1.數組的定義: 數組(Array)是相同數據類型的數據的有序集合。 2.數組的3個特點: 2.1數組長度是確定。數組一旦申請完空間,長度不能發生變化,用length屬性訪問。 2.2數組的元素都是同一數據類型。 2.3數組是有序的 。每個元素通過下標/索引標記,索引從0開始。 3.數組的3種聲明方 ...
1.數組的定義:
數組(Array)是相同數據類型的數據的有序集合。
2.數組的3個特點:
2.1數組長度是確定。數組一旦申請完空間,長度不能發生變化,用length屬性訪問。
2.2數組的元素都是同一數據類型。
2.3數組是有序的 。每個元素通過下標/索引標記,索引從0開始。
3.數組的3種聲明方式:
3.1:
int[] arr = new int[2];
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
3.2:
int[] arr2 = new int[]{10,20,30,40,50};
3.3 :
int[] arr3 = {10,20,30,40};
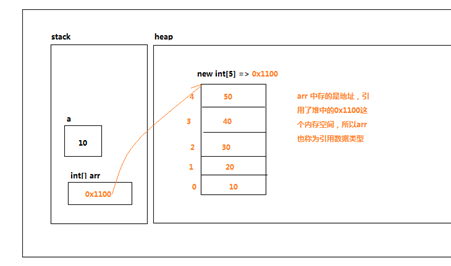
4.數組的記憶體空間
數組的數據存儲在堆空間中,聲明數組時,在棧空間中存儲數組在堆空間中的地址,所以數組時引用數據類型。
5.數組的遍歷演算法:
for(int i=0;i < arr.length;i++){
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "]" + "=" + arr[i]);
}
6.數組的常用演算法
6.1插入演算法
|
public class Test07{ public static void main(String[] args){
// 一個有序的數組,向該數組中添加一個元素,數組依然有序。 int[] arr = {1,3,7,9,12,20,0}; int t = 0;
// 【1】找位置 int loc = -1; // 表示t應該添加到的位置 for(int i = 0;i<arr.length-1;i++){ if(arr[i] >= t){ loc = i; break; } }
System.out.println("loc = "+loc);
if(loc < 0){ // 沒找到合適的位置 arr[arr.length-1] = t; }else{ // 【2】依次後移 for(int j=arr.length-1;j>loc;j--){ arr[j] = arr[j-1]; } // 【3】添加插入的值 arr[loc] = t; }
// 驗證 for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){ System.out.print(arr[i]+"\t"); } } } |
6.2刪除演算法:
|
public class Test08{ public static void main(String[] args){
// 刪除演算法 int[] arr = {1,3,7,9,12,20}; int t = 1;
// 【1】找位置 int loc = -1; for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(t == arr[i]){ loc = i; break; } }
// 【2】移動元素 if(loc < 0){ System.out.println(t+"在數組中不存在"); }else{ for(int j = loc;j<arr.length-1;j++){ arr[j] = arr[j+1]; }
// 【3】最後一個元素置0 arr[arr.length-1] = 0; }
// 驗證 for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){ System.out.print(arr[i]+"\t"); }
} } |
6.3冒泡排序演算法
|
|
|
public class Test10{ public static void main(String[] args){ // 對一個無序的數組進行排序 int[] arr = {10,5,3,4,2,9,7};
int tmp = 0; for(int i=0;i<arr.length-1;i++){ // 外層控制趟數
for(int j=0;j<arr.length-1-i;j++){ // 兩兩比較
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){ tmp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = tmp; } } }
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ System.out.print(arr[i]+"\t"); }
} } |



