app註冊感測器監聽 Android Sensor Framework 的整體架構如下圖所示: 前幾篇sensor相關的文章介紹了sensor的hal的知識,以press_sensor實時顯示氣壓坐標來分析,app層數據獲取的過程,其實實現數據監控非常簡單,主要分為下麵三個步驟: 獲取Sensor服 ...
app註冊感測器監聽
Android Sensor Framework 的整體架構如下圖所示:

前幾篇sensor相關的文章介紹了sensor的hal的知識,以press_sensor實時顯示氣壓坐標來分析,app層數據獲取的過程,其實實現數據監控非常簡單,主要分為下麵三個步驟:
- 獲取Sensor服務:getSystemService;
- 獲取具體Sensor對象:getDefaultSensor;
- 註冊數據監聽器:registerListener;
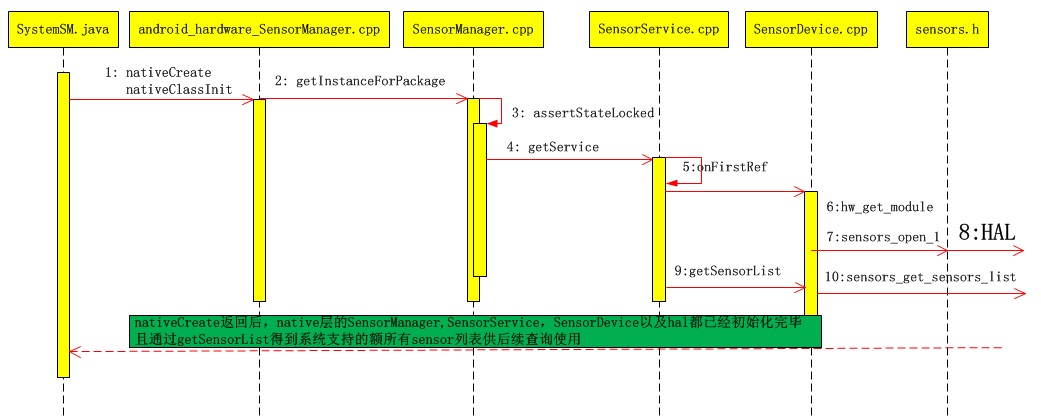
SensorService啟動
開機後,system server啟動時,就會初始化sensor service,也就是說,開機後她一直都在後臺運行著,客戶端部分,直接connect就行了。至於怎麼connect,這一切都被封裝到SensorManager里了。
SensorService服務啟動後,在隨後的第一次被強引用時,其onFirstRef會被調用,緊接著,它會獲取我們的SensorDevice實例:
void SensorService::onFirstRef() {
ALOGD("nuSensorService starting...");
SensorDevice& dev(SensorDevice::getInstance());
sHmacGlobalKeyIsValid = initializeHmacKey();
if (dev.initCheck() == NO_ERROR) {
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = dev.getSensorList(&list);
if (count > 0) {附上這部分的流程
SensorDevice作為Sensor架構中native的最後一個文件,與Hal層進行通信,故而在SensorDevice的構造方法中,我們就可以看到著名的hw_get_module和sensors_open_1方法了:
SensorDevice::SensorDevice()
: mSensorDevice(0),
mSensorModule(0) {
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't load %s module (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorModule) {
err = sensors_open_1(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't open device for module %s (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorDevice) {
if (mSensorDevice->common.version == SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1 ||
mSensorDevice->common.version == SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_2) {
ALOGE(">>>> WARNING <<< Upgrade sensor HAL to version 1_3");
}
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = mSensorModule->get_sensors_list(mSensorModule, &list);
mActivationCount.setCapacity(count);
Info model;
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) ; i++) {
mActivationCount.add(list[i].handle, model);
mSensorDevice->activate(
reinterpret_cast<struct sensors_poll_device_t *>(mSensorDevice),
list[i].handle, 0);
}
}
}
}
其中SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID是在hardware/sensors.h中定義的module名字:
/**
* The id of this module
*/
#define SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "sensors"而mSensorModule就是我們的sensors_module_t結構體,這些都是在hal層sensors.h中定義的:
/**
* Every hardware module must have a data structure named HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM
* and the fields of this data structure must begin with hw_module_t
* followed by module specific information.
*/
struct sensors_module_t {
struct hw_module_t common;
/**
* Enumerate all available sensors. The list is returned in "list".
* @return number of sensors in the list
*/
int (*get_sensors_list)(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list);
/**
* Place the module in a specific mode. The following modes are defined
*
* 0 - Normal operation. Default state of the module.
* 1 - Loopback mode. Data is injected for the supported
* sensors by the sensor service in this mode.
* @return 0 on success
* -EINVAL if requested mode is not supported
* -EPERM if operation is not allowed
*/
int (*set_operation_mode)(unsigned int mode);
};
可以看到sensors_module_t結構體擴展了hw_module_t,它裡面額外提供了get_sensor_list方法來獲取系統支持的sensor列表以及一個模式設置方法。
接下來,我們跟進hw_get_module方法,看看它到底做了什麼?
hw_get_module
該函數具體實現在hardware/libhardware/hardware.c中
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
return hw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
}int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
int i = 0;
char prop[PATH_MAX] = {0};
char path[PATH_MAX] = {0};
char name[PATH_MAX] = {0};
char prop_name[PATH_MAX] = {0};
if (inst)
snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst);
else
strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX);
/*
* Here we rely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on
* the same .so will simply increment a refcount (and not load
* a new copy of the library).
* We also assume that dlopen() is thread-safe.
*/
/* First try a property specific to the class and possibly instance */
snprintf(prop_name, sizeof(prop_name), "ro.hardware.%s", name);
if (property_get(prop_name, prop, NULL) > 0) {
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT; i++) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Nothing found, try the default */
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, "default") == 0) {
goto found;
}
return -ENOENT;
found:
/* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try
* to load a different variant. */
return load(class_id, path, module);
}我們主要看hw_get_module_by_class,這裡傳入的參數分別是“sensors”,null,以及我們的mSensorModule結構體。
首先將字元串拷貝給name:
strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX);接著拼接prop_name為ro.hardware.name,即prop_name=ro.hardware.sensors
通過property_get方法並沒有得到這個值的定義(因為在系統中並沒有對其定義),所以接下來會進入下麵的迴圈:
for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT; i++) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}/**
* There are a set of variant filename for modules. The form of the filename
* is "<MODULE_ID>.variant.so" so for the led module the Dream variants
* of base "ro.product.board", "ro.board.platform" and "ro.arch" would be:
*
* led.trout.so
* led.msm7k.so
* led.ARMV6.so
* led.default.so
*/
static const char *variant_keys[] = {
"ro.hardware", /* This goes first so that it can pick up a different
file on the emulator. */
"ro.product.board",
"ro.board.platform",
"ro.arch"
};根據上面的解析我門也可以看到,將會分別查找sensors.variant.so,sensors.product.so,sensors.platform.so,以及sensors.default.so,最終我們會在/system/lib/hw/路徑下找到sensors.msm8909.so,然後將其通過load方法載入進記憶體中運行。由此也可知,我分析的是高通8909平臺。
小細節:當我們實現了自己的HAL層module,並且寫了一個應用程式測試module是否正常工作,那麼在編譯的時候,下麵的參數應該要這樣寫:
LOCAL_MODULE := moduleName.default或者
LOCAL_MODULE := moduleName.$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM)由於上面源碼的原因,如果module名字對應不到,你的這個模塊將不會被正常的load進去,因而也就無法正常工作了。
接著我們分析load的實現。
static int load(const char *id,
const char *path,
const struct hw_module_t **pHmi)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
void *handle = NULL;
struct hw_module_t *hmi = NULL;
/*
* load the symbols resolving undefined symbols before
* dlopen returns. Since RTLD_GLOBAL is not or'd in with
* RTLD_NOW the external symbols will not be global
*/
handle = dlopen(path, RTLD_NOW);
if (handle == NULL) {
char const *err_str = dlerror();
ALOGE("load: module=%s\n%s", path, err_str?err_str:"unknown");
status = -EINVAL;
goto done;
}
/* Get the address of the struct hal_module_info. */
const char *sym = HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR;
hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);
if (hmi == NULL) {
ALOGE("load: couldn't find symbol %s", sym);
status = -EINVAL;
goto done;
}
/* Check that the id matches */
if (strcmp(id, hmi->id) != 0) {
ALOGE("load: id=%s != hmi->id=%s", id, hmi->id);
status = -EINVAL;
goto done;
}
hmi->dso = handle;
/* success */
status = 0;
done:
if (status != 0) {
hmi = NULL;
if (handle != NULL) {
dlclose(handle);
handle = NULL;
}
} else {
ALOGV("loaded HAL id=%s path=%s hmi=%p handle=%p",
id, path, *pHmi, handle);
}
*pHmi = hmi;
return status;
}- 首先通過dlopen打開sensors.xxx.so模塊,獲得其句柄handle
- 調用dlsym去獲取結構體hw_module_t結構體的地址,註意這裡傳入的字元串為HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR,定義在hardware.h頭文件中
/**
* Name of the hal_module_info
*/
#define HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM HMI
/**
* Name of the hal_module_info as a string
*/
#define HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR "HMI"這裡為什麼要去取名字為HMI的地址,我猜想它應該是HAL模塊的入口了。
ELF文件格式:
ELF = Executable and Linkable Format,可執行連接格式,是UNIX系統實驗室(USL)作為應用程式二進位介面(Application Binary Interface,ABI)而開發和發佈的,擴展名為elf。一個ELF頭在文件的開始,保存了路線圖(road map),描述了該文件的組織情況。sections保存著object 文件的信息,從連接角度看:包括指令,數據,符號表,重定位信息等等。通過file命令我們可知sensors.xx.so是一個ELF文件格式
tiny.hui@build-server:~$ file sensors.msm8909.so
sensors.msm8909.so: ELF 32-bit LSB shared object, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), BuildID[md5/uuid]=0x25812b01ab4700281b41f61327075611, not stripped因此,通過linux的readelf命令我們可以查看該文件的內部佈局及符號表等信息。
tiny.hui@build-server:~$ readelf -s sensors.msm8909.so
Symbol table '.dynsym' contains 157 entries:
Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name
0: 00000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND
1: 00000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __cxa_finalize@LIBC (2)
2: 00000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __cxa_atexit@LIBC (2)
3: 00000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __register_atfork@LIBC (2)
4: 00000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND pthread_mutex_lock@LIBC (2)
…………………………// 省略無關信息
179: 0000c179 120 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN19NativeSensorManager1
180: 0000bd21 392 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN19NativeSensorManager2
181: 0000a45b 114 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN24InputEventCircularRe
182: 000064d9 148 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN22sensors_poll_context
183: 0000d889 6 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN11sensors_XMLC1Ev
184: 0000663d 156 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN10SensorBaseC2EPKcS1_P
185: 000086d5 248 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN11AccelSensorC1Ev
186: 000088dd 248 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN11AccelSensorC2EP13Sen
187: 00014220 4 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 23 _ZN7android9SingletonI11s
188: 0000a53b 46 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN18CalibrationManager10
189: 00007775 56 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN15ProximitySensorD1Ev
190: 00014008 136 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 22 HMI
191: 0000721d 26 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZNK11AccelSensor16hasPen
192: 0000d475 16 FUNC WEAK DEFAULT 13 _ZNK7android12SortedVecto
193: 00006dd9 264 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN11LightSensorC2EPc
194: 00006181 48 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN22sensors_poll_context
195: 0000d4fd 48 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN13VirtualSensorD1Ev
196: 0000aa15 80 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN18CalibrationManagerD2
197: 000087cd 272 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 13 _ZN11AccelSensorC1EPc由符號表可知,HMI的地址為00014008,拿到函數地址,當然就可以執行對應的代碼了。
QualComm Sensor HAL
因此我們接著看sensor_hal層,高通的Sensor實現了自己的HAL,其源碼在hardware\qcom\sensors路徑下,通過Android.mk我們也可以確定他確實是我們前面load方法打開的動態鏈接庫,其編譯後會生成sensor.msm8909.so:
ifneq ($(filter msm8960 msm8610 msm8916 msm8909,$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM)),)
# Exclude SSC targets
ifneq ($(TARGET_USES_SSC),true)
# Disable temporarily for compilling error
ifneq ($(BUILD_TINY_ANDROID),true)
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
# HAL module implemenation stored in
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
ifeq ($(USE_SENSOR_MULTI_HAL),true)
LOCAL_MODULE := sensors.native
else
ifneq ($(filter msm8610,$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM)),)
LOCAL_MODULE := sensors.$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM)
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -DTARGET_8610
else
ifneq ($(filter msm8916 msm8909,$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM)),)
LOCAL_MODULE := sensors.$(TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM)
else
LOCAL_MODULE := sensors.msm8960
endif
endif
ifdef TARGET_2ND_ARCH
LOCAL_MODULE_RELATIVE_PATH := hw
else
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH := $(TARGET_OUT_SHARED_LIBRARIES)/hw
endif
endif
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DLOG_TAG=\"Sensors\"
ifeq ($(call is-board-platform,msm8960),true)
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DTARGET_8930
endif
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := $(TARGET_OUT_INTERMEDIATES)/KERNEL_OBJ/usr/include
LOCAL_ADDITIONAL_DEPENDENCIES := $(TARGET_OUT_INTERMEDIATES)/KERNEL_OBJ/usr
# Export calibration library needed dependency headers
LOCAL_COPY_HEADERS_TO := sensors/inc
LOCAL_COPY_HEADERS := \
CalibrationModule.h \
sensors_extension.h \
sensors.h
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
sensors.cpp \
SensorBase.cpp \
LightSensor.cpp \
ProximitySensor.cpp \
CompassSensor.cpp \
Accelerometer.cpp \
Gyroscope.cpp \
Bmp180.cpp \
InputEventReader.cpp \
CalibrationManager.cpp \
NativeSensorManager.cpp \
VirtualSensor.cpp \
sensors_XML.cpp \
SignificantMotion.cpp
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += external/libxml2/include \
ifeq ($(call is-platform-sdk-version-at-least,20),true)
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += external/icu/icu4c/source/common
else
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += external/icu4c/common
endif
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := liblog libcutils libdl libxml2 libutils
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := libcalmodule_common
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
algo/common/common_wrapper.c \
algo/common/compass/AKFS_AOC.c \
algo/common/compass/AKFS_Device.c \
algo/common/compass/AKFS_Direction.c \
algo/common/compass/AKFS_VNorm.c
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := liblog libcutils
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
ifdef TARGET_2ND_ARCH
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH_32 := $(TARGET_OUT_VENDOR)/lib
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH_64 := $(TARGET_OUT_VENDOR)/lib64
else
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH := $(TARGET_OUT_VENDOR_SHARED_LIBRARIES)
endif
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := calmodule.cfg
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
LOCAL_MODULE_CLASS := ETC
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH := $(TARGET_OUT_VENDOR_ETC)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := calmodule.cfg
include $(BUILD_PREBUILT)
endif #BUILD_TINY_ANDROID
endif #TARGET_USES_SSC
endif #TARGET_BOARD_PLATFORM那麼HMI的入口到底定義在這裡的那個文件中呢?
功夫不負有心人,在sensors.cpp中,我們終於找到了HMI的入口,即下麵的結構體:
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
.open = sensors_open
};
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = (uint16_t)SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "QTI Sensors Module",
.author = "Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
.dso = NULL,
.reserved = {0},
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors_get_sensors_list,
.set_operation_mode = sensors_set_operation_mode
};HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM即上文提到的HMI變數,恭喜各位,這裡我們就開啟了QualComm Sensor HAL的大門。
最後這個hw_module_t的結構體句柄會返回給我們的SensorDevice的構造函數里:
SensorDevice::SensorDevice()
: mSensorDevice(0),
mSensorModule(0)
{
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't load %s module (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorModule) {
err = sensors_open_1(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);接著,通過sensors_open_1方法將module->common傳入,打開我們的sensor驅動。
// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h
static inline int sensors_open_1(const struct hw_module_t* module,
sensors_poll_device_1_t** device) {
return module->methods->open(module,
SENSORS_HARDWARE_POLL, (struct hw_device_t**)device);
}
static inline int sensors_close_1(sensors_poll_device_1_t* device) {
return device->common.close(&device->common);
}回過頭去看看HMI的結構體定義,其中module->common->open被賦值為sensors_module_methods,其只有一個open方法,因此,module->methods->open最終會調用sensors_open方法來打開驅動程式。
到這裡native到hal層的邏輯其實已經基本上分析完了。



