前言 Web項目中很多網頁資源比如html、js、css通常會做伺服器端的緩存,加快網頁的載入速度 一些周期性變化的API數據也可以做緩存,例如廣告資源位數據,菜單數據,商品類目數據,商品詳情數據,商品列表數據,公共配置數據等,這樣就可以省去很多在服務端手動實現緩存的操作 最早資源緩存大部分都用Ex ...
前言
Web項目中很多網頁資源比如html、js、css通常會做伺服器端的緩存,加快網頁的載入速度
一些周期性變化的API數據也可以做緩存,例如廣告資源位數據,菜單數據,商品類目數據,商品詳情數據,商品列表數據,公共配置數據等,這樣就可以省去很多在服務端手動實現緩存的操作
最早資源緩存大部分都用Expires、Cache-Control或Etag實現的,我們可以在WebServer中統一設置響應頭,或者指定規則單獨設置
以上都是基於Http協議的緩存,如今很多WebServer,例如Nginx和阿裡二次開發的Tengine,都是自己的一套緩存實現,通過獨有的響應頭參數(X-Accel-Expires)來識別控制緩存,優先順序是大於Http協議那些的
通常Nginx都是作為代理伺服器,反向代理多台源伺服器,如果開啟了緩存,二次請求到了Nginx就會直接響應給客戶端了,能減輕源伺服器的壓力
本文主要是基於 X-Accel-Expires 來實現緩存的,前提是在Nginx中已經配置了Proxy Cache規則
Nginx的緩存原理
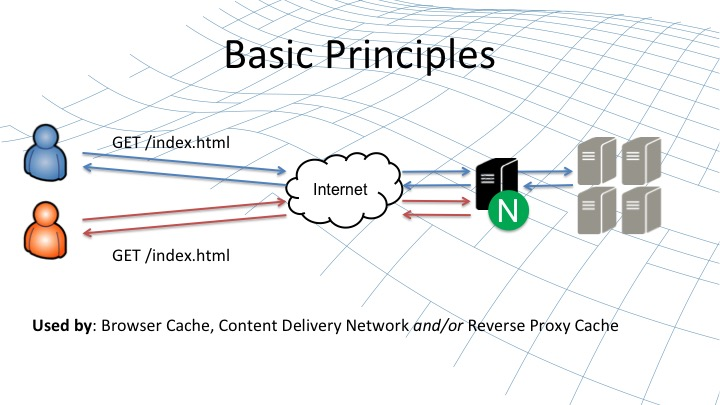
1. 這是資源訪問路徑,通過Nginx反向代理多個源伺服器,Nginx中配置了緩存,第二次訪問到了Nginx就直接返回了,不會再到後面的源伺服器
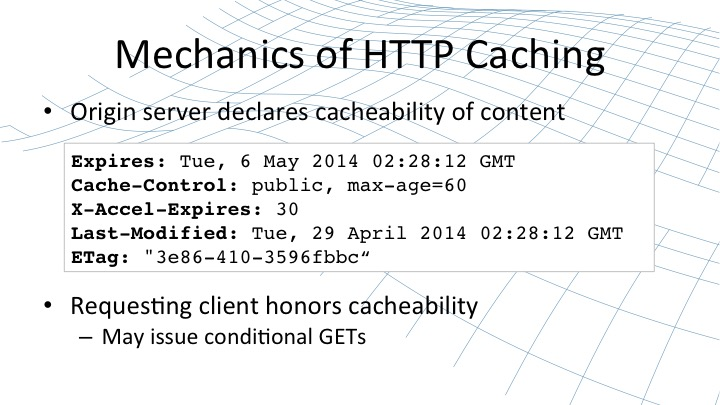
2. 常見的Http緩存響應頭設置有以下幾種,其中Etag和Last-Modified是組合使用的,X-Accel-Expires是Nginx獨有的參數,優先順序高於其他幾個設置,值的單位是秒,0為不生效
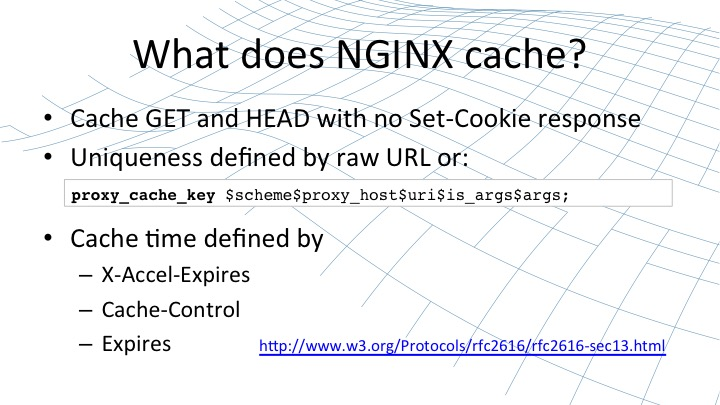
Nginx緩存識別優先順序如下
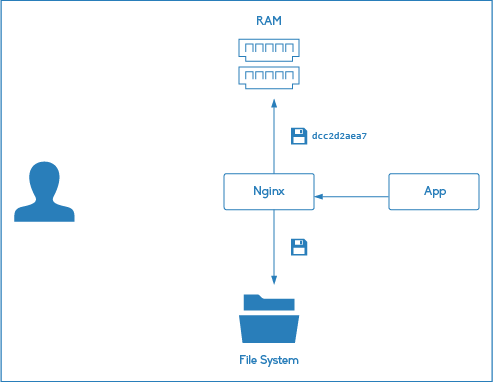
3. Nginx實現緩存的原理是把Url和相關參數,通過自定義組合作為Key,並使用MD5演算法對Key進行哈希,把響應結果存到硬碟上的對應目錄,支持通過命令清除緩存

具體可以參考以下文章,非常詳細:
https://www.nginx.com/blog/nginx-high-performance-caching/
https://czerasz.com/2015/03/30/nginx-caching-tutorial/
代碼實現
以下是通過過濾器實現控制該參數,支持在Controller或Action上傳入滑動時間,或者固定時間,靈活控制緩存時間
/// <summary>
/// 配合nginx緩存
/// </summary>
[AttributeUsageAttribute(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method,AllowMultiple = false)]
public class NginxCacheFilterAttribute : Attribute, IAsyncActionFilter
{
/// <summary>
/// 構造函數
/// </summary>
public NginxCacheFilterAttribute() { }
/// <summary>
/// 固定時間格式正則,例如:00:00 、10:30
/// <summary>
static Regex reg = new Regex(@"^(\d{1,2}):(\d{1,2})$",RegexOptions.IgnoreCase);
/// <summary>
/// 緩存清除固定時間,new string[] { "00:00", "10:00", "14:00", "15:00" }
/// </summary>
public string[] MustCleanTimes { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 緩存清除滑動時間,預設 300 (5分鐘)
/// </summary>
public int Period { get; set; } = 300;
/// <summary>
/// 請求頭變數
/// </summary>
const string X_Accel_Expires = "X-Accel-Expires";
const string ETag = "ETag";
const string Cache_Control = "Cache-Control";
/// <summary>
/// 過濾器執行
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
/// <param name="next"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Task OnActionExecutionAsync(ActionExecutingContext context,ActionExecutionDelegate next)
{
//非GET請求,不設置nginx緩存頭
if (context.HttpContext.Request.Method.ToUpper() != "GET") {
return next.Invoke();
}
var response = context.HttpContext.Response;
//判斷固定時間
if (MustCleanTimes != null && MustCleanTimes.Length > 0) {
var nowTime = DateTime.Now; //當前時間
var nowYmd = nowTime.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd"); //當前日期
List<DateTime> cleanTimes = new List<DateTime>();
foreach (var time in MustCleanTimes) {
if (reg.IsMatch(time) && DateTime.TryParse($"{nowYmd} {time}",out DateTime _date)) {
//已超時的推到第二天,例如設置的是00:00,刷新時間就應該是第二天的00:00
if (_date < nowTime)
cleanTimes.Add(_date.AddDays(1));
else
cleanTimes.Add(_date);
}
}
if (cleanTimes.Count > 0) {
var nextTime = cleanTimes.OrderBy(o => o).FirstOrDefault(); //下次刷新時間
var leftSeconds = nextTime.Subtract(nowTime).TotalSeconds; //下次刷新剩餘秒數
if (leftSeconds >= 0 && leftSeconds < Period)
Period = (int)leftSeconds;
}
}
//添加X_Accel_Expires
if (response.Headers.ContainsKey(X_Accel_Expires)) {
response.Headers.Remove(X_Accel_Expires);
}
response.Headers.Add(X_Accel_Expires,Period.ToString());
//添加ETag
if (response.Headers.ContainsKey(ETag)) {
response.Headers.Remove(ETag);
}
response.Headers.Add(ETag,new System.Net.Http.Headers.EntityTagHeaderValue($"\"{DateTime.Now.Ticks.ToString()}\"",true).ToString());
//移除Cache-Control
response.Headers.Remove(Cache_Control);
return next.Invoke();
}
}具體的使用方式如下:
1. 全局用法,全局Api都是設置的預設緩存時間,不需要緩存的Api在Controller或Action上單獨設置Period=0即可
//在Stratup中全局添加過濾器
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers(config => {
config.Filters.Add<NginxCacheFilterAttribute>();
});
}
/// <summary>
/// 設置滑動時間
/// Period=0為不生效
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpGet]
[NginxCacheFilter(Period = 0)]
public HttpResponseMessage TestCache1()
{
return new HttpResponseMessage() { StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK };
}2. 局部用法
/// <summary>
/// 設置滑動時間
/// 30秒後自動過期
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpGet]
[NginxCacheFilter(Period = 30)]
public HttpResponseMessage TestCache1()
{
return new HttpResponseMessage() { StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK };
}
/// <summary>
/// 設置固定時間
/// 例如:9點第一次請求,一直緩存到10點失效,12點第一次請求,一直緩存到15點失效
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpGet]
[NginxCacheFilter(MustCleanTimes = new[] { "10:00","15:00","22:00" })]
public HttpResponseMessage TestCache2()
{
return new HttpResponseMessage() { StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK };
}
具體效果
1. 我們第一次請求介面,返回200狀態碼,Nginx在響應頭上會返回X-Cache:MISS,代表緩存未命中
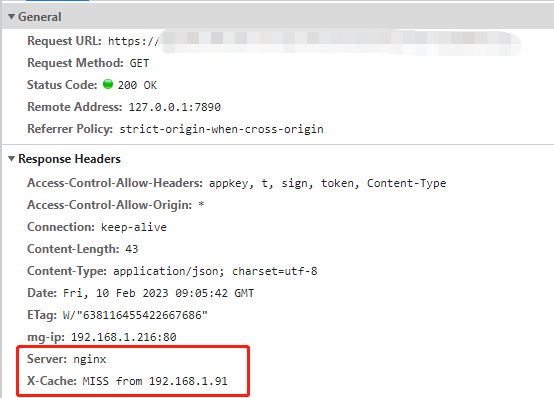
2. 第二次請求,會返回304狀態碼,Nginx在響應頭上會返回 X-Cache:HIT,代表已經命中緩存
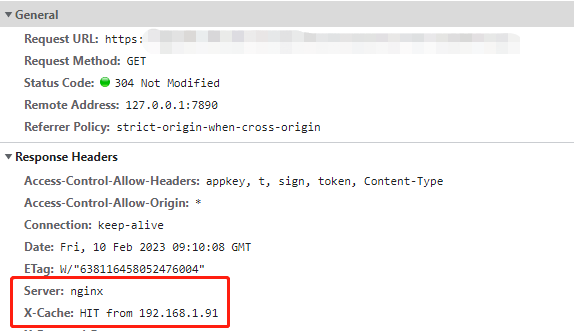
3. 我們開啟Chrome調試中的Disable Cache,這樣所有請求的請求頭中都會設置 Cache-Control: no-cache,再刷新下介面看下

發現介面返回200狀態碼,Nginx在響應頭上會返回X-Cache:EXPIRED,說明緩存已過期,已從源伺服器返回了數據,也說明通過請求頭設置Cache-Control為no cache是可以跳過緩存的
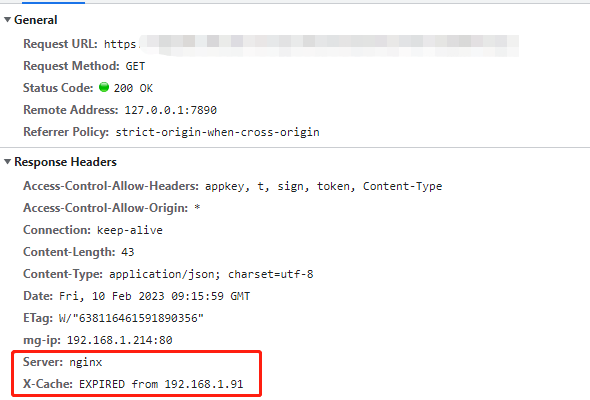
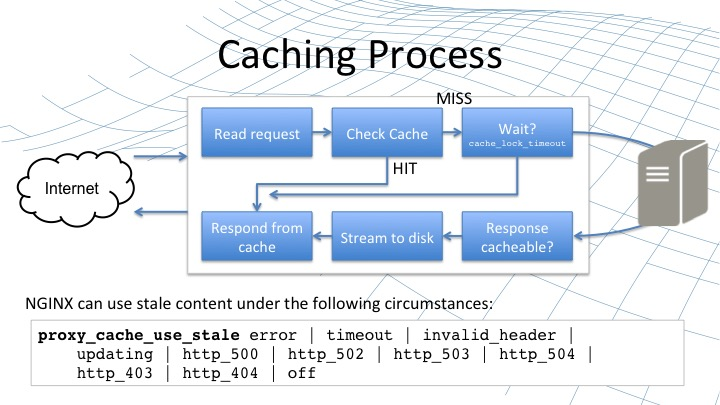
更多含義:

高性能用法:
proxy_cache_lock:緩存鎖
proxy_cache_lock_timeout:緩存鎖過期時間
如果給緩存規則設置了proxy_cache_lock,那麼該規則下同時進來多個同一個Key的請求,只會有一個請求被轉發到後面的源伺服器,其餘請求會被等待,直到源伺服器的內容被成功緩存
可以配合設置proxy_cache_lock_timeout,設置一個緩存鎖的過期時間,這樣其餘請求如果等待超時了,也會被釋放請求到後面的源伺服器
通過這兩個參數的組合使用,可以有效避免同一個請求大量打入時,瞬間壓垮後面的源伺服器
原創作者:Harry
原文出處:https://www.cnblogs.com/simendancer/articles/17109964.html


