前言 本篇幅是繼 MyBatis詳解(一)的下半部分。 MyBatis執行Sql的流程分析 【1】基於前面已經將XML文件進行build解析了並且返回了SqlSessionFactory 【1.1】那麼分析SqlSessionFactory.openSession()方法是怎麼返回SqlSessio ...
前言
本篇幅是繼 MyBatis詳解(一)的下半部分。
MyBatis執行Sql的流程分析
【1】基於前面已經將XML文件進行build解析了並且返回了SqlSessionFactory
【1.1】那麼分析SqlSessionFactory.openSession()方法是怎麼返回SqlSession的,且SqlSession又是什麼東西:
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); } /** * 方法實現說明:從session中開啟一個數據源 * @param execType:執行器類型 * @param level:隔離級別 */ private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { // 獲取環境變數 final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 獲取事務工廠 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 創建一個sql執行器對象 // 一般情況下 若我們的mybaits的全局配置文件的cacheEnabled預設為ture就返回一個cacheExecutor,若關閉的話返回的就是一個SimpleExecutor final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); // 創建返回一個DeaultSqlSessoin對象返回 return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
【1.1.1】分析newExecutor方法中執行器的產生:
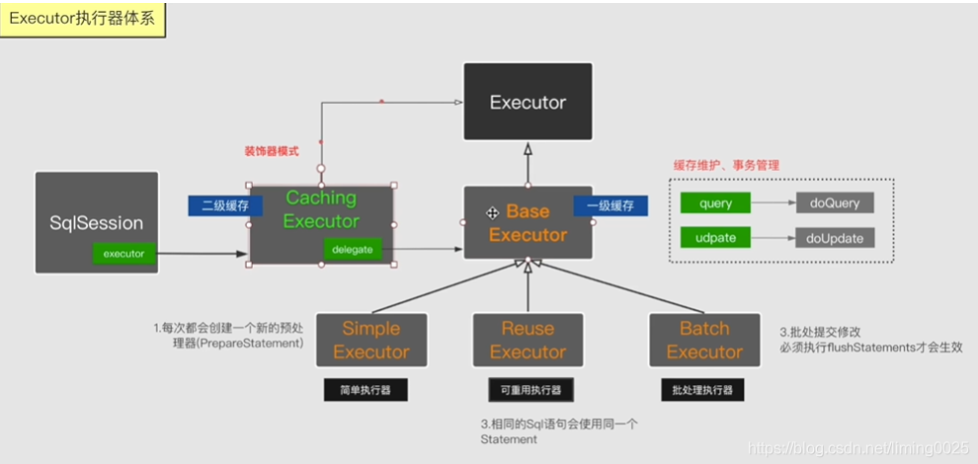
/** * 方法實現說明:創建一個sql語句執行器對象 * @param transaction:事務 * @param executorType:執行器類型 * @return:Executor執行器對象 */ public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; //判斷執行器的類型 // 批量的執行器 if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { //可重覆使用的執行器 executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { //簡單的sql執行器對象 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } //判斷mybatis的全局配置文件是否開啟緩存 if (cacheEnabled) { //把當前的簡單的執行器包裝成一個CachingExecutor executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } //調用所有的攔截器對象plugin方法,也就是生成代理對象 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
【1.1.1.1】圖示:
【1.1.2】分析底層如何執行JDBC【User user = (User)session.selectOne("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectById", 1);】
/** * 方法實現說明:查詢我們當個對象 * @param statement:SQL語句 * @param parameter:調用時候的參數 * @return: T 返回結果 */ @Override public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) { // 這裡selectOne調用也是調用selectList方法 List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter); //若查詢出來有且有一個一個對象,直接返回要給 if (list.size() == 1) { return list.get(0); } else if (list.size() > 1) { //查詢的有多個,那麼就拋出異常 throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size()); } else { return null; } } @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) { return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT); } /** * @param statement: statementId * @param parameter:參數對象 * @param rowBounds :mybiats的邏輯分頁對象 */ @Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { //第一步:通過我們的statement去我們的全局配置類中獲取MappedStatement MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); //通過執行器去執行我們的sql對象 //第一步:包裝我們的集合類參數 //第二步:一般情況下是executor為cacheExetory對象 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
【1.1.2.0】分析兩種方法的本質:
方法一:User user = (User)session.selectOne("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectById", 1); 源碼流程: //通過statement去我們的全局配置類中獲取MappedStatement MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id) { return this.getMappedStatement(id, true); } public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) { if (validateIncompleteStatements) { buildAllStatements(); } // 這個mappedStatements便是在SqlSessionFactory進行build過程中parse解析出來的 return mappedStatements.get(id); } 方法二:UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); 與 User user = mapper.selectById(1L); 源碼流程: @Override public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) { return configuration.getMapper(type, this); } public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); } /** * 方法實現說明:通過class類型和sqlSessionTemplate獲取Mapper(代理對象) * @param type:Mapper的介面類型 * @param sqlSession:介面類型實際上是我們的sqlSessionTemplate類型 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { // 直接去緩存knownMappers中通過Mapper的class類型去找mapperProxyFactory final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); // 緩存中沒有獲取到 直接拋出異常 if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { // 通過MapperProxyFactory來創建我們的實例 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }
【1.1.2.1】如果是定義了二級緩存,那麼會走CachingExecutor邏輯:
/** * 方法實現說明:通過我們的sql執行器對象執行sql * @param ms 用於封裝我們一個個的insert|delete|update|select 對象 * @param parameterObject:參數對象 * @param rowBounds :mybaits的邏輯分頁對象 * @param resultHandler:結果處理器對象 */ @Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { // 通過參數對象解析sql詳細信息1339025938:1570540512:com.project.mapper.selectById:0:2147483647:select id,user_name,create_time from t_user where id=?:1:development BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject); CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } @Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { //判斷mapper中是否開啟了二級緩存<cache></cache> Cache cache = ms.getCache(); // 判斷是否配置了cache if (cache != null) { //判斷是否需要刷新緩存 flushCacheIfRequired(ms); if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); // 先去二級緩存中獲取 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); //也就是去PerpetualCache裡面尋找 // 二級緩存中沒有獲取到 if (list == null) { //通過查詢資料庫去查詢 list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); //加入到二級緩存中 tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 } return list; } } //沒有整合二級緩存,直接去查詢 return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
【1.1.2.1.1】事務的TransactionalCacheManager:
【1.1.2.1.1.1】它存在的意義在於:避免事務不成功的sql語句填充到了Cache裡面,淘汰掉一些已經執行過的語句,相當於包裝了一層。
【1.1.2.1.1.2】存儲的地方:本質上會先存在自身類的屬性值private final Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<>();
【1.1.2.1.1.3】當成功後才會提交到PerpetualCache裡面。
【1.1.2.1.2】分析語句的解析【ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject)】:
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) { boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject); } // check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30) for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) { String rmId = pm.getResultMapId(); if (rmId != null) { ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId); if (rm != null) { hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps(); } } } return boundSql; } //DynamicSqlSource類#getBoundSql方法 @Override public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) { DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject); //責任鏈處理SqlNode,編譯出完整的sql rootSqlNode.apply(context); SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration); //處理sql中的#{..} Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass(); //將#{..}中的內容封裝為parameterMapping,替換為? SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings()); BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject); context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter); return boundSql; } //BoundSql類的結構 public class BoundSql { private final String sql; //語句 private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings; private final Object parameterObject; //參數處理 private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters; //結果集處理 private final MetaObject metaParameters; }
【1.1.2.2】如果沒有定義的話,則會選擇BaseExecutor的三個子類中的一個【但其實還是會走BaseExecutor的邏輯】:
//BaseExecutor類#query方法,子類重寫的是doQuery,如果是使用query方法本質上還是走BaseExecutor類的 @Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); //已經關閉,則拋出 ExecutorException 異常 if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } // 清空本地緩存,如果 queryStack 為零,並且要求清空本地緩存。 if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { // 從一級緩存中,獲取查詢結果 queryStack++; //BaseExecutor類的屬性值:protected PerpetualCache localCache; list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; // 獲取到,則進行處理 if (list != null) { //處理存過的 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { // 獲得不到,則從資料庫中查詢 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; } //至於為什麼會說一級緩存是session級別的,因為一旦提交或者回滾之後都會被清空 @Override public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException { if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed"); } clearLocalCache(); flushStatements(); if (required) { transaction.commit(); } } @Override public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException { if (!closed) { try { clearLocalCache(); flushStatements(true); } finally { if (required) { transaction.rollback(); } } } } // 清楚本地一級緩存 @Override public void clearLocalCache() { if (!closed) { localCache.clear(); localOutputParameterCache.clear(); } }
【1.1.2.3】分析queryFromDatabase方法:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List<E> list; //一級緩存中先占位 localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try { //調用子類的查詢方法 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { localCache.removeObject(key); } localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; } //以預設的SimpleExecutor為例查看doQuery方法 @Override public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); //創建StatementHandler,主要職責是拿到鏈接,拿到執行者 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } } //分析如何創建StatementHandler public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; } //存在三種StatementHandler public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { switch (ms.getStatementType()) { case STATEMENT: delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case PREPARED: delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; case CALLABLE: delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); break; default: throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); } } //但是這三種都是繼承BaseStatementHandler,因為BaseStatementHandler裡面才會有resultSetHandler和parameterHandler protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); this.executor = executor; this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement; this.rowBounds = rowBounds; this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement generateKeys(parameterObject); boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject); } this.boundSql = boundSql; this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql); }
【2.2】對於執行器Executor的分析,先分析介面的定義:
/** * 類的描述:sql執行器介面,主要用於維護一級緩存和二級緩存,並且提供事務管理功能 * Executor * --BaseExecutor(一級緩存) * --batchExecutor(批量執行器) * --ReUseExecutor(可重用的) * --SimpleExecutor簡單的 * --CacheExecutor(加入了二級緩存) */ public interface Executor { //ResultHandler 對象的枚舉 ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null; /** * 更新 or 插入 or 刪除,由傳入的 MappedStatement 的 SQL 所決定 * @param ms 我們的執行sql包裝對象(MappedStatement) * @param parameter 執行的參數 */ int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException; /** * 查詢帶緩存key查詢 * @param ms 我們的執行sql包裝對象(MappedStatement) * @param parameter:參數 * @param rowBounds 邏輯分頁參數 * @param resultHandler:返回結果處理器 * @param cacheKey:緩存key * @param boundSql:我們的sql對象 * @return 查詢結果集list * @throws SQLException */ <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException; /** * 不走緩存查詢 * @param ms 我們的執行sql包裝對象(MappedStatement) * @param parameter:參數 * @param rowBounds 邏輯分頁參數 * @param resultHandler:返回結果處理器 * @return 結果集list * @throws SQLException */ <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException; /** * 調用存過查詢返回游標對象 * @param ms 我們的執行sql包裝對象(MappedStatement) * @param parameter:參數 * @param rowBounds 邏輯分頁參數 * @return Cursor資料庫游標 * @throws SQLException */ <E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException; // 刷入批處理語句 List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException; //提交事務 void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException; //回滾事務 void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException; //創建緩存key CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql); // 判斷是否緩存 boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key); // 清除本地緩存 void clearLocalCache(); // 延遲載入 void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType); //獲取一個事務 Transaction getTransaction(); // 關閉事務 void close(boolean forceRollback); //判斷是否關閉 boolean isClosed(); // 設置包裝的 Executor 對象 void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor); }


