哈嘍兄弟們 在大家的日常python程式的編寫過程中,都會有自己解決某個問題的解決辦法,或者是在程式的調試過程中,用來幫助調試的程式公式。 小編通過幾十萬行代碼的總結處理,總結出了22個python萬用公式,可以幫助大家解決在日常的python編程中遇到的大多數問題,一起來看看吧。 1、一次性進行多 ...
77、組合

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
int index = 1;
travesal(n,k,index);
return result;
}
public void travesal(int n, int k, int index){
// 終止條件,得到k個數的組合
if(temp.size() == k){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <= n - (k - temp.size()) + 1; i++) {
temp.add(i);
travesal(n,k,i+1);//遞歸
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);//回溯
}
}
}
216、組合總和 III

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
// 邊界條件,不存在有效的組合
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
sum += i;
}
if(sum > n){
return result;
}
int index = 1;
combinationSumHelper(k,n,index);
return result;
}
public void combinationSumHelper(int k, int n,int index){
if(temp.size() == k){
// 判斷找出的組合是否滿足相加之和為n的條件
int sum = 0;
for(Integer i : temp){
sum += i;
}
if(sum == n){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
return;
}
for(int i = index; i <= 9 - (k - temp.size()) + 1; i++){
temp.add(i);
combinationSumHelper(k,n,i+1);//遞歸
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);//回溯
}
}
}
17、電話號碼的字母組合

class Solution {
public List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
public StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
// 邊界條件
if(digits == null || digits.length() == 0){
return result;
}
char[] digitsArr = digits.toCharArray();
// 映射關係
String[] find = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
int index = 0;
letterCombinationsHelper(digitsArr, find, index);
return result;
}
public void letterCombinationsHelper(char[] digitsArr, String[] find, int index){
if(index == digitsArr.length){
result.add(new String(str));
return;
}
// 第index個數字對應的字母
String strTemp = find[digitsArr[index] - '0'];
for(int i = 0; i < strTemp.length(); i++){
str.append(strTemp.charAt(i));//加入第Index個數字對應的字母的第i個
letterCombinationsHelper(digitsArr,find,index+1);
str.deleteCharAt(str.length() - 1);
}
}
}
39、組合總和
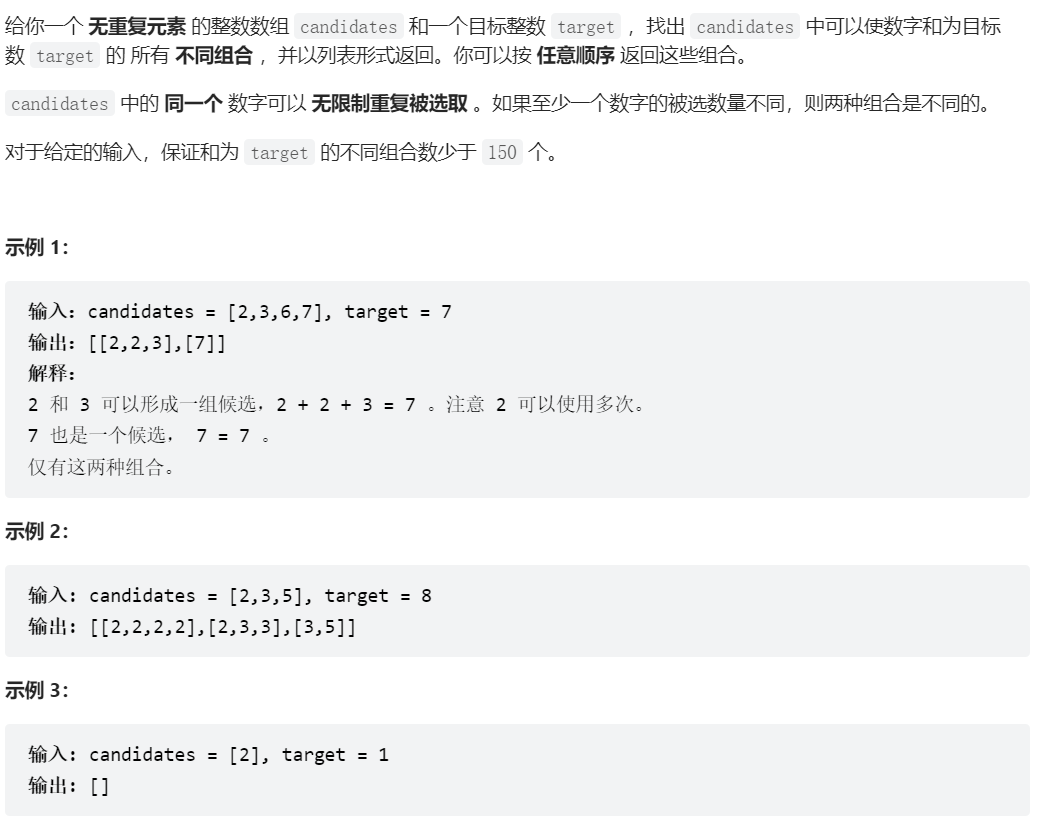
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
int sum = 0;
int index = 0;
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSumHelper(candidates,index,sum,target);
return result;
}
public void combinationSumHelper(int[] candidates, int index, int sum,int target){
if(sum >= target){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
}
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){
sum += candidates[i];
temp.add(candidates[i]);
combinationSumHelper(candidates,i,sum,target);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
}
}
}
40、 組合總和 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
int sum = 0;
int index = 0;
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSumHelper(candidates, target, index, sum);
return result;
}
public void combinationSumHelper(int[] candidates, int target, int index, int sum){
if(sum >= target){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
return;
}
// 每個數字在每個組合中只能使用一次
for(int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){
// 去重邏輯,同層剪枝,同枝可取
if(i > 0 &&i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]){
continue;
}
temp.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
combinationSumHelper(candidates, target, i + 1, sum);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
}
}
}
131、分割迴文串

class Solution {
public List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
public List<String> temp = new ArrayList<String>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
int index = 0;
partitionHelper(s, index);
return result;
}
public void partitionHelper(String s, int index){
if(index == s.length()){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < s.length(); i++){
String s1 = s.substring(index, i + 1);
if(!check(s1,0,s1.length() - 1)){
continue;//字元子串不迴文的話直接跳過該次分割方案
}
temp.add(s1);
partitionHelper(s,i+1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
// 判斷是否迴文
public boolean check(String s1, int left, int right){
while(left < right){
if(s1.charAt(left) == s1.charAt(right)){
left++;
right--;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
93、複原 IP 地址
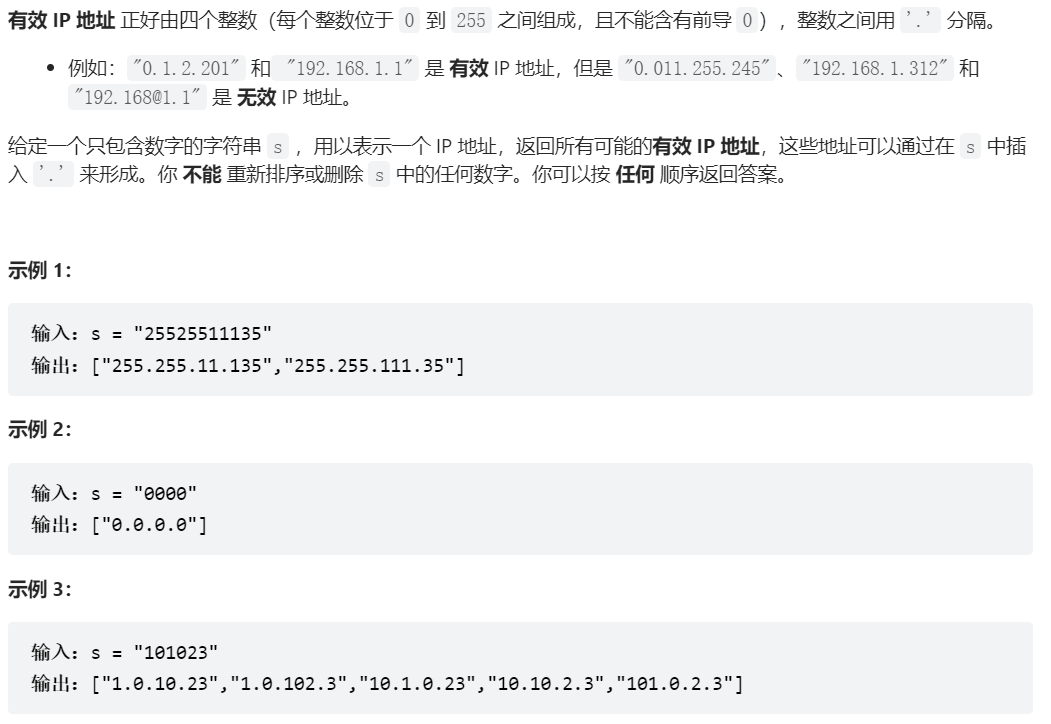
class Solution {
public List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
public StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
restoreIpAddressesHelper(s,0,0);
return result;
}
public void restoreIpAddressesHelper(String s, int index,int count){
if (index == s.length() && count == 4) {
result.add(stringBuilder.toString());
return;
}
if (index == s.length() || count == 4) {
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < s.length() && i - index < 3 && Integer.parseInt(s.substring(index, i + 1)) >= 0
&& Integer.parseInt(s.substring(index, i + 1)) <= 255; i++) {
if (i + 1 - index > 1 && s.charAt(index) - '0' == 0) {
continue;
}
stringBuilder.append(s.substring(index, i + 1));
if (count < 3) {
stringBuilder.append(".");
}
count++;
restoreIpAddressesHelper(s,i+1,count);
count--;
stringBuilder.delete(index + count, i + count + 2);
}
}
}
78、子集
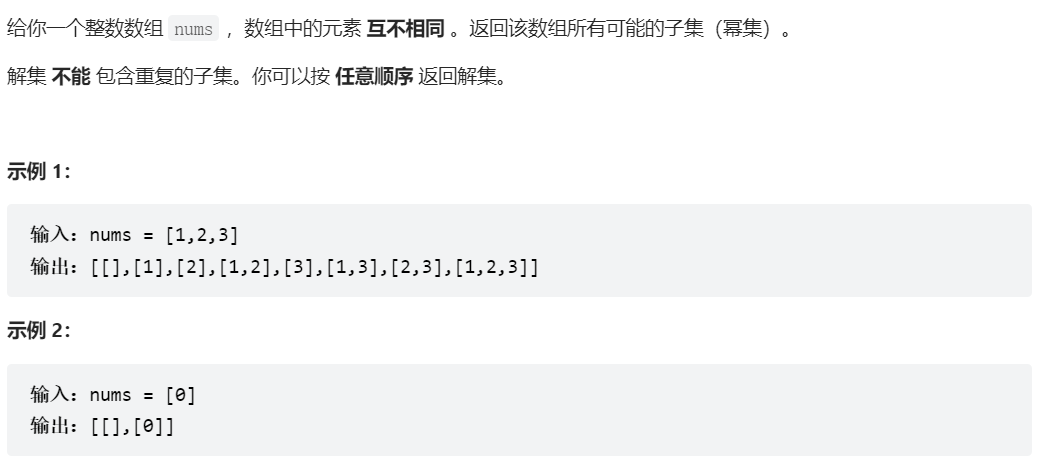
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
subsetsHandler(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void subsetsHandler(int[] nums, int index){
if(index == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
for(int i = index; i < nums.length; i++){
temp.add(nums[i]);
subsetsHandler(nums,i+1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
90、子集 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
subsetsWithDupHandler(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void subsetsWithDupHandler(int[] nums, int index){
if(index == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
for(int i = index; i < nums.length; i++){
// 不能 包含重覆的子集
if(i > 0 &&i > index && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
temp.add(nums[i]);
subsetsWithDupHandler(nums, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
491、遞增子序列

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
// 遞增子序列中 至少有兩個元素
findSubsequencesHandler(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void findSubsequencesHandler(int[] nums, int index){
if(temp.size() > 1){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
int[] used = new int[201];
for(int i = index; i < nums.length; i++){
if(temp.size() != 0 && nums[i] < temp.get(temp.size() - 1) || (used[nums[i] + 100] == 1)){
continue;
}
used[nums[i] + 100] = 1;
temp.add(nums[i]);
findSubsequencesHandler(nums, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
46、全排列

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
// 有序
int[] used = new int[30];
permuteHandler(nums, used);
return result;
}
public void permuteHandler(int[] nums, int[] used){
if(temp.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(used[nums[i]+10] == 1){
continue;
}
used[nums[i]+10] = 1;
temp.add(nums[i]);
permuteHandler(nums,used);
used[temp.get(temp.size() - 1)+10] = 0;
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
47、全排列 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(used, false);
Arrays.sort(nums);
permuteHandler(nums, used);
return result;
}
public void permuteHandler(int[] nums, boolean[] used){
if(temp.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false){
continue;
}
if(used[i] == false){
used[i] = true;
temp.add(nums[i]);
permuteHandler(nums,used);
used[i] = false;
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
332、重新安排行程
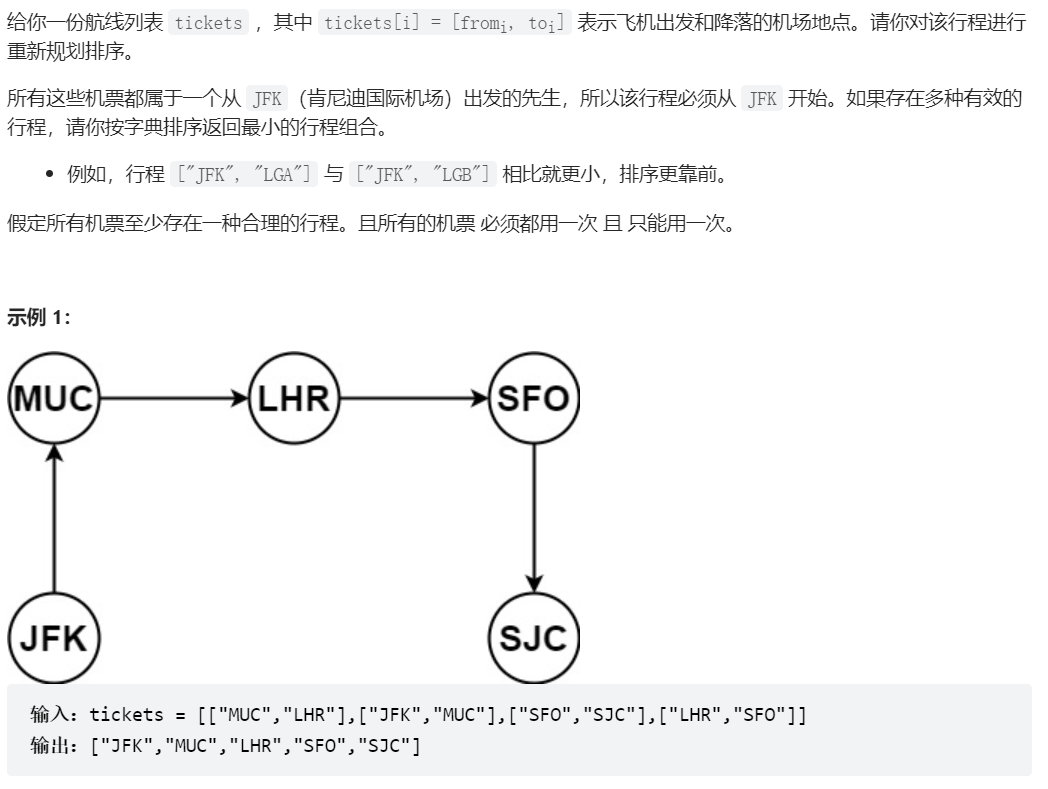
//基本參考代碼隨想錄
class Solution {
public LinkedList<String> result;
public LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<String>();
public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {
Collections.sort(tickets,(a,b)->a.get(1).compareTo(b.get(1)));
path.add("JFK");
int[] used = new int[tickets.size()];
findItineraryHanlder(tickets, used);
return result;
}
public boolean findItineraryHanlder(List<List<String>> tickets, int[] used){
if(path.size() == tickets.size() + 1){
result = new LinkedList<String>(path);
return true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < tickets.size(); i++){
if(used[i] != 1 && tickets.get(i).get(0).equals(path.getLast())){
path.add(tickets.get(i).get(1));
used[i] = 1;
if(findItineraryHanlder(tickets,used)){
return true;
}
path.removeLast();
used[i] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}
51、N 皇後

class Solution {
public List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
int[] arr = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(arr, -1);
find(arr, 0, n);
return result;
}
public void find(int[] arr, int index,int n){
if(index == n){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
arr[index] = i;
if(judge(arr,index)){
temp.add(setString(n,i));
find(arr, index+1,n);
arr[index]=-1;
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public boolean judge(int[] arr, int index){
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){
if(arr[i] == arr[index] || Math.abs(index - i)==Math.abs(arr[index]-arr[i])){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public String setString(int n, int m){
StringBuffer str1 = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(i == m){
str1.append("Q");
}else{
str1.append(".");
}
}
return new String(str1);
}
}
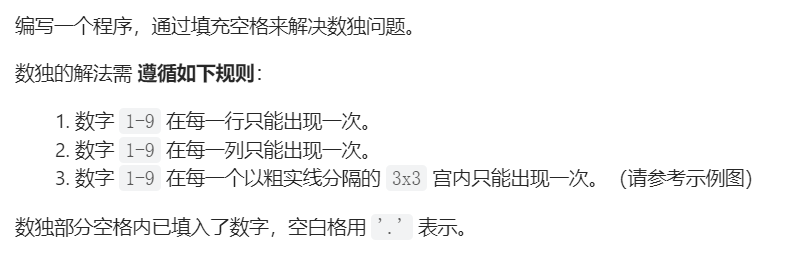
37、解數獨
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
solveSudokuHander(board);
}
public boolean solveSudokuHander(char[][] board){
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++){
if(board[i][j] != '.'){
continue;
}
for(char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++){
if(judge(board,i,j,k)){
board[i][j] = k;
if(solveSudokuHander(board)){
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean judge(char[][] board, int i, int j, char k){
for(int m = 0; m < 9; m++){
if(board[i][m]==k){
return false;
}
}
for(int n = 0; n < 9; n++){
if(board[n][j]==k){
return false;
}
}
int startRow = (i/3)*3;
int startCol = (j/3)*3;
for(int m = startRow; m < startRow+3; m++){
for(int n = startCol; n < startCol+3; n++){
if(board[m][n]==k){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}



