摘要: 玩轉Promise。 原文: "Promise 中的三兄弟 .all(), .race(), .allSettled()" 譯者:前端小智 "Fundebug" 經授權轉載,版權歸原作者所有。 從ES6 開始,我們大都使用的是 和`Promise.race() Promise.allSett ...
摘要: 玩轉Promise。
- 原文:Promise 中的三兄弟 .all(), .race(), .allSettled()
- 譯者:前端小智
Fundebug經授權轉載,版權歸原作者所有。
從ES6 開始,我們大都使用的是 Promise.all()和Promise.race(),Promise.allSettled() 提案已經到第4階段,因此將會成為ECMAScript 2020的一部分。
1.概述
Promise.all
Promise.all(iterable)方法返回一個Promise實例,此實例在iterable參數內所有的promise都“完成(resolved)”或參數中不包含promise時回調完成(resolve);如果參數中promise有一個失敗(rejected),此實例回調失敗(reject),失敗原因的是第一個失敗promise的結果
Promise.race
- Promise.race(iterable) 方法返回一個
promise,一旦迭代器中的某個promise解決或拒絕,返回的promise就會解決或拒絕。
Promise.allSettled
- Promise.allSettled()方法返回一個
promise,該promise在所有給定的promise已被解析或被拒絕後解析,並且每個對象都描述每個promise的結果。
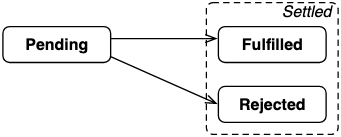
2. 回顧: Promise 狀態
給定一個返回Promise的非同步操作,以下這些是Promise的可能狀態:
- pending: 初始狀態,既不是成功,也不是失敗狀態。
- fulfilled: 意味著操作成功完成。
- rejected: 意味著操作失敗。
- Settled:
Promise要麼被完成,要麼被拒絕。Promise一旦達成,它的狀態就不再改變。
3.什麼是組合
又稱部分-整體模式,將對象整合成樹形結構以表示“部分整體”的層次結構。組合模式使得用戶對單個對象和組合對象的使用具有一致性,它基於兩種函數:
- 基元函數(簡短:基元)創建原子塊。
- 組合函數(簡稱:組合)將原子和/或複合件組合在一起以形成複合件。
對於 JS 的 Promises 來說
- 基元函數包括:
Promise.resolve()、Promise.reject() - 組合函數:
Promise.all(),Promise.race(),Promise.allSettled()
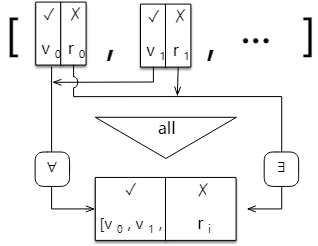
4. Promise.all()
Promise.all()的類型簽名:
- Promise.all
(promises: Iterable<Promise >): Promise<Array >
返回情況:
完成(Fulfillment):
如果傳入的可迭代對象為空,Promise.all 會同步地返回一個已完成(resolved)狀態的promise。
如果所有傳入的 promise 都變為完成狀態,或者傳入的可迭代對象內沒有 promise,Promise.all 返回的 promise 非同步地變為完成。
在任何情況下,Promise.all 返回的 promise 的完成狀態的結果都是一個數組,它包含所有的傳入迭代參數對象的值(也包括非 promise 值)。
失敗/拒絕(Rejection):
如果傳入的 promise 中有一個失敗(rejected),Promise.all 非同步地將失敗的那個結果給失敗狀態的回調函數,而不管其它 promise 是否完成。
來個例子:
const promises = [
Promise.resolve('a'),
Promise.resolve('b'),
Promise.resolve('c'),
];
Promise.all(promises)
.then((arr) => assert.deepEqual(
arr, ['a', 'b', 'c']
));如果其中的一個 promise 被拒絕,那麼又是什麼情況:
const promises = [
Promise.resolve('a'),
Promise.resolve('b'),
Promise.reject('ERROR'),
];
Promise.all(promises)
.catch((err) => assert.equal(
err, 'ERROR'
));下圖說明Promise.all()是如何工作的
4.1 非同步 .map() 與 Promise.all()
數組轉換方法,如.map()、.filter()等,用於同步計算。例如
function timesTwoSync(x) {
return 2 * x;
}
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const result = arr.map(timesTwoSync);
assert.deepEqual(result, [2, 4, 6]);如果.map()的回調是基於Promise的函數會發生什麼? 使用這種方式 .map()返回的的結果是一個Promises數組。
Promises數組不是普通代碼可以使用的數據,但我們可以通過Promise.all()來解決這個問題:它將Promises數組轉換為Promise,並使用一組普通值數組來實現。
function timesTwoAsync(x) {
return new Promise(resolve => resolve(x * 2));
}
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const promiseArr = arr.map(timesTwoAsync);
Promise.all(promiseArr)
.then(result => {
assert.deepEqual(result, [2, 4, 6]);
});更實際工作上關於 .map()示例
接下來,咱們使用.map()和Promise.all()從Web下載文件。 首先,咱們需要以下幫助函數:
function downloadText(url) {
return fetch(url)
.then((response) => { // (A)
if (!response.ok) { // (B)
throw new Error(response.statusText);
}
return response.text(); // (C)
});
}downloadText()使用基於Promise的fetch API 以字元串流的方式下載文件:
- 首先,它非同步檢索響應(第A行)。
- response.ok(B行)檢查是否存在“找不到文件”等錯誤。
- 如果沒有錯誤,使用
.text()(第C行)以字元串的形式取迴文件的內容。
在下麵的示例中,咱們 下載了兩個文件
const urls = [
'http://example.com/first.txt',
'http://example.com/second.txt',
];
const promises = urls.map(
url => downloadText(url));
Promise.all(promises)
.then(
(arr) => assert.deepEqual(
arr, ['First!', 'Second!']
));Promise.all()的一個簡版實現
function all(iterable) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let index = 0;
for (const promise of iterable) {
// Capture the current value of `index`
const currentIndex = index;
promise.then(
(value) => {
if (anErrorOccurred) return;
result[currentIndex] = value;
elementCount++;
if (elementCount === result.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(err) => {
if (anErrorOccurred) return;
anErrorOccurred = true;
reject(err);
});
index++;
}
if (index === 0) {
resolve([]);
return;
}
let elementCount = 0;
let anErrorOccurred = false;
const result = new Array(index);
});
}5. Promise.race()
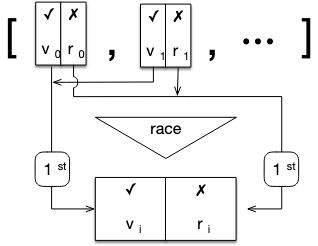
Promise.race()方法的定義:
Promise.race
Promise.race(iterable) 方法返回一個 promise,一旦迭代器中的某個promise解決或拒絕,返回的 promise就會解決或拒絕。來幾個例子,瞧瞧:
const promises = [
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
setTimeout(() => resolve('result'), 100)), // (A)
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
setTimeout(() => reject('ERROR'), 200)), // (B)
];
Promise.race(promises)
.then((result) => assert.equal( // (C)
result, 'result'));在第 A 行,Promise 是完成狀態 ,所以 第 C 行會執行(儘管第 B 行被拒絕)。
如果 Promise 被拒絕首先執行,在來看看情況是嘛樣的:
const promises = [
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
setTimeout(() => resolve('result'), 200)),
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
setTimeout(() => reject('ERROR'), 100)),
];
Promise.race(promises)
.then(
(result) => assert.fail(),
(err) => assert.equal(
err, 'ERROR'));註意,由於 Promse 先被拒絕,所以 Promise.race() 返回的是一個被拒絕的 Promise
這意味著Promise.race([])的結果永遠不會完成。
下圖演示了Promise.race()的工作原理:
Promise.race() 在 Promise 超時下的情況
在本節中,我們將使用Promise.race()來處理超時的 Promise。 以下輔助函數:
function resolveAfter(ms, value=undefined) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(value), ms);
});
}resolveAfter() 主要做的是在指定的時間內,返回一個狀態為 resolve 的 Promise,值為為傳入的 value
調用上面方法:
function timeout(timeoutInMs, promise) {
return Promise.race([
promise,
resolveAfter(timeoutInMs,
Promise.reject(new Error('Operation timed out'))),
]);
}timeout() 返回一個Promise,該 Promise 的狀態取決於傳入 promise 狀態 。
其中 timeout 函數中的 resolveAfter(timeoutInMs, Promise.reject(new Error('Operation timed out')) ,通過 resolveAfter 定義可知,該結果返回的是一個被拒絕狀態的 Promise。
再來看看timeout(timeoutInMs, promise)的運行情況。如果傳入promise在指定的時間之前狀態為完成時,timeout 返回結果就是一個完成狀態的 Promise,可以通過.then的第一個回調參數處理返回的結果。
timeout(200, resolveAfter(100, 'Result!'))
.then(result => assert.equal(result, 'Result!'));相反,如果是在指定的時間之後完成,剛 timeout 返回結果就是一個拒絕狀態的 Promise,從而觸發catch方法指定的回調函數。
timeout(100, resolveAfter(2000, 'Result!'))
.catch(err => assert.deepEqual(err, new Error('Operation timed out')));重要的是要瞭解“Promise 超時”的真正含義:
- 如果傳入入
Promise較到的得到解決,其結果就會給返回的Promise。 - 如果沒有足夠快得到解決,輸出的
Promise的狀態為拒絕。
也就是說,超時只會阻止傳入的Promise,影響輸出 Promise(因為Promise只能解決一次), 但它並沒有阻止傳入Promise的非同步操作。
5.2 Promise.race() 的一個簡版實現
以下是 Promise.race()的一個簡化實現(它不執行安全檢查)
function race(iterable) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
for (const promise of iterable) {
promise.then(
(value) => {
if (settlementOccurred) return;
settlementOccurred = true;
resolve(value);
},
(err) => {
if (settlementOccurred) return;
settlementOccurred = true;
reject(err);
});
}
let settlementOccurred = false;
});
}6.Promise.allSettled()
“Promise.allSettled”這一特性是由Jason Williams,Robert Pamely和Mathias Bynens提出。
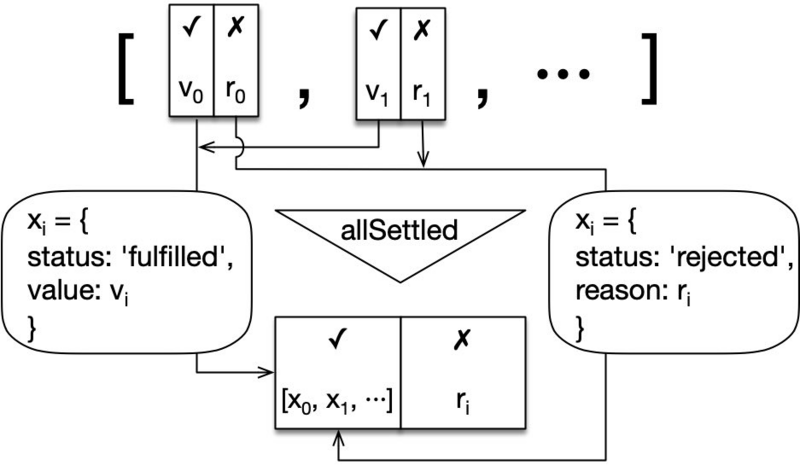
promise.allsettle()方法的定義:
- Promise.allSettled
(promises: Iterable<Promise >)
: Promise<Array<SettlementObject>>
它返回一個Array的Promise,其元素具有以下類型特征:
type SettlementObject<T> = FulfillmentObject<T> | RejectionObject;
interface FulfillmentObject<T> {
status: 'fulfilled';
value: T;
}
interface RejectionObject {
status: 'rejected';
reason: unknown;
}Promise.allSettled()方法返回一個promise,該promise在所有給定的promise已被解析或被拒絕後解析,並且每個對象都描述每個promise的結果。
舉例說明, 比如各位用戶在頁面上面同時填了3個獨立的表單, 這三個表單分三個介面提交到後端, 三個介面獨立, 沒有順序依賴, 這個時候我們需要等到請求全部完成後給與用戶提示表單提交的情況
在多個promise同時進行時咱們很快會想到使用Promise.all來進行包裝, 但是由於Promise.all的短路特性, 三個提交中若前面任意一個提交失敗, 則後面的表單也不會進行提交了, 這就與咱們需求不符合.
Promise.allSettled跟Promise.all類似, 其參數接受一個Promise的數組, 返回一個新的Promise, 唯一的不同在於, 其不會進行短路, 也就是說當Promise全部處理完成後我們可以拿到每個Promise的狀態, 而不管其是否處理成功.
下圖說明promise.allsettle()是如何工作的
6.1 Promise.allSettled() 例子
這是Promise.allSettled() 使用方式快速演示示例
Promise.allSettled([
Promise.resolve('a'),
Promise.reject('b'),
])
.then(arr => assert.deepEqual(arr, [
{ status: 'fulfilled', value: 'a' },
{ status: 'rejected', reason: 'b' },
]));6.2 Promise.allSettled() 較複雜點的例子
這個示例類似於.map()和Promise.all()示例(我們從其中借用了downloadText()函數):我們下載多個文本文件,這些文件的url存儲在一個數組中。但是,這一次,咱們不希望在出現錯誤時停止,而是希望繼續執行。Promise.allSettled()允許咱們這樣做:
const urls = [
'http://example.com/exists.txt',
'http://example.com/missing.txt',
];
const result = Promise.allSettled(
urls.map(u => downloadText(u)));
result.then(
arr => assert.deepEqual(
arr,
[
{
status: 'fulfilled',
value: 'Hello!',
},
{
status: 'rejected',
reason: new Error('Not Found'),
},
]
));
6.3 Promise.allSettled() 的簡化實現
這是promise.allsettle()的簡化實現(不執行安全檢查)
function allSettled(iterable) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
function addElementToResult(i, elem) {
result[i] = elem;
elementCount++;
if (elementCount === result.length) {
resolve(result);
}
}
let index = 0;
for (const promise of iterable) {
// Capture the current value of `index`
const currentIndex = index;
promise.then(
(value) => addElementToResult(
currentIndex, {
status: 'fulfilled',
value
}),
(reason) => addElementToResult(
currentIndex, {
status: 'rejected',
reason
}));
index++;
}
if (index === 0) {
resolve([]);
return;
}
let elementCount = 0;
const result = new Array(index);
});
}
7. 短路特性
Promise.all() 和 romise.race() 都具有 短路特性
- Promise.all(): 如果參數中
promise有一個失敗(rejected),此實例回調失敗(reject)
Promise.race():如果參數中某個promise解決或拒絕,返回的 promise就會解決或拒絕。
8.併發性和 Promise.all()
8.1 順序執行與併發執行
考慮下麵的代碼:
asyncFunc1()
.then(result1 => {
assert.equal(result1, 'one');
return asyncFunc2();
})
.then(result2 => {
assert.equal(result2, 'two');
});
使用.then()順序執行基於Promise的函數:只有在 asyncFunc1()的結果被解決後才會執行asyncFunc2() 。
而 Promise.all() 是併發執行的
Promise.all([asyncFunc1(), asyncFunc2()])
.then(arr => {
assert.deepEqual(arr, ['one', 'two']);
});
9.2 併發技巧:關註操作何時開始
確定併發非同步代碼的技巧:關註非同步操作何時啟動,而不是如何處理它們的Promises。
例如,下麵的每個函數都同時執行asyncFunc1()和asyncFunc2(),因為它們幾乎同時啟動。
function concurrentAll() {
return Promise.all([asyncFunc1(), asyncFunc2()]);
}
function concurrentThen() {
const p1 = asyncFunc1();
const p2 = asyncFunc2();
return p1.then(r1 => p2.then(r2 => [r1, r2]));
}
另一方面,以下兩個函數依次執行asyncFunc1()和asyncFunc2(): asyncFunc2()僅在asyncFunc1()的解決之後才調用。
function sequentialThen() {
return asyncFunc1()
.then(r1 => asyncFunc2()
.then(r2 => [r1, r2]));
}
function sequentialAll() {
const p1 = asyncFunc1();
const p2 = p1.then(() => asyncFunc2());
return Promise.all([p1, p2]);
}9.3 Promise.all() 與 Fork-Join 分治編程
Promise.all() 與併發模式“fork join”鬆散相關。重溫一下咱們前面的一個例子:
Promise.all([
// (A) fork
downloadText('http://example.com/first.txt'),
downloadText('http://example.com/second.txt'),
])
// (B) join
.then(
(arr) => assert.deepEqual(
arr, ['First!', 'Second!']
));- Fork:在
A行中,分割兩個非同步任務並同時執行它們。 - Join:在
B行中,對每個小任務得到的結果進行彙總。
代碼部署後可能存在的BUG沒法實時知道,事後為瞭解決這些BUG,花了大量的時間進行log 調試,這邊順便給大家推薦一個好用的BUG監控工具 Fundebug。
原文:https://2ality.com/2019/08/promise-combinators.html
關於Fundebug
Fundebug專註於JavaScript、微信小程式、微信小游戲、支付寶小程式、React Native、Node.js和Java線上應用實時BUG監控。 自從2016年雙十一正式上線,Fundebug累計處理了20億+錯誤事件,付費客戶有陽光保險、核桃編程、荔枝FM、掌門1對1、微脈、青團社等眾多品牌企業。歡迎大家免費試用!



