2022-11-03 一、base標簽 1、作用:用於添加web項目的首碼。 2、放置位置:放置在head標簽內部,一般放在首行。 3、使用方式:<base href="/項目名稱/">,在html網頁中的其他(例如:圖片,超鏈接...)使用下相對路徑的前面將“./”去掉。因為它是指的是base 之 ...
鏈表:插入快,查詢慢,存儲不連續
分為單鏈表,雙鏈表和迴圈鏈表
在鏈表中使用虛擬頭結點,可以減少增刪改查中對頭結點的特殊處理
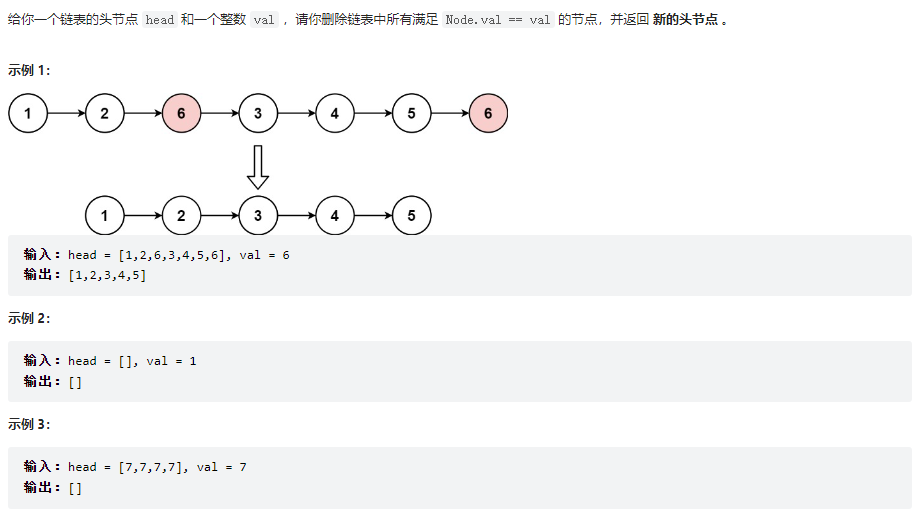
移除鏈表元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 時間複雜度O(n),空間複雜度O(1)
if(head == null){//空鏈表的情況
return head;
}
while(head != null && head.val == val){//頭結點為val的情況
head = head.next;
}
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null && temp.next != null){
while(temp != null && temp.next != null && temp.next.val == val){
if(temp.next.next != null){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else{//最後一個節點為val的情況
temp.next = null;
}
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
}
707、設計鏈表

class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head;
ListNode tail;
// 初始化鏈表,構建虛擬的頭結點和尾節點
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
tail = new ListNode(0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(index > size - 1 || index < 0){
return -1;
}
while(index >= 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > size){
return;
}
if(index < 0 ){
index = 0;
}
size++;
ListNode temp = new ListNode(val);
ListNode cur = head;
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
temp.prev = cur;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(index > size - 1 || index < 0){
return;
}
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
size--;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
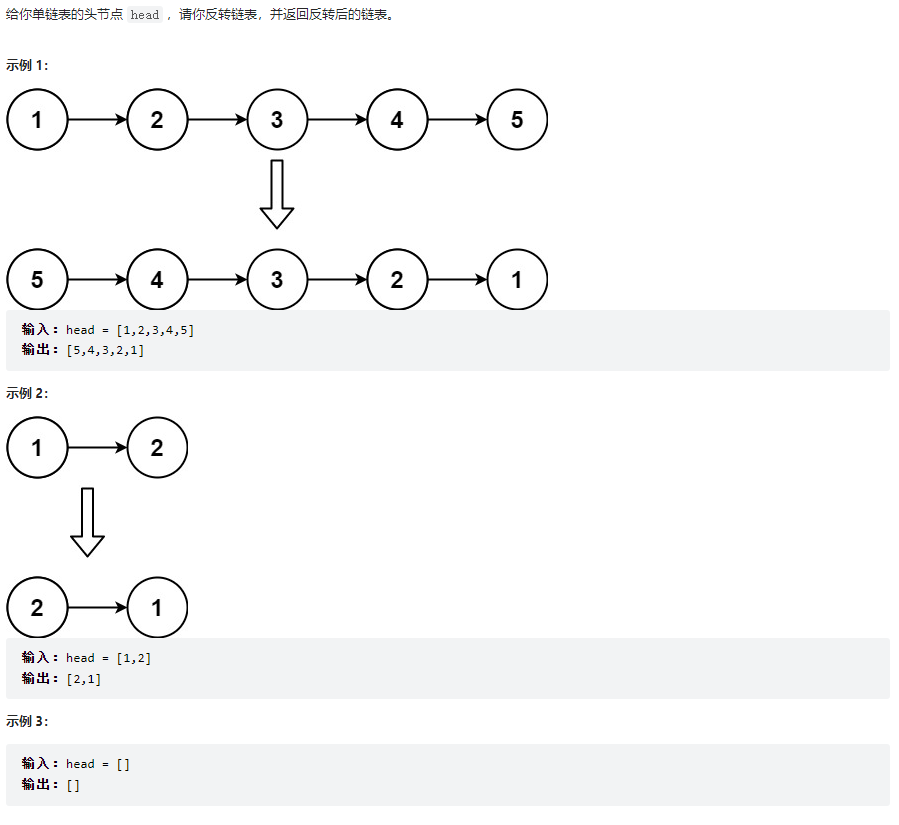
反轉鏈表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 方法一:在頭結點不斷插入
// if(head == null){
// return head;//空節點不需要反轉
// }
// ListNode temp = head.next;//臨時節點前移一位
// head.next = null;//代反轉鏈表的頭結點拆出來
// ListNode newHead = head;//待反轉鏈表的頭結點賦給新的鏈表
// while(temp != null){
// head = temp;//找出待反轉鏈表的新頭結點
// temp = temp.next;//臨時節點前移一位
// head.next = null;//待反轉鏈表的新頭拆出來
// head.next = newHead;//待反轉鏈表的心頭指向新的鏈表
// newHead = head;//得到新的鏈表的新頭
// }
// return newHead;
// 方法二:壓棧,利用棧的先入後出
// if(head == null){
// return head;
// }
// Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// ListNode temp = head;
// while(head != null){
// temp = head.next;
// head.next = null;
// stack.push(head);
// head = temp;
// }
// ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
// temp = newHead;
// while(!stack.isEmpty()){
// temp.next = stack.pop();
// temp = temp.next;
// }
// return newHead.next;
// 方法三:遞歸
return reverse(null, head);
// 方法四:從後往前遞歸
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// if(head.next == null){
// return head;
// }
// ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
// head.next.next = head;
// head.next = null;
// return newHead;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur){
if(cur == null){
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
}
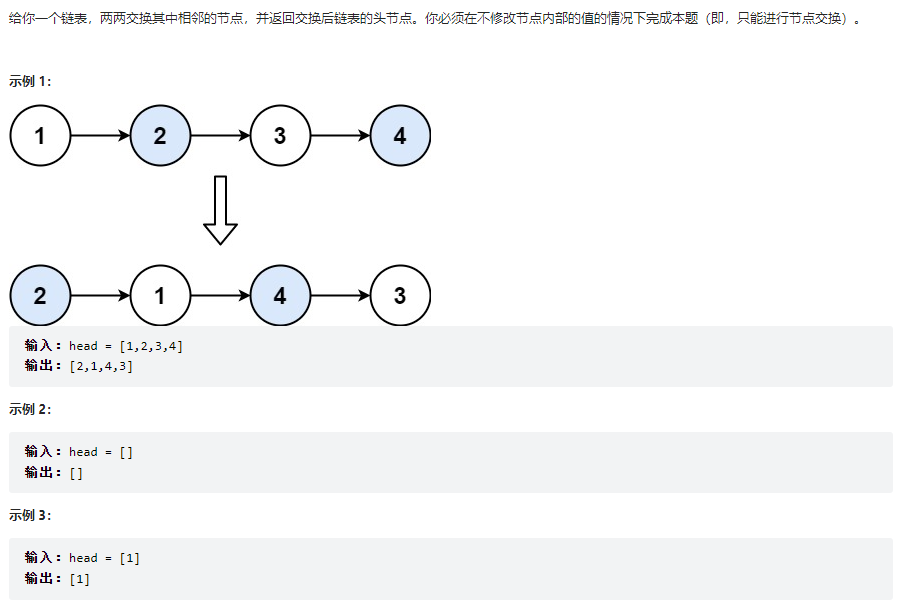
兩兩交換鏈表中的節點
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// 方法一:從前往後進行迭代
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// if(head.next == null){
// return head;
// }
// ListNode temp = head.next;//依次記錄偶數節點的位置
// head.next = head.next.next;//交換相鄰的節點
// temp.next = head;
// temp.next.next = swapPairs(temp.next.next);//迭代交換下一個相鄰的節點
// return temp;
// 方法二:雙指針
if(head == null){
return null;
}
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode temp = head.next;
ListNode pre = head.next;//記錄新的頭結點
while(temp != null){
head.next = head.next.next;//交換相鄰的節點
temp.next = head;
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
break;
}else{
head = head.next;//指向下一個相鄰節點的奇數節點
temp.next.next = temp.next.next.next;//上一個相鄰節點的偶數節點指向下一個節點的偶數節點
temp = head.next;//下一個相鄰節點的偶數節點
}
}
return pre;
}
}
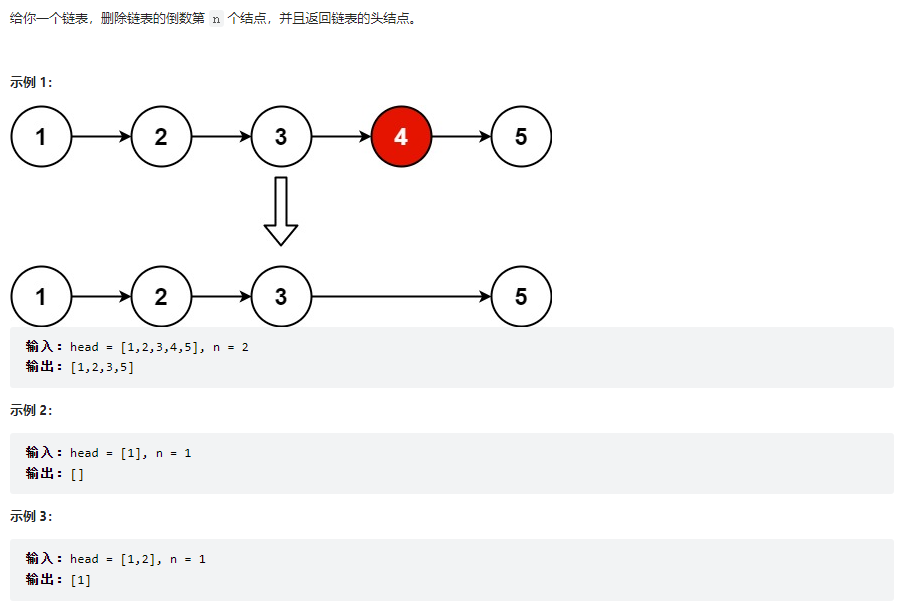
刪除鏈表的倒數第 N 個結點
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 方法一:快慢指針,返回頭結點說明head的頭結點不能動,所以把鏈表的地址賦給另外一個對象
// 添加虛擬頭結點,方便操作。比如需要刪除的是頭結點的時候不需要單獨考慮這種特殊情況
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
ListNode temp = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
while(temp.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
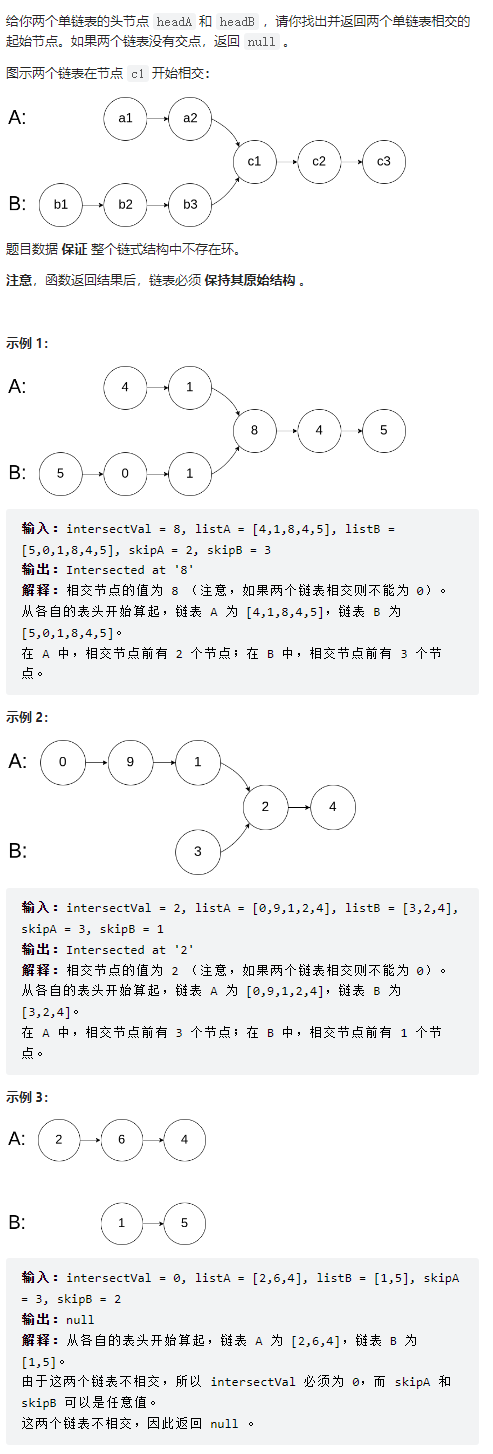
鏈表相交
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
ListNode dummyHeadA = headA;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
ListNode dummyHeadB = headB;
while(dummyHeadA.next != null){
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
countA++;
}
while(dummyHeadB.next != null){
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
countB++;
}
if(dummyHeadA != dummyHeadB){
return null;//尾節點不相交則說明不相交
}
dummyHeadA = headA;
dummyHeadB = headB;
int index = (countA - countB) > 0 ? (countA - countB) : -(countA - countB);//兩個鏈表的長度差
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){//讓較長的鏈表先移動index位
if((countA - countB) > 0){
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
}else{
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
}
}
while(dummyHeadA != dummyHeadB){//兩個鏈表逐次向前移動,找出相交的第一個節點
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
}
return dummyHeadA;
}
}
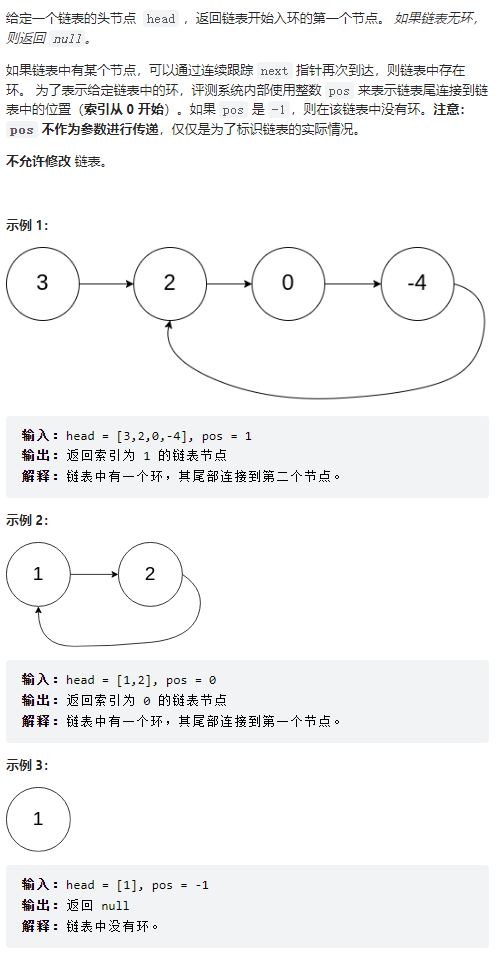
環形鏈表 II
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
// O(1)空間的要求,所以不能用遞歸
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode slowList = head;
ListNode fastList = head;
boolean flag = false;//判斷是否有環
while(fastList != null && fastList.next != null){
fastList = fastList.next.next;
slowList = slowList.next;
if(fastList == slowList){
flag = true;//有環
break;
}
}
if(!flag){//沒有環
return null;
}else{//有環,找出環的入口,也就是索引的位置
slowList = head;
while(fastList != slowList){
fastList = fastList.next;
slowList = slowList.next;
}
return slowList;
}
}
}
哈希表:也叫散列表,用來快速判斷一個元素是否出現在集合中,實際上是用空間換時間
有效的字母異位詞
242
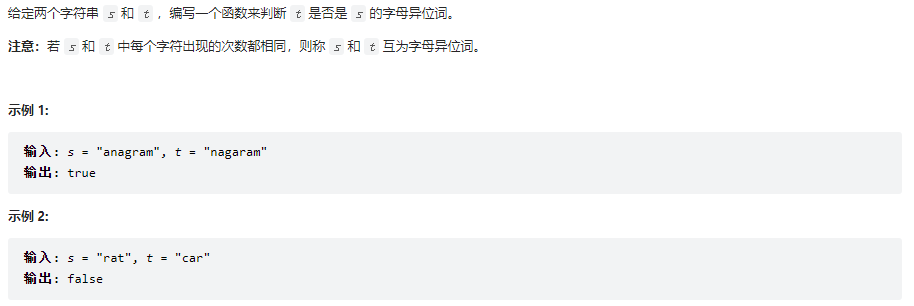
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
// 方法一:使用hashmap
// if(s.length() != t.length()){
// return false;
// }
// HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
// map.put(s.charAt(i), (map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0) + 1));
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
// if(map.containsKey(t.charAt(i))){
// if(map.get(t.charAt(i)) == 1){
// map.remove(t.charAt(i));
// }else{
// map.put(t.charAt(i), (map.get(t.charAt(i)) - 1));
// }
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// }
// return true;
// 方法二:用數組來構造哈希表,字典解法
if(s.length() != t.length()){
return false;
}
int[] arr = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
int index = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
arr[index] = arr[index] + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
int index = t.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(arr[index] != 0){
arr[index] = arr[index] - 1;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
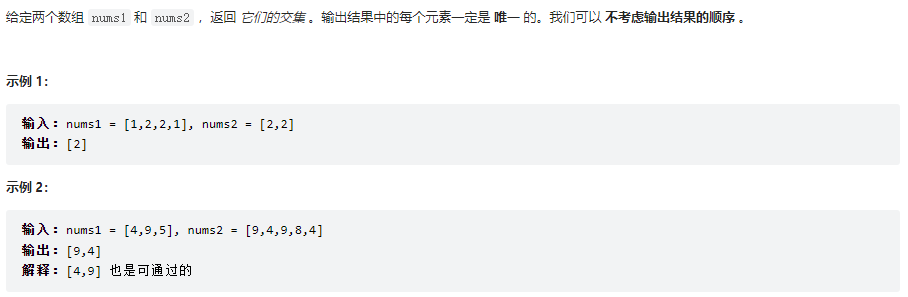
兩個數組的交集
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
// 使用hashset,無序,且不能存儲重覆數據,符合題目要求
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<Integer> record = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++){
set.add(nums1[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++){
if(set.remove(nums2[i])){
record.add(nums2[i]);
}
}
return record.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray();
}
}
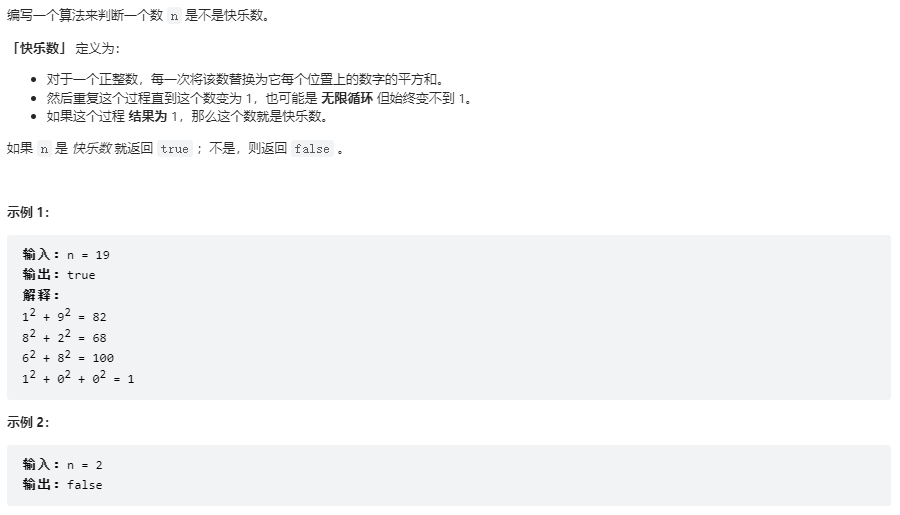
快樂數
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
// 使用hashset,當有重覆的數字出現時,說明開始重覆,這個數不是快樂數
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet();
int sum = 0;
while(true){
while(n != 0){
sum = sum + (n%10)*(n%10);
n = n / 10;
}
if(sum == 1){
return true;
}
if(!set.add(sum)){
return false;
}
n = sum;
sum = 0;
}
}
}
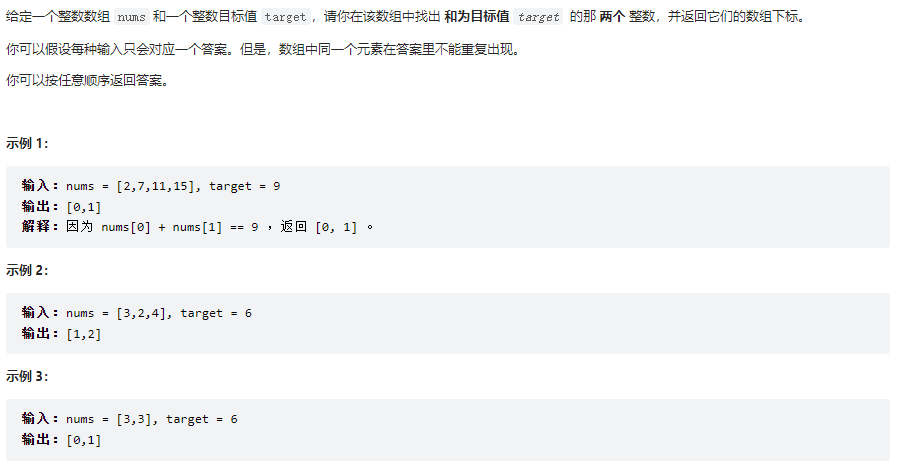
兩數之和
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 方法一:暴力解法
// int[] arr = new int[2];
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++){
// for(int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++){
// if(target == (nums[i] + nums[j])){
// return new int[]{i,j};
// }
// }
// }
// return new int[0];
// 方法二:HashMap
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
int find = target - nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(find)){
return new int[]{i, map.get(find)};
}else{
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
}
return null;
}
}
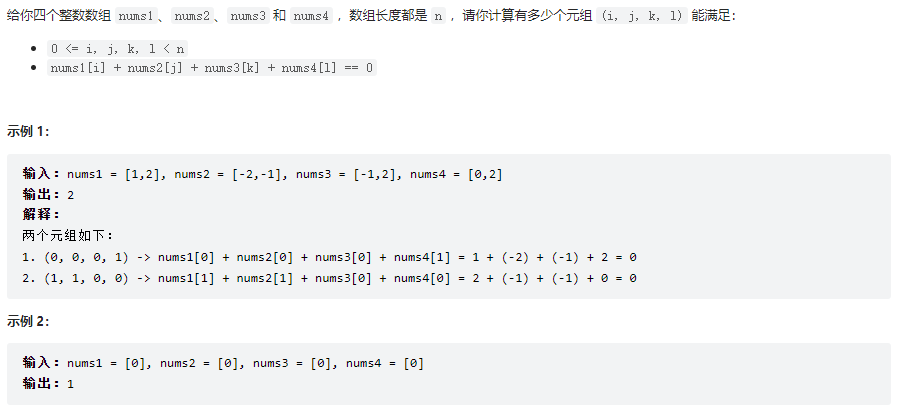
四數相加 II
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
// 四個數,用哈希表,參考代碼隨想錄
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int count = 0;
for(int i : nums1){
for(int j : nums2){
int temp = i + j;
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
}else{
map.put(temp, 1);
}
}
}
for(int i : nums3){
for(int j : nums4){
int temp = 0- (i + j);
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
count += map.get(temp);
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
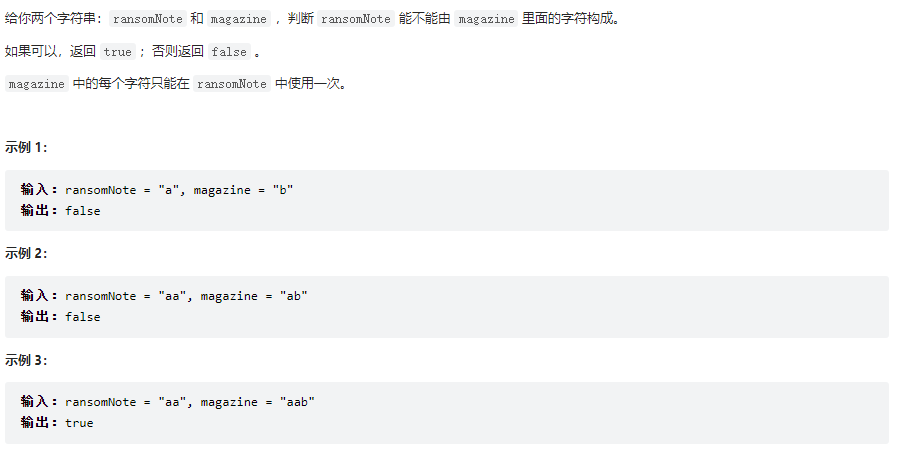
贖金信
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
// 方法一;hashmap
// HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// char temp;
// for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
// temp = ransomNote.charAt(i);
// if(map.containsKey(temp)){
// map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
// }else{
// map.put(temp, 1);
// }
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
// temp = magazine.charAt(i);
// if(map.containsKey(temp)){
// if(map.get(temp) == 1){
// map.remove(temp);
// }else{
// map.put(temp, map.get(temp) - 1);
// }
// }
// }
// if(map.isEmpty()){
// return true;
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// 方法二:數組在哈希法的應用,比起方法一更加節省空間,因為字元串只有小寫的英文字母組成
int[] arr = new int[26];
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
temp = ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a';
arr[temp] = arr[temp] + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
temp = magazine.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(arr[temp] != 0){
arr[temp] = arr[temp] - 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
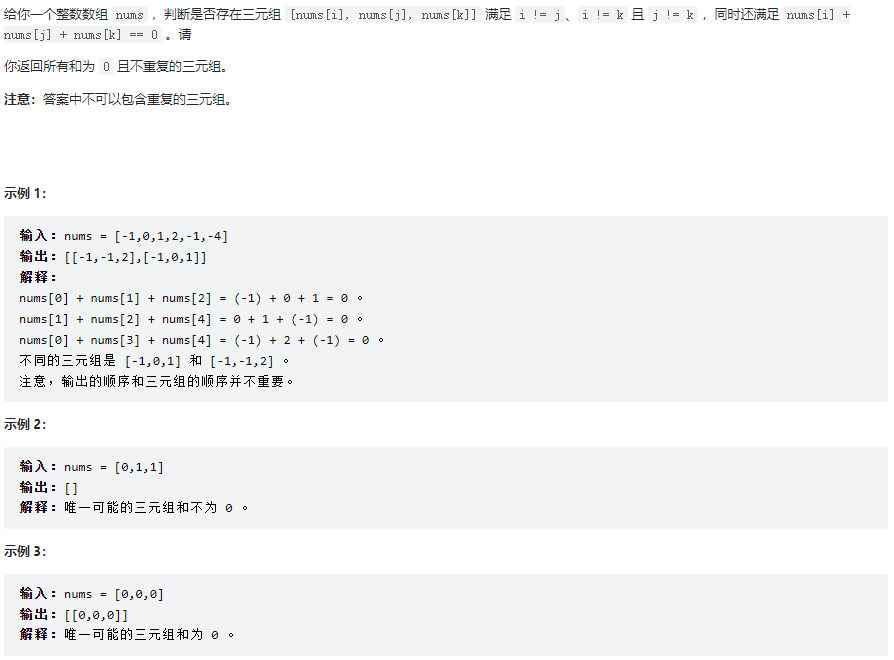
三數之和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
// 如果考慮使用跟四數之和類似的求解方式,由於三元組是在同一個數組中尋找的,且要求不重覆的三元組,因此求解會比較複雜
// 題目要求返回的是三元組的具體數值,而不是索引值,因此可以考慮使用雙指針
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-1-i;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
int temp = nums[j+1];
nums[j+1] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
int leftNode;
int rightNode;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (nums[i] > 0) {
return list;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
leftNode = i + 1;
rightNode = nums.length - 1;
while(leftNode < rightNode){
if((nums[i] + nums[leftNode] + nums[rightNode]) < 0){
leftNode++;
}else if((nums[i] + nums[leftNode] + nums[rightNode]) > 0){
rightNode--;
}else{
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[leftNode], nums[rightNode]));
while (rightNode > leftNode && nums[rightNode] == nums[rightNode - 1]) rightNode--;
while (rightNode > leftNode && nums[leftNode] == nums[leftNode + 1]) leftNode++;
rightNode--;
leftNode++;
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
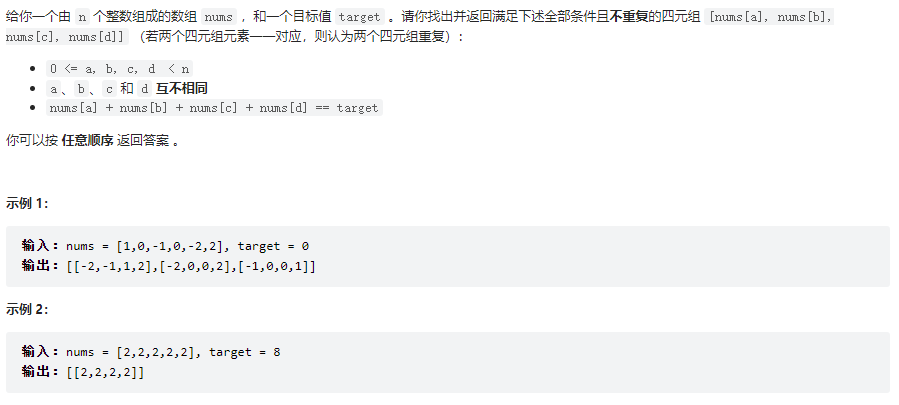
四數之和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-1-i;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
int temp = nums[j+1];
nums[j+1] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] > target) {
return list;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++){
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]){
continue;
}
int left = j + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
long sum = (long)(nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]);
if(sum > target){
right--;
}else if(sum < target){
left++;
}else{
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i] , nums[j] , nums[left] , nums[right]));
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]){
left++;
}
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]){
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}