ML.NET使用LearningPipeline類定義執行期望的機器學習任務所需的步驟,讓機器學習的流程變得直觀。 下麵用鳶尾花瓣預測快速入門的示例代碼講解流水線是如何工作的。 創建工作流實例 首先,創建LearningPipeline實例 添加步驟 然後,調用LearningPipeline實例的 ...
ML.NET使用LearningPipeline類定義執行期望的機器學習任務所需的步驟,讓機器學習的流程變得直觀。
下麵用鳶尾花瓣預測快速入門的示例代碼講解流水線是如何工作的。
using Microsoft.ML;
using Microsoft.ML.Data;
using Microsoft.ML.Runtime.Api;
using Microsoft.ML.Trainers;
using Microsoft.ML.Transforms;
using System;
namespace myApp
{
class Program
{
// STEP 1: Define your data structures
// IrisData is used to provide training data, and as
// input for prediction operations
// - First 4 properties are inputs/features used to predict the label
// - Label is what you are predicting, and is only set when training
public class IrisData
{
[Column("0")]
public float SepalLength;
[Column("1")]
public float SepalWidth;
[Column("2")]
public float PetalLength;
[Column("3")]
public float PetalWidth;
[Column("4")]
[ColumnName("Label")]
public string Label;
}
// IrisPrediction is the result returned from prediction operations
public class IrisPrediction
{
[ColumnName("PredictedLabel")]
public string PredictedLabels;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// STEP 2: Create a pipeline and load your data
var pipeline = new LearningPipeline();
// If working in Visual Studio, make sure the 'Copy to Output Directory'
// property of iris-data.txt is set to 'Copy always'
string dataPath = "iris-data.txt";
pipeline.Add(new TextLoader(dataPath).CreateFrom<IrisData>(separator: ','));
// STEP 3: Transform your data
// Assign numeric values to text in the "Label" column, because only
// numbers can be processed during model training
pipeline.Add(new Dictionarizer("Label"));
// Puts all features into a vector
pipeline.Add(new ColumnConcatenator("Features", "SepalLength", "SepalWidth", "PetalLength", "PetalWidth"));
// STEP 4: Add learner
// Add a learning algorithm to the pipeline.
// This is a classification scenario (What type of iris is this?)
pipeline.Add(new StochasticDualCoordinateAscentClassifier());
// Convert the Label back into original text (after converting to number in step 3)
pipeline.Add(new PredictedLabelColumnOriginalValueConverter() { PredictedLabelColumn = "PredictedLabel" });
// STEP 5: Train your model based on the data set
var model = pipeline.Train<IrisData, IrisPrediction>();
// STEP 6: Use your model to make a prediction
// You can change these numbers to test different predictions
var prediction = model.Predict(new IrisData()
{
SepalLength = 3.3f,
SepalWidth = 1.6f,
PetalLength = 0.2f,
PetalWidth = 5.1f,
});
Console.WriteLine($"Predicted flower type is: {prediction.PredictedLabels}");
}
}
}
創建工作流實例
首先,創建LearningPipeline實例
var pipeline = new LearningPipeline();
添加步驟
然後,調用LearningPipeline實例的Add方法向流水線添加步驟,每個步驟都繼承自ILearningPipelineItem介面。
一個基本的工作流包括以下幾個步驟,其中,藍色部分是可選的。
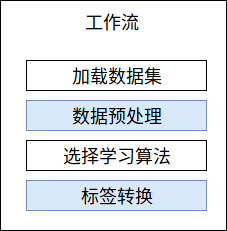
- 載入數據集
繼承自ILearningPipelineLoader介面。
一個工作流必須包含至少1個載入數據集步驟。
//使用TextLoader載入數據 string dataPath = "iris-data.txt"; pipeline.Add(new TextLoader(dataPath).CreateFrom<IrisData>(separator: ','));
- 數據預處理
繼承自CommonInputs.ITransformInput介面。
一個工作流可以包含0到多個數據預處理步驟,用於將已載入的數據集標準化,示例代碼中就包含2了個數據預處理步驟。
//由於Label文本數據,演算法不能識別數據,需要將其轉換為字典
pipeline.Add(new Dictionarizer("Label"));
//演算法只能從Features列獲取數據,需要數據中的多列連接到Features列中
pipeline.Add(new ColumnConcatenator("Features", "SepalLength", "SepalWidth", "PetalLength", "PetalWidth"));
- 選擇學習演算法
繼承自CommonInputs.ITrainerInput介面。
一個工作流必須且只能包含1個學習演算法。
//使用線性分類器 pipeline.Add(new StochasticDualCoordinateAscentClassifier());
- 標簽轉換
繼承自CommonInputs.ITransformInput介面。
一個工作流可以包含0到多個標簽轉換步驟,用於將預測得到的標簽轉換成方便識別的數據。
//將Label從字典轉換成文本數據
pipeline.Add(new PredictedLabelColumnOriginalValueConverter() { PredictedLabelColumn = "PredictedLabel" });
執行工作流
最後,調用LearningPipeline實例的Train方法,就可以執行工作流得到預測模型。
var model = pipeline.Train<IrisData, IrisPrediction>();



