MyBatis的關聯映射02 3.一對多 3.1基本介紹 mybatis – MyBatis 3 | XML 映射器 多對一關係也是一個基本的映射關係,多對一,也可以理解為一對多。例如: User--Pet:一個用戶可以有多只寵物 Dep--Emp:一個部門有多個員工 雙向的多對一關係:通過User ...
MyBatis的關聯映射02
3.一對多
3.1基本介紹
多對一關係也是一個基本的映射關係,多對一,也可以理解為一對多。例如:
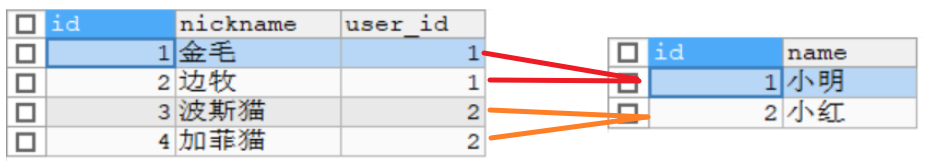
User--Pet:一個用戶可以有多只寵物
Dep--Emp:一個部門有多個員工
雙向的多對一關係:通過User可以查詢到對應的所有Pet,反之,通過Pet也可以級聯查詢到對應的User信息。
多對多的關係就是在多對一的關係上拓展
3.2案例實現
映射方式:
方式1:通過配置映射文件實現多對一
方式2:通過註解的方式實現多對一
需求說明:實現級聯查詢,通過user的user_id可以查詢到User信息和關聯的所有pet信息,反之,通過pet的pet_id也可以查詢到Pet信息和user的信息
先創建user表和pet表:
-- 創建user表
CREATE TABLE `user`(
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT ''
)CHARSET=utf8
DESC `user`;
-- 創建pet表
CREATE TABLE `pet`(
`id` INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`nickname` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`user_id` INT,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES `user`(id)
)CHARSET=utf8
3.2.1方式一:配置方式
(1)User和Pet實體類
package com.li.entity;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
//因為一個User可以養多個寵物,mybatis使用集合體現這個關係
private List<Pet> pets;
//setter、getter方法省略
//雙向映射不要使用toString方法,否則會造成棧溢出錯誤
}
package com.li.entity;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Pet {
private Integer id;
private String nickname;
//一個pet對應一個user對象
private User user;
//setter、getter方法省略
//雙向映射不要使用toString方法,否則會造成棧溢出錯誤
}
(2)UserMapper介面和PetMapper介面
public interface UserMapper {
//通過id獲取User對象
public User getUserById(Integer id);
}
public interface PetMapper {
//通過user的id獲取pet對象,可能有多個因此使用集合接收
public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);
}
(3)UserMapper.xml,思路:
1)先通過user_id查詢得到user信息
2)再根據user_id,查詢對應的pet信息,並映射到user-List< Per> pets
多對多的映射思路和一對一的實現類似,不同的使用使用resultMap映射屬性時使用的是collecting標簽。
<mapper namespace="com.li.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--通過id獲取User對象
public User getUserById(Integer id);-->
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="resultUserMap">
SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE id = #{id};
</select>
<!--User的屬性映射-->
<resultMap id="resultUserMap" type="User">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<!--1.因為pets屬性是一個集合,因此要使用collection標簽
2.column="id"的id是SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE id=#{id} 返回的欄位
3.ofType="Pet"指定返回的集合存放的數據類型-->
<collection property="pets" column="id" ofType="Pet"
select="com.li.mapper.PetMapper.getPetByUserId"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
(4)PetMapper.xml,思路和前面大體相同
<mapper namespace="com.li.mapper.PetMapper">
<!--通過user的id獲取pet對象,可能有多個因此使用集合接收
public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);-->
<select id="getPetByUserId" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="resultPetMap">
SELECT * FROM `pet` WHERE user_id =#{userId};
</select>
<resultMap id="resultPetMap" type="Pet">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="nickname" column="nickname"/>
<association property="user" column="user_id"
select="com.li.mapper.UserMapper.getUserById"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
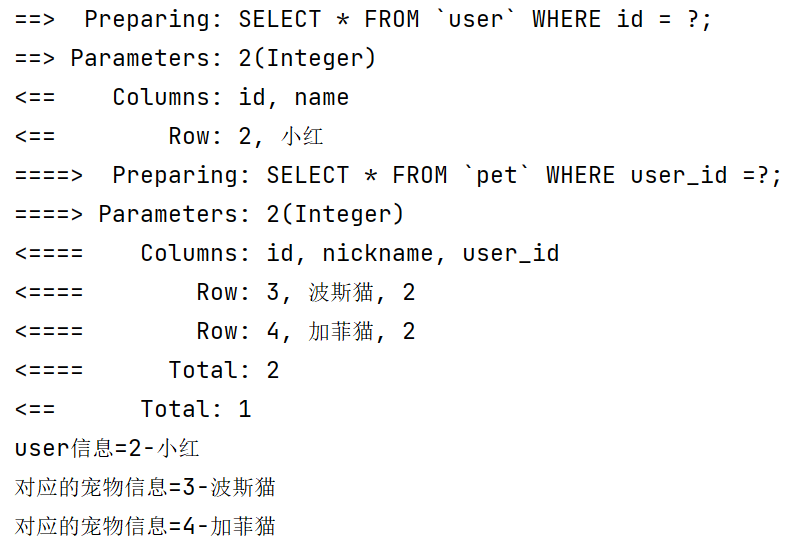
(5)測試getUserById()方法,通過UserId查找user對象和聯繫的pet信息
@Test
public void getUserById() {
User user = userMapper.getUserById(2);
System.out.println("user信息=" + user.getId() + "-" + user.getName());
for (Pet pet : user.getPets()) {
System.out.println("寵物信息=" + pet.getId() + "-" + pet.getNickname());
}
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
測試結果:
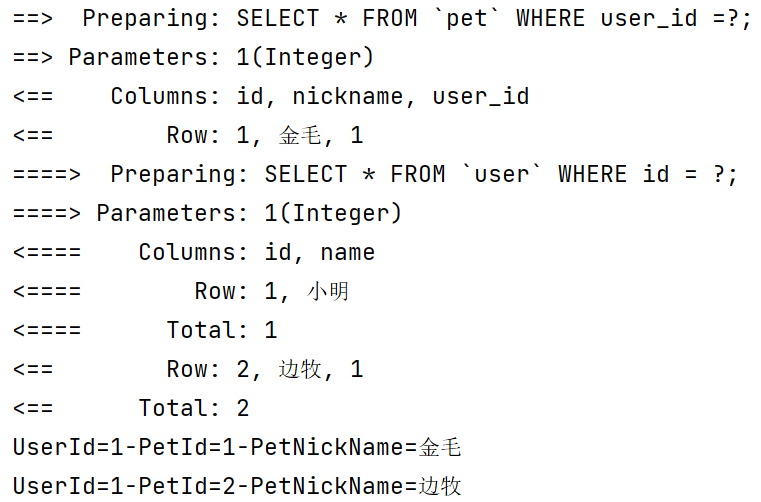
(6)測試getPetByUserId()方法,通過user的id獲取pet對象
@Test
public void getPetByUserId() {
List<Pet> pets = petMapper.getPetByUserId(1);
for (Pet pet : pets) {
System.out.println("UserId=" + pet.getUser().getId()
+ "-PetId=" + pet.getId()
+ "-PetNickName=" + pet.getNickname());
}
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
測試結果:
resultMap可以復用,如果有其他方法是返回的和resultMap一樣的類型,可以在實現該方法時引用該resultMap。
比如PetMapper介面中新聲明瞭一個方法:
//通過pet的id獲取Pet對象,同時查詢到pet對象關聯的user對象
public Pet getPetById(Integer id);
PerMapper.xml文件:
<!--這裡可以直接復用之前的resultPetMap-->
<select id="getPetById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="resultPetMap">
SELECT * FROM `pet` where id =#{id};
</select>
3.2.2方式二:註解方式
需求說明:通過註解的方式,實現雙向的級聯查詢。
在實際開發中推薦使用配置的方式來做
(1)User和Pet實體類不變
(2)直接在介面中,通過註解實現級聯查詢
UserMapperAnnotation.java
package com.li.mapper;
import com.li.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 以註解的方式來實現多對一
*/
public interface UserMapperAnnotation {
//通過id獲取User對象
@Select(value = "SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE id = #{id}")
@Results({
@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "name", column = "name"),
//這裡對應返回List類型屬性pets,使用註解的many屬性
@Result(property = "pets", column = "id",
many = @Many(select =
"com.li.mapper.PetMapperAnnotation.getPetByUserId"))
})
public User getUserById(Integer id);
}
PetMapperAnnotation.java
package com.li.mapper;
import com.li.entity.Pet;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface PetMapperAnnotation {
//通過user的id獲取pet對象
@Select(value = "SELECT * FROM `pet` WHERE user_id =#{userId}")
//配置了id之後就可以復用PetResuleMap
@Results(id = "PetResuleMap", value = {
@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "nickname", column = "nickname"),
@Result(property = "user", column = "user_id",
one = @One(select =
"com.li.mapper.UserMapperAnnotation.getUserById"))
})
public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);
//通過pet的id獲取pet信息
@Select(value = " SELECT * FROM `pet` where id =#{id}")
@ResultMap("PetResuleMap")//復用上面的PetResuleMap
public Pet getPetById(Integer id);
}
3.3練習
自己設計dept(部門)和emp(雇員)表,它們是一對多的關係。
- 通過查詢dept,可以級聯查詢到所有的emp信息
- 通過查詢emp,也可以級聯查詢到對應的dept信息
- 拓展思考:多對多關係



