今天主要和大家分享的是本人總結的分頁執行方法,也可以說就是分批執行;該篇採用java8新增的表達式來操作,希望能給各位帶來好的幫助和在日常工作中提供便利;同樣的操作流程和邏輯之前用C#代碼寫過一次,有需要的朋友可以看以前的博文; 分頁方式拆分List為多個子集List方法 執行統一方法-無返回值,關 ...
今天主要和大家分享的是本人總結的分頁執行方法,也可以說就是分批執行;該篇採用java8新增的表達式來操作,希望能給各位帶來好的幫助和在日常工作中提供便利;同樣的操作流程和邏輯之前用C#代碼寫過一次,有需要的朋友可以看以前的博文;
- 分頁方式拆分List為多個子集List方法
- 執行統一方法-無返回值,關鍵字:Consumer
- 執行統一方法-有返回值,關鍵字:Function
- 分批並行執行方法 採用:Executors+分頁方法
分頁方式拆分List為多個子集List方法
這裡我將會分享兩種拆分的方法,一種傳統subList來分割list數據,一種採用stream流來拆分;先來看第一種整體代碼:
1 /** 2 * list 分成多個子集list 3 * @param list 4 * @param pageCount 總頁數 ,如果list條數不夠,根據list條數來 5 * @param <T> 6 * @return 7 */ 8 public static <T> List<List<T>> funcToPage(List<T> list, int pageCount) { 9 10 int currentCount = list.size(); 11 //總頁數 真實線程數 12 int page = pageCount >= currentCount ? currentCount : pageCount; 13 //每頁條數 14 int pageSize = currentCount / page; 15 16 List<List<T>> pageList = new ArrayList<>(); 17 for (int i = 0; i < page; i++) { 18 //subList分頁 19 List<T> lastT = new ArrayList<>(); 20 //分頁部分 21 lastT.addAll(list.subList(i * pageSize, (i + 1) * pageSize)); 22 23 //把剩餘部分沒拆到每批次中 24 if (page * pageSize + i < currentCount) { 25 lastT.addAll(list.subList(page * pageSize + i, page * pageSize + i + 1)); 26 } 27 28 pageList.add(lastT); 29 } 30 return pageList; 31 }
這裡通過按分頁的方式來分割list數據,分頁幾乎是每個系統都會用到的方式;再來看看新特性分割的方法:
1 public static <T> List<List<T>> funcToPage(List<T> list, int pageCount) { 2 3 int currentCount = list.size(); 4 //總頁數 真實線程數 5 int page = pageCount >= currentCount ? currentCount : pageCount; 6 //每頁條數 7 int pageSize = currentCount / page; 8 9 List<List<T>> pageList = new ArrayList<>(); 10 for (int i = 0; i < page; i++) { 11 12 //採用流方式分頁 13 List<T> lastPage = list.stream(). 14 skip(i * pageSize). 15 limit(pageSize). 16 collect(Collectors.toList()); 17 18 if (page * pageSize + i < currentCount) { 19 lastPage.add( 20 list.stream(). 21 skip(page * pageSize + i). 22 limit(1). 23 findFirst(). 24 get() 25 ); 26 } 27 pageList.add(lastPage); 28 } 29 return pageList; 30 }
通過stream流藍分割,這裡用到了skip(),limit()兩個方法來分頁,這兩方法分別表示:跳到某條數據開始和限制多少條數據,最後有個findFirst()方法表示:查找第一條數據,看起來和C#的linq寫法類似;
執行統一方法-無返回值,關鍵字:Consumer
這裡要分享的關於list(當然也可以是其他)數據迴圈執行某個方法,這裡用到了Consumer提供的accept方法來接受參數,代碼如下:
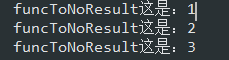
1 /** 2 * list 不返回值 3 * @param list 數據源 4 * @param consumer 5 * @param <T> 參數類型 6 */ 7 public static <T> void funcToNoResult(List<T> list, Consumer<T> consumer) { 8 list.forEach(b -> consumer.accept(b)); 9 }
測試用例:
1 List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); 2 FuncUtil.funcToNoResult(list, b -> { 3 System.out.println("funcToNoResult這是:" + b); 4 });
執行統一方法-有返回值,關鍵字:Function
和上面一樣這個方法也主要是對list數據在某個表達式中操作,但是該方法有返回值的概念,就是說先通過執行了表達式後,能夠得到執行的返回結果:
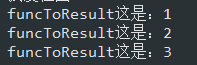
1 /** 2 * list 有返回值 3 * @param list 數據源 4 * @param function 5 * @param <T> 參數類型 6 * @param <V> 返回類型 7 * @return 8 */ 9 public static <T, V> List<V> funcToResult(List<T> list, Function<T, V> function) { 10 List<V> results = new ArrayList<>(); 11 list.forEach(b -> results.add(function.apply(b))); 12 return results; 13 }
關鍵字Function,要得到返回值主要是通過function.apply(b)方法來獲取,如下測試用例:
1 FuncUtil.funcToResult(list, b -> { 2 return "funcToResult這是:" + b; 3 }).forEach(b -> System.out.println(b));
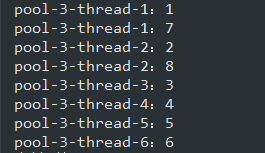
分批並行執行方法 採用:Executors+分頁方法
這裡來到今天分享的重點,該方法主要可拆分為以下幾個步驟:分批數據源-》分批並行執行-》合併結果;分配數據採用的就是上面的分頁方法,下麵具體看代碼:
1 /** 2 * 分批執行方法 採用:Executors+分頁方法 3 * @param list 數據源 4 * @param function 處理方法 lamda表達式 5 * @param maxThreadCount 處理線程數量 6 * @param <T> 參數類型 7 * @param <V> 返回類型 8 * @return 處理完成結果集 9 */ 10 public static <T, V> List<V> funcToExecutorPageSubmits(List<T> list, Function<T, V> function, int maxThreadCount) { 11 List<V> results = new ArrayList<>(); 12 13 if (list == null || list.isEmpty()) { 14 return results; 15 } 16 17 maxThreadCount = maxThreadCount <= 0 ? 1 : maxThreadCount; 18 maxThreadCount = maxThreadCount >= 10 ? 10 : maxThreadCount; 19 20 //分批數據源 21 List<List<T>> pageList = funcToPage(list, maxThreadCount); 22 23 //分批並行執行 24 List<Future<List<V>>> futures = new ArrayList<>(); 25 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(pageList.size()); 26 pageList.forEach(items -> { 27 futures.add( 28 executorService.submit(() -> { 29 List<V> childResults = new ArrayList<>(); 30 items.forEach(item -> childResults.add(function.apply(item))); 31 return childResults; 32 }) 33 ); 34 }); 35 36 //合併結果 37 futures.forEach(b -> { 38 try { 39 results.addAll(b.get()); 40 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 }); 46 47 return results; 48 }
並行執行就是用了ExecuteService+Future來接受結果,通過executorService.submit()提交執行某一批次數據需要執行的方法,最後再彙總結果;
因為有這種常見的場景:某一批數據或者url需要在執行某個按鈕事件時去調用第三方介面並同步返回數據給界面用戶,因此就有了上面方法的設計和產生。就目前該方法已被我用在了生產環境中,暫無什麼異常或者問題;以下是測試用例:
1 List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8); 2 FuncUtil.funcToExecutorPageSubmits( 3 //數據源 4 list 5 , 6 //待執行方法 7 b -> { 8 return Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + b; 9 }, 10 6). 11 //輸出返回結果 12 forEach(b -> System.out.println(b));