#返回表示該數字的時占用的最少位數
>>> (951).bit_length()
10
#返回絕對值
>>> (95).__abs__()
95
>>> (-95).__abs__()
95
#用來區分數字和字元串的
>>> (95).__add__(1)
96
>>> (95).__add__("1")
NotImplemented
#判斷一個整數對象是否為0,如果為0,則返回False,如果不為0,則返回True
>>> (95).__bool__()
True
>>> (0).__bool__()
False
#判斷兩個值是否相等
>>> (95).__eq__(95)
True
>>> (95).__eq__(9)
False
#判斷是否不等於
>>> (95).__ne__(9)
True
>>> (95).__ne__(95)
False
#判斷是否大於等於
>>> (95).__ge__(9)
True
>>> (95).__ge__(99)
False
#判斷是否大於
>>> (95).__gt__(9)
True
>>> (95).__gt__(99)
False
#判斷是否小於等於
>>> (95).__le__(99)
True
>>> (95).__le__(9)
False
#判斷是否小於
>>> (95).__lt__(9)
False
>>> (95).__lt__(99)
True
#加法運算
>>> (95).__add__(5)
100
#減法運算
>>> (95).__sub__(5)
90
#乘法運算
>>> (95).__mul__(10)
950
#除法運算
>>> (95).__truediv__(5)
19.0
#取模運算
>>> (95).__mod__(9)
5
#冪運算
>>> (2).__pow__(10)
1024
#整除,保留結果的整數部分
>>> (95).__floordiv__(9)
>>>
#轉換為整型
>>> (9.5).__int__()
9
#返回一個對象的整數部分
>>> (9.5).__trunc__()
9
#將正數變為負數,將負數變為正數
>>> (95).__neg__()
-95
>>> (-95).__neg__()
95
#將一個正數轉為字元串
>>> a = 95
>>> a = a.__str__()
>>> print(type(a))
<class 'str'>
#將一個整數轉換成浮點型
>>> (95).__float__()
95.0
#轉換對象的類型
>>> (95).__format__('f')
'95.000000'
>>> (95).__format__('b')
'1011111'
#在記憶體中占多少個位元組
>>> a = 95
>>> a.__sizeof__()
28

class int(object): """ int(x=0) -> integer int(x, base=10) -> integer Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point numbers, this truncates towards zero. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int('0b100', base=0) """ def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ int.bit_length() -> int Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. """ """ 表示該數字返回時占用的最少位數 >>> (951).bit_length() 10 """ return 0 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int.""" """ 返回該複數的共軛複數 #返回覆數的共軛複數 >>> (95 + 11j).conjugate() (95-11j) #返回覆數的實數部分 >>> (95 + 11j).real 95.0 #返回覆數的虛數部分 >>> (95 + 11j).imag 11.0 """ pass @classmethod # known case def from_bytes(cls, bytes, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ """ int.from_bytes(bytes, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> int Return the integer represented by the given array of bytes. The bytes argument must be a bytes-like object (e.g. bytes or bytearray). The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value. The signed keyword-only argument indicates whether two's complement is used to represent the integer. """ """ 這個方法是在Python3.2的時候加入的,python官方給出了下麵幾個例子: >>> int.from_bytes(b'\x00\x10', byteorder='big') >>> int.from_bytes(b'\x00\x10', byteorder='little') >>> int.from_bytes(b'\xfc\x00', byteorder='big', signed=True) -1024 >>> int.from_bytes(b'\xfc\x00', byteorder='big', signed=False) >>> int.from_bytes([255, 0, 0], byteorder='big') """ pass def to_bytes(self, length, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__ """ int.to_bytes(length, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> bytes Return an array of bytes representing an integer. The integer is represented using length bytes. An OverflowError is raised if the integer is not representable with the given number of bytes. The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value. The signed keyword-only argument determines whether two's complement is used to represent the integer. If signed is False and a negative integer is given, an OverflowError is raised. """ """ python官方給出了下麵幾個例子: >>> (1024).to_bytes(2, byteorder='big') b'\x04\x00' >>> (1024).to_bytes(10, byteorder='big') b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x04\x00' >>> (-1024).to_bytes(10, byteorder='big', signed=True) b'\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xfc\x00' >>> x = 1000 >>> x.to_bytes((x.bit_length() // 8) + 1, byteorder='little') b'\xe8\x03' """ pass def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ abs(self)""" """ 返回一個絕對值 >>> (95).__abs__() -95 >>> (-95).__abs__() 95 """ pass def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self+value.""" """ 加法,也可區分數字和字元串 >>> (95).__add__(1) 96 >>> (95).__add__("1") NotImplemented >>> """ pass def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self&value.""" pass def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ self != 0 """ """ 判斷一個整數對象是否為0,如果為0,則返回False,如果不為0,則返回True >>> (95).__bool__() True >>> (0).__bool__() False """ pass def __ceil__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Ceiling of an Integral returns itself. """ pass def __divmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return divmod(self, value). """ """ 返回一個元組,第一個元素為商,第二個元素為餘數 >>> (9).__divmod__(5) (1, 4) """ pass def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self==value. """ """ 判斷兩個值是否相等 >>> (95).__eq__(95) True >>> (95).__eq__(9) False """ pass def __float__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ float(self) """ """ 將一個整數轉換成浮點型 >>> (95).__float__() 95.0 """ pass def __floordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self//value. """ """ 整除,保留結果的整數部分 >>> (95).__floordiv__(9) 10 """ pass def __floor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Flooring an Integral returns itself. """ """ 返回本身 >>> (95).__floor__() 95 """ pass def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ 轉換對象的類型 >>> (95).__format__('f') '95.000000' >>> (95).__format__('b') '1011111' """ pass def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return getattr(self, name). """ """ 判斷這個類中是否包含這個屬性,如果包含則列印出值,如果不包含,就報錯了 >>> (95).__getattribute__('__abs__') <method-wrapper '__abs__' of int object at 0x9f93c0> >>> (95).__getattribute__('__aaa__') Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> AttributeError: 'int' object has no attribute '__aaa__' """ pass def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown pass def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>=value. """ """ 判斷是否大於等於 >>> (95).__ge__(9) True >>> (95).__ge__(99) False """ pass def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>value. """ """ 判斷是否大於 >>> (95).__gt__(9) True >>> (95).__gt__(99) False """ pass def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return hash(self). """ """ 計算哈希值,整數返回本身 >>> (95).__hash__() 95 >>> (95.95).__hash__() 2190550858753015903 """ pass def __index__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list. """ pass def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__ """ 這個是一個類的初始化方法,當int類被實例化的時候,這個方法預設就會被執行 """ """ int(x=0) -> integer int(x, base=10) -> integer Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point numbers, this truncates towards zero. If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string, bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. >>> int('0b100', base=0) # (copied from class doc) """ pass def __int__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ int(self) """ """ 轉換為整型 >>> (9.5).__int__() 9 """ pass def __invert__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ ~self """ pass def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<=value. """ """ 判斷是否小於等於 >>> (95).__le__(99) True >>> (95).__le__(9) False """ pass def __lshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<<value. """ """ 用於二進位位移,這個是向左移動 >>> bin(95) '0b1011111' >>> a = (95).__lshift__(2) >>> bin(a) '0b101111100' >>> """ pass def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self<value. """ """ 判斷是否小於 >>> (95).__lt__(9) False >>> (95).__lt__(99) True """ pass def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self%value. """ """ 取模 % >>> (95).__mod__(9) """ pass def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self*value. """ """ 乘法 * >>> (95).__mul__(10) """ pass def __neg__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ -self """ """ 將正數變為負數,將負數變為正數 >>> (95).__neg__() -95 >>> (-95).__neg__() 95 """ pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__ def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """ pass def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self!=value. """ """ 不等於 >>> (95).__ne__(9) True >>> (95).__ne__(95) False """ pass def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self|value. """ """ 二進位或的關係,只要有一個為真,就為真 >>> a = 4 >>> b = 0 >>> a.__or__(b) # a --> 00000100 b --> 00000000 >>> b = 1 # b --> 00000001 >>> a.__or__(b) """ pass def __pos__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ +self """ pass def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return pow(self, value, mod). """ """ 冪 >>> (2).__pow__(10) 1024 """ pass def __radd__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signatre unknown """ Return value+self. """ """ 加法,將value放在前面 >>> a.__radd__(b) # 相當於 b+a """ pass def __rand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value&self. """ """ 二進位與的關係,兩個都為真,才為真,有一個為假,就為假 """ pass def __rdivmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return divmod(value, self). """ pass def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return repr(self). """ pass def __rfloordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value//self. """ pass def __rlshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value<<self. """ pass def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value%self. """ pass def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value*self. """ pass def __ror__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value|self. """ pass def __round__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Rounding an Integral returns itself. Rounding with an ndigits argument also returns an integer. """ pass def __rpow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return pow(value, self, mod). """ pass def __rrshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value>>self. """ pass def __rshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self>>value. """ pass def __rsub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value-self. """ pass def __rtruediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value/self. """ pass def __rxor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return value^self. """ pass def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Returns size in memory, in bytes """ """ 在記憶體中占多少個位元組 >>> a = 95 >>> a.__sizeof__() 28 """ pass def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return str(self). """ """ 將一個正數轉為字元串 >>> a = 95 >>> a = a.__str__() >>> print(type(a)) <class 'str'> """ pass def __sub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self-value. """ """ 減法運算 >>> (95).__sub__(5) 90 """ pass def __truediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self/value. """ """ 除法運算 >>> (95).__truediv__(5) 19.0 """ pass def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Truncating an Integral returns itself. """ """ 返回一個對象的整數部分 >>> (95.95).__trunc__() 95 """ pass def __xor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown """ Return self^value. """ """ 將對象與值進行二進位的或運算,一個為真,就為真 >>> a = 4 >>> b = 1 >>> a.__xor__(b) >>> c = 0 >>> a.__xor__(c) """ pass denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 分母 = 1 """ """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 虛數 """ """the imaginary part of a complex number""" numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 分子 = 數字大小 """ """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default """ 實屬 """ """the real part of a complex number"""int
2、布爾值
真或假 1 或 03、字元串
"Hello World!"
s = "nick"
#索引
print(s[0])
print(s[1])
print(s[2])
print(s[3])
#長度
ret = len(s)
print(ret)
#切片
print(s[1:3])
print(s.rsplit("ic"))
#替換
name = "Nick is good, Today is nice day."
a = name.replace("good","man")
print(a)
#連接兩個字元串
li = ["nick","serven"]
a = "".join(li)
b = "_".join(li)
print(a)
print(b)
#指定的分隔符將字元串進行分割
a = s.rpartition("i")
print(a)
#分割,前,中,後三部分
name = "Nick is good, Today is nice day."
a = name.partition("good")
print(a)
#for迴圈
for i in s:
print(i)
for i in range(5):
print(i)

class str(object): """ str(object='') -> str str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler. Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined) or repr(object). encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding(). errors defaults to 'strict'. """ def capitalize(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 首字母變大寫 name = "nick is good, Today is nice day." a = name.capitalize() print(a) """ S.capitalize() -> str Return a capitalized version of S, i.e. make the first character have upper case and the rest lower case. """ return "" def casefold(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 首字母變小寫 name = "Nick is good, Today is nice day. a =name.casefold() print(a) """ S.casefold() -> str Return a version of S suitable for caseless comparisons. """ return "" def center(self, width, fillchar=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 內容居中,width:總長度;fillchar:空白處填充內容,預設無。 name = "Nick is good, Today is nice day. a = name.center(60,'$') print(a) """ S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is done using the specified fill character (default is a space) """ return "" def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 子序列個數,0到26中n出現了幾次。 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. a = name.count("n",0,26) print(a) """ S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. """ return 0 def encode(self, encoding='utf-8', errors='strict'): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ 編碼,針對unicode. temp = "燒餅 temp.encode("unicode") """ S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes Encode S using the codec registered for encoding. Default encoding is 'utf-8'. errors may be given to set a different error handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and 'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with codecs.register_error that can handle UnicodeEncodeErrors. """ return b"" def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ 是否以XX結束,0到4是否以k結尾 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. a = name.endswith("k",0,4) print(a) """ S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise. With optional start, test S beginning at that position. With optional end, stop comparing S at that position. suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try. """ return False def expandtabs(self, tabsize=8): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ 將tab轉換成空格,預設一個tab轉換成8個空格 a = n.expandtabs() b = n.expandtabs(16) print(a) print(b) """ S.expandtabs(tabsize=8) -> str Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces. If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed. """ return "" def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ 尋找子序列位置,如果沒找到,返回 -1。 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. " a = name.find("nickk") print(a) """ S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found, such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation. Return -1 on failure. """ return 0 def format(self, *args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format """ """ 字元串格式化,動態參數 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. " a = name.format() print(a) """ S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs. The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}'). """ pass def format_map(self, mapping): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ dict = {'Foo': 54.23345} fmt = "Foo = {Foo:.3f}" result = fmt.format_map(dict) print(result) #Foo = 54.233 """ S.format_map(mapping) -> str Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from mapping. The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}'). """ return "" def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ #子序列位置,如果沒有找到就報錯 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. " a = name.index("nick") print(a) """ S.index(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found. """ return 0 def isalnum(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ 是否是字母和數字 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. " a = name.isalnum() print(a) """ S.isalnum() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def isalpha(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ """ 是否是字母 name = "nck is good, Today is nice day. " a = name.isalpha() print(a) """ S.isalpha() -> bool Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise. """ return False def isdecimal(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """ 檢查字元串是否只包含十進位字元。這種方法只存在於unicode對象。 """ S.isdecimal() -> bool Return True if there are only decimal characters in S, False otherwise. """ return False def isdigit(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ """




