上一節看了一眼預編譯的總體代碼,這一節分析convert-argv模塊。 這個模塊主要是對命令參數的解析。 生成預設配置文件名數組 函數內部,首先判斷了argv.d與argv.p屬性是否存在,這個屬性來源於參數d與p,即webpack -d -p,測試如圖: 因為懶得加,所以直接跳過,進入到第二階段 ...
上一節看了一眼預編譯的總體代碼,這一節分析convert-argv模塊。
這個模塊主要是對命令參數的解析,也是yargs框架的核心用處。
生成預設配置文件名數組
module.exports = function(yargs, argv, convertOptions) { var options = []; // webapck -d // 生成map映射文件,告知模塊打包地點 if(argv.d) { /* ... */ } // webpack -p // 壓縮文件 if(argv.p) { /* ... */ } // 配置文件載入標記 var configFileLoaded = false; // 配置文件載入後的載體 var configFiles = []; // 排序 var extensions = Object.keys(interpret.extensions).sort(function(a, b) { return a === ".js" ? -1 : b === ".js" ? 1 : a.length - b.length; }); // 指定所有預設配置文件名 var defaultConfigFiles = ["webpack.config", "webpackfile"].map(function(filename) { return extensions.map(function(ext) { return { path: path.resolve(filename + ext), ext: ext }; }); }).reduce(function(a, i) { return a.concat(i); }, []); // more code... }
函數內部,首先判斷了argv.d與argv.p屬性是否存在,這個屬性來源於參數d與p,即webpack -d -p,測試如圖:
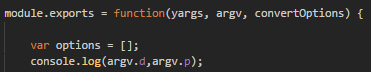

因為懶得加,所以直接跳過,進入到第二階段,生成預設配置文件名數組。
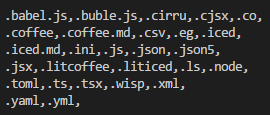
這裡引入了一個小的模塊interpret,調用Object.keys(interpret.extensions)返回一系列文件擴展名的數組,如圖:
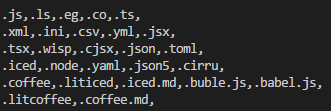
由於獲取到的數組為亂序,所以這裡首先進行排序,規則為.js放在第一位,後面的按長度從小到大,結果是這樣:
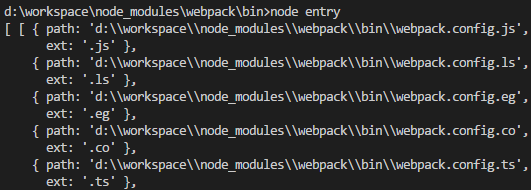
接下來是兩個map與一個reduce的調用,首先兩個map會返回一個數組,包含兩個對象數組,對象包含path、ext兩個屬性,path代表路徑+文件名+尾碼,ext就是尾碼,調用map後會得到如下數組 (截取部分):
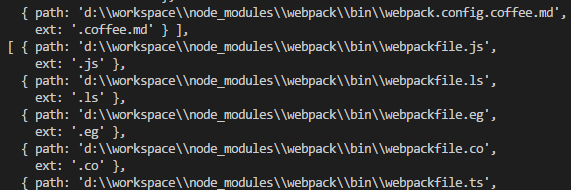
最後調用reduce方法將二維數組扁平化為一維數組,圖就不截了。
定義配置文件路徑與尾碼
有了預設列表,第二步就是嘗試獲取對應的配置文件:
var i; // 從命令行讀取--config // argv.config => config.js if(argv.config) { var getConfigExtension = function getConfigExtension(configPath) { for(i = extensions.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { var tmpExt = extensions[i]; if(configPath.indexOf(tmpExt, configPath.length - tmpExt.length) > -1) { return tmpExt; } } return path.extname(configPath); }; var mapConfigArg = function mapConfigArg(configArg) { // 獲取文件絕對路徑 var resolvedPath = path.resolve(configArg); // 獲取文件尾碼 var extension = getConfigExtension(resolvedPath); return { path: resolvedPath, ext: extension }; }; // 包裝成數組 統一處理單、多配置文件情況 var configArgList = Array.isArray(argv.config) ? argv.config : [argv.config]; configFiles = configArgList.map(mapConfigArg); } // 如果未指定配置文件 嘗試匹配預設文件名 else { for(i = 0; i < defaultConfigFiles.length; i++) { var webpackConfig = defaultConfigFiles[i].path; // 檢測路徑中是否存在對應文件 if(fs.existsSync(webpackConfig)) { configFiles.push({ path: webpackConfig, ext: defaultConfigFiles[i].ext }); break; } } }
這裡的代碼比較簡單,如果調用了--config自定義配置文件,該指令後面的會被當成參數傳給argv.config。
存在argv.config則會對文件名與合法尾碼數組進行匹配,檢測出配置文件的尾碼包裝成對象返回。
如果不指定配置文件,會進入else代碼段開始遍歷預設配置文件數組,fs.existsSync檢測當前路徑是否存在該文件,有就當成配置文件包裝返回。
獲取配置文件輸出模塊並做簡單處理
上一步只是代表接確定了配置文件的絕對路徑,這個文件並不一定是有效且存在的。
這一步會獲取到配置文件的輸出並簡單處理:
if(configFiles.length > 0) { var registerCompiler = function registerCompiler(moduleDescriptor) { // ... }; var requireConfig = function requireConfig(configPath) { // 獲取到modules.exports輸出的內容 var options = require(configPath); // 二次處理 options = prepareOptions(options, argv); return options; }; // 本例中configFiles => [{path:'d:\\workspace\\node_modules\\webpack\\bin\\config.js',ext:'.js'}] configFiles.forEach(function(file) { // interpret.extensions[.js]為null // 這裡直接跳出 registerCompiler(interpret.extensions[file.ext]); // 這裡的options是convert-argv.js開頭聲明的數組 options.push(requireConfig(file.path)); }); // 代表配置文件成功載入 configFileLoaded = true; }
這裡的處理情況有兩個:
1、根據尾碼名二次處理
2、將路徑傳進一個prepareOptions模塊處理
這個模塊內容十分簡單,可以看一下:
"use strict"; module.exports = function prepareOptions(options, argv) { argv = argv || {}; // 判斷是否通過export default輸出 options = handleExport(options); // 非數組 if(Array.isArray(options)) { options = options.map(_options => handleFunction(_options, argv)); } else { // 當options為函數時 options = handleFunction(options, argv); } return options; }; function handleExport(options) { const isES6DefaultExported = ( typeof options === "object" && options !== null && typeof options.default !== "undefined" ); options = isES6DefaultExported ? options.default : options; return options; } function handleFunction(options, argv) { if(typeof options === "function") { options = options(argv.env, argv); } return options; }
這裡針對多配置(數組)與單配置進行了處理,判斷了模塊輸出的方式(ES6、CMD)以及輸出的類型(對象、函數),最後返回處理後的配置對象並標記配置文件已被載入。
終極處理函數
接下來就是最後一個階段:
if(!configFileLoaded) { return processConfiguredOptions({}); } else if(options.length === 1) { return processConfiguredOptions(options[0]); } else { return processConfiguredOptions(options); } function processConfiguredOptions(options) { // 非法輸出類型 if(options === null || typeof options !== "object") { console.error("Config did not export an object or a function returning an object."); process.exit(-1); // eslint-disable-line } // promise檢測 if(typeof options.then === "function") { return options.then(processConfiguredOptions); } // export default檢測 if(typeof options === "object" && typeof options.default === "object") { return processConfiguredOptions(options.default); } // 數組 if(Array.isArray(options) && argv["config-name"]) { /* ... */ } // 數組 if(Array.isArray(options)) { /* ... */ } else { // 單配置 processOptions(options); } if(argv.context) { options.context = path.resolve(argv.context); } // 設置預設上下文為進程當前絕對路徑 if(!options.context) { options.context = process.cwd(); } // 跳過 if(argv.watch) { /* ... */ } if(argv["watch-aggregate-timeout"]) { /* ... */ } if(typeof argv["watch-poll"] !== "undefined") { /* ... */ } if(argv["watch-stdin"]) { /* ... */ } return options; }
這裡根據不同的情況傳入空對象、單配置對象、多配置數組。
在函數的開頭又再次檢測了合法性、promise、ES6模塊輸出方法,由於本例只有一個配置對象,所以直接進processOptions函數,這個函數很長,簡化後源碼如下:
function processOptions(options) { // 是否存在output.filename var noOutputFilenameDefined = !options.output || !options.output.filename; function ifArg(name, fn, init, finalize) { /* ... */ } function ifArgPair(name, fn, init, finalize) { /* ... */ } function ifBooleanArg(name, fn) { /* ... */ } function mapArgToBoolean(name, optionName) { /* ... */ } function loadPlugin(name) { /* ... */ } function ensureObject(parent, name) { /* ... */ } function ensureArray(parent, name) { /* ... */ }function bindRules(arg) { /* ... */ }var defineObject; // 中間穿插大量ifArgPair、ifArg、ifBooleanArg等 mapArgToBoolean("cache"); function processResolveAlias(arg, key) { /* ... */ } processResolveAlias("resolve-alias", "resolve"); processResolveAlias("resolve-loader-alias", "resolveLoader"); mapArgToBoolean("bail"); mapArgToBoolean("profile"); // 無輸出文件名配置 if (noOutputFilenameDefined) { /* ... */ } // 處理命令參數 if (argv._.length > 0) { /* ... */ } // 無入口文件配置 if (!options.entry) { /* ... */ } }
首先看一下裡面的工具函數,區別了不同參數類型的命令。
指令分類如下:
ifArg:基本處理函數
ifArgpair:命令參數存在鍵值對形式
ifBooleanArg:無參命令
mapArgToBoolean:命令參數為布爾類型
(這裡面的argv[name]均代表一個對應的指令,如:argv["entry"]代表--entry。)
1、ifArgpair、ifArg
function ifArgPair(name, fn, init, finalize) { // 直接進入ifArg函數 // content => argv[name]的數組元素 // idx => 索引 ifArg(name, function(content, idx) { // 字元"="索引 var i = content.indexOf("="); if (i < 0) { // 無等號的字元 return fn(null, content, idx); } else { // 傳入=號左邊與右邊的字元 return fn(content.substr(0, i), content.substr(i + 1), idx); } }, init, finalize); } // init => 構造函數 // finalize => 析構函數 function ifArg(name, fn, init, finalize) { if (Array.isArray(argv[name])) { if (init) { init(); } argv[name].forEach(fn); if (finalize) { finalize(); } } else if (typeof argv[name] !== "undefined" && argv[name] !== null) { if (init) { init(); } fn(argv[name], -1); if (finalize) { finalize(); } } }
2、ifBooleanArg
// 當argv[name]不為false時才執行fn函數 function ifBooleanArg(name, fn) { ifArg(name, function(bool) { if (bool) { fn(); } }); }
3、mapArgToBoolean
// 處理布爾值指令 function mapArgToBoolean(name, optionName) { ifArg(name, function(bool) { if (bool === true) options[optionName || name] = true; else if (bool === false) options[optionName || name] = false; }); }
4、ensureObject、ensureArray
// 保證指定屬性為對象 function ensureObject(parent, name) { if (typeof parent[name] !== "object" || parent[name] === null) { parent[name] = {}; } } // 保證指定屬性為數組 function ensureArray(parent, name) { if (!Array.isArray(parent[name])) { parent[name] = []; } }
5、bindRules
function bindRules(arg) { // 指令可以是a=b 也可以是單獨的a ifArgPair(arg, function(name, binding) { // 沒有等號的時候 if(name === null) { name = binding; binding += "-loader"; } // 生成對應的test正則與loader var rule = { test: new RegExp("\\." + name.replace(/[\-\[\]\/\{\}\(\)\*\+\?\.\\\^\$\|]/g, "\\$&") + "$"), // eslint-disable-line no-useless-escape loader: binding }; // 生成前置或後置loader if(arg === "module-bind-pre") { rule.enforce = "pre"; } else if(arg === "module-bind-post") { rule.enforce = "post"; } options.module.rules.push(rule); }, function() { ensureObject(options, "module"); ensureArray(options.module, "rules"); }); } bindRules("module-bind"); bindRules("module-bind-pre"); bindRules("module-bind-post");
後面的bindRules可以看出如果要在命令中引入loader,可以使用module-bind、module-bind-pre、module-bind-post三個參數。
該指令參數一般用“=”號連接需要轉換的文件類型與對應的loader,測試案例如下:

等號兩側的字元串會變成name與binding傳入函數中,並自動生成對應的test、loader並push進module.rules中。
也可以用沒有等號的字元串,此時name預設為該字元串,loader會在後面加一個-loader,測試代碼如下:

至於其餘兩個pre、post沒啥講的。
6、loadPlugin
function loadPlugin(name) { var loadUtils = require("loader-utils"); var args; try { var p = name && name.indexOf("?"); if(p > -1) { // 解析參數 args = loadUtils.parseQuery(name.substring(p)); name = name.substring(0, p); } } catch(e) { console.log("Invalid plugin arguments " + name + " (" + e + ")."); process.exit(-1); // eslint-disable-line } var path; try { var resolve = require("enhanced-resolve"); // 嘗試獲取插件模塊的絕對路徑 path = resolve.sync(process.cwd(), name); } catch(e) { console.log("Cannot resolve plugin " + name + "."); process.exit(-1); // eslint-disable-line } var Plugin; try { // 載入模塊 Plugin = require(path); } catch(e) { console.log("Cannot load plugin " + name + ". (" + path + ")"); throw e; } try { // 返回插件實例 return new Plugin(args); } catch(e) { console.log("Cannot instantiate plugin " + name + ". (" + path + ")"); throw e; } }
這裡的步驟比較清晰,如下:
1、判斷傳入參數是否形式類似於pluginname?params,對後面的參數進行解析
2、嘗試獲取插件的絕對路徑
3、嘗試載入模塊
4、嘗試調用new方法並返回模塊實例
參數解析用到了loadUtils模塊的parseQuery方法,這裡進去看一下源碼:
const specialValues = { "null": null, "true": true, "false": false }; function parseQuery(query) { // 傳入的query字元串必須以?開頭 if(query.substr(0, 1) !== "?") { throw new Error("A valid query string passed to parseQuery should begin with '?'"); } query = query.substr(1); // 如果只傳一個問號返回空對象 if(!query) { return {}; } // ?{...}的情況 // 調用JSON5嘗試進行對象解析 // JSON5是對JSON的擴展 if(query.substr(0, 1) === "{" && query.substr(-1) === "}") { return JSON5.parse(query); } // 其餘情況切割,或&符號 const queryArgs = query.split(/[,&]/g); const result = {}; queryArgs.forEach(arg => { const idx = arg.indexOf("="); // 類似於處理get請求的參數 例如:?a=1&b=2 if(idx >= 0) { let name = arg.substr(0, idx); // decodeURIComponent對URI進行解碼 let value = decodeURIComponent(arg.substr(idx + 1)); // 將null、true、false字元串轉換為值 if(specialValues.hasOwnProperty(value)) { value = specialValues[value]; } // key以[]結尾 if(name.substr(-2) === "[]") { // 截取key並設置值為數組 name = decodeURIComponent(name.substr(0, name.length - 2)); if(!Array.isArray(result[name])) result[name] = []; result[name].push(value); } // 正常情況直接在result對象上添加屬性 else { name = decodeURIComponent(name); result[name] = value; } } else { // ?-a&+b&c => result = {a:false,b:true,c:true} if(arg.substr(0, 1) === "-") { result[decodeURIComponent(arg.substr(1))] = false; } else if(arg.substr(0, 1) === "+") { result[decodeURIComponent(arg.substr(1))] = true; } else { result[decodeURIComponent(arg)] = true; } } }); return result; }
除去不合理的傳參,可以用兩種模式進行傳參:
1、正常模式:?a&a=1&-a&+b&a[]=1
首碼為"-"、"+"會在else被處理,"-"符號開頭值會被視為false,無首碼或者為"+"會被視為true。
類似於get請求參數會被一樣處理,進行字元串切割並依次添加進result對象。
最後一種比較特殊,代表參數a是一個數組,學過JAVA或者C++應該會熟悉這種聲明方式。
2、JSON模式:?{...}
以"{"開頭"}"結尾會被進行JSON解析,註意這裡不是普通的JSON.parse,而是引入了一個JSON的擴展JSON5,該工具相對於JSON擴展了多項功能,例如:
(1)JSON不允許有註釋
(2)JSON中的key必須要用雙引號包起來
(3)JSON對象、數組尾部不允許出現多餘的逗號
等等。
詳情可見:https://www.npmjs.com/package/json5
測試代碼如下:
普通模式: 
JSON模式:
7、processResolveAlias
function processResolveAlias(arg, key) { ifArgPair(arg, function(name, value) { // 必須以a=1這種鍵值對形式進行傳參 if(!name) { throw new Error("--" + arg + " <string>=<string>"); } /** * resolve:{ * alias:{ * * } * } */ ensureObject(options, key); ensureObject(options[key], "alias"); options[key].alias[name] = value; }); } processResolveAlias("resolve-alias", "resolve"); processResolveAlias("resolve-loader-alias", "resolveLoader");
這裡處理--resolve-alias指令與resolve-loader-alias指令,該指令參數必須嚴格按照a=b形式。
測試代碼如下:

因為配置文件只有entry和output,所以屬性都是undefined或false,都會跳過。
這裡簡單看幾個常用的:
// 熱重載 ifBooleanArg("hot", function() { ensureArray(options, "plugins"); var HotModuleReplacementPlugin = require("../lib/HotModuleReplacementPlugin"); options.plugins.push(new HotModuleReplacementPlugin()); }); // loaderOptionsPlugin插件 ifBooleanArg("debug", function() { ensureArray(options, "plugins"); var LoaderOptionsPlugin = require("../lib/LoaderOptionsPlugin"); options.plugins.push(new LoaderOptionsPlugin({ debug: true })); }); // 代碼壓縮插件 ifBooleanArg("optimize-minimize", function() { ensureArray(options, "plugins"); var UglifyJsPlugin = require("../lib/optimize/UglifyJsPlugin"); var LoaderOptionsPlugin = require("../lib/LoaderOptionsPlugin"); options.plugins.push(new UglifyJsPlugin({ // devtool參數 sourceMap: options.devtool && (options.devtool.indexOf("sourcemap") >= 0 || options.devtool.indexOf("source-map") >= 0) })); options.plugins.push(new LoaderOptionsPlugin({ minimize: true })); });
可以看到,使用--hot、--debug、--optimize-minimize指令會分別載入3個插件,一個是處理loader中Options屬性的LoaderOptionsPlugin插件,一個是代碼壓縮插件UglifyJsPlugin,還有一個就是熱重載插件,3個插件後面的章節有空再講。所有屬性在之前的config-yargs中被配置,但是預設值為false,而ifBooleanArg在傳入值為false時不會執行回調,所以這裡並不是載入任何東西。
其他還有很多指令類似於--output-path可以設置output.path參數等等,有興趣的可以自己去源碼看。
最後剩下3個代碼塊:
// 無輸出文件名配置 if (noOutputFilenameDefined) { /* ... */ } // 處理命令參數 if (argv._.length > 0) { /* ... */ } // 無入口文件配置 if (!options.entry) { /* ... */ }
由於指令沒有傳任何額外參數,所以argv._是一個空數組,中間的可以跳過。
所以只需要看其餘兩個,首先看簡單的無入口文件配置的情況,即配置文件沒有entry屬性:
if (!options.entry) { // 存在配置文件 但是沒有入口函數 if (configFileLoaded) { console.error("Configuration file found but no entry configured."); } // 未找到配置文件 else { console.error("No configuration file found and no entry configured via CLI option."); console.error("When using the CLI you need to provide at least two arguments: entry and output."); console.error("A configuration file could be named 'webpack.config.js' in the current directory."); } console.error("Use --help to display the CLI options."); // 退出進程 process.exit(-1); // eslint-disable-line }
可以看出這是必傳參數,根據是否找到對應的配置文件報不同的錯誤。
另一種情況是不存在ouput或output.filename屬性:
if (noOutputFilenameDefined) { ensureObject(options, "output"); // convertOptions來源於第三個參數 // module.exports = function(yargs, argv, convertOptions) {...} // var options = require("./convert-argv")(yargs, argv) // 只傳了兩個參數 所以跳過 if (convertOptions && convertOptions.outputFilename) { options.output.path = path.resolve(path.dirname(convertOptions.outputFilename)); options.output.filename = path.basename(convertOptions.outputFilename); } // 嘗試從命令參數獲取output.filename // 命令的最後一個參數會被當成入口文件名 else if (argv._.length > 0) { options.output.filename = argv._.pop(); options.output.path = path.resolve(path.dirname(options.output.filename)); options.output.filename = path.basename(options.output.filename); } // 老套的報錯 不解釋 else if (configFileLoaded) { throw new Error("'output.filename' is required, either in config file or as --output-filename"); } else { console.error("No configuration file found and no output filename configured via CLI option."); console.error("A configuration file could be named 'webpack.config.js' in the current directory."); console.error("Use --help to display the CLI options."); process.exit(-1); // eslint-disable-line } }
可以看出,output.filename也是必須的,但是不一定需要在配置文件中,有兩個方式可以傳入。
一個是作為convert-argv.js的第三個參數傳入,由於在之前解析時預設只傳了兩個,這裡會跳過,暫時不清楚傳入地點。
另外一個是在命令中傳入,測試代碼:


至此,模塊全部解析完畢,輸出options如圖所示:
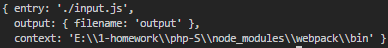
真是累……



