代理模式(Proxy Pattern)是一種結構型設計模式,結構型模式描述如何將類或對象按某種佈局組成更大的結構。它允許你提供一個代理對象來控制對另一個對象的訪問。代理對象擁有與實際對象相同的介面,因此它可以被用來代替實際對象。 ...
OOP 1-3次作業總結
22201303-範宇
前言
第一次BLOG,對第一階段的學習總結。
前三次題目集總體上更偏向於JAVA語法上的訓練,第二次與第三次題目集中的後兩道需要一點邏輯思維。題量我個人認為適中,整體難度我認為恰到好處,就是那種需要一定時間思考,但又不至於難到完成不了。
設計與分析
-
題目集一:7-7 有重覆的數據
題目集一:7-7 有重覆的數據,讀入數據,檢查是否有重覆的數據。如果有,輸出“YES”這三個字母;如果沒有,則輸出“NO”。你的程式首先會讀到一個正整數n,n∈[1,100000],然後是n個整數。
如果這些整數中存在重覆的,就輸出:
YES否則,就輸出:
NOimport java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
int [] num=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
num[i]=input.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(num);
int i;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){
if(num[i]==num[i+1]){
System.out.println("YES");
break;
}
}
i++;
if(i==n)
System.out.println("NO");
// int i;
// loop:
// for(i=0;i<n;i++){
// for(int j=n-1;j>i;j--){
// if(num[i]==num[j]){
// System.out.println("YES");
// break loop;
// }
// }
// }
// if(i==n)
// System.out.println("NO");
}
}
這道題的整體思路就是先排序,再遍曆數組,判斷前一個元素與後一個元素是否相等,如果是,則重覆,如果全部遍歷完(也就是i==n時),則說明沒有重覆。這道題的重點在於當n為最大值時,這一測試點非常容易超時,之前用了雙重for迴圈和ArrayList兩種方法,都沒有通過最大n這個測試點,在多次嘗試下,最後發現了這個先排序的方法;後面還遇到了相似的題目,使用Set也是可行的;
-
題目集二:7-8 判斷三角形類型
題目集二:7-8 判斷三角形類型,輸入三角形三條邊,判斷該三角形為什麼類型的三角形。
(1)如果輸入數據非法,則輸出“Wrong Format”;
(2)如果輸入數據合法,但三條邊不能構成三角形,則輸出“Not a triangle”;
(3)如果輸入數據合法且能夠成等邊三角形,則輸出“Equilateral triangle”;
(3)如果輸入數據合法且能夠成等腰直角三角形,則輸出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”;
(5)如果輸入數據合法且能夠成等腰三角形,則輸出“Isosceles triangle”;
(6)如果輸入數據合法且能夠成直角三角形,則輸出“Right-angled triangle”;
(7)如果輸入數據合法且能夠成一般三角形,則輸出“General triangle”。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double a=input.nextDouble();
double b=input.nextDouble();
double c=input.nextDouble();
if(a<1||a>200||b<1||b>200||c<1||c>200)
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
else{
double t;
if(a<b){
t=a;
a=b;
b=t;
}
if(a<c){
t=a;
a=c;
c=t;
}
if(b<c){
t=b;
b=c;
c=t;
}
if((b+c)<=a)
System.out.print("Not a triangle");
else if(a==b&&b==c)
System.out.print("Equilateral triangle");
else if(b==c&&(2*b*b-a*a)*(2*b*b-a*a)<0.00001*0.00001)
System.out.print("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
else if((b==c)||(b==a))
System.out.print("Isosceles triangle");
else if(b*b+c*c==a*a)
System.out.print("Right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.print("General triangle");
}
}
}這道題我先將三邊按大小排序,再利用三角形構成的條件(即,兩邊之和大於第三邊)來判斷三角形是否可以構成,最後通過三邊關係判斷三角形的種類,其中用到了勾股定理(這裡就可能涉及到無理數,而無理數在電腦中的運算是存在誤差的,所以這種情況下判斷條件需要把誤差範圍考慮進去)。
-
題目集二:7-9 求下一天
題目集二:7-9 求下一天,輸入年月日的值(均為整型數),輸出該日期的下一天。
- 當輸入數據非法及輸入日期不存在時,輸出“Wrong Format”;
- 當輸入日期合法,輸出下一天,格式如下:Next date is:年-月-日
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year=input.nextInt();
int month=input.nextInt();
int day=input.nextInt();
Main in=new Main();
if(year<1820||year>2020||month<1||month>12||day<1||day>31)
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
else{
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)){
in.nextDate(year,month,day);
}
else
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if(month==2&&day>29)
return false;
}
else{
if(month==2&&day>28)
return false;
}
if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11){
if(day>30)
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day){
day++;
if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11){
if(day>30){
month++;
day=1;
}
}
if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12){
if(day>31){
month++;
day=1;
if(month>12){
year++;
month=1;
}
}
}
if(month==2){
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if(day>29){
month++;
day=1;
}
}
else{
if(day>28){
month++;
day=1;
}
}
}
System.out.print("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
}這道題需要先根據題目給出的條件判斷輸入日期是否合法,然後再求下一天的日期,這裡需要考慮到這一天是否達到這一月的最後一天,以及這一月共有多少天,如果是二月份還需要是否是閏年,如果是閏年則二月份有29天;否則有28天,考慮完了月份還需要考慮年份,要考慮這一天是否是這一年的最後一天,如果是,則下一天日期變為一月一日,年份加一;
當時寫這道題的時候對JAVA語法方面的內容還不是很熟悉,現在看來完全可以用數組(int[] mon_maxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31})來取代冗長的if里的條件;
-
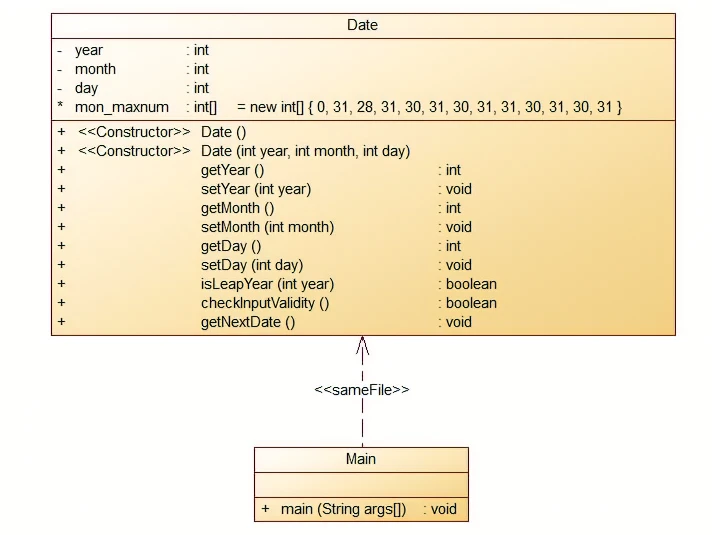
題目集三:7-3 定義日期類
題目集三:7-3 定義日期類,要求我們定義一個類Date(Date類結構如下圖所示)
- 當輸入數據非法及輸入日期不存在時,輸出“Date Format is Wrong”;
- 當輸入日期合法,輸出下一天,格式如下:Next day is:年-月-日;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = input.nextInt();
int month = input.nextInt();
int day = input.nextInt();
Date date1 = new Date(year,month,day);
if(date1.checkInputValidity()){
date1.getNextDate();
System.out.println("Next day is:"+date1.getYear()+"-"+date1.getMonth()+"-"+date1.getDay());
}
else
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
}
}
class Date{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
private int[] mon_maxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
Date(){
}
Date(int year,int month,int day){
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setyear(int year){
this.year=year;
}
public int getMonth(){
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month){
this.month=month;
}
public int getDay(){
return day;
}
public void getDay(int day){
this.day=day;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
mon_maxnum[2]=29;
}
else{
mon_maxnum[2]=28;
}
if(this.year>=1900&&this.year<=2000&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=mon_maxnum[month])
return true;
else
return false;
}
public void getNextDate(){
this.day++;
if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month]){
this.month++;
this.day=1;
}
if(this.month>12){
this.month=1;
this.year++;
}
}
}這道題我是一遍過的,畢竟計算量不大,僅僅只是下一天,需要考慮到這一天是否是這個月的最後一天,如果是,則下一天為下個月的第一天,還需要考慮到這個月是否是12月,如果是既12月又是最後一天,則下一天為下一年的1月1日。然後就是細節上的考慮,這裡主要體現在對閏年的判斷,對這道題來講,因為只求下一天,所以只需考慮是否有2月29日。
- 題目集三:7-4 日期類設計,要求參考7-3設計一個DateUtil,該類有三個私有屬性year、month、day(均為整型數),其中,year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31],設計類圖如下:
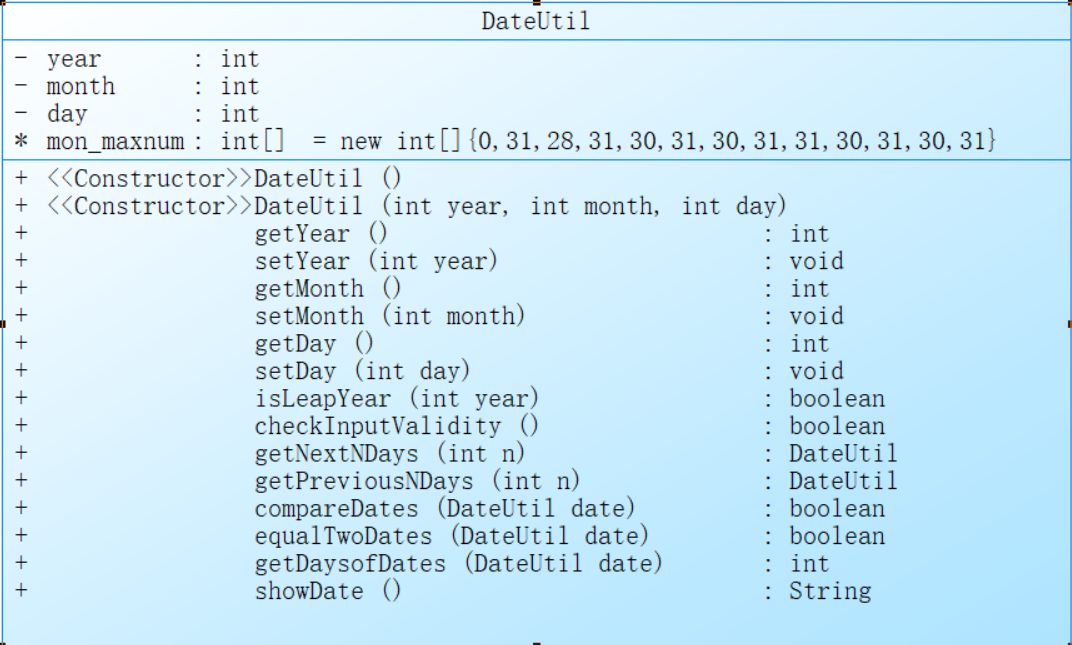
功能實現:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求兩個日期相差的天數
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
private int[] mon_maxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
DateUtil(){
}
DateUtil(int year,int month,int day){
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setyear(int year){
this.year=year;
}
public int getMonth(){
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month){
this.month=month;
}
public int getDay(){
return day;
}
public void getDay(int day){
this.day=day;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
mon_maxnum[2]=29;
}
else{
mon_maxnum[2]=28;
}
if(this.year>=1820&&this.year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=mon_maxnum[month])
return true;
else
return false;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){
//this.day=this.day+n;
while(n>mon_maxnum[this.month]){
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
mon_maxnum[2]=29;
}
else{
mon_maxnum[2]=28;
}
n=n-mon_maxnum[this.month];
this.month++;
if(this.month>12){
this.month=this.month-12;
this.year++;
}
}
this.day=this.day+n;
if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month]){
this.day=this.day-mon_maxnum[this.month];
this.month++;
if(this.month>12){
this.month=this.month-12;
this.year++;
}
}
return new DateUtil(year,month,day);
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){
this.day=this.day-n;
while(this.day<=0){
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
mon_maxnum[2]=29;
}
else{
mon_maxnum[2]=28;
}
this.month--;
if(this.month==0){
this.year--;
this.month=this.month+12;
}
this.day=mon_maxnum[this.month]+this.day;
}
return new DateUtil(year,month,day);
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){
if(this.year>date.getYear())
return true;
else if(this.year==date.getYear()){
if(this.month>date.getMonth())
return true;
else if(this.month==date.getMonth()){
if(this.day>date.getDay())
return true;
else if(this.day==date.getDay()){
return true;
}else
return false;
}else
return false;
}else
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){
if(this.year==date.getYear()&&this.month==date.getMonth()&&this.day==date.getDay())
return true;
else
return false;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){
int n=0;
n=n+mon_maxnum[this.month]-this.day;
for(int i=1;this.month+i<13;i++){
n=n+mon_maxnum[this.month+i];
}
while(this.year!=date.getYear()){
if(this.year<date.getYear())
this.year++;
else
this.year--;
if(this.year==date.getYear())
break;
if(isLeapYear(this.year))
n=n+366;
else
n=n+365;
}
for(int i=1;i<date.getMonth();i++){
n=n+mon_maxnum[i];
}
n=n+date.getDay();
return n;
}
public String showDate(){
String date="";
date=year+"-"+month+"-"+day;
return date;
}
}
這一題相當於是上一題的進階版,在上一題的基礎上改進,實現了求後n天的日期、前n天的日期和兩個日期間相距多少天。我實現getDaysofDates方法的主要思想是:使第一個日期不斷向第二個日期靠近,直至相等,同時用n不斷加上相應增加的天數,這裡重點在於日期的合法變化,要分月份和年份兩個條件討論;而實現getNextNDays、getPreviousNDays方法的主要思想是:n為天數,使n減少多少天,日期就相應增加多少天,直至n減少至0,而重點就在日期增加上,因為每個月的最大值不固定,每一年也不一定固定,所以這裡就需要細心分析,分類討論,判斷這一年是否是閏年,判斷這一月最大有多少天,進而來決定日期增加多少,n減少多少才能使日期合法增加。
踩坑心得
- 在題目集二:7-8 判斷三角形類型中,在判斷等腰直角三角形時,因為涉及到了無理數,所以數據運算一定存在一個誤差無法消除
if(b==c&&(2*b*b-a*a)==0),之後規定當誤差小於一個值時即為相等if(b==c&&(2*b*b-a*a)*(2*b*b-a*a)<0.00001*0.00001),這才解決; - 在題目集二:7-9 求下一天中,需要調取固定數值時,使用數組工具會更方便;
- 題目集三:7-4 日期類設計,這題中有個最大n值測試點花了很長時間才通過,這類測試點一般情況下是最容易被卡住的地方,這道題剛開始使一個正數加上n,所以導致超出了整型範圍,後面把它改在後面加,才成功;可更多情況下是一些題目需要遍曆數組或者列表(需要使用一個嵌套的雙重for迴圈),這種情況下更容易超出範圍,而且還不好解決,目前我能想到的就是如果需要排序,就使用現成的
sort方法,如果要判斷重覆,可以使用Set來輔助判斷;public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ //this.day=this.day+n;這個是之前的錯誤 while(n>mon_maxnum[this.month]){ if(isLeapYear(this.year)){ mon_maxnum[2]=29; } else{ mon_maxnum[2]=28; } n=n-mon_maxnum[this.month]; this.month++; if(this.month>12){ this.month=this.month-12; this.year++; } } this.day=this.day+n; if(this.day>mon_maxnum[this.month]){ this.day=this.day-mon_maxnum[this.month]; this.month++; if(this.month>12){ this.month=this.month-12; this.year++; } } return new DateUtil(year,month,day); } - 在很多題目中,由於C語言習慣用
System.out.printf()輸出,可往往這樣都通不過測試點,只能使用System.out.print()或System.out.println(),下麵是三者的一些區別:print為一般輸出,同樣不能保留精度格式轉化,也不能換行輸出;printf常用於格式轉換,但需要註意不是換行輸出,只用於精度轉換;println為換行輸出,不能用於格式化輸出;

- 基本類型轉換,有時候題目規定只能是單精度型或者只能是雙精度型的數據結果才能通過測試點
float w1=(float)(w/0.45359237); - 誤差判斷時,大部分情況下要加一個平方,因為誤差不僅是一個向左或向右的區間,誤差是一個既向左又向右的區間,如
while((g-m)>=0.00001)while((g-m)>=0.00001||(m-g)>=0.00001); - 在題目集一:7-7 有重覆的數據中,遇到了超時的問題,當時與其他同學討論發現,使用ArrayList類進行排序,再遍歷依舊超時,而使用Arrays類進行排序則不會超時,後面在查閱資料時發現,ArrayList是Array的複雜版本,ArrayList比Arrays的方法更多,功能更豐富,可以理解為Arrays是靜態數組,而ArrayList是動態數組,而Sort 方法是在內部數組的基礎上直接調用 Array 的對應方法,所以通常情況下:ArrayList的排序會比Arrays的排序時間要長;
改進建議
- 善用數組,在題目集二:7-9 求下一天中,使用數組來存儲12個月的最大天數,對m進行判斷時再通過數組下標來找出月份對應的天數,這會更加方便,而且易懂;
- 規範命名,儘可能寫出英文全稱,增加代碼可讀性;
- 多瞭解一些類的使用,比如String類,Arrays類,ArrayList類;
- 學習JAVA異常處理的相關內容,取代if判斷;
總結
三次題目集的訓練,使我從零開始入門JAVA這門編程語言,使我對JAVA有了一個初步的瞭解,同時也對面對對象程式設計有了一個初步認識。面對對象程式設計與上學期的C語言(面向過程程式設計)不同,面向過程程式設計從邏輯上來看感覺更直接,而面向對象程式設計感覺更加抽象,更易於模塊化。面向對象程式設計里,數據和數據上的操作是分離的,也就是對象和控制對象的方法,JAVA里的模塊化主要體現在類上,類是一個抽象的模塊,它包含了一系列對象及其方法,類的設計就是對現實世界的抽象化,所以面對對象程式設計也需要強大的抽象思維能力,在面對對象程式設計中,類的設計是重中之重,為了設計類,還需要探究類之間的關係,類之間的關係通常有關聯、聚合、組合及繼承,這也體現了面對對象程式設計的三大特點:封裝性、繼承性、多態性。
通過三次作業,能夠感覺到JAVA這門語言的強大,同時也能感覺到JAVA里的世界之大,目前我只學習到了它最基礎的語法部分以及少量的類,JAVA自帶了大量的類可以使用,這能大大方便我們解決問題。老師在上課時也帶我們接觸了一些從未聽過的東西,比如JAVA里的集合框架,這些內容需要我們自己花大量時間去探究學習。



