一個可以沉迷於技術的程式猿,wx加入加入技術群:fsx641385712 ...
每篇一句
我們應該做一個:胸中有藍圖,腳底有計劃的人
前言
Spring MVC提供的基於註釋的編程模型,極大的簡化了web應用的開發,我們都是受益者。比如我們在@RestController標註的Controller控制器組件上用@RequestMapping、@ExceptionHandler等註解來表示請求映射、異常處理等等。
使用這種註解的方式來開發控制器我認為最重要的優勢是:
- 靈活的方法簽名(入參隨意寫)
- 不必繼承基類
- 不必實現介面
==總之一句話:靈活性非常強,耦合度非常低。==
在眾多的註解使用中,Spring MVC中有一個非常強大但幾乎被忽視的一員:@ModelAttribute。關於這個註解的使用情況,我在群里/線下問了一些人,感覺很少人會使用這個註解(甚至有的不知道有這個註解),這著實讓我非常的意外。我認為至少這對於"久經戰場"的一個老程式員來說這是不應該的吧。
不過沒關係,有幸看到此文,能夠幫你彌補彌補這塊的盲區。
@ModelAttribute它不是開發必須的註解(不像@RequestMapping那麼重要),so即使你不知道它依舊能正常書寫控制器。當然,正所謂沒有最好只有更好,倘若你掌握了它,便能夠幫助你更加高效的寫代碼,讓你的代碼復用性更強、代碼更加簡潔、可維護性更高。
這種知識點就像反射、就像內省,即使你不知道它你完全也可以工作、寫業務需求。但是若你能夠熟練使用,那你的可想象空間就會更大了,未來可期。雖然它不是必須,但是它是個很好的輔助~
@ModelAttribute官方解釋
首先看看Spring官方的JavaDoc對它怎麼說:它將方法參數/方法返回值綁定到web view的Model裡面。只支持@RequestMapping這種類型的控制器哦。它既可以標註在方法入參上,也可以標註在方法(返回值)上。
但是請註意,當請求處理導致異常時,引用數據和所有其他模型內容對Web視圖不可用,因為該異常隨時可能引發,使Model內容不可靠。因此,標註有@Exceptionhandler的方法不提供對Model參數的訪問~
// @since 2.5 只能用在入參、方法上
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ModelAttribute {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
// The name of the model attribute to bind to. 註入如下預設規則
// 比如person對應的類是:mypackage.Person(類名首字母小寫)
// personList對應的是:List<Person> 這些都是預設規則咯~~~ 數組、Map的省略
// 具體可以參考方法:Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter)的處理規則
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
// 若是false表示禁用數據綁定。
// @since 4.3
boolean binding() default true;
}基本原理
我們知道@ModelAttribute能標註在入參上,也可以標註在方法上。下麵就從原理處深入理解,從而掌握它的使用,後面再給出多種使用場景的使用Demo。
和它相關的兩個類是ModelFactory和ModelAttributeMethodProcessor
@ModelAttribute預設處理的是Request請求域,Spring MVC還提供了@SessionAttributes來處理和Session域相關的模型數據,詳見:從原理層面掌握@SessionAttributes的使用【一起學Spring MVC】
關於ModelFactory的介紹,在這裡講解@SessionAttributes的時候已經介紹一大部分了,但特意留了一部分關於@ModelAttribute的內容,在本文繼續講解
ModelFactory
ModelFactory所在包org.springframework.web.method.annotation,可見它和web是強關聯的在一起的。作為上篇文章的補充說明,接下里只關心它對@ModelAttribute的解析部分:
// @since 3.1
public final class ModelFactory {
// 初始化Model 這個時候`@ModelAttribute`有很大作用
public void initModel(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
// 拿到sessionAttr的屬性
Map<String, ?> sessionAttributes = this.sessionAttributesHandler.retrieveAttributes(request);
// 合併進容器內
container.mergeAttributes(sessionAttributes);
// 這個方法就是調用執行標註有@ModelAttribute的方法們~~~~
invokeModelAttributeMethods(request, container);
...
}
//調用標註有註解的方法來填充Model
private void invokeModelAttributeMethods(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer container) throws Exception {
// modelMethods是構造函數進來的 一個個的處理吧
while (!this.modelMethods.isEmpty()) {
// getNextModelMethod:通過next其實能看出 執行是有順序的 拿到一個可執行的InvocableHandlerMethod
InvocableHandlerMethod modelMethod = getNextModelMethod(container).getHandlerMethod();
// 拿到方法級別的標註的@ModelAttribute~~
ModelAttribute ann = modelMethod.getMethodAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
Assert.state(ann != null, "No ModelAttribute annotation");
if (container.containsAttribute(ann.name())) {
if (!ann.binding()) { // 若binding是false 就禁用掉此name的屬性 讓不支持綁定了 此方法也處理完成
container.setBindingDisabled(ann.name());
}
continue;
}
// 調用目標的handler方法,拿到返回值returnValue
Object returnValue = modelMethod.invokeForRequest(request, container);
// 方法返回值不是void才需要繼續處理
if (!modelMethod.isVoid()){
// returnValueName的生成規則 上文有解釋過 本處略
String returnValueName = getNameForReturnValue(returnValue, modelMethod.getReturnType());
if (!ann.binding()) { // 同樣的 若禁用了綁定,此處也不會放進容器里
container.setBindingDisabled(returnValueName);
}
//在個判斷是個小細節:只有容器內不存在此屬性,才會放進去 因此並不會有覆蓋的效果哦~~~
// 所以若出現同名的 請自己控制好順序吧
if (!container.containsAttribute(returnValueName)) {
container.addAttribute(returnValueName, returnValue);
}
}
}
}
// 拿到下一個標註有此註解方法~~~
private ModelMethod getNextModelMethod(ModelAndViewContainer container) {
// 每次都會遍歷所有的構造進來的modelMethods
for (ModelMethod modelMethod : this.modelMethods) {
// dependencies:表示該方法的所有入參中 標註有@ModelAttribute的入參們
// checkDependencies的作用是:所有的dependencies依賴們必須都是container已經存在的屬性,才會進到這裡來
if (modelMethod.checkDependencies(container)) {
// 找到一個 就移除一個
// 這裡使用的是List的remove方法,不用擔心併發修改異常??? 哈哈其實不用擔心的 小伙伴能知道為什麼嗎??
this.modelMethods.remove(modelMethod);
return modelMethod;
}
}
// 若並不是所有的依賴屬性Model里都有,那就拿第一個吧~~~~
ModelMethod modelMethod = this.modelMethods.get(0);
this.modelMethods.remove(modelMethod);
return modelMethod;
}
...
}ModelFactory這部分做的事:執行所有的標註有@ModelAttribute註解的方法,並且是順序執行哦。那麼問題就來了,這些handlerMethods是什麼時候被“找到”的呢???這個時候就來到了RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,來看看它是如何找到這些標註有此註解@ModelAttribute的處理器的~~~
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter是個非常龐大的體系,本處我們只關心它對@ModelAttribute也就是對ModelFactory的創建,列出相關源碼如下:
// @since 3.1
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
// 該方法不能標註有@RequestMapping註解,只標註了@ModelAttribute才算哦~
public static final MethodFilter MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS = method ->
(!AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class) && AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(method, ModelAttribute.class));
...
// 從Advice裡面分析出來的標註有@ModelAttribute的方法(它是全局的)
private final Map<ControllerAdviceBean, Set<Method>> modelAttributeAdviceCache = new LinkedHashMap<>();
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
// 每調用一次都會生成一個ModelFactory ~~~
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
...
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
// 初始化Model
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
...
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
// 創建出一個ModelFactory,來管理Model
// 顯然和Model相關的就會有@ModelAttribute @SessionAttributes等註解啦~
private ModelFactory getModelFactory(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) {
// 從緩存中拿到和此Handler相關的SessionAttributesHandler處理器~~處理SessionAttr
SessionAttributesHandler sessionAttrHandler = getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod);
Class<?> handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
// 找到當前類(Controller)所有的標註的@ModelAttribute註解的方法
Set<Method> methods = this.modelAttributeCache.get(handlerType);
if (methods == null) {
methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
this.modelAttributeCache.put(handlerType, methods);
}
List<InvocableHandlerMethod> attrMethods = new ArrayList<>();
// Global methods first
// 全局的有限,最先放進List最先執行~~~~
this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.forEach((clazz, methodSet) -> {
if (clazz.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) {
Object bean = clazz.resolveBean();
for (Method method : methodSet) {
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
}
});
for (Method method : methods) {
Object bean = handlerMethod.getBean();
attrMethods.add(createModelAttributeMethod(binderFactory, bean, method));
}
return new ModelFactory(attrMethods, binderFactory, sessionAttrHandler);
}
// 構造InvocableHandlerMethod
private InvocableHandlerMethod createModelAttributeMethod(WebDataBinderFactory factory, Object bean, Method method) {
InvocableHandlerMethod attrMethod = new InvocableHandlerMethod(bean, method);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
attrMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
attrMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
attrMethod.setDataBinderFactory(factory);
return attrMethod;
}
}RequestMappingHandlerAdapter這部分處理邏輯:每次請求過來它都會創建一個ModelFactory,從而收集到全局的(來自@ControllerAdvice)+ 本Controller控制器上的所有的標註有@ModelAttribute註解的方法們。
@ModelAttribute標註在單獨的方法上(木有@RequestMapping註解),它可以在每個控制器方法調用之前,創建出一個ModelFactory從而管理Model數據~
ModelFactory管理著Model,提供了@ModelAttribute以及@SessionAttributes等對它的影響
同時@ModelAttribute可以標註在入參、方法(返回值)上的,標註在不同地方處理的方式是不一樣的,那麼接下來又一主菜ModelAttributeMethodProcessor就得登場了。
ModelAttributeMethodProcessor
從命名上看它是個Processor,所以根據經驗它既能處理入參,也能處理方法的返回值:HandlerMethodArgumentResolver + HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler。解析@ModelAttribute註解標註的方法參數,並處理@ModelAttribute標註的方法返回值。
==先看它對方法入參的處理(稍顯複雜):==
// 這個處理器用於處理入參、方法返回值~~~~
// @since 3.1
public class ModelAttributeMethodProcessor implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver, HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
private static final ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
private final boolean annotationNotRequired;
public ModelAttributeMethodProcessor(boolean annotationNotRequired) {
this.annotationNotRequired = annotationNotRequired;
}
// 入參里標註了@ModelAttribute 或者(註意這個或者) annotationNotRequired = true並且不是isSimpleProperty()
// isSimpleProperty():八大基本類型/包裝類型、Enum、Number等等 Date Class等等等等
// 所以劃重點:即使你沒標註@ModelAttribute 單子還要不是基本類型等類型,都會進入到這裡來處理
// 當然這個行為是是收到annotationNotRequired屬性影響的,具體的具體而論 它既有false的時候 也有true的時候
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return (parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class) ||
(this.annotationNotRequired && !BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(parameter.getParameterType())));
}
// 說明:能進入到這裡來的 證明入參里肯定是有對應註解的???
// 顯然不是,上面有說 這事和屬性值annotationNotRequired有關的~~~
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
// 拿到ModelKey名稱~~~(註解里有寫就以註解的為準)
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForParameter(parameter);
// 拿到參數的註解本身
ModelAttribute ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class);
if (ann != null) {
mavContainer.setBinding(name, ann.binding());
}
Object attribute = null;
BindingResult bindingResult = null;
// 如果model里有這個屬性,那就好說,直接拿出來完事~
if (mavContainer.containsAttribute(name)) {
attribute = mavContainer.getModel().get(name);
} else { // 若不存在,也不能讓是null呀
// Create attribute instance
// 這是一個複雜的創建邏輯:
// 1、如果是空構造,直接new一個實例出來
// 2、若不是空構造,支持@ConstructorProperties解析給構造賦值
// 註意:這裡就支持fieldDefaultPrefix首碼、fieldMarkerPrefix分隔符等能力了 最終完成獲取一個屬性
// 調用BeanUtils.instantiateClass(ctor, args)來創建實例
// 註意:但若是非空構造出來,是立馬會執行valid校驗的,此步驟若是空構造生成的實例,此步不會進行valid的,但是下一步會哦~
try {
attribute = createAttribute(name, parameter, binderFactory, webRequest);
} catch (BindException ex) {
if (isBindExceptionRequired(parameter)) {
// No BindingResult parameter -> fail with BindException
throw ex;
}
// Otherwise, expose null/empty value and associated BindingResult
if (parameter.getParameterType() == Optional.class) {
attribute = Optional.empty();
}
bindingResult = ex.getBindingResult();
}
}
// 若是空構造創建出來的實例,這裡會進行數據校驗 此處使用到了((WebRequestDataBinder) binder).bind(request); bind()方法 唯一一處
if (bindingResult == null) {
// Bean property binding and validation;
// skipped in case of binding failure on construction.
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, attribute, name);
if (binder.getTarget() != null) {
// 綁定request請求數據
if (!mavContainer.isBindingDisabled(name)) {
bindRequestParameters(binder, webRequest);
}
// 執行valid校驗~~~~
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
//註意:此處拋出的異常是BindException
//RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor拋出的異常是:MethodArgumentNotValidException
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new BindException(binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
// Value type adaptation, also covering java.util.Optional
if (!parameter.getParameterType().isInstance(attribute)) {
attribute = binder.convertIfNecessary(binder.getTarget(), parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
bindingResult = binder.getBindingResult();
}
// Add resolved attribute and BindingResult at the end of the model
// at the end of the model 把解決好的屬性放到Model的末尾~~~
// 可以即使是標註在入參上的@ModelAtrribute的屬性值,最終也都是會放進Model里的~~~可怕吧
Map<String, Object> bindingResultModel = bindingResult.getModel();
mavContainer.removeAttributes(bindingResultModel);
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);
return attribute;
}
// 此方法`ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor`子類是有覆寫的哦~~~~
// 使用了更強大的:ServletRequestDataBinder.bind(ServletRequest request)方法
protected void bindRequestParameters(WebDataBinder binder, NativeWebRequest request) {
((WebRequestDataBinder) binder).bind(request);
}
}模型屬性首先從Model中獲取,若沒有獲取到,就使用預設構造函數(可能是有無參,也可能是有參)創建,然後會把ServletRequest請求的數據綁定上來, 然後進行@Valid校驗(若添加有校驗註解的話),最後會把屬性添加到Model裡面
最後加進去的代碼是:mavContainer.addAllAttributes(bindingResultModel);這裡我貼出參考值:
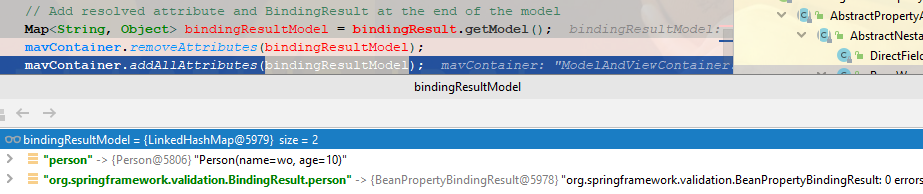
如下示例,它會正常列印person的值,而不是null(因為Model內有person了~)
請求鏈接是:/testModelAttr?name=wo&age=10
@GetMapping("/testModelAttr")
public void testModelAttr(@Valid Person person, ModelMap modelMap) {
Object personAttr = modelMap.get("person");
System.out.println(personAttr); //Person(name=wo, age=10)
}註意:雖然person上沒有標註@ModelAtrribute,但是modelMap.get("person")依然是能夠獲取到值的哦,至於為什麼,原因上面已經分析了,可自行思考。
下例中:
@GetMapping("/testModelAttr")
public void testModelAttr(Integer age, Person person, ModelMap modelMap) {
System.out.println(age); // 直接封裝的值
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println(modelMap.get("age"));
System.out.println(modelMap.get("person"));
}請求:/testModelAttr?name=wo&age=10 輸入為:
10
-------------------------------
null
Person(name=wo, age=10)可以看到普通類型(註意理解這個普通類型)若不標註@ModelAtrribute,它是不會自動識別為Model而放進來的喲~~~若你這麼寫:
@GetMapping("/testModelAttr")
public void testModelAttr(@ModelAttribute("age") Integer age, Person person, ModelMap modelMap) {
System.out.println(age); // 直接封裝的值
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
System.out.println(modelMap.get("age"));
System.out.println(modelMap.get("person"));
}列印如下:
10
-------------------------------
10
Person(name=wo, age=10)請務必註意以上case的區別,加深記憶。使用的時候可別踩坑了~
==再看它對方法(返回值)的處理(很簡單):==
public class ModelAttributeMethodProcessor implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver, HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
// 方法返回值上標註有@ModelAttribute註解(或者非簡單類型) 預設都會放進Model內哦~~
@Override
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
return (returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(ModelAttribute.class) ||
(this.annotationNotRequired && !BeanUtils.isSimpleProperty(returnType.getParameterType())));
}
// 這個處理就非常非常的簡單了,註意:null值是不放的哦~~~~
// 註意:void的話 returnValue也是null
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
if (returnValue != null) {
String name = ModelFactory.getNameForReturnValue(returnValue, returnType);
mavContainer.addAttribute(name, returnValue);
}
}
}它對方法返回值的處理非常簡單,只要不是null(當然不能是void)就都會放進Model裡面,供以使用
總結
本文介紹的是@ModelAttribute的核心原理,他對我們實際使用有重要的理論支撐。下麵系列文章主要在原理的基礎上,展示各種各樣場景下的使用Demo,敬請關註~
相關閱讀
從原理層面掌握@SessionAttributes的使用【一起學Spring MVC】
從原理層面掌握@RequestAttribute、@SessionAttribute的使用【一起學Spring MVC】
從原理層面掌握@ModelAttribute的使用(使用篇)【一起學Spring MVC】
知識交流
==The last:如果覺得本文對你有幫助,不妨點個贊唄。當然分享到你的朋友圈讓更多小伙伴看到也是被作者本人許可的~==
若對技術內容感興趣可以加入wx群交流:Java高工、架構師3群。
若群二維碼失效,請加wx號:fsx641385712(或者掃描下方wx二維碼)。並且備註:"java入群" 字樣,會手動邀請入群
若文章
格式混亂或者圖片裂開,請點擊`:原文鏈接-原文鏈接-原文鏈接


