tcp程式設計--客戶端獲取伺服器輸入輸出流 思路: 第一步:實例化一個ServerSocket對象(伺服器套接字),用來等待網路上的請求(也就是等待來連接的套接字) 第二步:調用accept()方法,返回一個與客戶端socket對象相連接的socket對象 第三步:伺服器端socket對象使用ge ...
tcp程式設計--客戶端獲取伺服器輸入輸出流
思路:
第一步:實例化一個ServerSocket對象(伺服器套接字),用來等待網路上的請求(也就是等待來連接的套接字)
第二步:調用accept()方法,返回一個與客戶端socket對象相連接的socket對象
第三步:伺服器端socket對象使用getOutputStream方法獲得的輸出流將指向客戶端socket對象使用getInputStream獲得的輸入流,反之亦然
伺服器端代碼:
1 public class Server { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8001); 5 while (!ss.isClosed()) { 6 Socket s = ss.accept(); 7 OutputStream ops = s.getOutputStream(); 8 String str = "歡迎進入程式\n編寫TCP伺服器程式," 9 + "實現創建一個在8001埠上等待的ServerSocket" 10 + "對象,當接收到一個客戶機的連接請求後," 11 + "程式從與客戶機建立了連接的Socket對象中獲得輸入輸出" 12 + "流。通過輸出流向客戶機發送信息。"; 13 ops.write(str.getBytes()); //將字元串變成byte數組寫入 14 ops.close(); 15 s.close(); 16 } 17 ss.close(); 18 } catch (IOException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 }
客戶端代碼:
1 public class Client extends JFrame { 2 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 4 private JTextArea textArea; 5 private JTextField portField; 6 private JTextField hostField; 7 8 public static void main(String args[]) { 9 10 Client frame = new Client(); 11 frame.setVisible(true); 12 } 13 14 public Client() { 15 super(); 16 setBounds(100, 100, 500, 212); 17 setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 18 19 final JPanel panel = new JPanel(); 20 panel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.X_AXIS)); 21 getContentPane().add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH); 22 23 final JLabel label = new JLabel(); 24 label.setText("連接主機:"); 25 panel.add(label); 26 27 hostField = new JTextField(); 28 hostField.setText("localhost"); 29 panel.add(hostField); 30 31 final JLabel label_1 = new JLabel(); 32 label_1.setText("埠:"); 33 panel.add(label_1); 34 35 portField = new JTextField(); 36 portField.setText("8001"); 37 panel.add(portField); 38 39 final JButton button = new JButton(); 40 button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { 41 public void actionPerformed(final ActionEvent e) { 42 final String hostName = hostField.getText(); 43 String portNum = portField.getText(); 44 final int port = Integer.parseInt(portNum); 45 try { 46 final InetAddress host = InetAddress.getByName(hostName);//實例化對應主機的InetAddress對象 47 Socket socket = new Socket(host, port); //實例化socket 48 final InputStream is = socket.getInputStream(); //對應伺服器端的getoutputstream 49 InputStreamReader reader=new InputStreamReader(is); 50 int data = 0; 51 while ((data=reader.read()) != -1) { 52 textArea.append((char)data+""); 53 } 54 } catch (Exception e1) { 55 textArea.append(e1.toString()); 56 e1.printStackTrace(); 57 } 58 } 59 }); 60 button.setText("連接"); 61 panel.add(button); 62 63 final JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(); 64 getContentPane().add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER); 65 66 textArea = new JTextArea(); 67 textArea.setLineWrap(true); //自動換行 68 scrollPane.setViewportView(textArea); 69 } 70 }
結果如下:
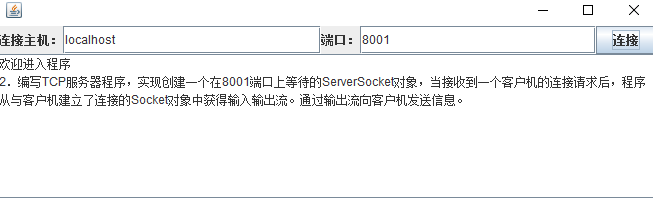
備註:
BoxLayout 箱式佈局
BoxLayout 可以把控制項依次進行水平或者垂直排列佈局,這是通過參數 X_AXIS、Y_AXIS 來決定的。X_AXIS 表示水平排列,而 Y_AXIS 表示垂直排列。BoxLayout 的構造函數有兩個參數,一個參數定義使用該 BoxLayout 的容器,另一個參數是指定 BoxLayout 是採用水平還是垂直排列



