生產環境伺服器安全策略與系統性能優化評估 1. Linux的運維經驗分享與故障排查思路 1.1 線上伺服器安裝基本策略和經驗 精簡安裝策略: 僅安裝需要的,按需安裝,不用不裝 開發包,基本網路包,基本應用包 1.1.1 CentOS 6.x ![image.png 93kB][1] 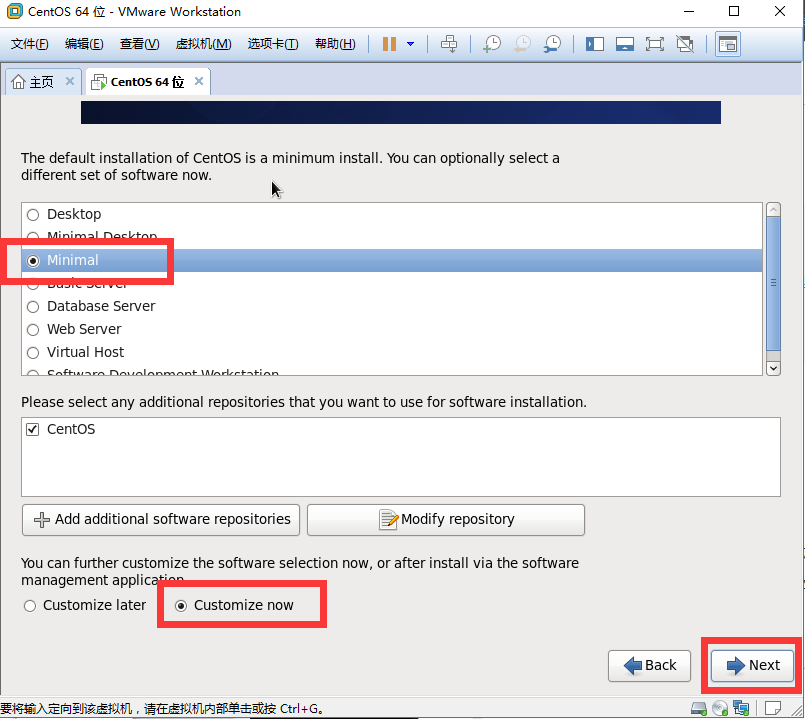
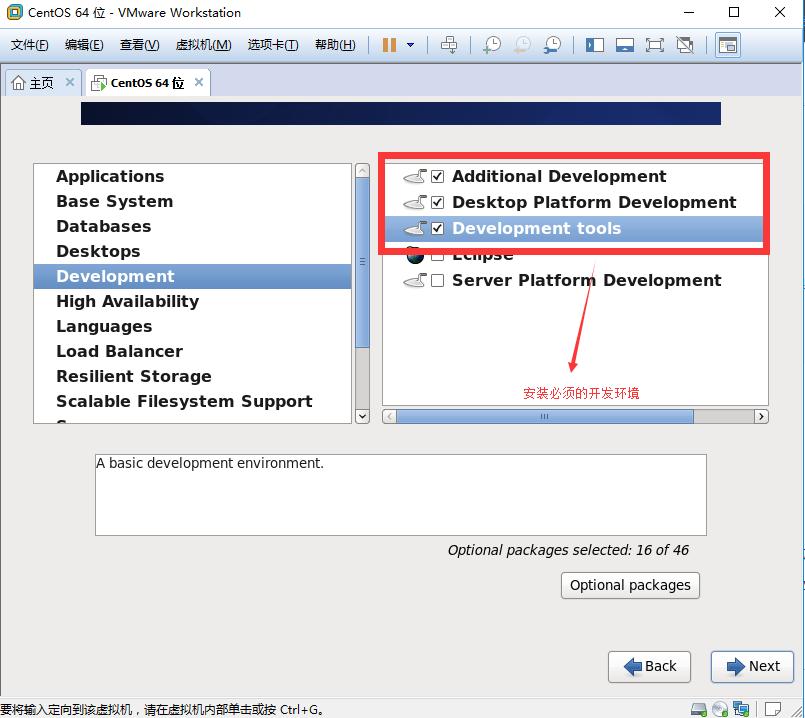
1.1.2 CentOS-7.x
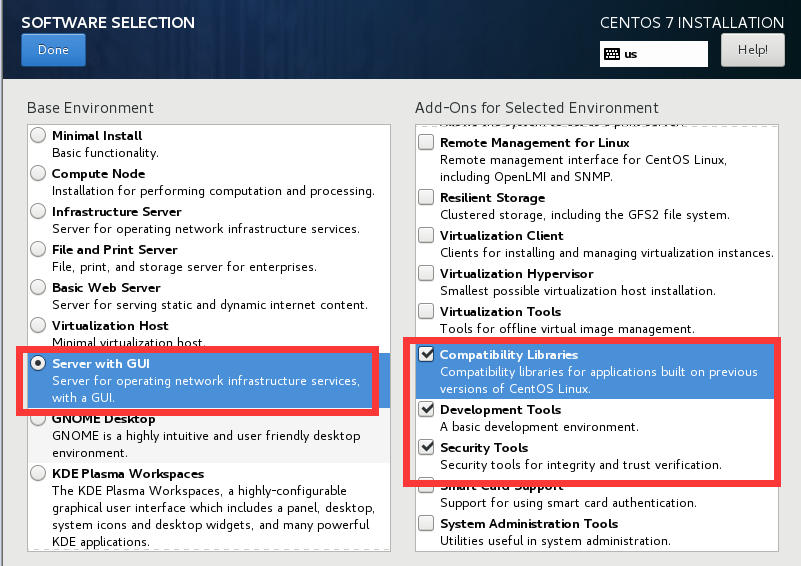
盤系統-預設按照分區方式
數據盤單獨掛載
1.2 線上伺服器網路設置經驗和技巧
1.2.1 Centos7.x下最好關閉的服務
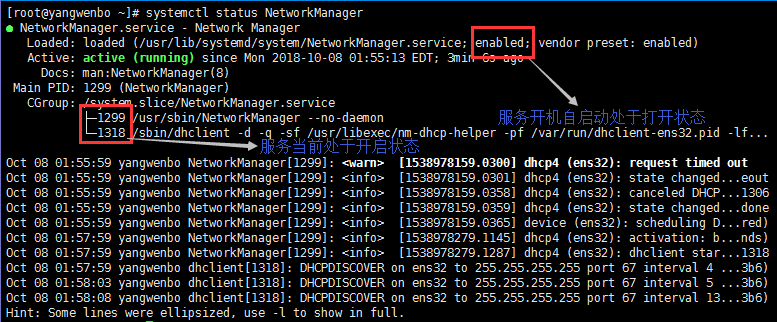
#關閉NetworkManager服務,並關閉開機啟動
[root@yangwenbo ~]# systemctl stop NetworkManager
[root@yangwenbo ~]# systemctl disable NetworkManager
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/NetworkManager.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.freedesktop.nm-dispatcher.service.
[root@yangwenbo ~]# systemctl status NetworkManager
● NetworkManager.service - Network Manager
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/NetworkManager.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Mon 2018-10-08 02:01:14 EDT; 18s ago
Docs: man:NetworkManager(8)
Main PID: 1299 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CGroup: /system.slice/NetworkManager.service
└─1344 /sbin/dhclient -d -q -sf /usr/libexec/nm-dhcp-helper -pf /var/run/dhclient-ens32.pid -lf...如果不關閉此服務,那麼此服務會接管的Linux的網路設置。有時候會導致修改了網卡配置文件IP,但是網卡的IP不變的情況
開啟NetworkManager服務,打開開機自啟動的命令
[root@yangwenbo ~]# systemctl start NetworkManager
[root@yangwenbo ~]# systemctl enable NetworkManager1.2.2 關於DNS的設置
(1)臨時修改DNS設置,修改立即生效,重啟伺服器或重啟網路後恢復
[root@yangwenbo ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
; generated by /usr/sbin/dhclient-script
search localdomain
nameserver 192.168.200.2 #修改此條配置,DNS即可被修改。立即生效修改的/etc/resolv.conf文件里的功能變數名稱伺服器,DNS即可被修改,生效立刻
但是重啟網路或者重啟伺服器的/etc/resolv.conf里的功能變數名稱伺服器設置會被網卡配置文件的設置覆蓋
[root@yangwenbo ~]# vim /etc/resolv.conf
[root@yangwenbo ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
; generated by /usr/sbin/dhclient-script
search localdomain
nameserver 192.168.200.3 #修改了此行配置
[root@yangwenbo ~]# systemctl restart network
#中間有可能會掉線
[root@yangwenbo ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
; generated by /usr/sbin/dhclient-script
search localdomain
nameserver 192.168.200.2 #配置還原了(2)永久修改DNS設置
[root@yangwenbo ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens32
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=static
DEVICE=ens32
ONBOOT=yes
NM_CONTROLLED=yes
IPADDR=192.168.200.141
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.200.2
DNS1=192.168.200.2 #永久修改需要修改網卡配置文件本行
DNS2=202.106.0.201.2.3 關於伺服器自身主機名的修改
Centos7.x
#永久修改主機名
[root@yangwenbo ~]# cat /etc/hostname
localhost.localdomain
[root@yangwenbo ~]# vim /etc/hostname
[root@yangwenbo ~]# cat /etc/hostname
Centos7.5
[root@yangwenbo ~]# hostname Centos7.5
[root@yangwenbo ~]# bash
[root@Centos7 ~]# 1.2.4 關於伺服器對自身主機名的映射
#映射伺服器自身的主機名
[root@Centos7 ~]# echo "127.0.0.1 Centos7" >> /etc/hosts
[root@Centos7 ~]# tail -1 /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 Centos7請註意伺服器映射自己的主機名,務必映射為127.0.0.1不要映射成網卡的IP 這是因為很多服務的運行都要驗證自身的主機名是否被映射,不然會導致未知的故障
1.3 線上伺服器Selinux,iptables策略設置
1.3.1 selinux配置(如何關閉selinux)
[root@Centos7 ~]# sestatus
SELinux status: enabled
#以下省略。。。
#永久關閉selinux開機自啟動
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled #當然selinux開啟自啟動不能(enforcing開啟;disabled關閉)
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
#臨時關閉selinux
[root@Centos7 ~]# setenforce 01.3.2 iptables配置
如果我們的機房沒有硬體防火牆的話,那麼我們必須通過的iptables對擁有公網網卡的伺服器做安全
#防火牆配置文件/etc/sysconfig/iptables
#推薦配置
iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT
iptables -F
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -s 1.1.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -s 2.2.2.2/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -i eth1 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags FIN,SYN,RST,PSH,ACK,URG NONE -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags FIN,SYN FIN,SYN -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN,RST -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags FIN,RST FIN,RST -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags FIN,ACK FIN -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags PSH,ACK PSH -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags ACK,URG URG -j DROP
iptables -P INPUT DROP
iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
iptables -P FORWARD DROP1.4 線上伺服器ssh登陸安全策略
1.4.1 ssh登陸策略
(1)登陸策略
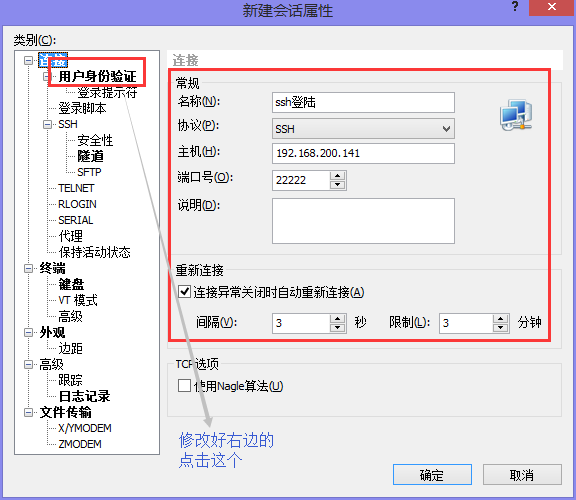
[root@Centos7 ~]# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config{,.bak} #備份
#修改前
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat -n /etc/ssh/sshd_config | sed -n '17p;38p;43p;47p;65p;79p;115p'
17 #Port 22 #修改ssh連接埠
38 #PermitRootLogin yes #是否允許root賬號遠程登陸
43 #PubkeyAuthentication yes #是否開啟公鑰連接認證
47 AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #公鑰文件的放置位置
65 PasswordAuthentication yes #是否開啟密碼驗證登陸
79 GSSAPIAuthentication yes #是否關閉GSSAPI認證
115 #UseDNS yes #是否關閉DNS反向解析
#修改後
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat -n /etc/ssh/sshd_config | sed -n '17p;38p;43p;47p;65p;79p;115p'
17 Port 22221 #工作中需要設定到1萬以上的埠,避免被掃描出來。
38 PermitRootLogin yes #如果不是超大規模的伺服器,為了方便我們可以暫時開啟root遠程登錄
43 PubkeyAuthentication yes #開啟公鑰認證模式
47 AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #公鑰放置位置
65 PasswordAuthentication no #因為我們開啟了root遠程登錄,因此為了安全我們關閉密碼認證的方式
79 GSSAPIAuthentication no #關閉GSSAPI認證,極大提高ssh連接速度
115 UseDNS no #關閉DNS反向解析,極大提高ssh連接速度(2)設置XSHELL私鑰登陸Linux的
#查看伺服器端IP
[root@Centos7 ~]# hostname -I
192.168.200.141
#在Linux伺服器端生成rsa密鑰對
[root@Centos7 ~]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M [email protected]
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| |
| |
| . |
| o . Eo|
| o . S o +.+|
| o . o * + = *.|
| o o B * O +.=|
| o * O . B ==|
| o. oOoo + .o=|
+----[SHA256]-----+#將生成的公鑰導入到伺服器端的~/.ssh/authorized_keys文件里
[root@Centos7 ~]# cd .ssh/
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# ls
id_rsa id_rsa.pub
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# cat id_rsa.pub > authorized_keys
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# ls
authorized_keys id_rsa id_rsa.pub
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# cat authorized_keys
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDmNGBvYnNojir7tfB9l7N2DplsoRHeUB4747xT2q5Z3g9CvM/D5AsyFogcCPFyfXIZuNFiH2IEQOS8ZXjpNU/1jy6sUxpwld2sMXHYiP+PtQJimS568ASVS1pzhXksHcPk8yXenPId73vQX8p8H9nD5/y94UwMksC8YsnoDSW7tOUUG9vdtjZw06lUwXfAkUapT6tEb3Mq6mA2LZMDUck1NicrdbmpAdcdsFaL3mzCHqxTvt3sNIruTiE8DhtLGpYCEBpWVOJuoZ8hRQTzaMHJaF7XHf4Yw5d0m937KY16RQnTziJOEVfHEJaUmV875SUsEacHjggj5PJfxJhq6d/P [email protected]#將私鑰文件id_rsa改名為rd_rsa_root並導出到宿主機桌面上
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# ls
authorized_keys id_rsa id_rsa.pub
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# mv id_rsa id_rsa_root
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# ls
authorized_keys id_rsa.pub id_rsa_root查看導入到桌面上的私鑰文件

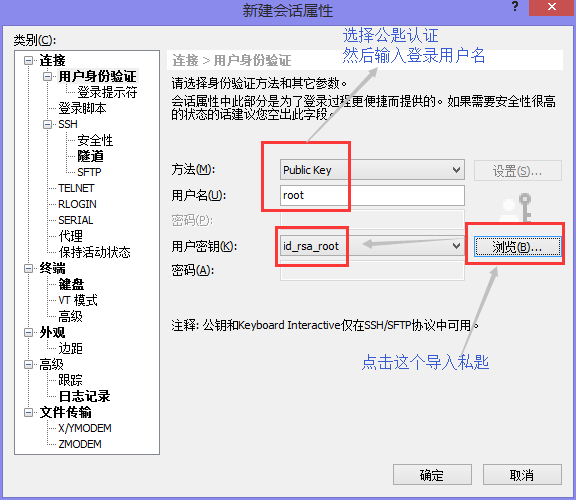
而後XSHELL顯示登陸成功!
其實這個私鑰id_rsa_root,其他發給人作為金鑰就都可以登陸伺服器端的了
也。可以發給其他的Linux伺服器使得他們可以SSH登陸金鑰到192.168.200.141伺服器端的
具體操作過程如下
#將桌面上的id_rsa_root私鑰文件拷貝到任意Linux伺服器上
[root@yangwenbo .ssh]# ls
id_rsa_root
#在Linux伺服器上就不能隨意改名字了。將id_rsa_root改名id_rsa
[root@yangwenbo .ssh]# mv id_rsa_root id_rsa
#授權600許可權
[root@yangwenbo .ssh]# chmod 600 id_rsa
#進行登陸測試
[root@yangwenbo .ssh]# ssh [email protected] -p 22222
Last login: Mon Oct 8 04:52:42 2018 from 192.168.200.143
[root@Centos7 ~]# hostname -I
192.168.200.141
[root@Centos7 ~]# exit
logout
Connection to 192.168.200.141 closed.
[root@yangwenbo .ssh]# hostname -I
192.168.200.143 XSHELL密鑰登陸伺服器端的普通用戶yunjisuan
#創建用戶
[root@Centos7 ~]# useradd yunjisuan
#創建普通用戶雲計算下的.ssh密鑰目錄
[root@Centos7 ~]# mkdir -p /home/yunjisuan/.ssh
#授權普通用戶屬主屬組
[root@Centos7 ~]# chown yunjisuan.yunjisuan /home/yunjisuan/.ssh
#.ssh目錄必須700許可權
[root@Centos7 ~]# chmod 700 /home/yunjisuan/.ssh
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# pwd
/root/.ssh
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# ll
total 12
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 396 Oct 8 03:09 authorized_keys
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 396 Oct 8 03:07 id_rsa.pub
-rw-------. 1 root root 1679 Oct 8 03:07 id_rsa_root
#將之前root下的authorized_keys文件拷貝過去,然後修改屬主屬組
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# cp -p authorized_keys /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# chown yunjisuan.yunjisuan /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/authorized_keys
[root@Centos7 .ssh]# ll /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/authorized_keys
-rw-r--r-- 1 yunjisuan yunjisuan 396 Oct 8 03:09 /home/yunjisuan/.ssh/authorized_keys最後在XSHELL端用同樣的方法遠程登錄yunjisuan用戶選擇密鑰認證方式即可。
(3)用戶許可權策略
禁止根用戶遠程登錄系統,授權僅普通用戶登陸系統,需要管理員許可權執行須藤即可,避免根用戶之間登陸
#以root賬號授權普通用戶yunjisuan所有許可權並免輸入密碼
[root@Centos7 ~]# sed -n '93p' /etc/sudoers
yunjisuan ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL#以yunjisuan用戶測試提權
[yunjisuan@Centos7 ~]$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for yunjisuan on Centos7:
!visiblepw, always_set_home, match_group_by_gid, env_reset, env_keep="COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE
KDEDIR LS_COLORS", env_keep+="MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE",
env_keep+="LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES", env_keep+="LC_MONETARY LC_NAME
LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE", env_keep+="LC_TIME LC_ALL LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY",
secure_path=/sbin\:/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin
User yunjisuan may run the following commands on Centos7:
(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL[yunjisuan@Centos7 ~]$ ls /root/ #許可權不夠
ls: cannot open directory /root/: Permission denied
[yunjisuan@Centos7 ~]$ sudo ls /root/
anaconda-ks.cfg
#如果ssh設置了不然root用戶遠程登錄的配置
#那麼我們可以通過此普通用戶面密碼方式切換成root賬戶
[yunjisuan@Centos7 ~]$ sudo su -
Last login: Mon Oct 8 04:54:17 EDT 2018 from 192.168.200.143 on pts/1
[root@Centos7 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@Centos7 ~]# exit
logout
[yunjisuan@Centos7 ~]$ ls
[yunjisuan@Centos7 ~]$ 1.5 線上伺服器更新yum源及必要軟體安裝以及NTP時鐘服務設置
1.5.1 更新常用的yum源及必要軟體包的安裝
CentOS7.x伺服器
#在CentOS7.x伺服器上
#測試一下本機是否能上網
[root@Centos7 ~]# ping -c 1 www.baidu.com
PING www.a.shifen.com (119.75.213.61) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1 (119.75.213.61): icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=7.47 ms
--- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 7.475/7.475/7.475/0.000 ms#刪除原yum本地源
[root@Centos7 ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# rm -rf *#安裝epel源
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# yum -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# ls
epel.repo epel-testing.repo#下載並安裝repoforge源
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# yum -y install http://repository.it4i.cz/mirrors/repoforge/redhat/el7/en/x86_64/rpmforge/RPMS/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el7.rf.x86_64.rpm
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# ls
epel.repo mirrors-rpmforge mirrors-rpmforge-testing
epel-testing.repo mirrors-rpmforge-extras rpmforge.repo#清空舊yum緩存,創建新yum緩存
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# yum -y clean all
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# yum makecache
#更新系統中已經安裝的軟體包
[root@Centos7 yum.repos.d]# yum -y updateCentOS6.x伺服器
#在CentOS6.x伺服器上
[root@Centos6 ~]# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/
bak CentOS-Media.repo
#測試一下伺服器是否能上網
[root@Centos6 ~]# ping -c 1 www.baidu.com
PING www.a.shifen.com (119.75.213.61) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1 (119.75.213.61): icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=15.2 ms
--- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 1463ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 15.251/15.251/15.251/0.000 ms#安裝epel源
[root@Centos6 ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# yum -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-6.noarch.rpm
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# ls
bak CentOS-Media.repo epel.repo epel-testing.repo#下載並安裝repoforge源
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# yum -y install http://repository.it4i.cz/mirrors/repoforge/redhat/el6/en/x86_64/rpmforge/RPMS/rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# ls
bak epel.repo mirrors-rpmforge mirrors-rpmforge-testing
CentOS-Media.repo epel-testing.repo mirrors-rpmforge-extras rpmforge.repo#清空舊yum緩存,創建新yum緩存
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# yum -y clean all
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# yum makecache
#更新系統中已經安裝的軟體包
[root@Centos6 yum.repos.d]# yum -y update1.5.2 修改時區與定時自動更新伺服器時間
推薦時間伺服器:ntp.sjtu.edu.cn ntp1.aliyun.com
#安裝ntpdate時間同步客戶端
[root@Centos6 ~]# yum -y install ntpdate
[root@Centos6 ~]# rpm -qa ntpdate
ntpdate-4.2.6p5-1.el6.centos.x86_64
#修改時區
[root@Centos6 ~]# cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
#進行時間同步
[root@Centos6 ~]# ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
8 Oct 17:45:36 ntpdate[1573]: adjust time server 120.25.115.20 offset -0.000011 sec
#將時間同步加入定時任務
[root@Centos6 ~]# echo '*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp.sjtu.edu.cn >> /var/log/ntp.log 2>&1;/sbin/hwclock -w' >> /var/spool/cron/root
[root@Centos6 ~]# crontab -l
*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp.sjtu.edu.cn >> /var/log/ntp.log 2>&1;/sbin/hwclock -w
#說明:/sbin/hwclock -w :將時鐘信息刷新到bios里1.6 精簡開機服務,刪除無關用戶,清理垃圾文件,重要文件安全策略
1.6.1 線上伺服器必須開啟的五個服務
crond的,網路,系統日誌,sshd的,SYSSTAT
1.6.2 刪除無關用戶
略
1.6.3 定時自動清理垃圾文件
(1)查找大文件的方法
[root@Centos7 /]# du -sh ./*
0 ./bin
97M ./boot
0 ./dev
31M ./etc
16K ./home
0 ./lib
0 ./lib64
4.2G ./media
0 ./mnt
0 ./opt
du: cannot access ‘./proc/1486/task/1486/fd/4’: No such file or directory
du: cannot access ‘./proc/1486/task/1486/fdinfo/4’: No such file or directory
du: cannot access ‘./proc/1486/fd/4’: No such file or directory
du: cannot access ‘./proc/1486/fdinfo/4’: No such file or directory
0 ./proc
48K ./root
7.6M ./run
0 ./sbin
0 ./srv
0 ./sys
0 ./tmp
998M ./usr
759M ./var[root@Centos7 /]# cd /usr/
[root@Centos7 usr]# du -sh ./*
65M ./bin
0 ./etc
0 ./games
36K ./include
437M ./lib
168M ./lib64
12M ./libexec
0 ./local
42M ./sbin
276M ./share
0 ./src
0 ./tmp(2)定時任務清理的關鍵目錄路徑
/var/spool/mail/ #郵件路徑
/var/spool/postfix/maildrop #小碎片路徑1.6.4 重要文件安全策略
- chattr + i / etc / sudoers
- chattr + i / etc / shadow
- chattr + i / etc / passwd
- chattr + i /etc/grub.conf
1.7 線上伺服器系統內核參數優化策略
1.7.1 顯示當前所有系統資源使用限制
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) 0 #core文件的最大值為100blocks
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited #進程的數據段可以任意大
scheduling priority (-e) 0 #調度優先順序
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited #文件可以任意大
pending signals (-i) 3802 #最多有3802個待處理的信號
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64 #一個任務鎖住的物理記憶體的最大值為64KB
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited #一個任務的常駐物理記憶體的最大值
open files (-n) 1024 #一個任務最多可以同時打開1024個文件
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8 #管道的最大空間為4096(512*8)位元組
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200 #POSIX的消息隊列的最大值為819200位元組
real-time priority (-r) 0 #real-time調度優先順序
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192 #進程的棧的最大值為8192位元組
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited #進程使用的CPU時間
max user processes (-u) 3802 #當前用戶同時打開的進程(包括線程)的最大個數為3802
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited #沒有限制進程的最大地址空間
file locks (-x) unlimited #所能鎖住的文件的最大個數沒有限制需要重點關註的內核參數(1):ulimit -c
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -c #查看core file size大小,預設0是關閉狀態,unlimited是沒有限制狀態
0
說明:
系統調試時用,當系統的某些進程出現問題,內部會生成一些core文件,我們通過查看這個core文件我們就可以知道發生了什麼問題。具體使用在C和C++程式中,它們利用這些文件進行調試#打開core file size無限制狀態
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -c unlimited
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -c
unlimited需要重點關註的內核參數(2):ulimit -f
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -f #系統文件的最大大小,預設unlimited是沒有限制
unlimited
說明:
控制操作系統中文本文件的大小,有時候,我們的一些應用程式的日誌文件,如果我們想控制日誌文件的最大的量值的話,我們就需要對這個參數做一些限制。這個參數具體到底限制還是不限制,要具體思考。因為如果限制文件的大小。那麼一旦到了文件設定的最大大小,應用程式就不能再寫入日誌文件了。需要重點關註的內核參數(3):ulimit -n
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -n
1024
說明:
這個參數是我們必須要調整的參數,在生產中1024這個數值基本是不夠的。1024就代表系統的記憶體中同時只能放1024個文件的句柄(打開文件)。一般來說65536就夠用了。[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -n 65536
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -n
65536需要重點關註的內核參數(4):ulimit -u
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -u #系統用戶同時打開的進程(線程)的最大數
3802
說明:
很多程式都是用普通用戶運行的。用戶能夠同時併發啟用的進程(線程)個數,就代表了我們程式的性能,很多程式都是支持高併發的。因此,這個參數我們是需要修改大的。一般來說65536就夠用了[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -u 65536
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -u
655361.7.2 修改內核參數的幾種修改方法
- / etc / profile:所有用戶生效,永久有效;
- 〜/ .bash_profile中:當前用戶生效,永久有效;
- 直接在控制台輸入,當前用戶有效,臨時生效;
- 在/etc/security/limits.conf:指定用戶或用戶組生效,永久生效;
#在/etc/security/limits.conf中設定對內核的修改,永久生效
[root@Centos7 ~]# tail -12 /etc/security/limits.conf
#<domain> <type> <item> <value>
#
#* soft core 0
#* hard rss 10000
#@student hard nproc 20
#@faculty soft nproc 20
#@faculty hard nproc 50
#ftp hard nproc 0
#@student - maxlogins 4
# End of file
說明:
<domain> 指定匹配參數修改的用戶和用戶組,*代表所有用戶;
<type> 限制的類型soft軟限制,hard硬限制;
<item> nproc代表最大進程數;nofile代表最大文件打開數;core代表限制內核文件大小;maxlogins代表此用戶允許登陸的最大數目
<value> 具體的限制數值
hard硬限制:用戶在任何時候都可以活動的進程的最大數量,這是上限。沒有任何非root進程能夠增加hard ulimit;
soft軟限制:是對會話或進程實際執行的限制,但任何進程都可以將其增加到hard ulimit的最大值#增加對系統內核參數的限制,修改完畢,退出登陸在進入即可生效
[root@Centos7 ~]# tail -4 /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 65536
* soft nproc 65536
* hard nproc 65536#退出登錄後,再驗證
[root@Centos7 ~]# ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) unlimited
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 3802
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 65536 #已經改變
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 65536 #已經改變
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited1.8 線上伺服器系統故障排查思路與關註點
(1)tail -f /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log#服務應用類日誌查詢
(2)tail -f / var / log / messages#系統應用類日誌查詢
(3)tail -f / var / log / secure#登錄日誌查詢
(4)dmesg#系統日誌查詢
(5)/ var / tmp,/ tmp#容易被攻擊的點查詢
(6)crontab -l,/ etc / crontab#計劃任務查詢(經常攻擊對象)
[root@Centos7 ~]# tail -1000 /var/log/secure | grep Accepted
Oct 8 01:48:27 localhost sshd[1235]: Accepted password for root from 192.168.200.1 port 50704 ssh2
Oct 8 02:19:58 localhost sshd[1832]: Accepted password for root from 192.168.200.1 port 50882 ssh2
Oct 8 03:12:44 localhost sshd[11788]: Accepted password for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51149 ssh2
Oct 8 03:18:29 Centos7 sshd[907]: Accepted password for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51185 ssh2
Oct 8 03:32:35 Centos7 sshd[1103]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51258 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 03:41:10 Centos7 sshd[905]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51326 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 03:41:46 Centos7 sshd[1107]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51331 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 03:42:38 Centos7 sshd[1127]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51341 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 03:42:59 Centos7 sshd[1146]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51352 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 03:44:46 Centos7 sshd[1166]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.1 port 51355 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 04:52:42 Centos7 sshd[1239]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.143 port 49638 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 04:54:17 Centos7 sshd[1257]: Accepted publickey for root from 192.168.200.143 port 49640 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M
Oct 8 05:09:39 Centos7 sshd[1318]: Accepted publickey for yunjisuan from 192.168.200.1 port 51755 ssh2: RSA SHA256:niDwzrv1Xq4er0zH0FqfHpvRiCJfPUcnL3vT89ZEt0M2. Linux的系統性能優化思路和方法
2.1 影響Linux性能的CPU,記憶體,磁碟,網路等因素分析
2.1.1 CPU
如何判斷多核CPU與超線程
- 頂部命令按數字1,可以看到CPU一共有多少核
- 在/ PROC內/ cpuinfo查看並過濾
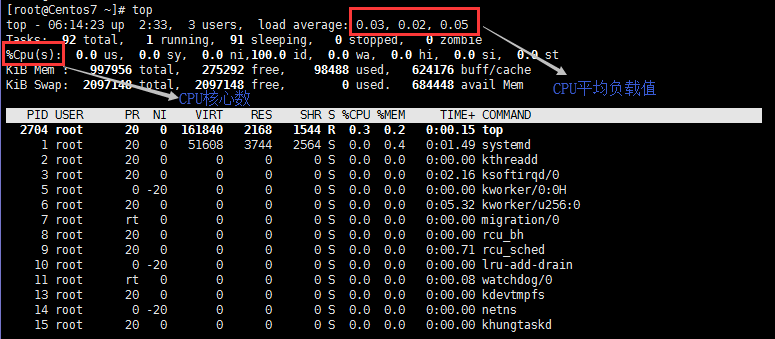
#查看/proc/cpuinfo里部分信息
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0 #CPU的線程號,過濾這個獲得伺服器的匯流排程數
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 61
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-5200U CPU @ 2.20GHz
stepping : 4
microcode : 0x11
cpu MHz : 2194.917
cache size : 3072 KB
physical id : 0 #CPU的物理ID號。過濾這個獲得伺服器的物理CPU數
siblings : 1
core id : 0 #表示當前的信息出自physical id為0的CPU上的第一個核心
cpu cores : 1 #表示當前物理physical id為0的CPU上有4個核心
apicid : 0
initial apicid : 0
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 20
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon pebs bts nopl xtopology tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc aperfmperf eagerfpu pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch epb fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 invpcid rdseed adx smap xsaveopt dtherm ida arat pln pts
bogomips : 4389.83
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 42 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:#查看物理伺服器有幾個物理CPU
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "physical id"
physical id : 0 #物理id號
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "physical id" | uniq
physical id : 0
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "physical id" | uniq | wc -l #伺服器一共有一個物理CPU
1
#查看物理伺服器的CPU的匯流排程數
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "processor" | uniq | wc -l
1
#查看物理伺服器的CPU的總核心數
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "core id" | wc -l
1主要消耗CPU的業務:動態Web服務,郵件服務
2.1.2 記憶體
- 物理記憶體與交換的取捨
- 選擇64位的Linux操作系統
如果物理記憶體大於16G,那麼交換等於物理記憶體或者是物理記憶體兩倍都是可以的。
如果物理記憶體小於16G,那麼交換和記憶體大小保持一致。
消耗記憶體的業務:記憶體資料庫(redis的/ HBase的/ mongodb的)
2.1.3 磁碟I / O.
- RAID技術(RAID 0/1/5/10)
- SSD磁碟
消耗磁碟的業務:資料庫伺服器
2.1.4 網路帶寬
- 網卡/交換機的選擇:起碼千兆網卡/千兆普通交換機/萬兆核心交換機
- 操作系統雙網卡綁定:通過綁定提高網卡帶寬吞吐量
消耗帶寬的業務:分散式文件系統,視頻業務平臺
2.2 影響Linux性能的操作系統相關資源分析
2.2.1 系統安裝優化
磁碟分區,RAID設置,交換設置
2.2.2 內核參數優化
- ulimit -n(文件最大打開數)
- ulimit -u(最大用戶的進程數)
2.2.3 文件系統優化
- EXT4:Linux的原生態文件格式
- XFS:Centos7開始預設支持
應用建議:
讀操作頻繁,同時小文件眾多的應用:首選EXT4系統-文件
寫操作頻繁的應用,首選的xfs。
2.2.4 程式問題
此類問題需要開發人員查看代碼,介入處理。但作為運維人員需要給出程式問題的有力證據。
2.3 系統性能調優之CPU性能評估工具與優化經驗
2.3.1 vmstat(系統預設自帶)
利用vmstat的命令可以對操作系統的記憶體信息,進程狀態,CPU活動等進行監視。
[root@Centos7 ~]# which vmstat
/usr/bin/vmstat
[root@Centos7 ~]# vmstat 3 5 #每3秒刷新一次,輸出5次數據
procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- -system-- ------cpu-----
r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st
2 0 0 810276 2124 108028 0 0 13 1 41 63 0 0 99 0 0
1 0 0 810276 2124 108060 0 0 0 0 66 82 0 0 100 0 0
0 0 0 810276 2124 108060 0 0 0 0 65 78 0 0 100 0 0
0 0 0 810276 2124 108060 0 0 0 0 64 78 0 0 100 0 0
0 0 0 810276 2124 108060 0 0 0 0 65 76 0 0 100 0 0特效:
- r列表示運行和等待cpu時間片的進程數,這個值如果長期大於系統CPU個數,說明CPU不足,需要增加CPU
- b列表示在等待資源的進程數,比如正在等待I / O,或者記憶體交換等。長期大於0,那麼說明CPU不足
記憶:
- swpd列表示切換到記憶體交換區的記憶體數量(以k為單位)。如果swpd的值不為0,或者比較大,只要si,so的值長期為0,這種情況下一般不用擔心,不會影響系統性能。
- 免費列表示當前空閑的物理記憶體數量(以k為單位)
- buff列表示緩存的記憶體數量,一般對塊設備的讀寫才需要緩衝。
- 緩存列表示頁面緩存的記憶體數量,一般作為文件系統緩存,頻繁訪問的文件都會被緩存,如果緩存值較大,說明緩存的文件數較多,如果此時IO中bi比較小,說明文件系統效率比較好。
交換
- si列表示由磁碟調入記憶體,也就是記憶體進入記憶體交換區的數量
- 所以列表示由記憶體調入磁碟,也就是記憶體交換區進入記憶體的數量
一般情況下,SI,SO的值都為0,如果SI,SO的值長期不為0,則表示系統記憶體不足。需要增加系統記憶體。
IO項顯示磁碟讀寫狀況
- 雙列表示從塊設備讀入數據的總量(即讀磁碟)(每秒KB)
- 柏列表示寫入到塊設備的數據重量(即寫磁碟)(每秒KB)
這裡我們設置的雙+博參考值為1000,如果超過1000,而且WA值較大,則表示系統磁碟IO有問題,應該考慮提高磁碟的讀寫性能。
system顯示採集間隔內發生的中斷數
- 在列表示在某一時間間隔中觀測到的每秒設備中斷數
- cs列表示每秒產生的上下文切換次數
上邊這兩個值越大,會看到由內核消耗的CPU時間會越多
CPU項顯示了CPU的使用狀態,此列是我們關註的重點
- 我們列顯示了用戶進程消耗的CPU時間百分比.us的值比較高時,說明用戶進程消耗的cpu時間多,但是如果長期大於50%,就需要考慮優化程式或演算法。
- sy列顯示了內核進程消耗的CPU時間百分比.Sy的值比較高時,說明內核消耗的CPU資源很多。
- 美國+ SY的參考值為80%,如果我們+ SY大於80%說明可能存在CPU資源不足。
- d列顯示了CPU處於空閑狀態的時間百分比。
- wa列顯示了IO等待所占用的CPU時間百分比。
- WA值越高,說明IO等待越嚴重,根據經驗,WA的參考值為20%時,如果WA超過20%,說明IO等待嚴重,引起IO等待的原因可能是磁碟大量隨機讀寫造成的,也可能是磁碟或者磁碟控制器的帶寬瓶頸造成的(主要是塊操作)
綜上所述:
在對CPU的評估中,需要重點註意的是特效項[R列的值和CPU項中我們,SY和ID列的值
2.3.2 iostat
[root@Centos7 ~]# iostat -c 3 5
Linux 3.10.0-862.3.3.el7.x86_64 (Centos7.5) 2018年09月01日 _x86_64_ (8 CPU)
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.03 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 99.95
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.00 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 99.96
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.002.3.3 正常運行時間和w
[root@Centos7 ~]# uptime
00:40:01 up 2:01, 2 users, load average: 0.03, 0.05, 0.05
[root@Centos7 ~]# w
00:40:03 up 2:01, 2 users, load average: 0.03, 0.05, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root tty1 00:22 16:11 0.03s 0.03s -bash
root pts/0 192.168.200.1 00:25 3.00s 0.03s 0.00s w2.4 系統性能調優之記憶體性能,磁碟性能評估工具與優化經驗
2.4.1 free -m(評估記憶體)
#查看Centos6.x的記憶體情況
[root@Centos6 ~]# free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 980 300 680 0 17 187
-/+ buffers/cache: 96 884
Swap: 1983 0 1983
說明:
系統可使用的剩餘記憶體容量:884M ===> 系統剩餘記憶體 680M + buffers 17M + cached 187M
通過swap可以看出來,交換分區使用量為0,說明系統記憶體資源還非常充足。#查看Centos7.x的記憶體情況
[root@Centos7 ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 974 76 710 7 187 737
Swap: 2047 0 2047
說明:
系統剩餘記憶體容量:710M
buffers+cache容量:187M
系統可用剩餘記憶體容量為:available 737M一般情況我們可以這樣去判斷記憶體:
- 系統可用剩餘記憶體總量/系統物理記憶體重量> 70%時,表示系統記憶體資源非常充足,不影響系統性能;
- 系統可用剩餘記憶體總量/系統物理記憶體重量<20%時,表示系統記憶體資源緊缺,需要增加系統記憶體;
- 20%<系統可用剩餘記憶體總量/系統物理記憶體重量<70%時,表示系統記憶體資源基本能滿足應用需求,暫時不影響系統性能。
2.4.2 sar(主要評估記憶體)
此兩個命令主要用於監控全部或指定進程占用系統資源的情況,如CPU,記憶體,設備I / O
三個公用參數:-u(獲取CPU狀態), - R(獲取記憶體狀態), - d(獲取磁碟)
[root@Centos7 ~]# sar -u 3 #每3秒獲取一次CPU狀態信息
Linux 3.10.0-862.3.3.el7.x86_64 (Centos7.5) 2018年09月02日 _x86_64_ (8 CPU)
15時46分38秒 CPU %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
15時46分41秒 all 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 99.96
15時46分44秒 all 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
[root@Centos7 ~]# sar -r 3 #每3秒獲取一次MEM狀態信息
Linux 3.10.0-862.3.3.el7.x86_64 (Centos7.5) 2018年09月02日 _x86_64_ (8 CPU)
15時47分57秒 kbmemfree kbmemused %memused kbbuffers kbcached kbcommit %commit kbactive kbinact kbdirty
15時48分00秒 586576 411396 41.22 2684 256608 193496 6.25 191660 103324 0
15時48分03秒 586584 411388 41.22 2684 256608 193496 6.25 191660 103324 0
說明:
kbmemfree:表示空閑物理記憶體大小
kbmemused:表示已經使用的物理記憶體大小
%memused:表示已經使用記憶體占總記憶體百分比
kbbuffers和kbcached:表示buffers和cache占用的大小
kbcommit和%commit分別表示應用程式當前使用的記憶體大小和使用百分比2.4.3 iostat -d組合(主要評估磁碟)
[root@Centos7 ~]# iostat -d 2 3
Linux 3.10.0-862.3.3.el7.x86_64 (Centos7.5) 2018年09月02日 _x86_64_ (8 CPU)
Device: tps kB_read/s kB_wrtn/s kB_read kB_wrtn
sda 0.62 16.00 6.85 207832 89039
scd0 0.02 0.23 0.00 2978 0
dm-0 0.48 15.20 6.70 197510 86991
dm-1 0.01 0.17 0.00 2228 0
Device: tps kB_read/s kB_wrtn/s kB_read kB_wrtn
sda 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
scd0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
dm-0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
dm-1 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
Device: tps kB_read/s kB_wrtn/s kB_read kB_wrtn
sda 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
scd0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
dm-0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
dm-1 0.00 0.00 0.00 0 0
說明:
DEV:表示磁碟設備名稱
tps:表示每秒到物理磁碟的傳送數,也就是每秒的I/O流量。一個傳送就是一個I/O請求,多個邏輯請求可以被合併為一個物理I/O請求。
kB_read/s:每秒讀取的數據塊
kB_wrtn/s:每秒寫入的數據塊
kB_read:讀取的所有數據塊總數
kB_wrtn:寫入的所有數據塊總數2.5 系統性能調優之網路性能評估工具
2.5.1 ping命令
[root@Centos7 ~]# ping 127.0.0.1
PING 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.016 ms
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.049 ms
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.051 ms
^C
--- 127.0.0.1 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 1999ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.016/0.038/0.051/0.017 ms
說明:
在這個輸出中,time值表示了兩台主機之間的網路延時情況,如果值很大,則表示網路的延時很大,單位為毫秒。在這個輸出的最後,還有一個統計總結。packet loss表示網路丟包率,值越小,網路質量越高2.5.2 netstat命令
- netstat -rn(查看路由情況)<====> route -n
- netstat -i(查看網路介面狀態)
[root@Centos7 ~]# netstat -rn
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.200.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 ens32
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 ens32
192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 ens32
[root@Centos7 ~]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.200.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 ens32
169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 ens32
192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 ens32
[root@Centos7 ~]# netstat -i
Kernel Interface table
Iface MTU RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flg
ens32 1500 1189 0 0 0 868 0 0 0 BMRU
lo 65536 70 0 0 0 70 0 0 0 LRU2.5.3 mtr / traceroute命令
跟蹤網路路由狀態,推薦使用地鐵,動態跟蹤網路路由,用於排除網路問題非常方便。
#安裝命令
[root@Centos6 ~]# yum -y install traceroute mtr
[root@Centos6 ~]# rpm -qa traceroute mtr
traceroute-2.0.14-2.el6.x86_64
mtr-0.75-5.el6.x86_64
#traceroute追蹤到www.baidu.com的路由器
[root@Centos6 ~]# traceroute www.baidu.com
traceroute to www.baidu.com (111.13.100.92), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 192.168.200.2 (192.168.200.2) 0.327 ms 0.206 ms 0.172 ms
2 * * *
3 * * *
4 * * *
5 * * *
6 * * *
7 * * *
#中間省略。。。
29 * * *
30 * * *traceroute雖然也能追蹤數據包,但是並不能直觀的看
mtr命令-n不用主機解析-c發送數據包個數--report結果顯示,不動態
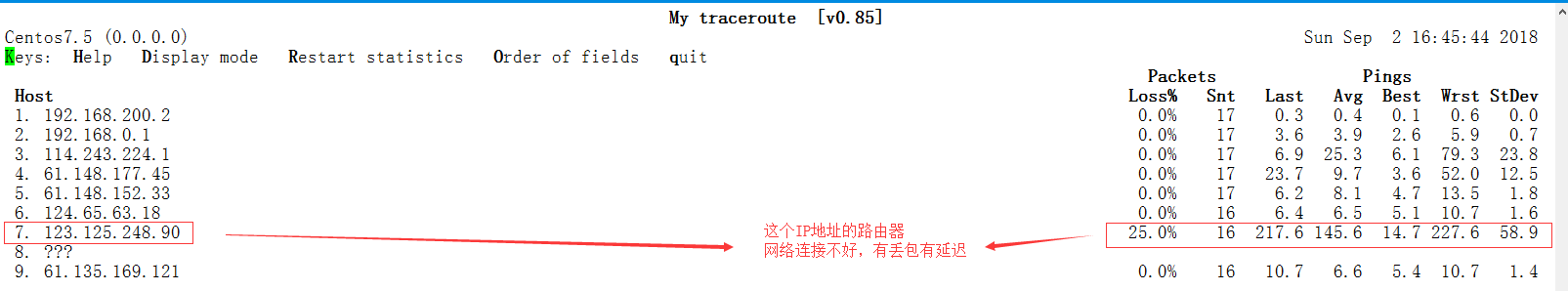
2.6 Linux操作系統性能分析標準
| 影響性能因素 | 評判標準 | 評判標準 | 評判標準 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 好 | 壞 | 糟糕 | |
| 中央處理器 | 用戶%+ SYS%<70% | 用戶%+ SYS%= 85% | 用戶%+ SYS%> = 90% |
| 記憶體 | 交換輸入(si)= 0;交換輸出(so)= 0 | 每CPU 10頁/秒 | 更多交換和交換 |
| 磁碟 | 愛荷華州%<20% | iowait%= 35% | iowait%> = 50% |
- %用戶:表示CPU處在用戶模式下的時間百分比
- %SYS:表示CPU處在系統模式下的時間百分比
- %IOWAIT:表示CPU等待輸入輸出完成時間的百分比
- 交換:即si,表示虛擬記憶體的頁導入,即從SWAP DISK交換到RAM


