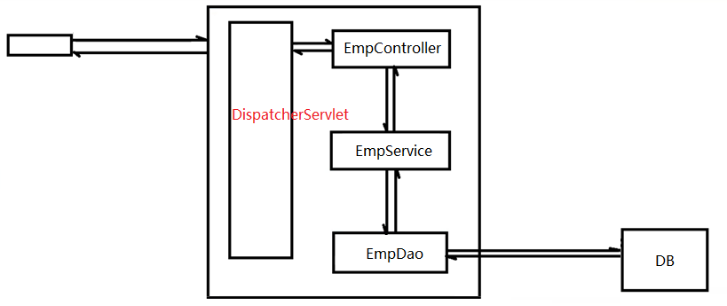
4. 業務層 4.1 MVC模型 MVC:Model(模型),View(視圖),Controller(控制器) 視圖層:用於做數據的展示以及和用戶交互的一個界面=>jsp 控制層:能夠接受客戶端的請求並且進行請求轉發,具體的業務功能還是需要藉助模型層組件來完成。CoreServlet => Disp ...
4. 業務層
4.1 MVC模型
MVC:Model(模型),View(視圖),Controller(控制器)
視圖層:用於做數據的展示以及和用戶交互的一個界面=>jsp
控制層:能夠接受客戶端的請求並且進行請求轉發,具體的業務功能還是需要藉助模型層組件來完成。CoreServlet => DispacherServlet + EmpController
模型層:模型分為很多種:
1) 存值的值對象: POJO/VO(value object)/entity/bean -> Emp
2) 有數據訪問對象:DAO---數據訪問對象:xxxDao
3) 有業務模型對象:BO,業務對象 比如:xxxService
4) 數據傳輸對象:DTO data transfer object
4.1 什麼是業務對象
4.2 區分業務對象和數據訪問對象
4.2.1 單精度方法
DAO中的方法都是單精度方法 或者稱之為細粒度方法。
什麼叫單精度?一個方法只考慮一個操作,比如,添加,那就是insert操作。查詢那就是select操作。
4.2.2 BO也就是Service層屬於業務方法
BO中的方法屬於業務方法,但實際的業務是比較複雜的,因此業務方法的粒度是比較粗的
比如:註冊這個功能屬於業務功能,也就是說註冊這個方法屬於業務方法。
那麼在這個業務方法中包含了多少個DAO方法呢,也就是說註冊這個業務功能需要通過調用多個DAO方法的組合調用才能完成註冊功能。
4.2.3 註冊的功能步驟:
1、檢查用戶名是否已經被註冊—DAO中的select操作。
2、向用戶表新增一條新用戶記錄—DAO的insert操作。
3、向用戶積分表新增一條記錄(新用戶預設初始化積分假如是100分)--DAO中的insert操作
4、向系統消息表新增一條記錄(某某新用戶註冊了,需要根據通訊錄信息向他的聯繫人推送消息)--DAO中的insert操作。
5、向系統日誌表新增一條記錄(某用戶在某IP在某年某月某日某時某分某秒註冊)--DAO中的insert操作。
4.3 代碼的編寫(mymvc4)
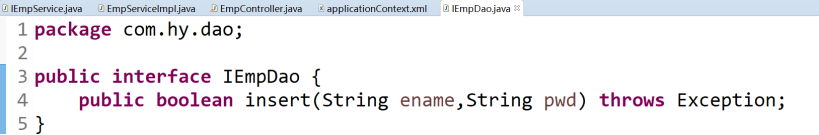
4.4 新建IEmpDao & EmpDaoImpl
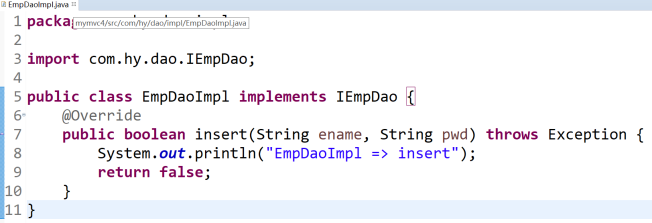
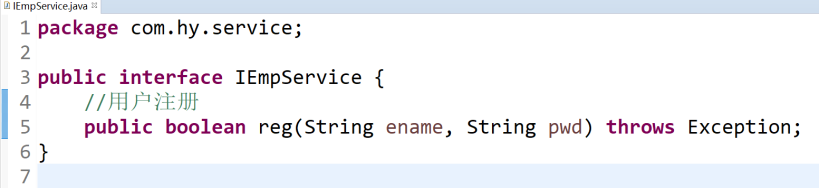
4.5 新建IEmpService & EmpServiceImpl,寫一個reg方法
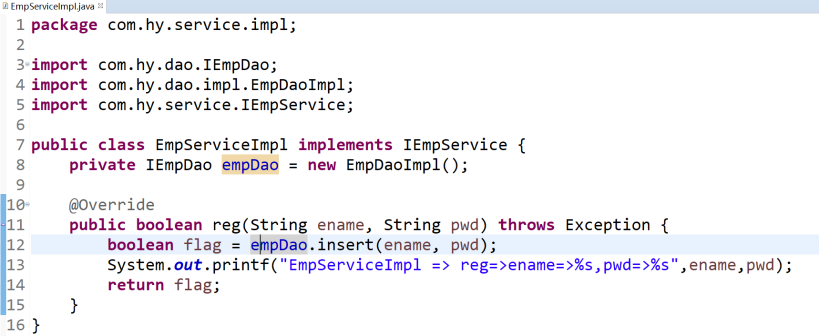
4.6 EmpController中的代碼
|
package com.hy.controller;
import com.hy.service.IEmpService; import com.hy.service.impl.EmpServiceImpl;
public class EmpController { private IEmpService empService = new EmpServiceImpl();
public void add(String ename,String pwd) { try { boolean flag = empService.reg(ename, pwd); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
public String index() { System.out.println("EmpController...index"); return "forward:/WEB-INF/emp/index.jsp"; }
public String login(String ename,String pwd) { System.out.printf("EmpController的login方法獲取的參數值ename=%s,pwd=%s",ename,pwd); return "redirect:emp.do?ac=index"; }
public String delete(Integer eid) { if(eid !=null ) { System.out.println("EmpController eid=="+eid); //empDao.delete(eid); return "forward:xxx"; } return "forward:error.xxx"; } } |
5. 什麼是耦合/依賴
耦合/依賴 :依賴指的是誰離不開誰,這叫依賴。比如:你離不開你女朋友。你依賴你女朋友
在我們系統當中的每個層之間,層與層之間也存在依賴。比如:Controller層必須依賴Service層,例如:現在將Service層EmpServiceImpl刪除了,然後EmpController層就會報錯。
同樣,Service層依賴Dao層。
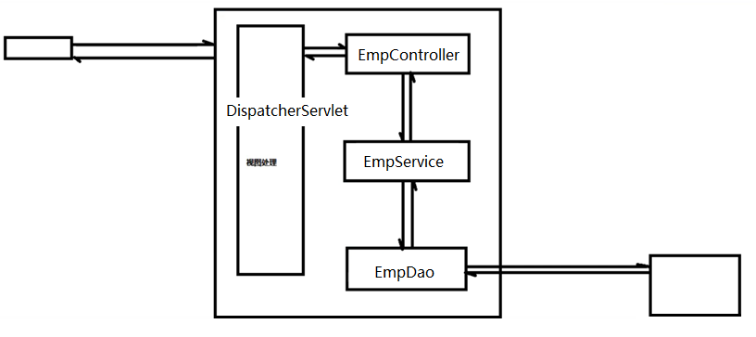
依賴指的是 某某某 離不開 某某某
在軟體系統中,層與層之間是存在依賴的。我們也稱之為耦合。
我們系統架構或是設計的一個原則就是:高內聚 低耦合。
層內部的組成應該是高度聚合的,而層與層之間的關係應該是低耦合的。
而所謂的低耦合,就是我們熟稱的炮友。
我想做到的是什麼??刪除EmpServiceImpl , EmpController不報錯,EmpController中有new EmpServiceImpl( ) ; 這麼new的會就表示和下層的EmpServiceImpl有關係了。

6. 如何解決耦合和依賴?
IOC-反轉控制/ DI-依賴註入
6.1 第一步,將=new 刪掉


6.2 第二步,解決空指針的問題
6.2.1 編寫applicationContext.xml配置文件,
在applicationContext.xml再寫兩行配置文件,在當前的整個配置文件中配置了三個bean,這三個bean就是對應了三個組件。下一步,計劃在系統啟動的時候,它就會把這三個組件準備好,放在一個容器裡面,誰需要的時候就給誰用。
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans> <!-- 這個bean標簽的作用是,id中的值,要和將來和ServletPath 中路徑的名做對應,emp對應的就要EmpController這個類來處理。 --> <bean id="emp" class="com.hy.controller.EmpController"/>
<bean id="empService" class="com.hy.service.impl.EmpServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="empDao" class="com.hy.dao.impl.EmpDaoImpl"/> </beans> |
6.2.2 新建一個介面 BeanFactory & 實現類ClassPathXMLApplicationContext

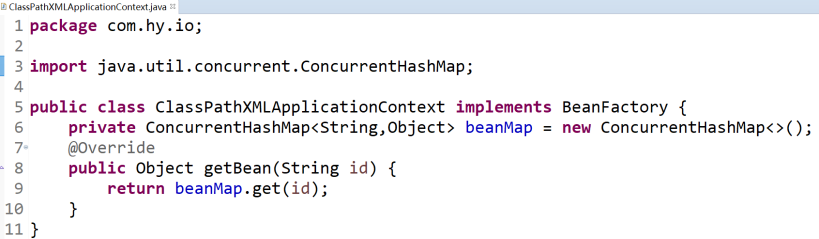
6.2.3 ClassPathXMLApplicationContext的代碼
|
package com.hy.io;
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document; import org.w3c.dom.Element; import org.w3c.dom.Node; import org.w3c.dom.NodeList; import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public class ClassPathXMLApplicationContext implements BeanFactory { private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 在預設構造方法中載入配置文件 public ClassPathXMLApplicationContext() {
try { InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("applicationContext.xml");
// 1,創建DocumentBuilderFactory工廠對象 DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 2,創建DocumentBuilder對象 DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
// 3,得到Document對象( 註意導入org.w3c.dom包中的) Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
// 4,獲得所有的Bean標簽 NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0, len = nodeList.getLength(); i < len; i++) { Node node = nodeList.item(i);
System.out.println(node.getNodeType() );//1,1,1
if( node.getNodeType() == node.ELEMENT_NODE) { Element element = (Element)node; String id = element.getAttribute("id"); String className = element.getAttribute("class");
boolean flag = map.containsKey(id);
if(flag == true) return;
Class clazz = Class.forName(className); Object o = clazz.newInstance();
map.put(id, o); } }
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SAXException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
@Override public Object getBean(String id) { return map.get(id); }
public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXMLApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXMLApplicationContext(); } } |
運行main方法測試一下。
6.2.4 回到DispatcherServlet修改代碼
|
package com.hy.servlet;
import java.io.IOException; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.hy.io.BeanFactory; import com.hy.io.ClassPathXMLApplicationContext; import com.hy.utils.StringUtil;
@WebServlet("*.do") public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet { private BeanFactory beanFactory;
public DispatcherServlet() { }
@Override public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { super.init(config); beanFactory = new ClassPathXMLApplicationContext(); }
@Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // 設置編碼 request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
// 假設url是: http://localhost:8080/mymvc2/hello.do // ServletPath是Servlet的訪問路徑: /hello.do // 思路是: // 第1步: /hello.do -> hello 或者 /book.do -> book // 第2步: hello -> HelloController 或者 book -> BookController String servletPath = request.getServletPath(); // /hello.do int lastDotIndex = servletPath.lastIndexOf(".do"); servletPath = servletPath.substring(1, lastDotIndex); // hello
// 通過ServletPath獲取對應的Controller對象 // Object xxxController = map.get(servletPath); Object xxxController = beanFactory.getBean(servletPath);
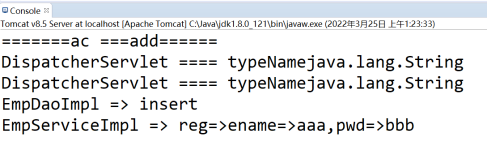
String ac = request.getParameter("ac"); System.out.println("=======ac ===" + ac + "======"); if (StringUtil.isEmpty(ac)) ac = "index";
String methodReturnStr = null; try { // 這裡只能try...catch異常,因為在重寫的方法里,不能拋出比父類更大的異常 Method[] methods = xxxController.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
if (methods != null) { for (Method method : methods) { if (ac.equals(method.getName())) { // 1,統一獲取請求參數 // 1.1 獲取當前方法的參數,返回參數數組 Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters(); // 1.2 有幾個參數就需要準備同等容量的Object類型的數組。這個數組用來存放參數的值得 Object[] parameterValues = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0, len = parameters.length; i < len; i++) { Parameter parameter = parameters[i];
// 1.3 從請求中獲取參數的值 String parameterValue = request.getParameter(parameter.getName()); /** * 註意,這裡沒有考慮 覆選框的情況,因為覆選框name相同, * 打了好幾個勾,一提交,返回給我們值的是一個數組 獲取的方法: * request.getParameterValues(name); */
// 1.5 EmpController中delete方法的參數需要的是一個Integer類型, // 通過反射機制我們該方法需要的類型Parameter是Integer, // 但是前臺傳遞到後臺的是字元串”1”,而不是數字1,所以需要進行類型轉換。 String typeName = parameter.getType().getName(); System.out.println("DispatcherServlet ==== typeName"+typeName);
//註意:這裡一定要先將String 轉成 Object Object parameterObj = parameterValue;
if(parameterObj != null) { //註意:這裡如果需要完善, 還需要寫Float,Double等類型 if("java.lang.Integer".equals(typeName)) { parameterObj = Integer.parseInt(parameterValue); } } // 1.4 將獲取的參數值保存在Object類型的數組當中 //parameterValues[i] = parameterValue; parameterValues[i] = parameterObj; }
// 2. xxxController中的方法調用 // Object returnObj = method.invoke(xxxController, request, response); Object returnObj = method.invoke(xxxController,parameterValues);
// 3, 視圖跳轉處理 if (returnObj != null) { methodReturnStr = (String) returnObj; if (methodReturnStr.startsWith("redirect:")) { String redirectStr = methodReturnStr.substring("redirect:".length()); response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/" + redirectStr); return; } else if (methodReturnStr.startsWith("forward:")) { String forwardtStr = methodReturnStr.substring("forward:".length()); request.getRequestDispatcher(forwardtStr).forward(request, response); return; } } return; } } throw new RuntimeException("ac值違法"); } } catch (SecurityException | IllegalAccessException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
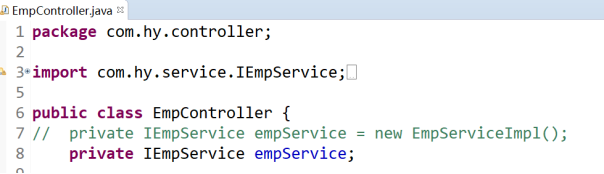
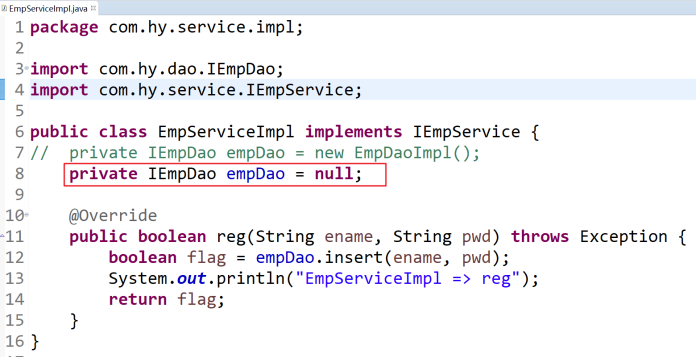
6.2.5 回到XxxController中,如何給xxxService賦值??
我們將new EmpServiceImpl();刪除了,去掉了依賴,如何賦值?
而且service層也依賴dao,改成null後,去掉了依賴,如何賦值?
6.2.6 如何解決?
在applicationContext.xml文件中先描述我們需要哪些組件。然後再描述組件與組件之間的依賴關係。XxxController中需要XxxService,XxxService中需要XxxDao。

6.2.7 修改ClassPathXMLApplicationContext代碼, 查看獲取了xml中的哪些對象
|
package com.hy.io;
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document; import org.w3c.dom.Element; import org.w3c.dom.Node; import org.w3c.dom.NodeList; import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public class ClassPathXMLApplicationContext implements BeanFactory { private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 在預設構造方法中載入配置文件 public ClassPathXMLApplicationContext() {
try { InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("applicationContext.xml");
// 1,創建DocumentBuilderFactory工廠對象 DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 2,創建DocumentBuilder對象 DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
// 3,得到Document對象( 註意導入org.w3c.dom包中的) Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
// 4,獲得所有的Bean標簽 NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0, len = nodeList.getLength(); i < len; i++) { Node node = nodeList.item(i); System.out.println(node.getNodeType());// 1,1,1
if (node.getNodeType() == node.ELEMENT_NODE) { Element element = (Element) node; String id = element.getAttribute("id"); String className = element.getAttribute("class");
boolean flag = map.containsKey(id);
if (flag == true) return;
Class clazz = Class.forName(className); // 創建bean對象 Object o = clazz.newInstance(); // 將bean對象存儲到容器當中 map.put(id, o); // 到目前為止,我們將所有的bean,已經實例化(new了一個對象), // 並且存放到了容器當中,但是bean與bean對象之間的依賴關係還沒有處理 } } System.out.println("================="); // 5, 組裝bean之間的依賴關係,拿到bean對象之後,如果裡面有property標簽則進行組裝 for (int i = 0, len = nodeList.getLength(); i < len; i++) { Node node = nodeList.item(i); if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { Element element = (Element) node; String id = element.getAttribute("id"); // //element 就是獲取的bean對象,通過getChildNodes()方法 //來獲取這個對象有三個子節點,1和3是文本節點
NodeList childNodes = element.getChildNodes(); // System.out.println(childNodes.getLength());// 3,5,0 // //if (i == 1) { //查看第二個bean標簽的5個子元素的類型分別是什麼, // for (int j = 0; j < childNodes.getLength(); j++) { // //NodeType為 3,8,3,1,3, // //Node.TEXT_NODE = 3; // //Node.COMMENT_NODE = 8; // //Node.ELEMENT_NODE = 1; // System.out.print(childNodes.item(j).getNodeType()+","); // } //} } }
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SAXException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
@Override public Object getBean(String id) { return map.get(id); }
public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXMLApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXMLApplicationContext(); } } |
6.3 正式組裝bean之間的依賴關係
|
package com.hy.io;
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder; import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory; import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document; import org.w3c.dom.Element; import org.w3c.dom.Node; import org.w3c.dom.NodeList; import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
public class ClassPathXMLApplicationContext implements BeanFactory { private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 在預設構造方法中載入配置文件 public ClassPathXMLApplicationContext() {
try { InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("applicationContext.xml");
// 1,創建DocumentBuilderFactory工廠對象 DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 2,創建DocumentBuilder對象 DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
// 3,得到Document對象( 註意導入org.w3c.dom包中的) Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
// 4,獲得所有的Bean標簽 NodeList nodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0, len = nodeList.getLength(); i < len; i++) { Node node = nodeList.item(i);
System.out.println(node.getNodeType());// 1,1,1
if (node.getNodeType() == node.ELEMENT_NODE) { Element element = (Element) node; String id = element.getAttribute("id"); String className = element.getAttribute("class");
boolean flag = map.containsKey(id);
if (flag == true) return;
Class clazz = Class.forName(className); // 創建bean對象 Object o = clazz.newInstance(); // 將bean對象存儲到容器當中 map.put(id, o); // 到目前為止,我們將所有的bean,已經實例化(new了一個對象), // 並且存放到了容器當中,但是bean與bean對象之間的依賴關係還沒有處理 } } System.out.println("================="); // 5, 組裝bean之間的依賴關係,拿到bean對象之後,如果裡面有property標簽則進行組裝 for (int i = 0, len = nodeList.getLength(); i < len; i++) { Node node = nodeList.item(i); if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { Element element = (Element) node; String id = element.getAttribute("id"); // // element 就是獲取的bean對象,通過getChildNodes()方法 // 來獲取這個對象有三個子節點,1和3是文本節點
NodeList childNodes = element.getChildNodes(); // System.out.println(childNodes.getLength());// 3,5,0 // // if (i == 1) { //查看第二個bean標簽的5個子元素的類型分別是什麼, // for (int j = 0; j < childNodes.getLength(); j++) { // //NodeType為 3,8,3,1,3, // //Node.TEXT_NODE = 3; // //Node.COMMENT_NODE = 8; // //Node.ELEMENT_NODE = 1; // System.out.print(childNodes.item(j).getNodeType()+","); // } // }
for (int j = 0; j < childNodes.getLength(); j++) { Node childNode = childNodes.item(j);
if (childNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE && "property".equals(childNode.getNodeName())) { Element propertyElement = (Element)childNode;
//獲取其name屬性和ref屬性 String propertyName = propertyElement.getAttribute("name"); String propertyRef = propertyElement.getAttribute("ref");
//找到ref對應的實例對象 Object refObj = map.get(propertyRef);
//當refObj設置到當前bean對應的對象的property屬性上來 Object beanObj = map.get(id);
//獲取該對象的類對象 Class beanClazz = beanObj.getClass();
//獲得該類對象的屬性 Field propertyField = beanClazz.getDeclaredField(propertyName);
//設置其可訪問性 propertyField.setAccessible(true);
propertyField.set(beanObj, refObj); } } } }
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SAXException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
@Override public Object getBean(String id) { return map.get(id); }
public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXMLApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXMLApplicationContext(); } } |
http://127.0.0.1:8080/mymvc4/emp.do?ac=add&ename=aaa&pwd=bbb