本文主要對Java IO相關知識點做了結構性梳理,包括了Java IO的作用,數據源File類,輸入流,輸出流,位元組流,字元流,以及緩衝流,不同場景下的更細化的流操作類型,同時用了一個文件拷貝代碼簡單地說明瞭主要的流操作 ...
目錄
我們從兩個方面來理解Java IO,數據源(流)、數據傳輸,即IO的核心就是對數據源產生的數據進行讀寫並高效傳輸的過程。
一. 數據源(流)
數據源可以理解為水源,指可以產生數據的事物,如硬碟(文檔、資料庫等文件...)、網路(填寫的form表單、物聯感知信息..),在Java中有對文件及文件夾操作的類File,常用的文件方法如下:
public static void printFileDetail(File file) throws IOException {
System.out.println("文件是否存在:" + file.exists());
if(!file.exists()){
System.out.println("創建文件:" + file.getName());
file.createNewFile();
}
if(file.exists()){
System.out.println("是否為文件:" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("是否為文件夾:" + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("文件名稱:" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件構造路徑:" + file.getPath());
System.out.println("文件絕對路徑:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件標準路徑:" + file.getCanonicalPath());
System.out.println("文件大小:" + file.length());
System.out.println("所在文件夾路徑:" + file.getParentFile().getCanonicalPath());
System.out.println("設置為只讀文件:" + file.setReadOnly());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("./遮天.txt");
printFileDetail(file);
}結果如下:
文件是否存在:false
創建文件:遮天.txt
是否為文件:true
是否為文件夾:false
文件名稱:遮天.txt
文件構造路徑:.\遮天.txt
文件絕對路徑:E:\idea-work\javase-learning\.\遮天.txt
文件標準路徑:E:\idea-work\javase-learning\遮天.txt
文件大小:0
所在文件夾路徑:E:\idea-work\javase-learning
設置為只讀文件:true二. 數據傳輸
數據傳輸的核心在於傳輸數據源產生的數據,Java IO對此過程從兩方面進行了考慮,分別為輸入流和輸出流,輸入流完成外部數據向電腦記憶體寫入,輸出流則反之。
而針對輸入流和輸出流,Java IO又從位元組和字元的不同,再次細分了位元組流和字元流。
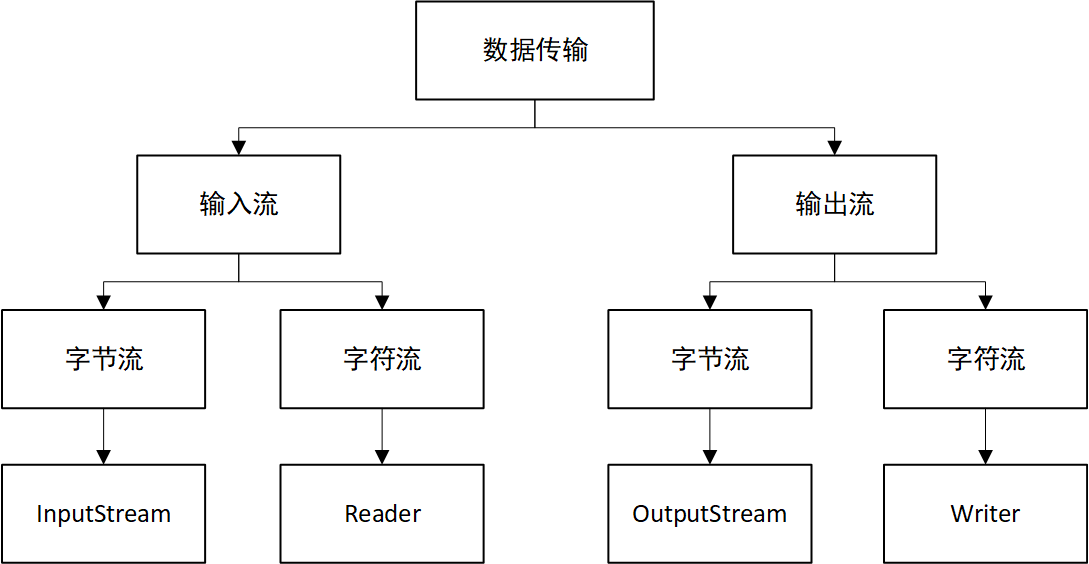
說明:Java中最小的計算單元是位元組,沒有字元流也能進行IO操作,只是因為現實中大量的數據都是文本字元數據,基於此單獨設計了字元流,使操作更簡便。
4個頂層介面有了,接下來Java IO又從多種應用場景(包括了基礎數據類型、文件、數組、管道、列印、序列化)和傳輸效率(緩衝操作)進行了考慮,提供了種類眾多的Java IO流的實現類,看下圖:
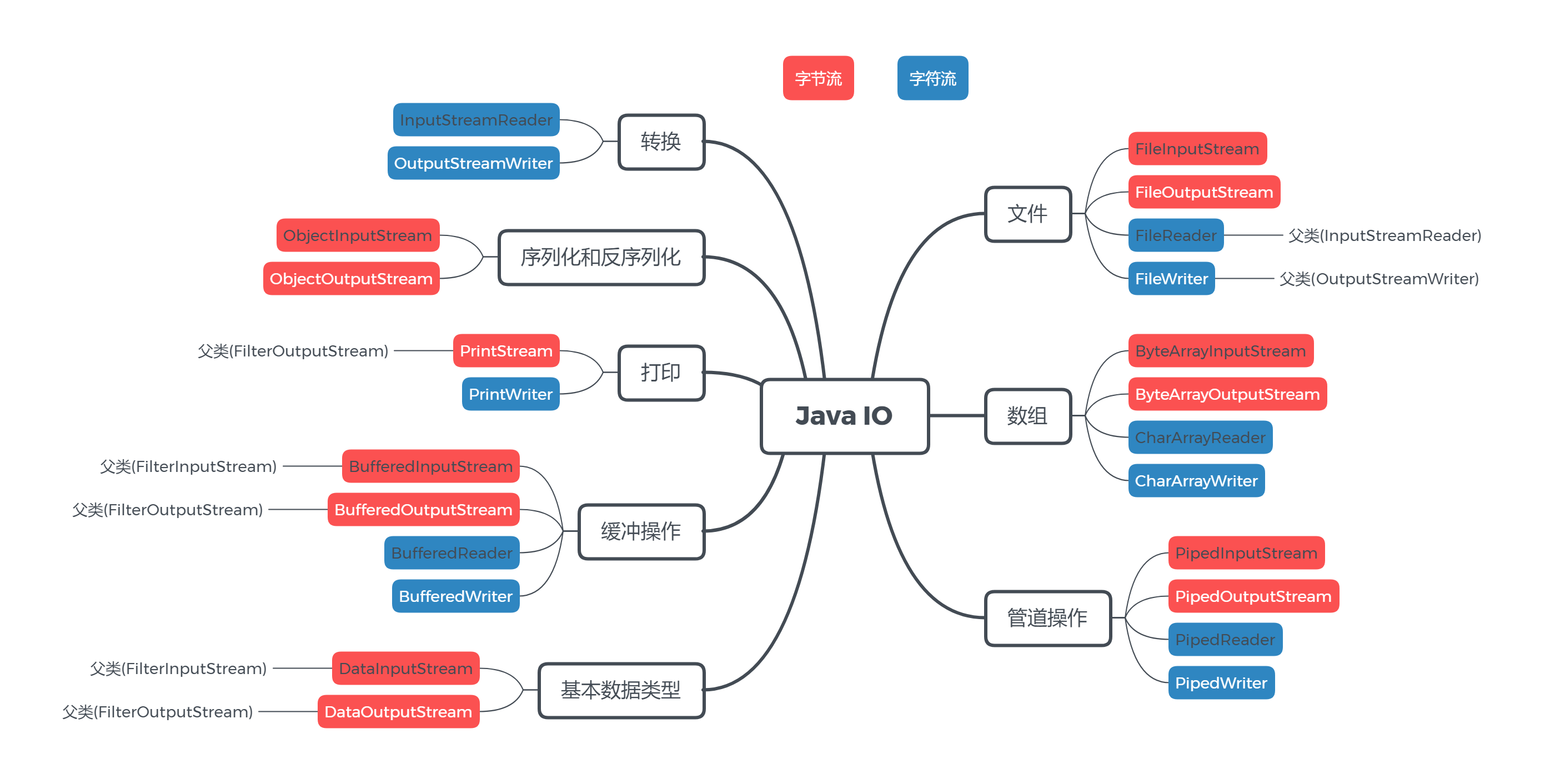
當然我們不用都記住,而實際在使用過程中用的最多的還是文件類操作、轉換類操作、序列化操作,當然在此基礎上我們可以使用Buffered來提高效率(Java IO使用了裝飾器模式)。下麵我們通過文件拷貝來簡單說明一下主要類的使用
/**
* 文件拷貝(所有文件,文檔、視頻、音頻、可執行文件...),未使用緩衝
* @param sourceFileName 源文件路徑
* @param targetFileName 拷貝後目標文件路徑
* @throws IOException IO異常
*/
public static void slowlyCopyFile(String sourceFileName, String targetFileName) throws IOException{
//獲取位元組輸入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(sourceFileName);
//File targetFile = new File(targetFileName);
//獲取位元組輸出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(targetFileName);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//當為-1時說明讀取到最後一行了
while ((fileInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
/**
* 文件拷貝(所有文件,文檔、視頻、音頻、可執行文件...),使用緩衝
* @param sourceFileName 源文件路徑
* @param targetFileName 拷貝後目標文件路徑
* @throws IOException IO異常
*/
public static void fastCopyFile(String sourceFileName, String targetFileName) throws IOException{
//獲取位元組輸入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(sourceFileName);
//緩衝位元組輸入流
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
//獲取位元組輸出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(targetFileName);
//緩衝位元組輸出流
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//當為-1時說明讀取到最後一行了
while ((bufferedInputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes);
}
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
bufferedInputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//文件215M
slowlyCopyFile("D:\\Download\\jdk-8u221.exe","D:\\jdk-8u221.exe");//執行:1938ms
fastCopyFile("D:\\Download\\jdk-8u221.exe","D:\\jdk-8u221.exe");//執行:490ms
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
} /**
* 文本文件拷貝,不使用緩衝
* @param sourceFileName 源文件路徑
* @param targetFileName 拷貝後目標文件路徑
* @throws IOException IO異常
*/
public static void slowlyCopyTextFile(String sourceFileName, String targetFileName) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(sourceFileName);
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(targetFileName);
int c;
while ((c = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
fileWriter.write((char)c);
}
fileReader.close();
fileWriter.close();
}
/**
* 文本文件拷貝,使用緩衝
* @param sourceFileName 源文件路徑
* @param targetFileName 拷貝後目標文件路徑
* @throws IOException IO異常
*/
public static void fastCopyTextFile(String sourceFileName, String targetFileName) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(sourceFileName);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(targetFileName);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
String str;
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
bufferedWriter.write(str + "\n");
}
bufferedReader.close();
fileReader.close();
bufferedWriter.close();
fileWriter.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//文件30M
slowlyCopyTextFile("D:\\Download\\小說合集.txt","D:\\小說合集.txt");//3182ms
fastCopyTextFile("D:\\Download\\小說合集.txt","D:\\小說合集.txt");//1583ms
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
}三. 總結
本文主要對Java IO相關知識點做了結構性梳理,包括了Java IO的作用,數據源File類,輸入流,輸出流,位元組流,字元流,以及緩衝流,不同場景下的更細化的流操作類型,同時用了一個文件拷貝代碼簡單地說明瞭主要的流操作,若有不對之處,請批評指正,望共同進步,謝謝!。



