大佬的理解->《深入理解Java中的String》 1、String 1.1 String 實例化 String str1 = "xxx"; String string1 = "hello KH96"; System.out.println(string1); //hello KH96 String ...
大佬的理解->《深入理解Java中的String》
1、String
1.1 String 實例化
String str1 = "xxx";
String string1 = "hello KH96";
System.out.println(string1); //hello KH96
String str1 = new String("xxx");
String string2 = "hello KH96";
System.out.println(string2); //hello KH96
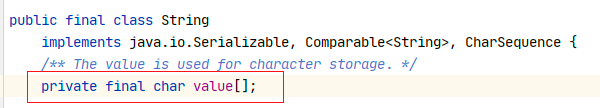
String底層實現 private final char value[];
String底層是由私有final的數組實現的,對外沒有提供修改的方法,字元串多次賦值,不是修改字元串的內容,而是改變字元串的引用地址;
源碼
1.2 String常用方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| length() | 字元串的長度 |
| equals() | 比較的是字元串的內容 |
| equalsIgnoreCase(String str) | 忽略大小比較 |
| toUpperCase() | 轉大寫 |
| toLowerCase() | 轉小寫 |
| concat(String str) | 返回拼接後的字元串 |
length()
字元串的長度:length()方法,返回的是字元串的長度,即字元串的長度(不是位元組數),區別去數組的length
String string1 = "hello KH96";
System.out.println(string1+"的長度:"+string1.length()); //hello KH96的長度:10
equals()
重寫了Object類的equals方法,比較的是字元串的內容,不是對象
String string2 = "KH96";
String string3 = "KH97";
System.out.println(string2.equals(string3)); //false
equalsIgnoreCase(String str)
忽略大小比較
String string7 = "kh96";
String string8 = "KH96";
System.out.println("不忽略大小寫比較:"+string7.equals(string8)); //false
System.out.println("忽略大小寫比:"+string7.equalsIgnoreCase(string8)); //true
toUpperCase() 轉大寫 toLowerCase() 轉小寫
String string9 = "abCD";
System.out.println(string9.toUpperCase()); //ABCD
System.out.println(string9.toLowerCase());//abcd
concat(String str) 返回拼接後的字元串
"+"號也可以進行字元串拼接
concat(String str)
拼接字元串都創建了新的對象,在迴圈中儘量不要拼接字元串,會造成棧溢出;
String strig10 = "abc";
System.out.println(strig10.concat("bcd").concat("def"));//abcbcddef
1.3 String 字元查找/提取相關方法
| 方法 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| indexOf(String str) | 返回str首次出現的下標 |
| lastIndexOf(String str) | 返回str最後一次出現的下標 |
| substring(int index1) | 截取下標index1,及以後的所有字元 |
| substring(int index1,int index2) | 截取下標index1到index2之間的字元串,包括index1,不包括index2 |
| trim() | 去除字元串的首尾空格 |
| startsWith(String str) | 是否以str開頭 |
| endsWith(String str) | 是否以str結尾 |
| contains(String str) | 是否包含str |
| split(String str) | 根據指定分割字元,將字元串拆分成字元串數組返回 |
| toCharArray() | 將字元串轉為字元數組 |
| replace(String str1,String str2) | 用 str2 替換 str1 |
| getBytes() | 字元串轉換為位元組數組 |
| getBytes("UTF-8") | 字元串轉換為位元組數組,可指定編碼 |
| new String(byte[] bytes) | 將位元組數組轉換為字元串 |
indexOf(String str)
返回str首次出現的下標,沒有查到就返回-1
String string11 = "I am a good student in kh96";
System.out.println("good首次出現的位置:"+string11.indexOf("good")); //7
還可以通過ascii碼值查詢
String string11 = "I am a good student in kh96";
char char1 = 97;
System.out.println(char1); //a
System.out.println("參數支持int assic碼值:"+string11.indexOf(97)); //2
lastIndexOf(String str)
返回str最後一次出現的下標,沒有就返回-1
String string11 = "I am a good student in kh96";
System.out.println(string11);
System.out.println("t最後一次出現的下標:"+string11.lastIndexOf("t")); //18
substring(int index1)
截取下標index1,及以後的所有字元
index的範圍[0,string.length()]
String string12 = "abcdefghijklmn";
System.out.println(string12.substring(5)); //fghijklmn
substring(int index1,int index2)
截取下標index1到index2之間的字元串,包括index1,不包括index2
index的範圍[0,string.length()]
String string12 = "abcdefghijklmn";
System.out.println(string12.substring(5,8)); //fgh
小應用
String string14 = "KH90,KH91,KH92,KH93,KH94,KH95,";
System.out.println(string14.substring(0,string14.lastIndexOf(",")));//KH90,KH91,KH92,KH93,KH94,KH95
trim()
去除字元串的首尾空格
String string13 = " KH 96 ";
System.out.println("原始長度"+string13.length()); //10
System.out.println("取出空格後長度"+string13.trim().length()); //6 "KH 96"
startsWith(String str) endsWith(String str)
startsWith(String str) 是否以str開頭
endsWith(String str) 是否以str結尾
String string15 = "KH96.mp3";
System.out.println("是否是KH開頭?"+ string15.startsWith("KH")); //true
System.out.println("是否是.mp3結尾?"+ string15.endsWith(".mp3")); //true
contains(String str)
判斷字元串是否包含str
String string16 = "aaa bbb cc ddd";
System.out.println("是否包含bbb:"+ string16.contains("bbb")); //true
System.out.println("是否包含eee:"+ string16.contains("eee")); //false
split(String str)
根據指定分割字元,將字元串拆分成字元串數組返回
String string17_1 = "13501020304;15801020304;18901020304";
String[] phoneNumbers1 = string17_1.split(";"); //一種字元分割
System.out.println("手機號數組內容:"+ Arrays.toString(phoneNumbers2));
String string17_2 = "13501020304;15801020304!18901020304";
String[] phoneNumbers2 = string17_2.split(";|!"); //多種字元分割 用 | 隔開
System.out.println("手機號數組內容:"+ Arrays.toString(phoneNumbers2));
//[13501020304, 15801020304, 18901020304]
toCharArray()
將字元串轉為字元數組
char[] chars1 = string18.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars1)); //[K, H, 9, 8, 正, 在, 學, 習, 實, 用, 類]
replace(String str1,String str2)
用 str2 替換 str1
//獲取一個16位的隨機字元串
String string19 = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println(string19); //65c0844a-c437-4a65-89ca-84d4166325ff
//轉換字元串,將-轉換為*
System.out.println(string19.replace("-","*"));//65c0844a*c437*4a65*89ca*84d4166325ff
//去除字元串,將所有的-去除
System.out.println(string19.replace("-",""));//65c0844ac4374a6589ca84d4166325ff
//去16位隨機數
System.out.println(string19.replace("-","").substring(0,16));//65c0844ac4374a65
getBytes() getBytes("UTF-8")
字元串轉換為位元組數組
String string20 = "abcd";
//getBytes() 沒有指定編碼
byte[] bytes = string20.getBytes();
try {
//getBytes("UTF-8") 指定編碼
byte[] bytes2 = string20.getBytes("UTF-8");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2)); //[97, 98, 99, 100]
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); //Arrays.toString(bytes)
new String(byte[] bytes)
將位元組數組轉換為字元串
byte[] bytes3 ={100,101,102}; //ascii碼值
System.out.println(new String(bytes3)); //def
//配合上面getBytes進行轉碼
try {
System.out.println(new String(bytes3,"utf-8")); //可以指定編碼 def
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
char[] chars3 = {'K','H','9','6'};
System.out.println(new String(chars3));//KH96
2、StringBuffer
可變字元串類:StringBuffer
不同於String類:可以實現動態拼接字元串,而不會創建新的對象;
即:是一個可變字元串的對象,改變的是字元串對象中的內容;
不可以直接賦值,必須通過new創建對象;
2.1 StringBuffer實例化
new StringBuffer()
預設初始容量 16
StringBuffer sbf1 = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("預設初始容量:"+sbf1.capacity());//16
底層實現
//StringBuffer()
public StringBuffer() {
super(16); //初始容量16
}
//AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity)
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}
new StringBuffer(int capacity)
指定初始容量
StringBuffer sbf2 = new StringBuffer(32);
System.out.println("只定始容量:"+sbf2.capacity()); //32
底層實現
public StringBuffer(int capacity) {
super(capacity); //指定初始容量
}
StringBuffer(String str)
指定初始字元串,容量為字元串長度+16
StringBuffer sbf3 = new StringBuffer("Kh96");
System.out.println("指定初始字元串初始容量:"+sbf3.capacity()); //20
底層實現
public StringBuffer(String str) {
super(str.length() + 16); //容量為字元串長度+16
append(str);
}
2.2 StringBuffer常用方法
append(String str)
拼接字元串
StringBuffer sbf4 = new StringBuffer("userId=");
sbf4.append("U0001")
.append(",userName=")
.append("張三,age=")
.append("18"); //userId=U0001,userName=張三,age=18
擴容機制
底層擴容,當拼接一個新的字元串,字元串數組長度不夠,會進行動態擴容,
每次擴容都是前一個數組長度的2倍+2
最大擴容長度不能超過Integer的最大值 - 8;
void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) {
int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2; //每次擴容都是前一個數組長度的2倍+2
if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minimumCapacity;
if (newCapacity < 0) {
if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity);
}
toString()
獲取動態字元串內容
StringBuffer sbf4 = new StringBuffer("userId=");
sbf4.append("U0001")
.append(",userName=")
.append("張三,age=")
.append("18");
String userInfo = sbf4.toString();
System.out.println(userInfo); //userId=U0001,userName=張三,age=18
3、StringBuilder
用法和StringBuffer沒有區別,唯一的區別就是StringBuffer是線程安全的,StringBuilder是非線程安全的;



