1. 核心概念 StreamingContext Create StreamingContext StreamingContext的構造函數 batch interval 可以根據你的應用程式需求的延遲要求以及集群可用的資源狀況來設置 創建StreamingContext可以做什麼? 1. Defi ...
1. 核心概念
- StreamingContext
- Create StreamingContext
import org.apache.spark._ import org.apache.spark.streaming._ val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName(appName).setMaster(master) //Second(1) #表示處理的批次, 當前1秒處理一次 val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Second(1))- StreamingContext的構造函數
//StreamingContext構造函數-最常用的兩個 /** * Create a StreamingContext using an existing SparkContext. * @param sparkContext existing SparkContext * @param batchDuration the time interval at which streaming data will be divided into batches */ def this(sparkContext: SparkContext, batchDuration: Duration) = { this(sparkContext, null, batchDuration) } /** * Create a StreamingContext by providing the configuration necessary for a new SparkContext. * @param conf a org.apache.spark.SparkConf object specifying Spark parameters * @param batchDuration the time interval at which streaming data will be divided into batches */ def this(conf: SparkConf, batchDuration: Duration) = { this(StreamingContext.createNewSparkContext(conf), null, batchDuration) }batch interval可以根據你的應用程式需求的延遲要求以及集群可用的資源狀況來設置
- 創建StreamingContext可以做什麼?
- Define the input sources by creating input DStreams(通過StreamingContext可以創建輸入元數據)
- Define the streaming computations by applying transformation and output operations to DStreams(可以通過 transformation 或者 output operations 去操作DStreams)
- Start receiving data and processing it using streamingContext.start()(通過使用streamingContext.start()來接受處理數據)
- Wait for the processing to be stopped(manually or due to any error) using streamingContext.awaitTermination()(等在處理停止(自然或者發生錯誤)使用streamingContext.awaitTermination())
- The processing can be manually stopped using streamingContext.stop()(處理時可以使用streamingContext.stop()來停止)
- 創建了StreamingContext後需要註意什麼?
- Once a context has been started, no new streaming computations can be set up or added to it.(啟動一個context後,是不可以再添加計算邏輯)
- Once a context has been stopped, it cannot be restarted.(一但context停止,那麼就不能再使用代碼重新啟動)
- Only one StreamingContext can be active in a JVM at the same time.(一個StreamingContext只能在一個JVM中存活)
- stop() on StreamingContext also stops the SparkContext. To stop only the StreamingContext, set the optional parameter of stop() called stopSparkContext to false.(stop()可以停止SparkContext,如果你只想停止StreamingContext,請設置參數)
- A SparkContext can be re-used to create multiple StreamingContexts, as long as the previous StreamingContext is stopped (without stopping the SparkContext) before the next StreamingContext is created.(一個SparkContext可以創建多個StreamingContext)
DStream (Discretized Streams)
Discretized Stream or DStream is the basic abstraction provided by Spark Streaming. It represents a continuous stream of data, either the input data stream received from source, or the processed data stream generated by transforming the input stream. Internally, a DStream is represented by a continuous series of RDDs, which is Spark’s abstraction of an immutable, distributed dataset (see Spark Programming Guide for more details). Each RDD in a DStream contains data from a certain interval, as shown in the following figure.
Discretized Stream or DStream 是Spark Streaming的一個基礎抽象。它代表程式化數據流(源源不斷,不停止),可以從輸入數據流,或者通過Data Stream轉換的。換句話說,一個DStream代表的是一系列的持續不斷的RDDs。RDDs是Spark的不可變的一個分散式數據集,每一個RDD是在DStream裡面一個間隔包含的數據。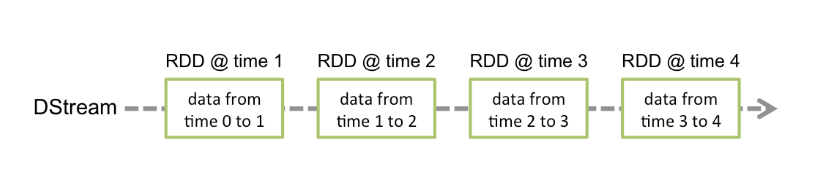
Any operation applied on a DStream translates to operations on the underlying RDDs. For example, in the earlier example of converting a stream of lines to words, the flatMap operation is applied on each RDD in the lines DStream to generate the RDDs of the words DStream. This is shown in the following figure.
對DStream操作運算元,比如map/flatMap,其實底層會被翻譯為對DStream中的每個RDD做相同的操作。因為一個DStream是由不同批次的RDD構成的。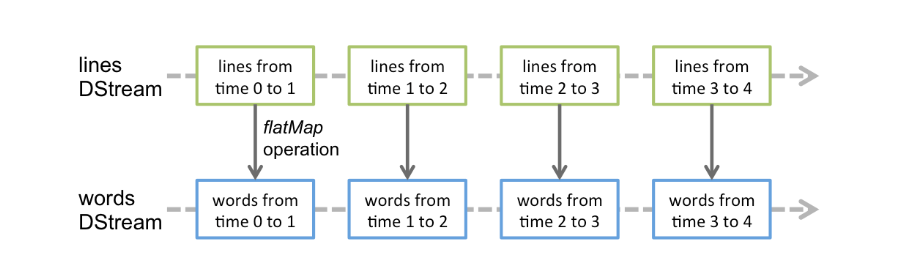
Input DStream and Receives
Input DStreams are DStreams representing the stream of input data received from streaming sources. In the quick example, lines was an input DStream as it represented the stream of data received from the netcat server. Every input DStream (except file stream, discussed later in this section) is associated with a Receiver (Scala doc, Java doc) object which receives the data from a source and stores it in Spark’s memory for processing.
Input DStreams 輸入數據的流是從數據源頭接收過來的數據。每一個Input DStream 都要關聯一個Receiver用來接收數據從數據源存到Spark的記憶體中。- Spark支持兩種數據源
- Basic sources: file systems, and socket connections.
- Advanced sources: Kafka, Flume
- Spark支持兩種數據源
2. Transformations
Similar to that of RDDs, transformations allow the data from the input DStream to be modified. DStreams support many of the transformations available on normal Spark RDD’s. Some of the common ones are as follows.
和RDD操作很相似,可以從input DStream 轉換成一個新的。函數和RDD操作差不多!
| Transformation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| map(func) | Return a new DStream by passing each element of the source DStream through a function func. |
| flatMap(func) | Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items. |
| filter(func) | Return a new DStream by selecting only the records of the source DStream on which func returns true. |
| repartition(numPartitions) | Changes the level of parallelism in this DStream by creating more or fewer partitions. |
| union(otherStream) | Return a new DStream that contains the union of the elements in the source DStream and otherDStream. |
| count() | Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by counting the number of elements in each RDD of the source DStream. |
| reduce(func) | Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by aggregating the elements in each RDD of the source DStream using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be associative and commutative so that it can be computed in parallel. |
| countByValue() | When called on a DStream of elements of type K, return a new DStream of (K, Long) pairs where the value of each key is its frequency in each RDD of the source DStream. |
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | When called on a DStream of (K, V) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function. Note: By default, this uses Spark's default number of parallel tasks (2 for local mode, and in cluster mode the number is determined by the config property spark.default.parallelism) to do the grouping. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks. |
| join(otherStream, [numTasks]) | When called on two DStreams of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. |
| cogroup(otherStream, [numTasks]) | When called on a DStream of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, Seq[V], Seq[W]) tuples. |
| transform(func) | Return a new DStream by applying a RDD-to-RDD function to every RDD of the source DStream. This can be used to do arbitrary RDD operations on the DStream. |
| updateStateByKey(func) | Return a new "state" DStream where the state for each key is updated by applying the given function on the previous state of the key and the new values for the key. This can be used to maintain arbitrary state data for each key. |
3. Output Operations
Output operations allow DStream’s data to be pushed out to external systems like a database or a file systems. Since the output operations actually allow the transformed data to be consumed by external systems, they trigger the actual execution of all the DStream transformations (similar to actions for RDDs). Currently, the following output operations are defined:
Output operations可以把數據寫到外部的數據源(database, file system)
| Output Operation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| print() | Prints the first ten elements of every batch of data in a DStream on the driver node running the streaming application. This is useful for development and debugging. Python API This is called pprint() in the Python API. |
| saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]) | Save this DStream's contents as text files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
| saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]) | Save this DStream's contents as SequenceFiles of serialized Java objects. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". Python API This is not available in the Python API. |
| saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]) | Save this DStream's contents as Hadoop files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". Python API This is not available in the Python API. |
| foreachRDD(func) | The most generic output operator that applies a function, func, to each RDD generated from the stream. This function should push the data in each RDD to an external system, such as saving the RDD to files, or writing it over the network to a database. Note that the function func is executed in the driver process running the streaming application, and will usually have RDD actions in it that will force the computation of the streaming RDDs. |
4. 實戰案例
- 基礎 Maven pom.xml 依賴配置
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<groupId>org.ko</groupId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>spark-streaming</artifactId>
<inceptionYear>2008</inceptionYear>
<properties>
<scala.version>2.11.12</scala.version>
<kafka.version>2.0.0</kafka.version>
<spark.version>2.2.1</spark.version>
<hadoop.version>3.1.0</hadoop.version>
<hbase.version>2.1.0</hbase.version>
<jackson.version>2.9.2</jackson.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--Hadoop 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>${hadoop.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Spark Streaming 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming_2.11</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--HBase Client 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Jackson json處理工具包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.module</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-module-scala_2.11</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--HBase Server 依賴-->
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-server</artifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}</version>
</dependency>-->
<!--Scala Library-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>${scala.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--Kafka 依賴-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka_2.11</artifactId>
<version>${kafka.version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.xerial.snappy</groupId>
<artifactId>snappy-java</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>*</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.xerial.snappy</groupId>
<artifactId>snappy-java</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--cdh hadoop repository-->
<!--<repositories>
<repository>
<id>cloudera</id>
<url>https://repository.cloudera.com/artifactory/cloudera-repos/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>-->
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/scala</sourceDirectory>
<testSourceDirectory>src/test/scala</testSourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.scala-tools</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-scala-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.15.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>testCompile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<scalaVersion>${scala.version}</scalaVersion>
<args>
<arg>-target:jvm-1.5</arg>
</args>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<buildcommands>
<buildcommand>ch.epfl.lamp.sdt.core.scalabuilder</buildcommand>
</buildcommands>
<additionalProjectnatures>
<projectnature>ch.epfl.lamp.sdt.core.scalanature</projectnature>
</additionalProjectnatures>
<classpathContainers>
<classpathContainer>org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER</classpathContainer>
<classpathContainer>ch.epfl.lamp.sdt.launching.SCALA_CONTAINER</classpathContainer>
</classpathContainers>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>8</source>
<target>8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.scala-tools</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-scala-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<scalaVersion>${scala.version}</scalaVersion>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
</project>Spark Streaming處理socket數據
- 1.代碼實現
/** * Spark Streaming 處理socket數據 * * 測試: nc -lk 6789 */ object NetworkWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //1. 創建spark conf配置 val sparkConf = new SparkConf() .setMaster("local[2]") .setAppName("NetworkWordCount") //2. 創建StreamingContext需要兩個參數: SparkConf 和 batch interval val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(5)) val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("192.168.37.128", 6789) val result = lines.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_+_) result.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }- 2.為什麼local[?], 一定要設置為2
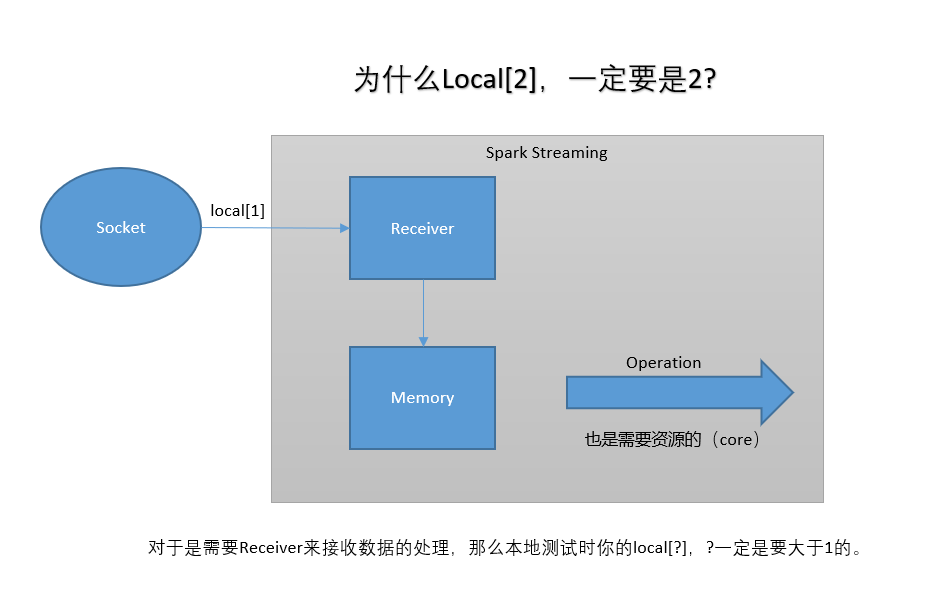
Receiver 和 Spark Core 處理都需要系統資源,所有2個是最低的數量。
Spark Streaming 處理 HDFS 文件數據
- 代碼實現
/** * <p> * 使用Spark Streaming 處理文件系統(local/HDFS)的數據 * </p> */ object FileWordCount { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val sparkConf = new SparkConf() .setMaster("local") .setAppName("FileWordCount") val ssc = new StreamingContext(sparkConf, Seconds(5)) val lines = ssc.textFileStream("D:\\tmp") val result = lines.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_+_) result.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() } }Spark Streaming會持續監控數據文件夾變化,現在不支持遞歸嵌套文件夾。
- 註意事項
- The files must have the same data format.(文件格式必須一樣)
- The files must be create in the dataDirectory by atomically moving or renaming them into the data directory.(這個文件必須創建在數據文件夾,並且是原子性的移動或者改變名字到監控文件夾)
- Once moved, the files must not be changed. So if the files are being continuously appended, the new data will not be read.(一但移動就不可以再改變,是持久的被添加進去,新寫入數據不會被處理。)



