概念 什麼是·Mysql/Mariadb主從複製? Mysql/Mariadb主從複製:當Master(主)資料庫發生變化的時候,變化實時會同步到slave(從)資料庫中; 類似於:Samba共用文件(C/S)、NFS網路文件共用(C/S),當服務端(Server)發生變化時,客戶端(client) ...
概念
什麼是·Mysql/Mariadb主從複製?
Mysql/Mariadb主從複製:當Master(主)資料庫發生變化的時候,變化實時會同步到slave(從)資料庫中; 類似於:Samba共用文件(C/S)、NFS網路文件共用(C/S),當服務端(Server)發生變化時,客戶端(client)數據內容會根據服務端進行改變;
好處
- 水平擴展資料庫的負載能力,後備資料庫,主資料庫伺服器故障後,可切換到從資料庫繼續工作;
- 容錯、高可用,從資料庫可用來做備份、數據統計等工作,這樣不影響主資料庫的性能;
- 數據分佈;
- 數據備份;
實現原理
在master機器上,主從同步事件會被寫到特殊的log文件中(binary-log);
主從同步事件有3種形式:statement、row、mixed。
statement:會將對資料庫操作的sql語句寫入到binlog中。 row:會將每一條數據的變化寫入到binlog中。 mixed:statement與row的混合。Mysql決定什麼時候寫statement格式的,什麼時候寫row格式的binlog。
整體上來說,複製有3個步驟:
- master將改變記錄到二進位日誌(binary log)中(這些記錄叫做二進位日誌事件,binary log events);
- slave將master的binary log events拷貝到它的中繼日誌(relay log);
- slave重做中繼日誌中的事件,將改變反映它自己的數據。
下麵這章圖可以詳細解釋其原理:
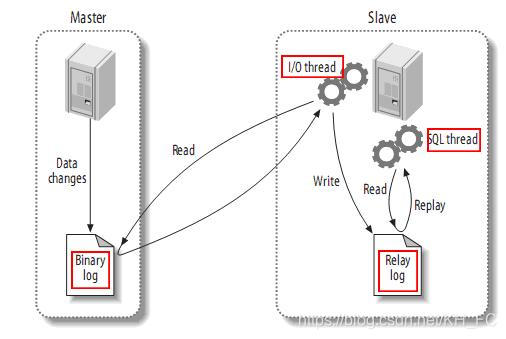
說的簡單一些就是:
當對Master資料庫不管做了增、刪、改還是創建了資料庫、表等操作時,Slave就會快速的接受這些數據以及對象的操作,從而實現主從數據複製,保證數據的一致性。
實戰
我記得我學PHP開發的時候,教員經常說的一句話就是:學習半小時,實戰一分鐘;
好了,接下來到我們實戰的時刻了,認真聽講喲!!!
環境介紹
系統環境:系統基本上都差不多,一般多數都是Linux平臺和Windows平臺比較多,不管什麼樣的系統環境對這次實戰的操作都影響不大,我在這裡使用的是Docker虛擬出來的CentOS操作系統,當然您可以選用Ubuntu、RedHat以及Windows系統,這些都不會影響到大的操作;
我這裡使用的系統版本:
[root@master /]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 8.0.1905 (Core)
這裡會用到兩台伺服器:其中一臺MasterIP172.18.0.2,另外一個slaveIP172.18.0.3
資料庫版本:(我這裡使用的Mariadb,你可以使用mysql資料庫)
[root@master /]# mysql --version mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.3.11-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using readline 5.1
配置Master資料庫
1.更改Master配置文件
找到下麵文件:
mysql資料庫:/etc/mysql/mysql,conf.d/mysqld.cnf mariadb資料庫:/etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb.cnf
註意:我這裡是使用yum進行安裝的所以預設配置文件是在/etc下麵,建議在修改上面兩個文件時要先將配置文件進行備份
修改以下配置:
bind-address=172.18.0.2 \\指定Master地址 server-id = 1 \\指定唯一的serverid 部分版本沒有需手動寫入 log_bin = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin.log \\開啟binlog 部分版本沒有需手動寫入
註意:log_bin這個欄位需根據實際情況來定,需找到資料庫的日誌文件,預設實在 /var/log
2.重新啟動資料庫
[root@master my.cnf.d]# systemctl restart mariadb \\centos7、centos8、ubuntu重新啟動方式 [root@master my.cnf.d]# server mariadb restart \\centos6及以下版本使用這個重新啟動方式
mysql重新啟動:
[root@master my.cnf.d]# systemctl restart mysqld \\centos7、centos8、ubuntu重新啟動方式 [root@master my.cnf.d]# server mysqld restart \\centos6及以下版本使用這個重新啟動方式
3.初始化資料庫
[root@master my.cnf.d]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): //這裡敲回車
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y //這裡是設置root密碼,可不進行設置
New password: //新密碼
Re-enter new password: //舊密碼
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
[root@master my.cnf.d]#
4.創建主從同步的用戶
[root@master ~]# mysql -u root -p \\登陸資料庫 Enter password: \\輸入root密碼 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 18 Server version: 10.3.11-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE on *.* to 'slave'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'redhat'; \\創建用戶,並設置相應的許可權 \\此處%表示允許從任何地方(除本地外)使用此賬號進行登陸使用,在正式環境建議具體到某台主機IP Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec) \\表示sql語句執行成功
5.更新Slave用戶許可權
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; \\每次修改用戶許可權,都要使用這個sql語句進行更新 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec)
6.導出資料庫中所有數據(此步驟取決於slave的許可權)
[root@master ~]# mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases --master-data > mariadb.bat.sql --all-databases \\此參數表示備份所有資料庫 --master-data \\此參數表示將二進位的信息寫入到輸出文件中,在這裡是寫入到備份的sql文件中 Enter password:
7.查看MASTERr REPLICATION LOG位置
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mariadb-bin.000002 | 1974 | | | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
配置Slave資料庫
1.更改Slave配置文件
文件位置與Master位置一致
mysql資料庫:/etc/mysql/mysql,conf.d/mysqld.cnf mariadb資料庫:/etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb.cnf
註意:我這裡是使用yum進行安裝的所以預設配置文件是在/etc下麵,建議在修改上面兩個文件時要先將配置文件進行備份
修改以下配置:
bind-address=172.18.0.3 \\指定Master地址 server-id = 2 \\指定唯一的serverid 部分版本沒有需手動寫入 log_bin = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin.log \\開啟binlog 部分版本沒有需手動寫入
註意:log_bin這個欄位需根據實際情況來定,需找到資料庫的日誌文件,預設實在 /var/log
2.重新啟動資料庫
[root@master my.cnf.d]# systemctl restart mariadb \\centos7、centos8、ubuntu重新啟動方式 [root@master my.cnf.d]# server mariadb restart \\centos6及以下版本使用這個重新啟動方式
mysql重新啟動:
[root@master my.cnf.d]# systemctl restart mysqld \\centos7、centos8、ubuntu重新啟動方式 [root@master my.cnf.d]# server mysqld restart \\centos6及以下版本使用這個重新啟動方式
3.初始化資料庫
[root@master my.cnf.d]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): //這裡敲回車
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y //這裡是設置root密碼,可不進行設置
New password: //新密碼
Re-enter new password: //舊密碼
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
[root@master my.cnf.d]#
4.從Master將資料庫備份複製到slave伺服器
[root@slave my.cnf.d]# scp [email protected]:/opt/mariadb.bat.sql /opt/ [email protected]'s password: mariadb.bat.sql
5.將備份數據恢復到slave資料庫
[root@slave my.cnf.d]# mysql -u root -p < /opt/mariadb.bat.sql Enter password:
6.使slave與master建立連接
[root@slave my.cnf.d]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
[root@slave my.cnf.d]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 22
Server version: 10.3.11-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> stop slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> CHANGE MASTER TO
-> MASTER_HOST = '172.18.0.2', \\指定Master資料庫地址
-> MASTER_USER = 'slave', \\指定主從複製用戶名
-> MASTER_PASSWORD = 'redhat', \\指定主從複製用戶密碼
-> MASTER_LOG_FILE = 'mariadb-bin.000002', \\指定Master資料庫的binlog文件名
-> MASTER_LOG_POS=1974;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.290 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave; \\開啟複製功能
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.019 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]>
註意:lMASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000002與MASTER_LOG_POS=1974的值,是從上面的 SHOW MASTER STATUS 得到的。
到這裡已經可以做到主從複製了下麵讓我們測試一下吧
驗證資料庫是否同步
測試方法很簡單,只需要在主資料庫上面創建資料庫或者增加一條記錄就可以測試是否主從複製配置成功
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | +--------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.018 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> create database a; \\在主資料庫創建a資料庫 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.063 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | a | | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.000 sec)
下麵我們來看看從資料庫上面有沒有a這個資料庫吧
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | a | | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | +--------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.075 sec)
我們會發現已經有了a這個資料庫



