CSS基礎 2.幾種佈局方式1)table佈局 當年主流的佈局方式,第一種是通過table tr td佈局 示例: <style type="text/css"> table{ width: 800px; height: 300px; border-collapse: collapse; } .le ...
CSS基礎
2.幾種佈局方式
1)table佈局
當年主流的佈局方式,第一種是通過table tr td佈局
示例:
<style type="text/css"> table{ width: 800px; height: 300px; border-collapse: collapse; } .left{ background-color: red; } .right{ background-color: blue; } </style> <body> <table> <tr> <td class="left">左</td> <td class="right">右</td> </tr> </table> </body>
頁面效果: 文字自動垂直居中,很方便 同樣可以設置左右的width
第二種是類比表格的table class
示例:
<style type="text/css"> .table{ display: table; width: 800px; height: 300px; /*border-collapse: collapse;*/ } .tb_row{ display: table-row; } .tb_cell{ display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle; } .left{ background-color: red; } .right{ background-color: blue; } table </style> <body> <div class="table"> <div class="tb_row"> <div class="left tb_cell">左</div> <div class="right tb_cell">右</div> </div> </div> </body>
頁面效果: 跟表格佈局一樣 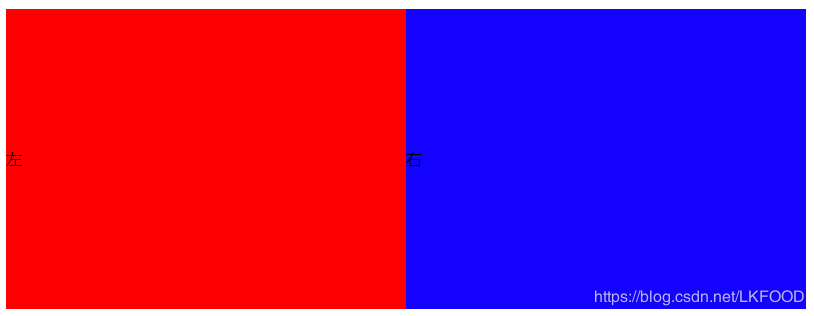
2)flexbox佈局
- 兩列佈局
**關鍵:父級元素設置display:flex**
示例:
<style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .parent{ width: 800px; height: 300px; display: flex; } .left{ width: 300px; height: 100%; background: red; } .right{ flex: 1; height: 100%; background: blue; } </style> <body> <div class="parent"> <div class="left">左</div> <div class="right">右</div> </div> </body>
頁面效果: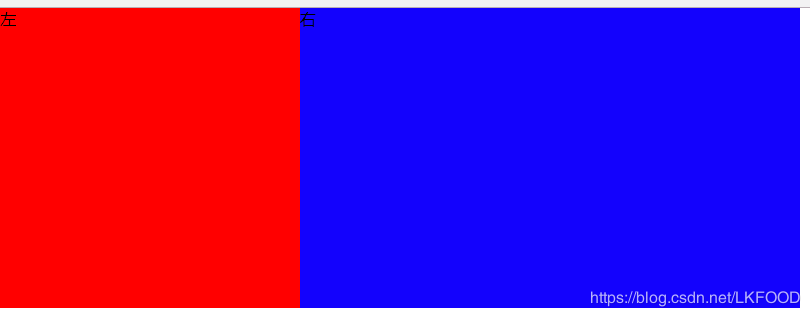
- 三列佈局
**關鍵:父級元素設置display:flex**
示例:
<style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .parent{ width: 800px; height: 300px; display: flex; } .left{ width: 300px; height: 100%; background: red; } .middle{ width: 200px; height: 100%; } .right{ flex: 1; height: 100%; background: blue; } </style> <body> <div class="parent"> <div class="left">左</div> <div class="middle">中</div> <div class="right">右</div> </div> </body>
頁面效果: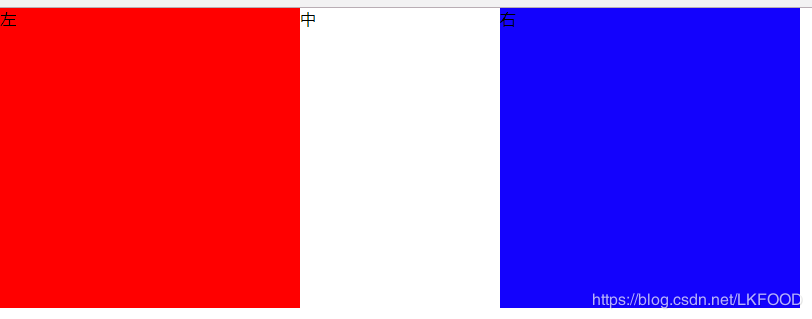
3)float佈局 (float+margin)
相容性好 但是要註意清楚浮動(clear: both display:block)
- 兩列佈局——左側定寬,右側自適應
**關鍵:**
*左側設置float:left
右側:margin-left: leftWidth*
示例:
<style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .parent{ width:800px; height:200px; } .left{ width:200px; height:100%; float:left; background-color:red; } .right{ height:100%; margin-left:200px; background-color:blue; } </style> <body> <div class="parent"> <div class="left">左</div> <div class="left">右</div> </div> </body>
頁面效果:
- 三列佈局
**關鍵:**
*左側設置float:left
右側設置float:right
中間:margin-left: leftWidth;margin-right:rightWidth*
示例:
<style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .parent{ width: 800px; height: 200px; } .left{ width: 200px; height: 100%; background-color: red; float: left; } .right{ float: right; width: 200px; background-color: blue; height: 100%; } .middle{ margin-left: 200px; margin-right: 200px; } </style> <body> <div class="parent"> <div class="left">左</div> <div class="right">右</div> <div class="middle">中</div> </div> </body>
頁面效果:
**註意:float特點:儘量靠上,儘量靠左(右),所以右側浮動div要先寫,中間div後寫**
4)inline-block佈局——不存在清除浮動問題 適用與定寬的佈局
<style type="text/css"> .parent{ font-size: 0; width: 800px; height: 200px; } .left{ font-size: 14px; width: 300px; height: 200px; display: inline-block; background-color: red; } .right{ font-size: 14px; width: 500px; height: 200px; display: inline-block; background-color: blue; } </style> <div class="parent"> <div class="left">左</div> <div class="right">右</div> </div>
頁面效果:
註意: 想要父級元素的寬度等於兩個子元素寬度之和,需要設置父級元素的 font-size:0 否則兩個子元素不會再一行展示
同時,需要設置兩個子元素的font-size: 14px; 否則子元素內的文字不會展示!
**想象成文字,註意間隙的處理!!!** 間隙存在於兩個div間的空白: 
5)響應式佈局
讓前臺頁面可以再不同的設備,不同大小的屏幕上正常展示,一般都是指處理屏幕大小問題
首先設置viewport
利用rem 1rem=html.font-size
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
利用media query
@media (max-width: 640px){ .left{ display: none; } }
三.Q&A
1) position: absolute 和fixed 的區別:
前者是相對於最近的relative/absolute 元素
後者是相對於屏幕 (viewport)
2) display:inline-block 間隙的原因
原因: 空白字元間距
解決:清除空白字元或者消滅間距
—中間不留空白
<div> </div></div> </div>
—將空白字元註釋
<div> </div><!-- --><div></div>
—消滅間距
font-size: 0
3)如何清除浮動以及原因
浮動的元素不占用父元素的空間,有可能會超出父元素進而對其他元素產生影響,所以要清除父元素浮動
方法:
讓盒子負責自己的佈局:
overflow: hidden(auto)
在元素後面加上:
::after{clear: both}
4)如何適配移動端頁面
- viewport
- rem/viewport/media query
- 設計上: 隱藏 折行 自適應



