2024/07/15 1.問題描述 2.問題處理 3.其他問題 1.問題描述 昨天伺服器突然斷電,今天重啟後,網路出了些問題,具體情況如下: 能ping通本機IP ping不通網關 ping不通本網段其他IP地址 ping不通其他網段地址 2.問題處理 vi /etc/sysconfig/netwo ...
一.主從相關的配置
1.1 masterauth
# If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration # directive below) it is possible to tell the replica to authenticate before # starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will # refuse the replica request. # # masterauth <master-password> #
因為我們要搭建主從集群,且每個主機都有可能會是Master,如果設置驗證屬性requirepass。一定要每個主機的密碼都設置為相同的。此時每個配置文件中都要設置兩個完全相同的屬性:requirepass與masterauth。其中requirepass用戶指定當前主機的訪問密碼,而masterauth用於指定當前slave訪問master時向master提交的訪問密碼,用於讓master驗證請求者身份是否合法。
1.2 repl-disable-tcp-nodelay
# Disable TCP_NODELAY on the replica socket after SYNC? # # If you select "yes" Redis will use a smaller number of TCP packets and # less bandwidth to send data to replicas. But this can add a delay for # the data to appear on the replica side, up to 40 milliseconds with # Linux kernels using a default configuration. # # If you select "no" the delay for data to appear on the replica side will # be reduced but more bandwidth will be used for replication. # # By default we optimize for low latency, but in very high traffic conditions # or when the master and replicas are many hops away, turning this to "yes" may # be a good idea. repl-disable-tcp-nodelay no
該屬性用於設置是否禁用TCP特性tcp-nodelay。設置為yes則禁用tcp-nodelay,此時master與slave間的通信會產生延遲,但使用的TCP包數量較少,占用的網路帶寬會較小。相反,如果設置為no,則網路延遲會變小,但使用的TCP包數量會較多,相應占用的網路帶寬會變大。
知識點補充---tcp-nodelay
為了充分復用網路帶寬,TCP總是希望發送儘可能大的數據塊。為了達到該目的,TCP中使用了一個名為Nagle的演算法。
Nagle演算法的原理是,網路在接收到要發送的數據後,並不直接發送,而是等待著數據量足夠大(由TCP網路特性決定)時再一次性發送出去。這樣,網路上傳輸的有效數據的比例就等到了大大提升,無效數據的傳輸極大減少,於是就節省了網路帶寬,緩解了網路壓力。
tcp-nodelay 則是TCP協議中Nagle演算法的開關。
1.3 pidfile
# If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup # and removes it at exit. # # When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is # specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file # is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid". # # Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it # nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally. # # Note that on modern Linux systems "/run/redis.pid" is more conforming # and should be used instead. pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
如果是多實例安裝(一臺機器上安裝多個redis實例),記得要修改這個參數。
當然,另外一些參數配置
埠號(port)、dbfilename、appendfilename、logfile、replica-priority
簡單說下 replica-priority
# The replica priority is an integer number published by Redis in the INFO # output. It is used by Redis Sentinel in order to select a replica to promote【提升;晉升;】 # into a master if the master is no longer working correctly. # # A replica with a low priority number is considered better for promotion, so ##越小優先順序越高 # for instance if there are three replicas with priority 10, 100, 25 Sentinel # will pick the one with priority 10, that is the lowest. # # However a special priority of 0 marks the replica as not able to perform the ##特殊的優先順序的值為0 # role of master, so a replica with priority of 0 will never be selected by ##0喪失了稱為master的可能性 # Redis Sentinel for promotion. # # By default the priority is 100. replica-priority 100
1.4 個性化的配置依賴參數include
################################## INCLUDES ################################### # Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you # have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need # to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include # other files, so use this wisely. # # Note that option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE" # from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed # line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes # at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runtime. # # If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration # options, it is better to use include as the last line. # # Included paths may contain wildcards. All files matching the wildcards will # be included in alphabetical order. # Note that if an include path contains a wildcards but no files match it when # the server is started, the include statement will be ignored and no error will # be emitted. It is safe, therefore, to include wildcard files from empty # directories. # # include /path/to/local.conf # include /path/to/other.conf # include /path/to/fragments/*.conf # ################################## MODULES #####################################
例如我們想獨立出一個配置文件,但是呢,只想修改幾個或者少部分參數項,這時候,可以include進基本的配置文件,只把需要修改的參數,重寫下即可。
二. 設置主從關係
2.1 查看
先查看下主從關係,查看指令
> info replication
在主節點上執行,
返回值 role 代表當前節點的角色;
connected_slaves的數值代表 從節點 的個數;
如果有slave節點的話,會以slave0、slave1 呈現出具體的slave信息(ip:port:state:offset:lag)。
而在從節點上執行的話,返回值是不一樣的:
返回值role 代表集群角色,其他的返回值還有master_ip、master_port、master_link_status、master_last_io_seconds_age、master_sync_in_process、slave_read_only等等。
需要註意的是從節點是不可以執行寫命令的,否則報錯
(error)READONLY You can't write against a read only replica.
2.2 設置命令
在從節點上執行命令,如下
> slaveof host(主節點ip) port(主節點的埠號)
只執行上面的命令,如果從節點重啟的話,主從關係就會失效,即丟失已設置的主從關係。
2.3. 分級管理
若redis主從集群中的slave較多時,他們的數據同步過程會對master形成較大的性能壓力。此時,可以對這些slave進行分級管理。
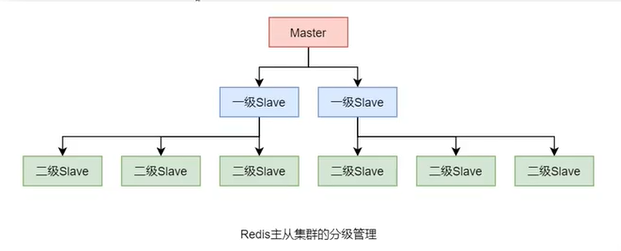
設置方式很簡單,只需要讓低級別slave指定其slaveof的主機為上一級slave即可。不過,上一級slave的狀態仍為slave,只不過,其是更上一級的slave。
調整主從關係,不需要關閉已有關係,再重建,而是直接執行 slaveof host port 進行調整即可。
2.4 容災冷處理
在master/slave的redis集群中,若master出現了宕機怎麼辦?有兩種處理方式,一種是通過手工角色調整,使slave晉升為master的冷處理;一種是使用哨兵模式,實現redis集群的高可用HA,即熱處理。
無論master是否宕機,slave都可以通過下麵的命令,將自己提升為master。
> slaveof no one
如果其原本就有下一級的slave,那麼,其就直接變為了這些slave的真正的master了。而原來的master就會失去了這個原來的slave。
三. 主從複製原理
3.1 主從複製過程
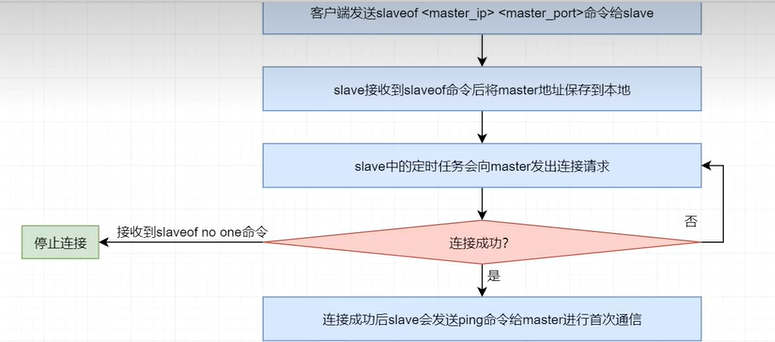
當一個redis節點(slave)接收到類似slaveof 127.0..1 6379 的指令後直至其可以從master持續複製數據,大體經歷瞭如下幾個過程:
(1)保存master地址
當slave接收到slaveof <master_ip> <master_port>指令後,slave會立即將新的master的地址保存下來。
(2)建立連接
slave中維護著一個定時任務,該定時任務會嘗試著與該master建立socker連接。
(3)slave發送ping命令
連接成功後,slave會發送ping命令,進行首次通信。如果slave沒有收到master的回覆,則slave就會主動斷開連接,下次的定時任務會重新嘗試連接。
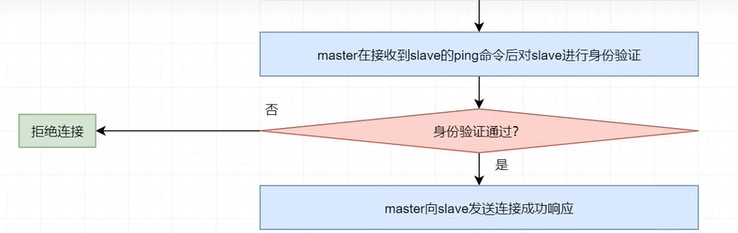
(4)對slave身份驗證
master 在接收到slave的ping命令後,並不會立即對其進行回覆,而是先對Salve進行身份驗證。如果驗證不通過,則會發送消息拒絕連接;。驗證通過,master 向slave發送連接成功響應。
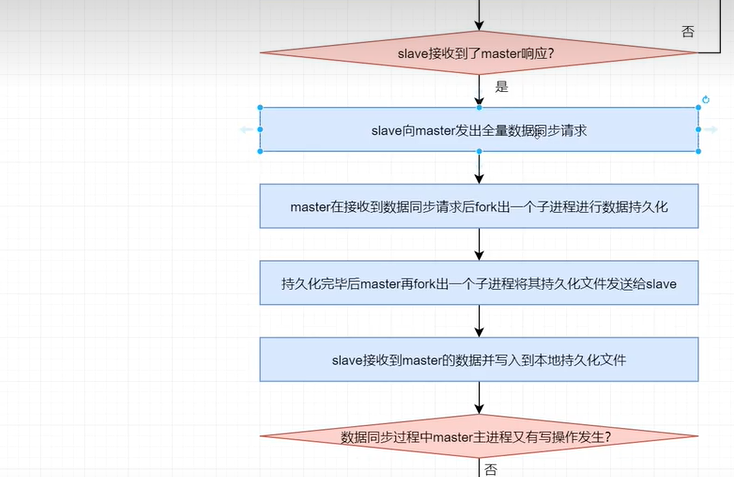
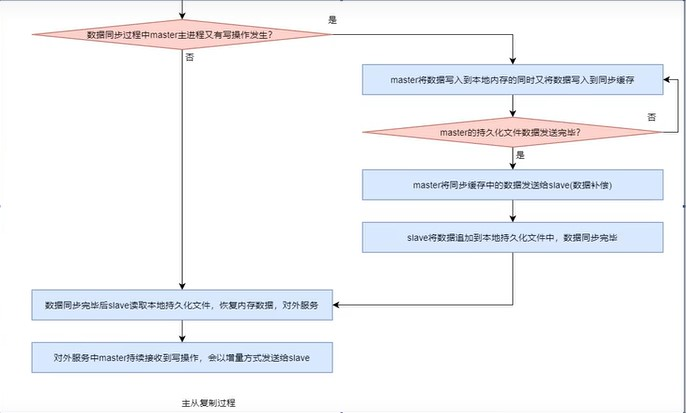
(5)master持久化
slave在成功接收到master的響應後,slave向master發出數據同步請求。master在接收到數據同步請求後,fork出一個子進程,讓子進程以非同步方式立即進行數據持久化。
(6)數據發送
持久化完畢後,master再fork出一個子進程,讓子進程以非同步方式將數據發送給slave。slave會將接收到的數據不斷寫入到本地的持久化文件中。
在slave數據同步過程中,master的主進程仍在不斷地接受著客戶端的寫操作,且不僅將新的數據寫入到master記憶體,同時也寫入到了同步緩存。當master的持久化文件中的數據發送完畢後,master會再將同步緩存中新的數據發送給slave,由slave將其寫入到本地持久化文件中。數據同步完成。
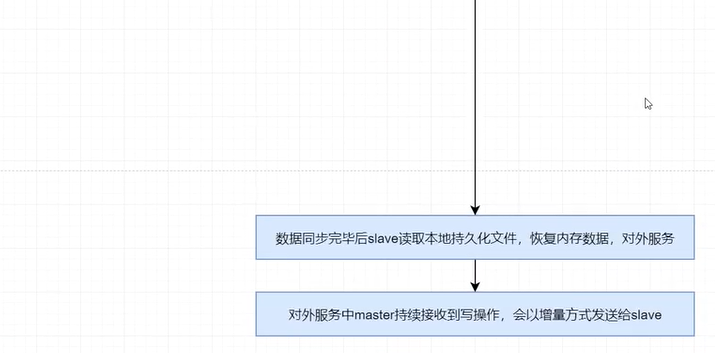
(7)slave恢復記憶體數據
數據同步完畢後,slave就會讀取本地持久化文件,將其恢復到本地記憶體數據,然後就可以對外提供服務了。
(8)持續增量複製
對外服務中master持續接收到寫操作,會以增量方式發送給slave,以保證主從數據的一致性。
流程概況如下
考慮到數據發送過程中,仍由數據進來,補充如下:
3.2 數據同步演變過程
(1)sync 同步
redis 2.8 版本之前,首次通信成功後,slave會向master發送sync數據同步請求,然後master就會將其所有數據全部發送給slave,由slave保存到其本地的持久化文件中。這個過程稱為全量複製。
但這裡存在一個問題:在全量複製過程中可能會出現網路抖動而導致複製過程中斷。當網路恢復後,slave與master重新連接成功,此時slave會重新發送sync請求,然後會從頭開始全量複製。
由於全量複製過程非常耗時,所以期間出現網路抖動的概率很高。而中斷後的從頭開始不僅需要消耗大量的系統資源、網路帶寬,而且可能會出現長時間無法完成全量複製的情況。
(2)psync
redis 2.8 版本之後,全量複製採用了psync(Partial Sync,不完全同步)同步策略。當全量複製過程出現由於網路抖動而導致複製過程中斷時,當重新連接成功後,複製過程可以“斷點續傳”。即從斷點位置開始繼續複製,而不用從頭再來。這樣大大提升了性能。
為了實現psync,整個系統做了三個大的變化:
A. 複製偏移量
系統為每個需要傳送數據進行了編號,該編號從0開始,每個位元組一個編號。該編號稱為複製偏移量。參與複製的主從節點都會維護該複製偏移量。
可以通過 命令info replication 的返回結果中的 slave_repl_offset (從節點)或 master_repl_offset(主節點 代表已發送出去的數據)值查看。
B.主節點複製ID
當master啟動後,就會動態生成一個長度為40位的16進位字元串作為當前master的複製ID,該ID是在進行數據同步時slave識別master使用的。通過 info replication 的master_replid屬性可查看到該ID。
特別註意:master redis 重啟,動態生成的複製ID就會變化。
C.複製積壓緩衝區
當master有連接的slave時,在master中就會創建並維護一個隊列backlog,預設大小為1MB,該隊列稱為複製積壓緩衝區。master接收到了寫操作,數據不僅會寫入到了master主存,寫入到了master中為每個slave配置的發送緩存,而且還會寫入到複製積壓緩衝區。其作用就是用於保存最近操作的數據,以備“斷點續傳”時做數據補償,防止數據丟失。
D. psync 同步過程
psync是一個由slave提交的命令,其格式為psync <master_replid> <repl_offset> ,表示當前slave要從指定中的repl_offset+1處開始複製。 repl_offset表示當前slave已經完成複製的數據的offset。該命令保證了“斷點續傳”的實現。
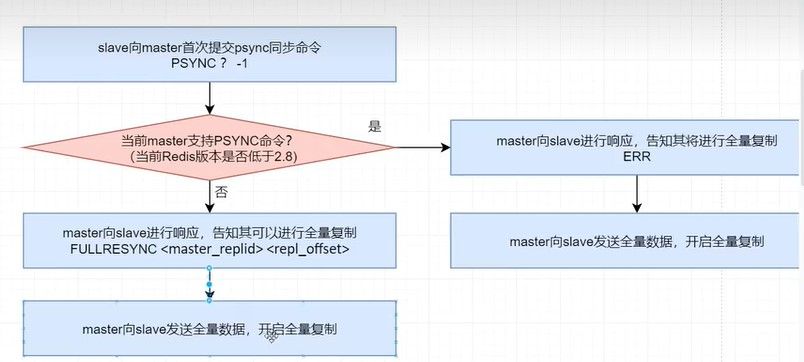
在第一次開始複製時,slave並不直到master的動態ID,並且一定時從頭開始複製,所以其提交的psync命令為PSYNC ? -1。即master_replid 為問號(?),repl_offset為-1。
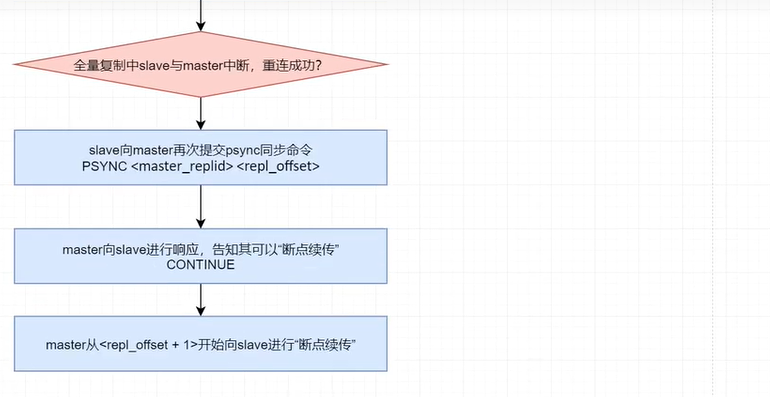
如果複製過程中斷後,slave與master成功連接,則save再次提交psync命令。此時psync命令的repl_offset參數為其前面已經完成複製的數據的偏移量。
其實,並不是slave提交psync命令後就可以立即從master處開始複製,而是需要master給出響應結果後,根據響應結果來執行。master根據slave提交的請求及master自身情況會給出不同的響應結果。響應結果有三種可能:
- FULLRESYNC <master_replid> <repl_offset>:告知slave當前master的動態ID及可以開始全量複製了,這裡的repl_offset一般為0。
- CONTINUE:告知slave可以按照你提交的repl_offset後面位置開始“續傳”了。
- ERR:告知slave,當前master的版本低於redis 2.8 ,不支持psync,你可以開始全量複製。
psync過程概況如下
E. psync存在的問題
- 在psync數據同步過程中,若slave重啟,在slave記憶體中保存的master的動態ID與續傳需要的offset都會消失,“斷點續傳”將無法進行,從而只能進行全量複製,導致資源浪費。
- 在psync數據同步過程中,master宕機後slave會發生“易主”,從而導致slave需要從新master進行全量複製,形成資源浪費。
(3)psync 同步的改進
Redis 4.0 對psync進行了改進,提出了“同源增量同步”策略。
A. 解決slave重啟問題
針對“slave重啟時master動態ID丟失問題”,改進後的psync將master的動態ID直接寫入到了slave的持久化文件中。
slave重啟後直接從本地持久化文件中讀取master的動態ID,然後向master提交獲取複製偏移量的請求。master會根據提交請求的slave地址,查找到保存在master中的複製偏移量,然後向slave回覆FULLRESYNC <master_replid> <repl_offset>,以告知slave其馬上要開始發送的位置。然後master開始“斷點續傳”。
B. 解決slave易主問題
slave易主後需要和新master進行全量複製,本質原因是新master不認識slave提交的psync請求中的“原master的動態ID”。如果slave發送psync <原master_replid> <repl_offset> 命令,新的master能夠識別出該slave要從原master複製數據,而自己的數據都是從該master複製來的。那麼新master就會明白,其與該slave"師出同門",應該接收其“斷點續傳”同步請求。
而新master中恰好保存的有“原master的動態ID”。由於改進後的psync中每個slave都在本地保存了當前的master的動態ID,所以當slave晉升為新的master後,其本地仍保存有之前master的動態ID。而這一點也恰恰為解決“slave易主”問題提供了條件。通過master的info replication 中master_replid2 可以查看到。如果尚未發送易主,則該值為40個0。
(4) 無盤操作
Redis 6.0 對同步過程又進行了改進,提出了“無盤全量同步”與“無盤載入”策略,避免了耗時的IO操作。
- 無盤全量同步:master的主進程fork出的子進程直接將記憶體中的數據發送給slave,無需經過磁碟。
- 無盤載入:slave在接收到master發送來的數據後不需要將其寫入到磁碟文件,而是直接寫入到記憶體,這樣slave就可快速完成數據恢復。
(5) 共用複製積壓緩衝區
Redis 7.0 版本對複製積壓緩衝區進行了改進,讓各個slave的發送緩衝區共用複製積壓緩衝區。這使得複製積壓緩衝區的作用,除了可以保障數據的安全性外,還作為所有slave的發送緩衝區,充分利用了複製積壓緩衝區。
學習參閱特別聲明
【Redis視頻從入門到高級】
【https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1U24y1y7jF?p=11&vd_source=0e347fbc6c2b049143afaa5a15abfc1c】


