前言 本文基於Dubbo2.6.x版本,中文註釋版源碼已上傳github:xiaoguyu/dubbo 負載均衡,英文名稱為Load Balance,其含義就是指將負載(工作任務)進行平衡、分攤到多個操作單元上進行運行。 例如:在Dubbo中,同一個服務有多個服務提供者,每個服務提供者所在的機器性能 ...
前言
本文基於Dubbo2.6.x版本,中文註釋版源碼已上傳github:xiaoguyu/dubbo
負載均衡,英文名稱為Load Balance,其含義就是指將負載(工作任務)進行平衡、分攤到多個操作單元上進行運行。
例如:在Dubbo中,同一個服務有多個服務提供者,每個服務提供者所在的機器性能不一致。如果流量均勻分攤,則會導致有些服務提供者負載過高,有些則輕輕鬆松,導致資源浪費。負載均衡就解決這個問題。
源碼
LoadBalance就是負載均衡的介面,咱們先看看類圖
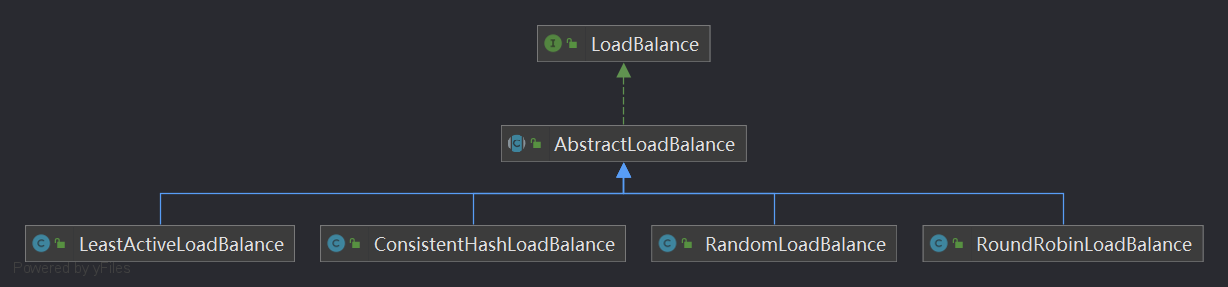
Dubbo提供了4中內置的負載均衡實現:
- RandomLoadBalance:基於權重隨機演算法
- LeastActiveLoadBalance:基於最少活躍調用數演算法
- ConsistentHashLoadBalance:基於 hash 一致性演算法
- RoundRobinLoadBalance:基於加權輪詢演算法
那麼負載均衡是在哪裡被用的的呢?
AbstractClusterInvoker的select和reselect方法。不熟悉這兩個方法的,可以去看《Dubbo集群》
AbstractLoadBalance
抽象類封裝了一些公共的邏輯,在看具體實現類之前,我們先看看抽象類AbstractLoadBalance中的方法
public <T> Invoker<T> select(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
return null;
// 如果 invokers 列表中僅有一個 Invoker,直接返回即可,無需進行負載均衡
if (invokers.size() == 1)
return invokers.get(0);
// 調用 doSelect 方法進行負載均衡,該方法為抽象方法,由子類實現
return doSelect(invokers, url, invocation);
}
LoadBalance介面只有一個方法,那就是 select 方法,這是負載均衡的入口。根據 invoker 數量判斷是否需要進行負載均衡。這裡的 doSelect 是個抽象方法,由子類實現。
protected int getWeight(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
int weight = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.WEIGHT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WEIGHT);
if (weight > 0) {
// 獲取服務提供者啟動時間戳
long timestamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.REMOTE_TIMESTAMP_KEY, 0L);
if (timestamp > 0L) {
// 計算服務提供者運行時長
int uptime = (int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp);
// 獲取服務預熱時間,預設為10分鐘
int warmup = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.WARMUP_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WARMUP);
// 如果服務運行時間小於預熱時間,則重新計算服務權重,即降權
if (uptime > 0 && uptime < warmup) {
// 重新計算服務權重
weight = calculateWarmupWeight(uptime, warmup, weight);
}
}
}
return weight;
}
static int calculateWarmupWeight(int uptime, int warmup, int weight) {
// 計算權重,下麵代碼邏輯上形似於 (uptime / warmup) * weight。
// 隨著服務運行時間 uptime 增大,權重計算值 ww 會慢慢接近配置值 weight
int ww = (int) ((float) uptime / ((float) warmup / (float) weight));
return ww < 1 ? 1 : (ww > weight ? weight : ww);
}
getWeight 是獲取權重的方法,預設權重為100,這裡有個服務預熱的操作,當服務的啟動時間小於預熱時間,權重會減少,這個權重由 calculateWarmupWeight 方法計算。
預熱的目的是讓服務啟動後“低功率”運行一段時間,使其效率慢慢提升至最佳狀態。
以上就是抽象類的全部方法。下麵我們看實現類的。
RandomLoadBalance
RandomLoadBalance 是加權隨機演算法的具體實現,是Dubbo預設的負載均衡策略。
假設我們有一組伺服器 servers = [A, B, C],他們對應的權重為 weights = [5, 3, 2],權重總和為10。
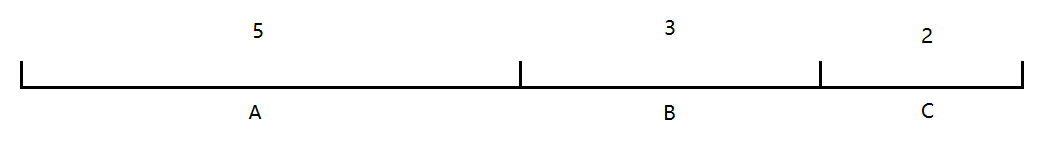
我們取一個大於等於0,小於10的隨機數,計算隨機數落在哪個區間。例如4在A區間,7在B區間。
權重越大,落在該區間的概率就越大。這就是加權隨機演算法。
下麵看具體代碼實現
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "random";
private final Random random = new Random();
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // Number of invokers
int totalWeight = 0; // The sum of weights
boolean sameWeight = true; // Every invoker has the same weight?
// 下麵這個迴圈有兩個作用,第一是計算總權重 totalWeight,
// 第二是檢測每個服務提供者的權重是否相同
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
totalWeight += weight; // Sum
// 檢測當前服務提供者的權重與上一個服務提供者的權重是否相同,
// 不相同的話,則將 sameWeight 置為 false。
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != getWeight(invokers.get(i - 1), invocation)) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
// 隨機獲取一個 [0, totalWeight) 區間內的數字
int offset = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
// 迴圈讓 offset 數減去服務提供者權重值,當 offset 小於0時,返回相應的 Invoker。
// 舉例說明一下,我們有 servers = [A, B, C],weights = [5, 3, 2],offset = 7。
// 第一次迴圈,offset - 5 = 2 > 0,即 offset > 5,
// 表明其不會落在伺服器 A 對應的區間上。
// 第二次迴圈,offset - 3 = -1 < 0,即 5 < offset < 8,
// 表明其會落在伺服器 B 對應的區間上
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 讓隨機值 offset 減去權重值
offset -= getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
if (offset < 0) {
// 返回相應的 Invoker
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 如果所有服務提供者權重值相同,此時直接隨機返回一個即可
return invokers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}
}
如果權重一致,就隨機選擇一個。如果權重不同,則根據權重分配。
LeastActiveLoadBalance
最小活躍數負載均衡。這個活躍數表示執行中的請求數量。每個服務提供者對應一個活躍數 active。初始情況下,所有服務提供者活躍數均為0。每收到一個請求,活躍數加1,完成請求後則將活躍數減1。
在流量均勻的情況下,活躍數越低的服務提供者,其性能越好。
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size(); // Number of invokers
// 最小的活躍數
int leastActive = -1; // The least active value of all invokers
// 具有相同“最小活躍數”的服務者提供者(以下用 Invoker 代稱)數量
int leastCount = 0; // The number of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive)
// leastIndexs 用於記錄具有相同“最小活躍數”的 Invoker 在 invokers 列表中的下標信息
int[] leastIndexs = new int[length]; // The index of invokers having the same least active value (leastActive)
int totalWeight = 0; // The sum of with warmup weights
// 第一個最小活躍數的 Invoker 權重值,用於與其他具有相同最小活躍數的 Invoker 的權重進行對比,
// 以檢測是否“所有具有相同最小活躍數的 Invoker 的權重”均相等
int firstWeight = 0; // Initial value, used for comparision
boolean sameWeight = true; // Every invoker has the same weight value?
// 遍歷 invokers 列表
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
// 獲取 Invoker 對應的活躍數
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive(); // Active number
// 獲取權重
int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation); // Weight
// 發現更小的活躍數,重新開始
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) { // Restart, when find a invoker having smaller least active value.
// 使用當前活躍數 active 更新最小活躍數 leastActive
leastActive = active; // Record the current least active value
// 更新 leastCount 為 1
leastCount = 1; // Reset leastCount, count again based on current leastCount
// 記錄當前下標值到 leastIndexs 中
leastIndexs[0] = i; // Reset
totalWeight = afterWarmup; // Reset
firstWeight = afterWarmup; // Record the weight the first invoker
sameWeight = true; // Reset, every invoker has the same weight value?
// 當前 Invoker 的活躍數 active 與最小活躍數 leastActive 相同
} else if (active == leastActive) { // If current invoker's active value equals with leaseActive, then accumulating.
// 在 leastIndexs 中記錄下當前 Invoker 在 invokers 集合中的下標
leastIndexs[leastCount++] = i; // Record index number of this invoker
// 累加權重
totalWeight += afterWarmup; // Add this invoker's weight to totalWeight.
// If every invoker has the same weight?
// 檢測當前 Invoker 的權重與 firstWeight 是否相等,
// 不相等則將 sameWeight 置為 false
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& afterWarmup != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
}
// assert(leastCount > 0)
// 當只有一個 Invoker 具有最小活躍數,此時直接返回該 Invoker 即可
if (leastCount == 1) {
// If we got exactly one invoker having the least active value, return this invoker directly.
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[0]);
}
// 有多個 Invoker 具有相同的最小活躍數,但它們之間的權重不同
if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
// If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on totalWeight.
// 隨機生成一個 [0, totalWeight) 之間的數字
int offsetWeight = random.nextInt(totalWeight) + 1;
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
// 迴圈讓隨機數減去具有最小活躍數的 Invoker 的權重值,
// 當 offset 小於等於0時,返回相應的 Invoker
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
int leastIndex = leastIndexs[i];
// 獲取權重值,並讓隨機數減去權重值
offsetWeight -= getWeight(invokers.get(leastIndex), invocation);
if (offsetWeight <= 0)
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
// If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly.
// 如果權重相同或權重為0時,隨機返回一個 Invoker
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[random.nextInt(leastCount)]);
}
代碼比較多,不過都有註釋,耐心看即可。這裡大體做了幾件事:
- 遍歷 invokers 集合,找出活躍數最小的 invoker
- 如果只有一個 invoker 有最小活躍數,則返回
- 如果有多個 invoker 有相同的最小活躍數,則這些 invoker 進行加權隨機演算法處理(也就是對這幾個最小活躍數 invoker 進行 RandomLoadBalance 的邏輯)
這裡有個點想擴展說下,就是獲取活躍數的方法
RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
RpcStatus記錄著當前調用次數、總數、失敗數、調用間隔等狀態信息。
這些信息,在服務消費者端由ActiveLimitFilter記錄,在服務提供者端由ExecuteLimitFilter記錄。也就是,想要拿到正確的活躍數,需要ActiveLimitFilter生效才行。
@Activate(group = Constants.CONSUMER, value = Constants.ACTIVES_KEY)
public class ActiveLimitFilter implements Filter
ActiveLimitFilter生效需要滿足兩個條件,消費者端以及URL中攜帶actives參數。actives可在消費者端或生產者端配置,含義為:每服務消費者每服務每方法最大併發調用數
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoService" registry="remoteRegistry" actives="5" />
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" loadbalance="leastactive" actives="5" />
當然,也能給消費者介面指定過濾器的方法來啟用ActiveLimitFilter
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" filter="activelimit" />
RoundRobinLoadBalance
RoundRobinLoadBalance是加權輪詢負載均衡的實現。加權輪詢的原理步驟如下:
假設服務 [A, B, C] 的權重為 [5, 1, 1] ,即總權重為 7, 當前權重currentWeight初始為[0, 0, 0]
-
當前權重加上每個服務各自的權重,跳轉步驟2
此時currentWeight為 [0+5, 0+1, 0+1] = [5, 1, 1]
-
返回currentWeight中最高的服務,跳轉步驟3
currentWeight為 [5, 1, 1] ,返回服務A
-
將第2步中的那個最高權重在currentWeight對應的值減去總權重,跳轉步驟4
currentWeight為 [5 - 7, 1, 1] = [-2, 1, 1]
-
重覆步驟1
下麵的GIF圖為了好表示柱狀圖,所以我將currentWeight初始權重變為10
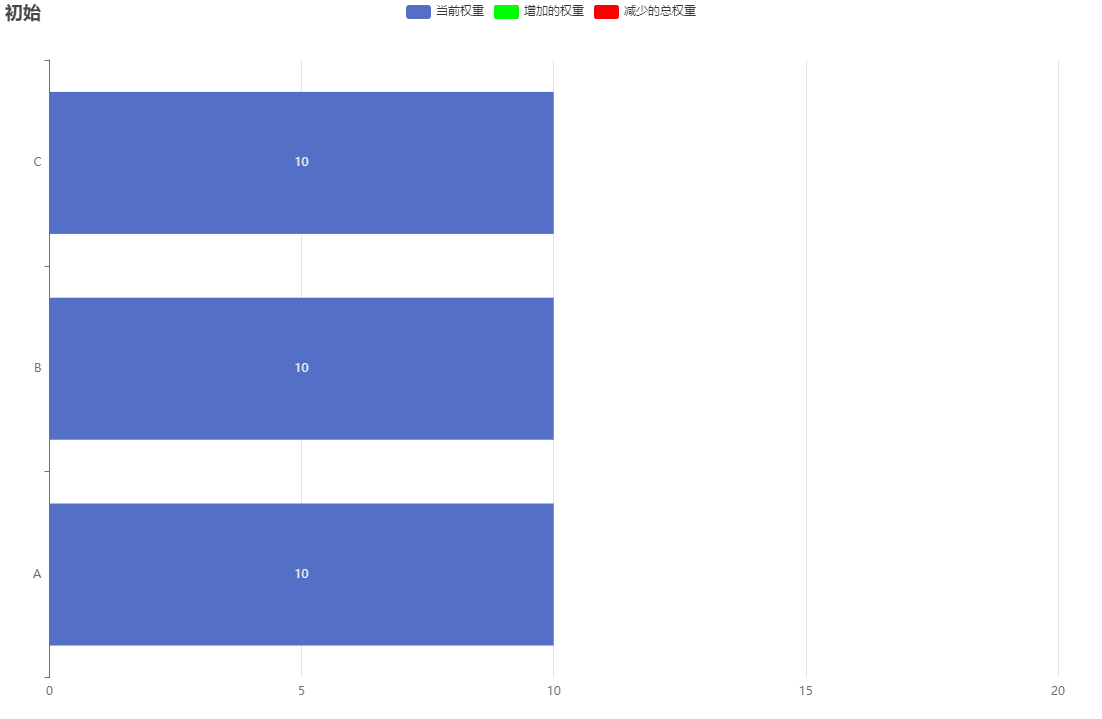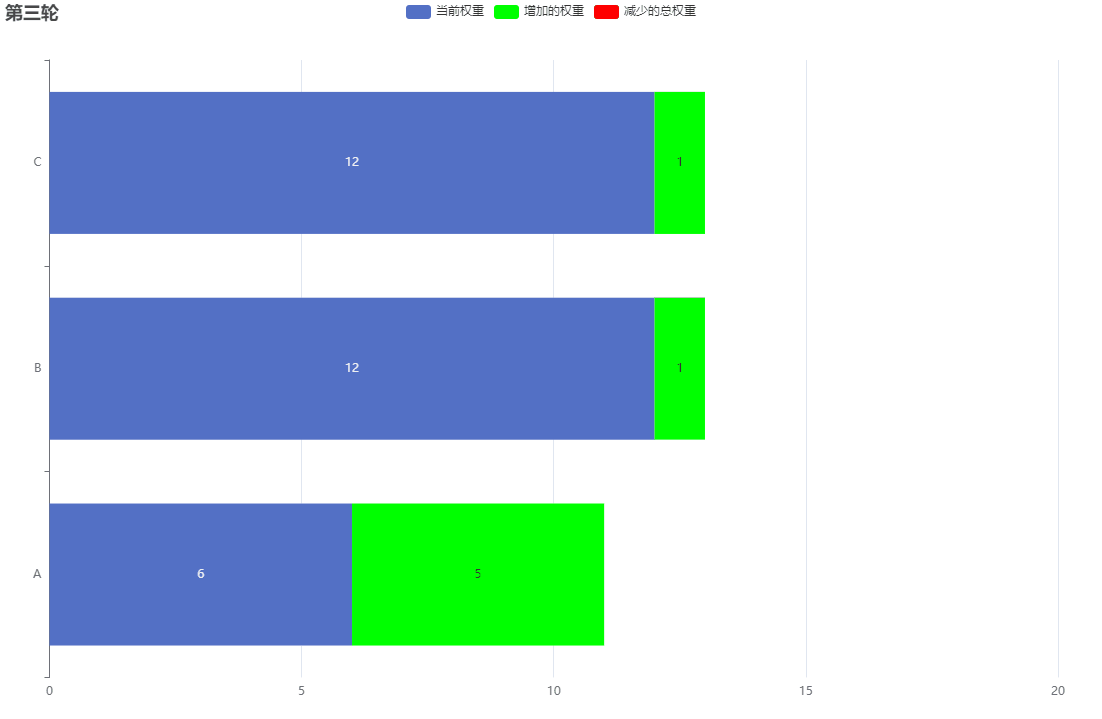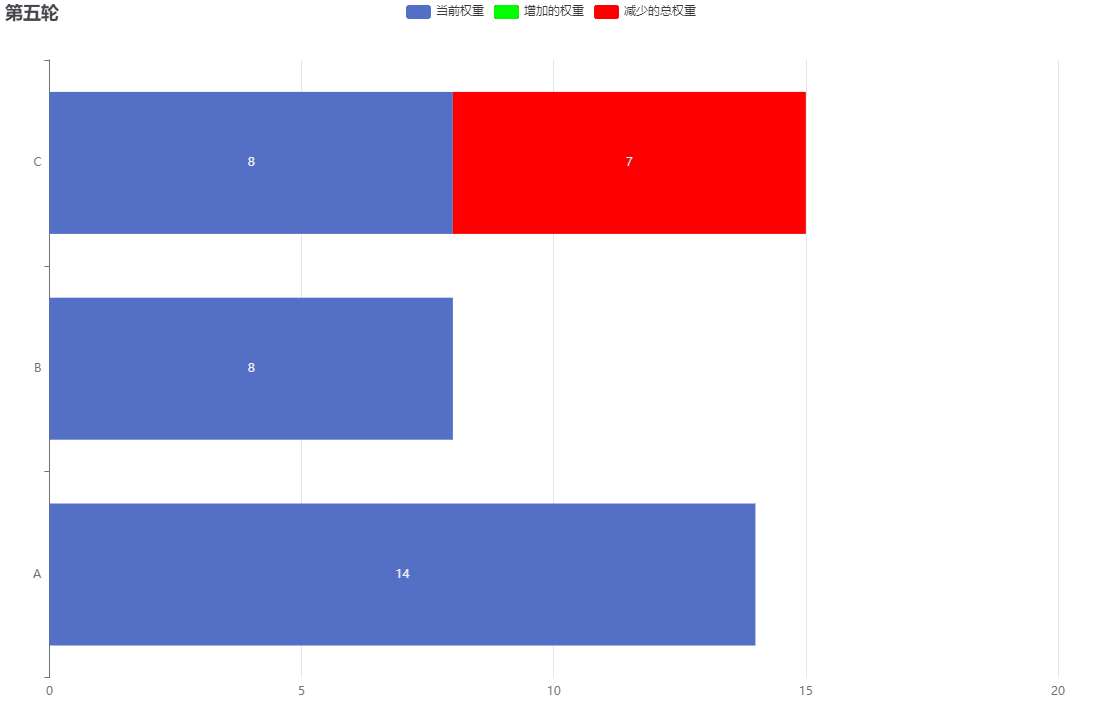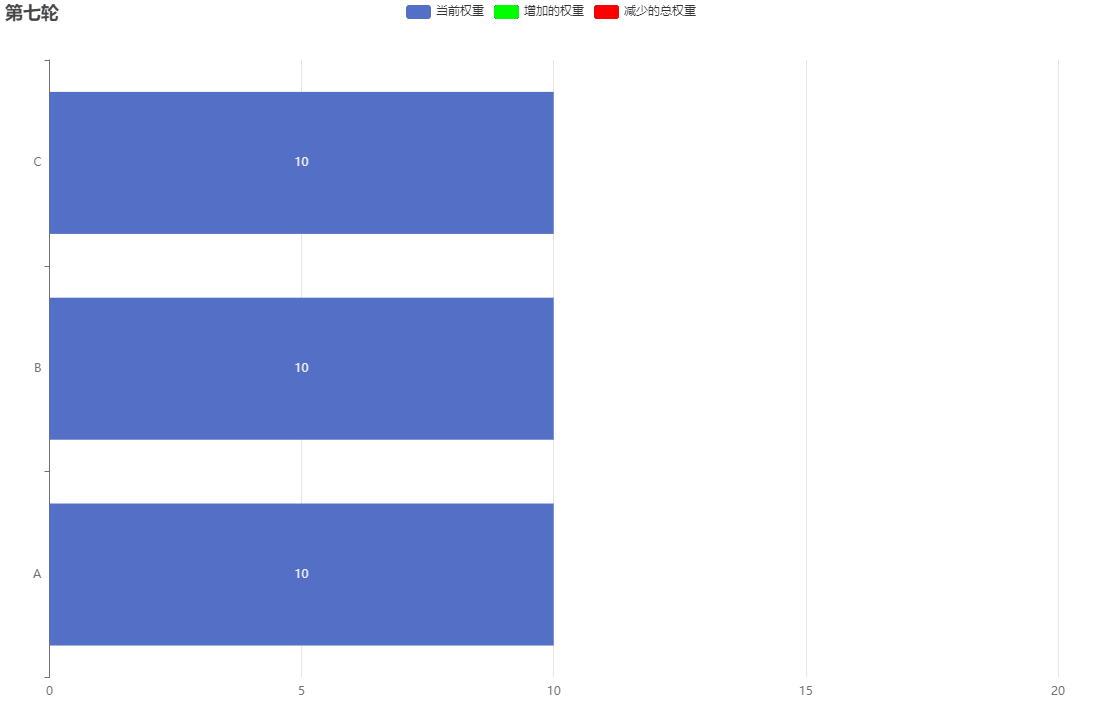
經過一定迴圈次數,最終currentWeight又會回歸初始值。而這個迴圈次數計算如下:
次數 = 服務A的權重 + 服務B的權重 + …
每個服務的調用次數也等於它的權重
看完原理,我們繼續看源碼
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
// key = 全限定類名 + "." + 方法名,比如 com.xxx.DemoService.sayHello
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
// 獲取 url 到 WeightedRoundRobin 映射表,如果為空,則創建一個新的
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.get(key);
if (map == null) {
methodWeightMap.putIfAbsent(key, new ConcurrentHashMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>());
map = methodWeightMap.get(key);
}
// 權重總和
int totalWeight = 0;
// 最大權重
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Invoker<T> selectedInvoker = null;
WeightedRoundRobin selectedWRR = null;
// 下麵這個迴圈主要做了這樣幾件事情:
// 1. 遍歷 Invoker 列表,檢測當前 Invoker 是否有
// 相應的 WeightedRoundRobin,沒有則創建
// 2. 檢測 Invoker 權重是否發生了變化,若變化了,
// 則更新 WeightedRoundRobin 的 weight 欄位
// 3. 讓 current 欄位加上自身權重,等價於 current += weight
// 4. 設置 lastUpdate 欄位,即 lastUpdate = now
// 5. 尋找具有最大 current 的 Invoker,以及 Invoker 對應的 WeightedRoundRobin,
// 暫存起來,留作後用
// 6. 計算權重總和
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String identifyString = invoker.getUrl().toIdentityString();
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.get(identifyString);
int weight = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
if (weight < 0) {
weight = 0;
}
// 檢測當前 Invoker 是否有對應的 WeightedRoundRobin,沒有則創建
if (weightedRoundRobin == null) {
weightedRoundRobin = new WeightedRoundRobin();
// 設置 Invoker 權重
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
// 存儲 url 唯一標識 identifyString 到 weightedRoundRobin 的映射關係
map.putIfAbsent(identifyString, weightedRoundRobin);
weightedRoundRobin = map.get(identifyString);
}
// Invoker 權重不等於 WeightedRoundRobin 中保存的權重,說明權重變化了,此時進行更新
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
//weight changed
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
// 讓 current 加上自身權重,等價於 current += weight
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
// 設置 lastUpdate,表示近期更新過
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
maxCurrent = cur;
// 將具有最大 current 權重的 Invoker 賦值給 selectedInvoker
selectedInvoker = invoker;
// 將 Invoker 對應的 weightedRoundRobin 賦值給 selectedWRR,留作後用
selectedWRR = weightedRoundRobin;
}
// 計算權重總和
totalWeight += weight;
}
// 對 <identifyString, WeightedRoundRobin> 進行檢查,過濾掉長時間未被更新的節點。
// 該節點可能掛了,invokers 中不包含該節點,所以該節點的 lastUpdate 長時間無法被更新。
// 若未更新時長超過閾值後,就會被移除掉,預設閾值為60秒。
if (!updateLock.get() && invokers.size() != map.size()) {
if (updateLock.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
// copy -> modify -> update reference
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> newMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>();
// 拷貝
newMap.putAll(map);
// 遍歷修改,即移除過期記錄
Iterator<Entry<String, WeightedRoundRobin>> it = newMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, WeightedRoundRobin> item = it.next();
if (now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > RECYCLE_PERIOD) {
it.remove();
}
}
// 更新引用
methodWeightMap.put(key, newMap);
} finally {
updateLock.set(false);
}
}
}
if (selectedInvoker != null) {
// 讓 current 減去權重總和,等價於 current -= totalWeight
selectedWRR.sel(totalWeight);
// 返回具有最大 current 的 Invoker
return selectedInvoker;
}
// should not happen here
return invokers.get(0);
}
註釋寫的很詳細了,和原理步驟差不多,源碼中多個對長時間未更新 invoker 的處理。
ConsistentHashLoadBalance
一致性Hash演算法。
其原理簡單講,就是假定有一個圓環,每個服務根據其 hash 值,在圓環上有個位置(如圖的cache-1、cache-2等)。當有請求過來的,同樣根據請求的 hash 值確定請求的位置,並根據請求的位置去獲取最近的下一個服務的位置。如下圖:
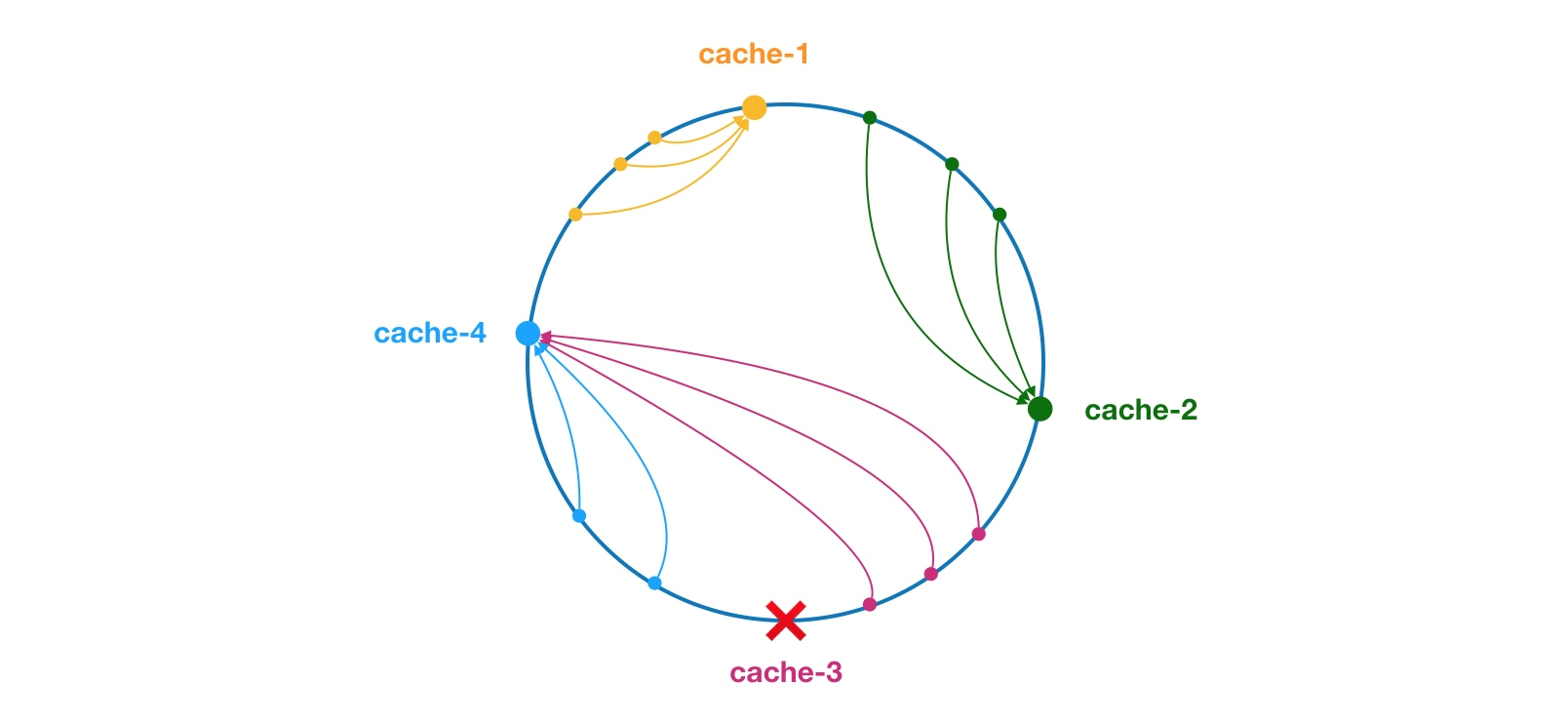
當請求落在 cache-2 和 cache-3 之間時,下一個最近的是 cache-3,如果 cache-3 服務不可用,那麼最近的下個服務就是 cache-4
這時,又引入了一個資源傾斜的問題,那就是大量請求集中在同一個服務中。由於服務在圓環上分佈不均,導致大部分請求都落在cache-2中,如下圖:
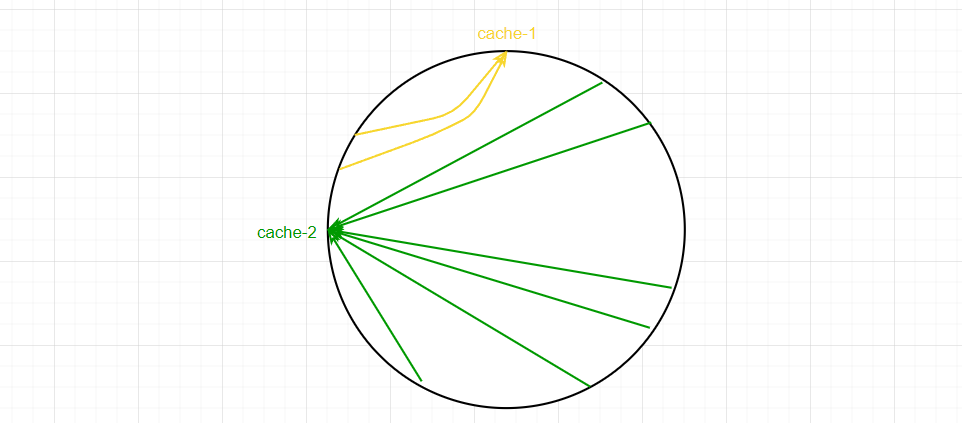
那麼該如何處理資源傾斜的問題?引入虛擬節點,就是一個服務有多個多個位置,這樣就能使請求更均勻,如下圖:
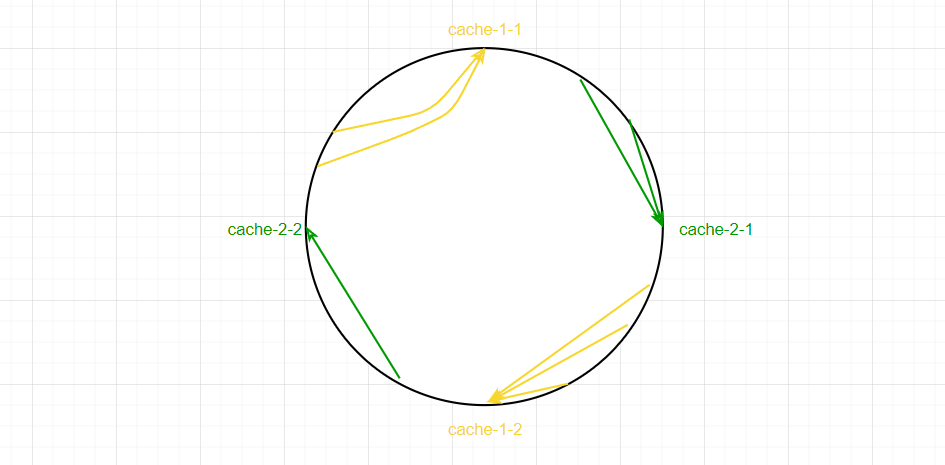
以上就是一致性hash演算法的原理。下麵講講Dubbo的源碼
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>> selectors = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>>();
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName;
// 獲取 invokers 原始的 hashcode
int identityHashCode = System.identityHashCode(invokers);
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
// 如果 invokers 是一個新的 List 對象,意味著服務提供者數量發生了變化,可能新增也可能減少了。
// 此時 selector.identityHashCode != identityHashCode 條件成立
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != identityHashCode) {
// 創建新的 ConsistentHashSelector
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, methodName, identityHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
// 調用 ConsistentHashSelector 的 select 方法選擇 Invoker
return selector.select(invocation);
}
private static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {...}
}
doSelect 方法先從緩存獲取 selector ,如果緩存沒有,則創建並放入緩存。然後調用 selector.select 方法獲取 invoker 。所以一致性 hash 的實現,在ConsistentHashSelector中。我們先看其構造方法
ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
// 可以認為virtualInvokers組成了hash環
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode;
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
// 獲取虛擬節點數,預設為160
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, "hash.nodes", 160);
// 獲取參與 hash 計算的參數下標值,預設對第一個參數進行 hash 運算
String[] index = Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, "hash.arguments", "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
// 對 address + i 進行 md5 運算,得到一個長度為16的位元組數組
byte[] digest = md5(address + i);
// 對 digest 部分位元組進行4次 hash 運算,得到四個不同的 long 型正整數
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
// h = 0 時,取 digest 中下標為 0 ~ 3 的4個位元組進行位運算
// h = 1 時,取 digest 中下標為 4 ~ 7 的4個位元組進行位運算
// h = 2, h = 3 時過程同上
long m = hash(digest, h);
// 將 hash 到 invoker 的映射關係存儲到 virtualInvokers 中,
// virtualInvokers 需要提供高效的查詢操作,因此選用 TreeMap 作為存儲結構
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
ConsistentHashSelector的構造方法,主要是計算 invokers 的每一個 invoker 的hash,並將其放入 virtualInvokers 中。從這裡可以看到,Dubbo預設的虛擬節點為160個。對比一致性 hash 演算法中,virtualInvokers 就是 hash 環,invoker 就是節點。
我們繼續看如何從 hash 環中找到最近的節點
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
// 將參數轉為 key
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments());
// 對參數 key 進行 md5 運算
byte[] digest = md5(key);
// 取 digest 數組的前四個位元組進行 hash 運算,再將 hash 值傳給 selectForKey 方法,
// 尋找合適的 Invoker
return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
}
private Invoker<T> selectForKey(long hash) {
// 到 TreeMap 中查找第一個節點值大於或等於當前 hash 的 Invoker
Map.Entry<Long, Invoker<T>> entry = virtualInvokers.tailMap(hash, true).firstEntry();
// 如果 hash 大於 Invoker 在圓環上最大的位置,此時 entry = null,
// 需要將 TreeMap 的頭節點賦值給 entry
if (entry == null) {
entry = virtualInvokers.firstEntry();
}
return entry.getValue();
}
選擇的過程也很簡單,依賴的是 TreeMap 的 tailMap 方法。
總結
本文介紹了Dubbo內置的4中負載均衡實現。至此,Dubbo的集群容錯的四個部分,也就是服務目錄 Directory、服務路由 Router、集群 Cluster 和負載均衡 LoadBalance 都已全部講完。
參考資料



