好消息:與上題的Emergency是同樣的方法。壞消息:又錯了&&c++真的比c方便太多太多。 A family hierarchy is usually presented by a pedigree tree. Your job is to count those family members ...
好消息:與上題的Emergency是同樣的方法。壞消息:又錯了&&c++真的比c方便太多太多。
A family hierarchy is usually presented by a pedigree tree. Your job is to count those family members who have no child.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N<100, the number of nodes in a tree, and M (<N), the number of non-leaf nodes. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K]
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID's of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 01.
The input ends with N being 0. That case must NOT be processed.
Output Specification:
For each test case, you are supposed to count those family members who have no child for every seniority level starting from the root. The numbers must be printed in a line, separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of each line.
The sample case represents a tree with only 2 nodes, where 01 is the root and 02 is its only child. Hence on the root 01 level, there is 0 leaf node; and on the next level, there is 1 leaf node. Then we should output 0 1 in a line.
Sample Input:
2 1
01 1 02
Sample Output:
0 1
題目分析
分析家族族譜,算出非葉子節點,就是非孩子數量。,所有的節點用兩位數字表示,例如:01,02,06等,其中為了方便,令01為根節點。
輸入: N(100個以內的的節點) M(非葉子節點數)
【接下的M行內】 ID(非葉子節點)K(所連的葉子 / 孩子節點個數)ID[0] ID[1]...ID[K](K個葉子節點)
輸出:(每層的葉子節點個數)中間用空格隔開————>註意,pat對輸出有著固定且嚴格的格式,所以最後結果的第一個數字前是沒有空格的。
就是用廣度優先或深度優先遍歷每一層,同時標記每層葉子節點並記錄,最後數組輸出
個人想法
其實一開始,我覺得很簡單,既然只看葉子節點個數,那每次輸入ID[0-K]時,我進行記錄不就行了嗎,每次輸入ID都是不同的層級,最後得到的的不就是每層孩子數,所以我在寫輸入的時候加了一點點變數,最後輸出。

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 5 int ID[101]; 6 int book[101];//記錄輸出每層葉節點個數 7 int b; //每層的葉節點數 8 9 int main() { 10 int N, M; 11 scanf("%d%d", &N, &M); 12 int K; 13 int a = 1; 14 for (int i = 1; i <= N; i+=K+1) { 15 scanf("%d%d", &ID[i], &K); 16 if( K != 0) 17 for (int j = i+1; j <= i+K; j++) { 18 scanf("%d", &ID[j]); 19 b++; //沒輸入一次葉節點數就增加一個 20 } 21 book[a] = b;//記錄 22 b = 0;//歸零進行下次計算 23 a++;//記錄數組下標移動 24 } 25 printf("%d", book[0]);//輸出第一層 26 for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) { 27 printf(" %d", book[i]);//輸出接下來的每層,並於上一個數字隔開 28 29 } 30 return 0; 31 }View Code
最後得分13分。。。意料之中,舉例思考的時候都只考慮了二叉樹,編寫的過程中便覺的那如果一個節點有有多個非葉節點甚至沒有葉節點應該怎麼填寫。回過頭來再看這段,更是覺得搞笑,如果這樣可行,那直接記錄K就好了。於是嘗試著寫了第二種,先構建一顆完整的樹,然後深度遍歷。
首先,變數的設置
1 int N, M;//同題目N,M 2 int K; 3 typedef struct NODE{ 4 int nodes;//記錄每個節點擁有的葉子節點數 5 int ID[101]; //記錄各個葉子節點 6 }; 7 struct NODE child[101];//樹 8 int book[101];//保存、輸出每層葉子節點數 9 int max; //比較和更新每層的葉子節點數,因為左邊的遍歷完,右邊的還要遍歷並記錄
這裡使用了結構體而不是簡單的數組或者二維數組記錄,是因為退出遞歸的條件需要知道此時節點後續有無別的節點。對比之前的深度遍歷我們可以知道,在每次遞歸的結束條件語句中,會判斷後續“無路可走”後才停止並return,1003中是
if (curlen > mindis[curcity])return;
,即如果所求的路徑走這時變長就停止這條路。在此題則是你所談的節點後面無節點就說明是葉子節點,那麼就停止遍歷,並記錄數量。但是我開始在這使用二維數組,判定條件:
if(child[curnode]==0) return;
認為全局變數初始化為0,而這樣判斷說明此行均為0時就說明它是空的是葉子節點,但是實際運行出現了死迴圈,因為你在輸入的for語句中都會因為預設給每一行賦值,導致你輸入的值令每行都不是全為0(有點混亂)。而c++中用 child.[curnode]size()【child是vector型】判斷長度,如果等於0 ,則進入葉子節點的計數。所以對c語言使用結構體記錄每個節點的葉子節點數和葉子節點編號。
1 void dfs(int curnode ,int curlevel); 2 int main() { 3 int a; 4 scanf("%d%d", &N, &M); 5 for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { 6 scanf("%d%d", &a, &K); 7 child[a].node = K;//非葉節點ID,所有的葉子節點數 8 for (int j = 0; j <K; j++) { 9 scanf("%d", &child[a].ID[j]); //葉子節點序號 10 } 11 } 12 dfs(1, 0);//從 1 開始是因為01為根節點,所有存放元素的是child[01]不是child[0] 13 printf("%d", book[0]); 14 for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) { 15 printf(" %d", book[i]); 16 17 } 18 return 0; 19 } 20 void dfs(int curnode, int curlevel) { 21 if (child[curnode].node == 0) { //判斷有無葉節點,無則進入此記錄保存 22 if(max<curlevel) 23 max = curlevel; //更新當前遍歷所在的葉子節點層數 24 book[curlevel]++; //沒到該層,葉子節點數加 1 25 return; 26 } 27 for (int i = 0; i < child[curnode].node; i++) { //因為對該節點進行遍歷,所以在它有的葉子節點數範圍內迴圈 28 dfs(child[curnode].ID[i], curlevel + 1); //把當前的某個葉子節點的數值帶入下一個節點的索引,層級加1. 29 } 30 }
<-----------------------------------完整代碼----------------------------------->

1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<string.h> 5 6 7 int N, M; 8 int K; 9 typedef struct NODE{ 10 int node; 11 int ID[101]; 12 }; 13 struct NODE child[101]; 14 int book[101]; 15 int max; 16 17 void dfs(int curnode ,int curlevel); 18 int main() { 19 int a; 20 scanf("%d%d", &N, &M); 21 for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { 22 scanf("%d%d", &a, &K); 23 child[a].node = K; 24 for (int j = 0; j <K; j++) { 25 scanf("%d", &child[a].ID[j]); 26 } 27 } 28 dfs(1, 0); 29 printf("%d", book[0]); 30 for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) { 31 printf(" %d", book[i]); 32 33 } 34 return 0; 35 } 36 void dfs(int curnode, int curlevel) { 37 if (child[curnode].node == 0) { 38 if(max<curlevel) 39 max = curlevel; 40 book[curlevel]++; 41 return; 42 } 43 for (int i = 0; i < child[curnode].node; i++) { 44 dfs(child[curnode].ID[i], curlevel + 1); 45 } 46 }View Code
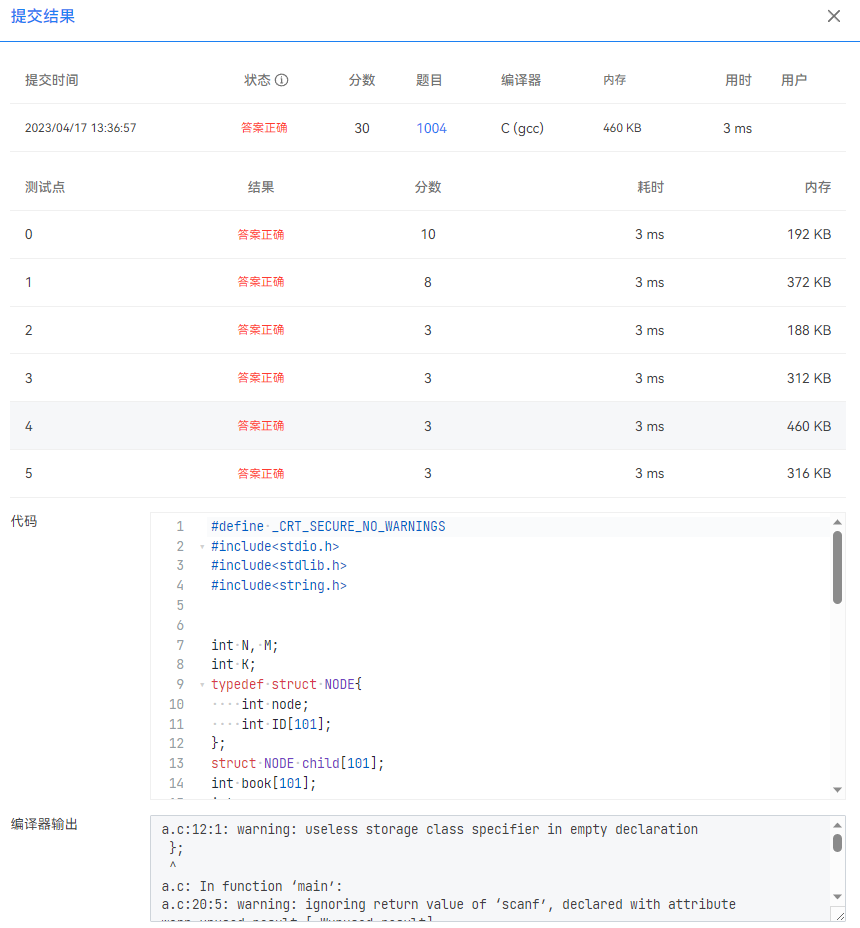
總結
其實掌握深度遍歷總體大概的流程,結合題目改變判定條件寫出總體的框架基本都能得分,然後調試以後進行修改就大差不差了。