浮動基本介紹 在標準文檔流中元素分為2種, 和`行內元素`,如果想讓一些元素既要有塊級元素的特點也同時保留行內元素特點,只能讓這些元素脫離標準文檔流即可。 浮動可以讓元素脫離標準文檔流,可以實現讓多個元素排在同一行,並且可以設置寬高度。 其實浮動是通過 屬性來實現的。 屬性值說明表: 屬性值 |描述 ...
浮動基本介紹
- 在標準文檔流中元素分為2種,
塊級元素和行內元素,如果想讓一些元素既要有塊級元素的特點也同時保留行內元素特點,只能讓這些元素脫離標準文檔流即可。 - 浮動可以讓元素脫離標準文檔流,可以實現讓多個元素排在同一行,並且可以設置寬高度。
- 其實浮動是通過
float屬性來實現的。 float屬性值說明表:
| 屬性值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| left | 設置元素向左浮動。 |
| right | 設置元素向右浮動。 |
右浮動實踐
- 讓我們進入右浮動的實踐,實踐內容如:將
class屬性值為.box1元素設置為右浮動。 - 在進入有浮動實踐之前我們先看看要浮動元素結構是什麼。
代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 為什麼結果圖是一條邊框線呢?因為在
div標簽中還沒有內容呢,現在我們將子div標簽設置寬高度為100px像素並且添加背景顏色。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 為什麼會排列為3行呢,因為3個
div標簽都是塊級元素。 - 現在我們將
class屬性值為.box1的元素設置為右浮動。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float:right;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

註意:現在我們發現
calss屬性值為.box元素高度變矮了,這就說明瞭(浮動元素它已經脫離了標準文檔流,不再占用空間了)、並且向右浮動,浮動到自身的父元素的邊緣位置就停止了浮動。
左浮動實踐
- 讓我們進入左浮動的實踐,實踐內容如:將
class屬性值為.box1元素設置為左浮動。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float:left;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 我們先理解浮動的原理之後再解釋下
class屬性值為.box2元素看不見的原因。 - 現在筆者給大家看2張實踐結果圖如:
結果圖A

結果圖B

- 通過這2張結果圖我們可以把浮動簡單的理解為“漂”舉例:
- 假設
class屬性值為.box是一個池塘,3個子元素都是能夠漂浮在池塘水面上的東西,現在我們將calss屬性值為.box1元素浮動起來,漂在池塘水面上,是不是就不再占用池塘內的空間了。 - 既然我們理解為“漂”它一定是漂浮在池塘水面之上,但是沒有浮動的元素在池塘水面之內,所以
class屬性值為.box2元素看不見,並不代表它不存在只是被class屬性值為.box1元素給遮擋住了,現在我們將class屬性值為.box2元素寬度設置為150px像素。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float:left;
}
.box2{
width: 150px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

註意:事實證明
class屬性值為.box2元素是存在的。- 下麵我們將
calss屬性值為.box2元素設置為左浮動看看有什麼不一樣的效果 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float:left;
}
.box2{
width: 150px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 但是
class屬性值為.box2的元素左浮動並沒有左浮動到本身父元素的邊緣位置,為什麼在class屬性值為.box1後面呢?因為父元素已經有了浮動的子元素後面的子元素在浮動就浮動到前面浮動的元素之後。 - 現在我們將
class屬性值為.box3的元素設置為左浮動,看看有什麼不一樣的效果。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float:left;
}
.box2{
width: 150px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖
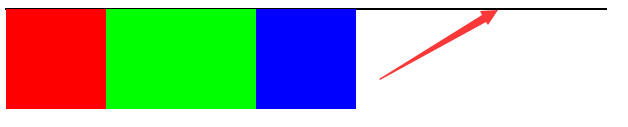
註意:浮動元素浮動以後,其父元素不再將浮動的子元素包裹在父元素之內,所以結果圖出現一條黑色的邊框線,若有不明白的看第一個實踐內容。
將行內元素設置浮動
- 如果我們給行內元素設置了浮動,行內元素就擁有了塊級元素的特點。
- 讓我們進入行內元素設置浮動實踐,實踐內容如:將
div標簽中的span標簽設置為左浮動。 - 在設置左浮動之前我們先看看給
span標簽設置寬高度和背景顏色有什麼效果。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span class="box1">微笑是最初的信仰1</span>
<span class="box2">微笑是最初的信仰2</span>
<span class="box3">微笑是最初的信仰3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 現在發現我們給
span標簽設置了寬高度為100px像素並沒有生效,因為現在span標簽還是行內元素。 - 現在我們給
span標簽設置左浮動,然後我們在看看效果如何。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<span class="box1">微笑是最初的信仰1</span>
<span class="box2">微笑是最初的信仰2</span>
<span class="box3">微笑是最初的信仰</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

註意:行內元素設置為浮動之後就擁有了塊級元素的特點。
設置浮動總結
- 浮動的特點如:
- 浮動元素脫離了標準的文檔流,不再占用父元素的任何空間。
- 浮動元素比標準文檔流的元素層級要高,會將標準文檔流的元素遮擋住。
- 浮動元素會向左浮動或向右浮動。
- 浮動元素會遇到父元素的邊緣就停止了浮動。
- 浮動元素會遇到已經有了浮動的元素,後者會浮動到前者之後就停止了浮動。
- 浮動元素浮動之後就脫離了父元素,並且父元素不再包裹浮動的元素。
- 行內元素設置為浮動,就擁有了塊級元素的特點。
為什麼要清除浮動呢?
- 因為浮動的元素會影響到下麵元素,具體看實踐結果圖大家就明白了。
class屬性值為.box元素的子類元素沒有浮動前的效果實踐。代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>清除浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
<h1>清除浮動</h1>
</body>
</html>結果圖

class屬性值為.box元素的子元素左浮動之後影響到下麵的元素排版佈局實踐。代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
<h1>清除浮動</h1>
</body>
</html>結果圖

現在大家應該明白了為什麼要清除浮動了,有浮動就必須清除浮動,因為上面的元素設置了浮動就會影響到下麵元素排版佈局。
清除浮動有3種方式
第一種方式
- 給浮動的元素父元素設置一個固定的高度,從視覺上看到浮動的元素在父元素包裹之內。
- 我們給浮動元素的父元素設置一個固定
600px像素的高度,一起來看看效果如何。 代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>清除浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
<h1>清除浮動</h1>
</body>
</html>結果圖

這樣是解決了下麵元素排版佈局問題,但是筆者不推薦這麼做,因為高度是由子元素的內容撐起來的高度,而不是我們給的固定高度。
第二種方式
- 其實在
CSS中也有清除浮動的屬性,清除浮動屬性名為clear。 clear屬性值說明表
| 屬性值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| left | 清除左側浮動元素。 |
| right | 清除右側浮動元素。 |
| both | 清除左右側浮動元素。 |
- 要使用這個
clear屬性必須創建一個新的div元素,創建新的div元素不能放置任何內容,它只能做一個件事情,那就是清除浮動並且將這個新創建的div元素放在最後一個浮動元素的後面才會生效。 - 左右清除浮動的屬性值筆者在這裡就不一一實踐了,一般我們就用
both屬性值就可以了,左右清除浮動,幹嘛還要計較它是左浮動或右浮動呢,直接清除左右浮動就ok了。 - 具體的看我們實踐的結果圖。
代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>清除浮動</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 600px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #00f;
float: left;
}
.clear{
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
<div class="clear"></div>
</div>
<h1>清除浮動</h1>
</body>
</html>結果圖

註意:這才是我們真正想要的結果,並且從視覺上來看浮動的元素包裹在父元素之內的效果。
第三種方式
- 使用屬性為
overflow並且屬性值為hidden來清除浮動,必須將這個屬性設置在浮動元素的父元素身上。 給大家普及下屬性為
overflow並且屬性值為hidden,它原意是用來將溢出的部分內容進行隱藏,但是它還可以清除浮動。- 筆者先將內容溢出然後在隱藏溢出的內容,那我們一起來看看唄。
代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>溢出內容進行隱藏</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰。
微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰。
微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰。
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 下麵筆者將溢出的內容進行隱藏。
代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>溢出內容進行隱藏</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid #000;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰。
微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰。
微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰,微笑是最初的信仰。
</div>
</body>
</html>結果圖

- 使用屬性為
overflow並且屬性值為hidden來清除浮動。 - 清除浮動之前我們先看看結構是如何的。
代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>清除浮動</title>
<style>
ul{
list-style: none;
}
ul li{
float: left;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰1</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰2</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰3</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰4</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰5</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰6</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰7</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰8</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>結果圖

註意:在這裡筆者還沒有給浮動元素清除浮動呢,大家可以明顯的看到
ul標簽高度為0。- 清除浮動實踐
代碼塊
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>清除浮動</title>
<style>
ul{
list-style: none;
overflow: hidden;
}
ul li{
float: left;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰1</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰2</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰3</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰4</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰5</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰6</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰7</li>
<li>微笑是最初的信仰8</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>結果圖
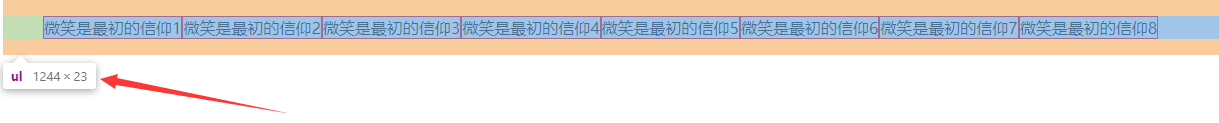
現在我們很清楚的看到
ul標簽高度為23px像素,為什麼要使用:屬性為overflow並且屬性值為hidden來清除浮動,因為ul標簽中只能使用li標簽元素不能使用其它元素,所以屬性為overflow並且屬性值為hidden來清除浮動是最好不過啦。



