本文講解了決策樹的創鍵的過程,包括熵,信息增益的計算,還有決策樹的創建,以及使用matplotlib讓決策樹可視化的詳細過程 ...
1.決策樹的構造
1.1優缺點
優點:-
計算複雜度不高:以ID3為例,每次運算都是基於某一列特征,特征計算完後,下次計算不考慮該最有特征,並且通過適當剪枝可以簡化複雜度
-
輸出結果易於理解:因為輸出的是一個樹的結構,樹的走向一目瞭然
-
對中間值的缺失不敏感
-
可以處理不相關特 徵數據:是基於每列特征來計算,不考慮特征之間的依賴關係
缺點:可能會產生過度匹配問題。
適用數據類型:數值型和標稱型。
1.2信息熵
主要用來度量信息的混亂程度,信息越混亂,說明能夠包含的信息量越多,則熵越大。反之若信息越有序說明包含的信息量越少,則熵越小。1.3信息增益
標準的說法就是:一個隨機變數的引入導致了另一個隨機變數的混亂性變化(約束),如果約束越大,信息增益就越大。舉個通俗易懂的例子就是:比如你去銀行貸款,如果你自己的個人信息你對貸款員什麼都不說,那貸款員是不是就很不確定是否貸款給你,如果你只說了你的薪資,那較之前相比,貸款員是否給你貸款是不是就多了一種判斷的依據,也就是說,你告訴貸款員你的個人信息越多,貸款員是否給你貸款就越確定,此時的信息增益也就是最大。在舉一個例子:瞭解一個人的信息,如果給一個身份證號,由於每個人的身份證號都是唯一的,所以一個身份證號就可以判斷這個的所有信息,也就是引入身份證號這個屬性之後,就會唯一確定一個人,這時身份證號對判斷這個人的約束是最大,信息增益也就是最大。2.決策樹的構造
2.1熵的計算
數據集:
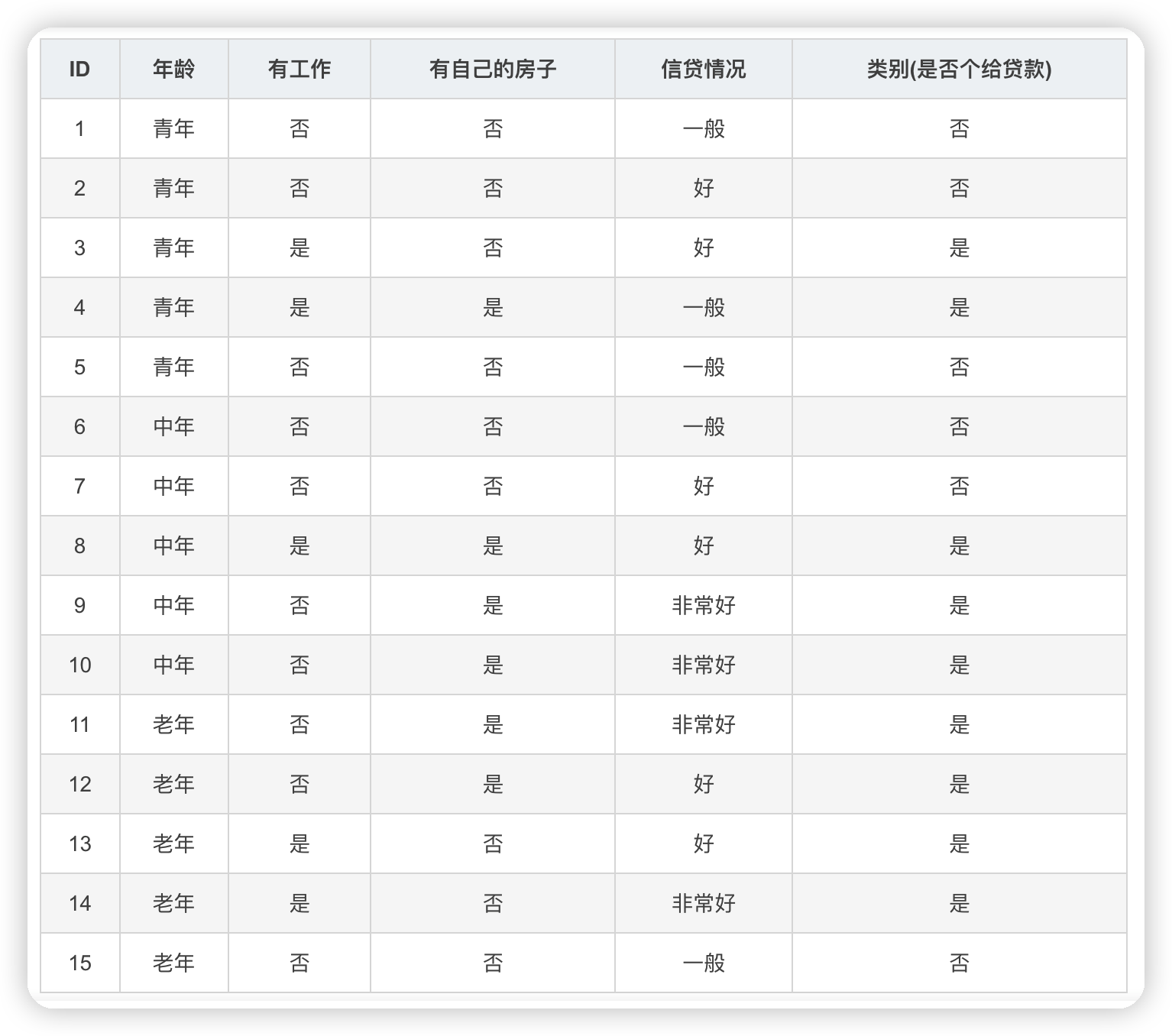
根據表中的數據統計可知,在15個數據中,9個數據的結果為放貸,6個數據的結果為不放貸。所以數據集D的經驗熵H(D)為:
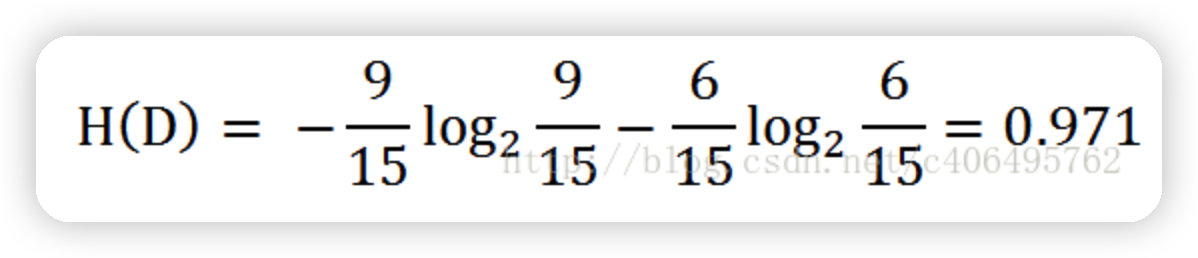
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntires = len(dataSet) #返回數據集的行數
labelCounts = {} #保存每個標簽(Label)出現次數的字典
for featVec in dataSet: #featVec代表一行一行的數據 #對每組特征向量進行統計
currentLabel = featVec[-1] #取每一行的最後一列也即是否貸款的值
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): #如果標簽(Label)沒有放入統計次數的字典,添加進去
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0#鍵對應的值設為零
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #鍵對應的值加一
shannonEnt = 0.0 #經驗熵(香農熵)
for key in labelCounts: #計算香農熵
prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntires #選擇該標簽(Label)的概率
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) #利用公式計算
return shannonEnt
def createDataSet():
#年齡:0代表青年,1代表中年,2代表老年
#信貸情況:0代表一般,1代表好,2代表非常好
dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], # 數據集
[0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']]
labels = ['年齡', '有工作', '有自己的房子', '信貸情況'] # 特征標簽
return dataSet, labels # 返回數據集和分類屬性
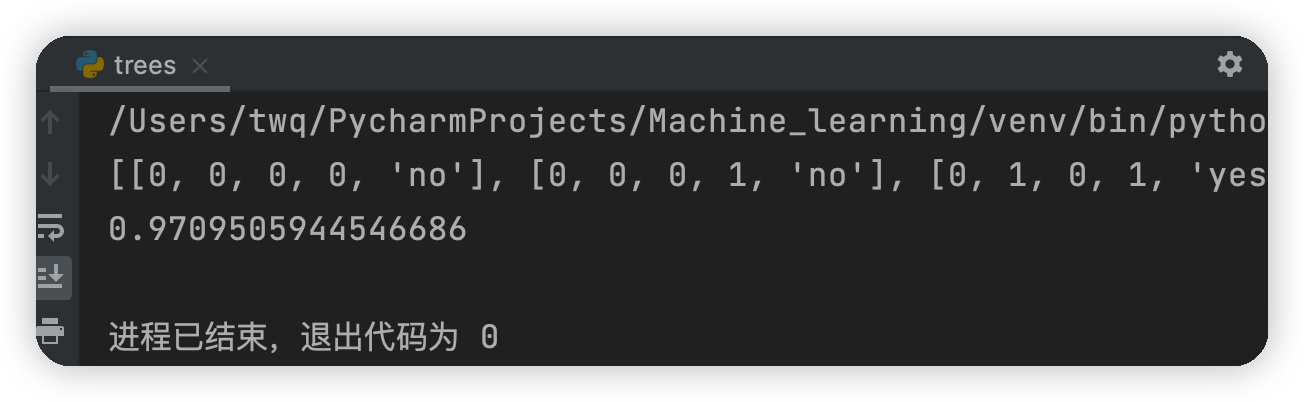
myDat,labels=createDataSet()
print(myDat)
print(calcShannonEnt(myDat))
測試結果:
2.2劃分數據集
2.2.1按照給定特征劃分數據集
#三個輸入參數:待劃分的數據集、劃分數據集的特征、需要返回的特征的值
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
retDataSet = [] #創建返回的數據集列表
for featVec in dataSet: #遍曆數據集
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #去掉axis特征
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #將符合條件的添加到返回的數據集
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet #返回劃分後的數據集
上面代碼的解釋,假設axis=0,value=1,表示的是在第一列年齡的屬性中,找到值為1(也即為中年)的所有行,然後去掉每一行中第一列的數據(其實很多餘,因為在算熵的時候只取最後一列的數據),然後每一行的剩餘列的數據保存
以添加年齡之後算此時是否貸款的信息增益的方法如下圖:

2.2.2選擇最好的數據集劃分方式
代碼實現:def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征數量
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #計算數據集的香農熵
bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益
bestFeature = -1 #最優特征的索引值
for i in range(numFeatures): #遍歷所有特征
#獲取dataSet的第i個所有特征-第i列全部的值
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList) #創建set集合{},元素不可重覆
newEntropy = 0.0 #經驗條件熵
for value in uniqueVals: #計算信息增益
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) #subDataSet劃分後的子集
prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #計運算元集的概率如上圖的p(youth),p(middle),p(old)的值
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) #根據公式計算經驗條件熵
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益=h(D)-h(D|A)
# print("第%d個特征的增益為%.3f" % (i, infoGain)) #列印每個特征的信息增益
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #取出信息增益的最大值 #計算信息增益
bestInfoGain = infoGain #更新信息增益,找到最大的信息增益
bestFeature = i #記錄信息增益最大的特征的索引值
return bestFeature
2.3遞歸構建決策樹
#當所有的特征及屬性都遍歷完成之後任然不能確定是否貸款
#此時可根據classlist中是否貸款各自的數量,取最大票數的即可
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount = {}
for vote in classList: #統計classList中每個元素出現的次數
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True) #根據字典的值降序排序
return sortedClassCount[0][0] #返回classList中出現次數最多的元素
#創建樹的函數代碼
def createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]#取分類標簽(是否放貸:yes or no)
# print("classlist:")
# print(classList)
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #如果類別完全相同則停止繼續劃分
return classList[0]
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #遍歷完所有特征時返回出現次數最多的類標簽
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) #選擇最優特征
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]#最優特征的標簽
featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel)
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}#根據最優特征的標簽生成樹
del(labels[bestFeat]) #刪除已經使用特征標簽
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] #得到訓練集中所有最優特征的屬性值
uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重覆的屬性值
for value in uniqueVals: #遍歷特征,創建決策樹。
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), labels, featLabels)
return myTree
遞歸函數的第一個停止條件是所有的
類標簽完全相同,則直接返回該類標簽。遞歸函數的第二個停止條件是使用完了所有特征,任然不能將數據集劃分成僅包含唯一類別的分組 。由於第二個條件無法簡單地返回唯一的類標 簽,這裡使用投票表決的函數挑選出現次數最多的類別作為返回值
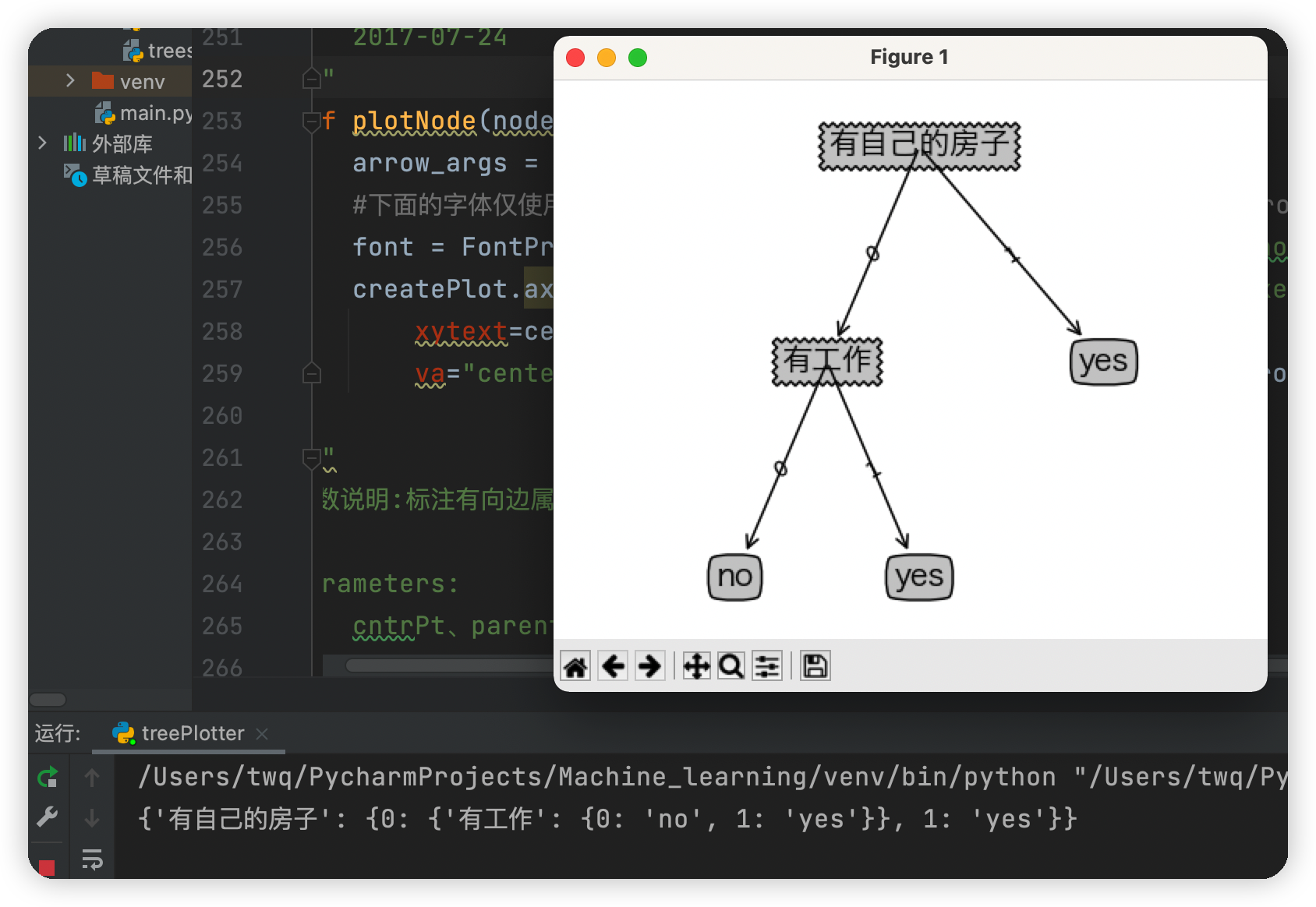
運行結果
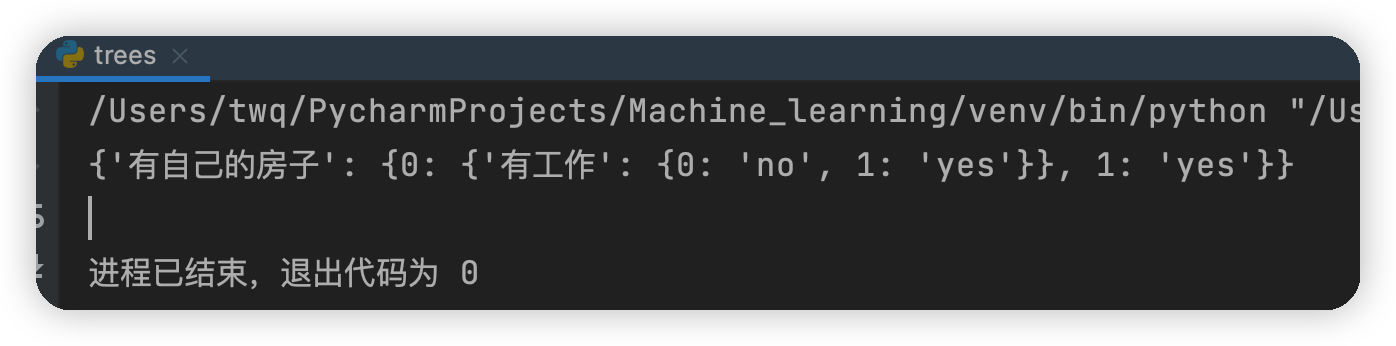
由上面建立的決策樹可知,首先判斷你是否有房子,如果有就可以貸款給你,如果沒有房子再看你是否有工作,如果既沒有房子也沒有工作,就不貸款給你,如果有沒有房子,但有工作,也貸款給你
3.使用 Matplotlib 註解繪製樹形圖
使用Matplotlib的註解功能繪製樹形圖,它可以對文字著色並提供多種形狀以供選擇, 而且我們還可以反轉箭頭,將它指向文本框而不是數據點。#獲取決策樹葉子結點的數目
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0 #初始化葉子
firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #python3中myTree.keys()返回的是dict_keys,不在是list,所以不能使用myTree.keys()[0]的方法獲取結點屬性,可以使用list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #獲取下一組字典
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #測試該結點是否為字典,如果不是字典,代表此結點為葉子結點
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else: numLeafs +=1
return numLeafs
#獲取決策樹的層數
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0 #初始化決策樹深度
firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #python3中myTree.keys()返回的是dict_keys,不在是list,所以不能使用myTree.keys()[0]的方法獲取結點屬性,可以使用list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #獲取下一個字典
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #測試該結點是否為字典,如果不是字典,代表此結點為葉子結點
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else: thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth #更新層數
return maxDepth
#繪製結點
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-") #定義箭頭格式
#下麵的字體僅使用與Mac用戶,如果您是Windows用戶請修改為font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc", size=14)
font = FontProperties(fname=r'/System/Library/Fonts/Hiragino Sans GB.ttc', size=14) #設置中文字體
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', #繪製結點
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args, fontproperties=font)
#標註有向邊屬性值
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0] #計算標註位置
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
#繪製決策樹
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8") #設置結點格式
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8") #設置葉結點格式
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #獲取決策樹葉結點數目,決定了樹的寬度
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) #獲取決策樹層數
firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #下個字典
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) #中心位置
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) #標註有向邊屬性值
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) #繪製結點
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #下一個字典,也就是繼續繪製子結點
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD #y偏移
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict': #測試該結點是否為字典,如果不是字典,代表此結點為葉子結點
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #不是葉結點,遞歸調用繼續繪製
else: #如果是葉結點,繪製葉結點,並標註有向邊屬性值
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
#創建繪製面板
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white') #創建fig
fig.clf() #清空fig
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #去掉x、y軸
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) #獲取決策樹葉結點數目
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) #獲取決策樹層數
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0; #x偏移
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '') #繪製決策樹
plt.show() #顯示繪製結果
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataSet, labels = createDataSet()
featLabels = []
myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels)
print(myTree)
createPlot(myTree)
運行遇到的錯誤:
-
1.AttributeError:module 'backend_interagg' has no attribute 'FigureCanvas'
解決方法:
在pycharm中打開" File --> Settings --> Tools --> Python Scientific ",將"Show plots in toolwindow"去掉勾選,並應用。 -
2.'Annotation' object has no property 'FontProperties'
解決方法:
找了一會發現是字體問題,因為我的電腦是Mac系統,在字體設置與Windows有些區別,讀者可以根據如下步驟修改:首先在終端輸入open /System/Library/Fonts然後找到一種字體,並複製其路徑,另外在調用的時候FontProperties要寫成小寫,否則也會報錯,如下圖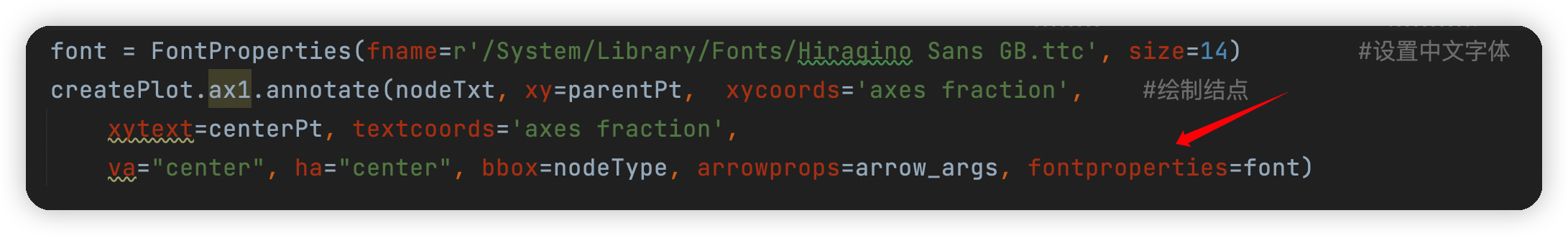
最終問題解決之後,運行結果如下圖