排序演算法總結 1.十大經典演算法及性能 2.具體排序演算法 1.冒泡排序 迴圈過程中比較相鄰兩個數大小,通過交換正確排位,迴圈整個數組即可完成排序 圖片演示 代碼實現Java //冒泡排序 public static Integer[] Bubble(Integer[] array){ boolean ...
排序演算法總結
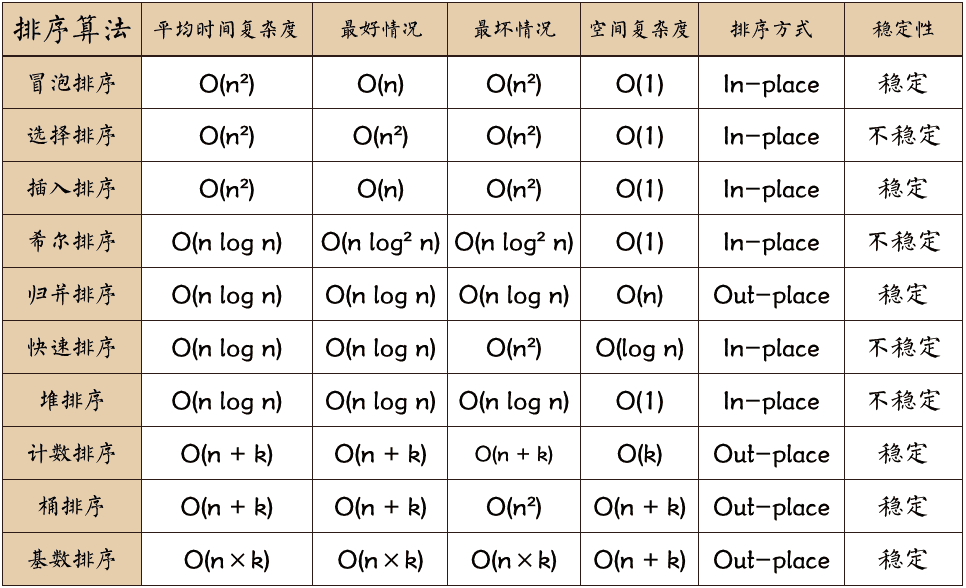
1.十大經典演算法及性能
2.具體排序演算法
1.冒泡排序
-
迴圈過程中比較相鄰兩個數大小,通過交換正確排位,迴圈整個數組即可完成排序
-
圖片演示
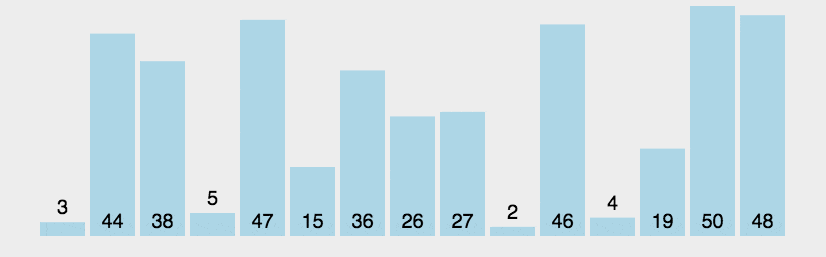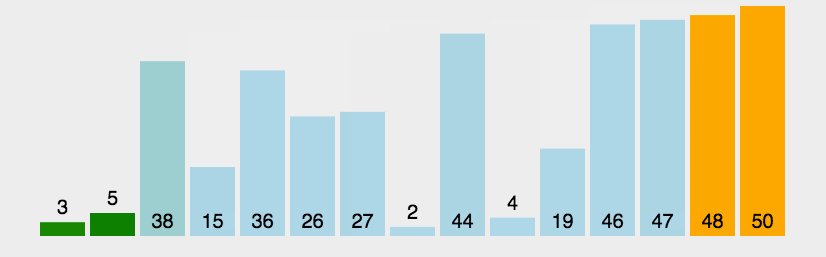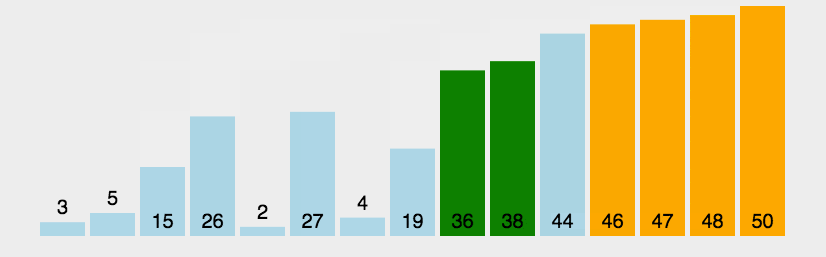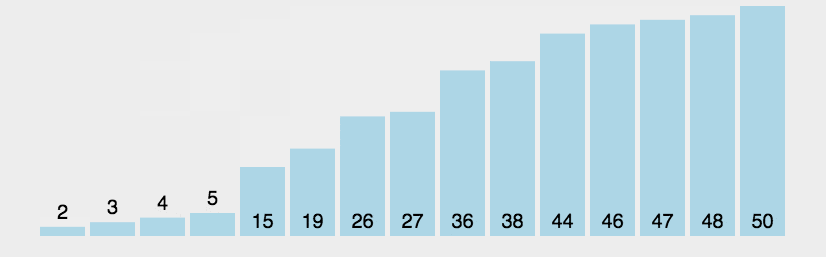
-
代碼實現Java
//冒泡排序 public static Integer[] Bubble(Integer[] array){ boolean ranked = false; for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { for(int j=0;j<array.length-i-1;j++){ if(array[j]>array[j+1]){ int c = array[j]; array[j] = array[j+1]; array[j+1] = c; ranked = true; } } if(!ranked){ break; } } return array; }
2.選擇排序
-
選擇最大的排到最右邊或選擇最小的排到最左邊
-
圖片演示
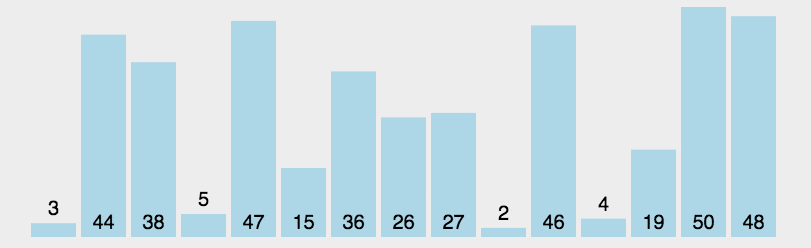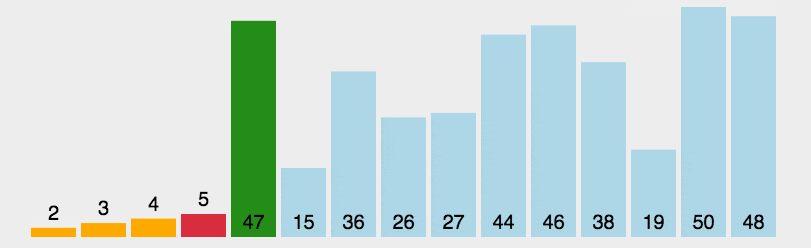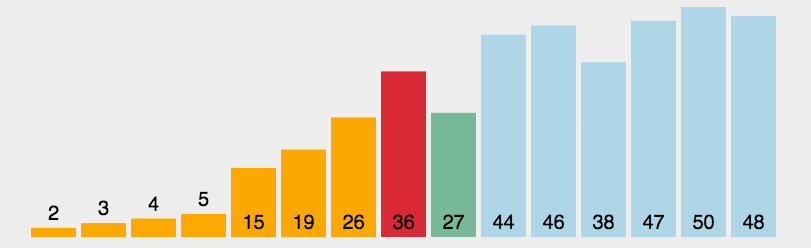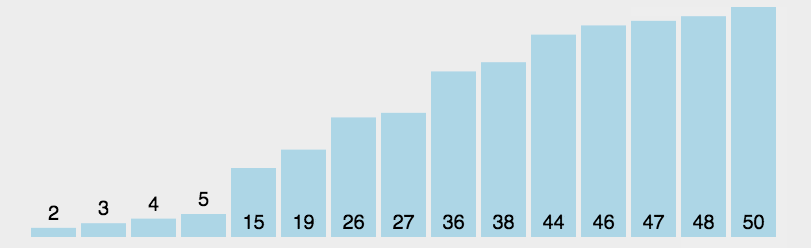
-
代碼實現(Java)
public static int[] SelectSort( int[] array){ for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { int min = i; for(int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++){ if(array[j]<min){ min = j; } } int c = array[i]; array[i] = array[min]; array[min] = c; } return array; }
3.插入排序
-
把左邊當做已完成序列,右邊作為未完成排序,遍歷右邊插入到左邊已完成序列中
-
圖片演示

-
代碼實現
public static int[] insertionSort(int[] array){ for(int i = 1; i < array.length; i++){ int complete = i-1; int current = array[i]; while(complete >=0 && array[complete]>current){ array[complete+1] = array[complete]; complete--; } array[complete+1] = current; } return array; }
4.希爾排序
-
希爾排序是插入排序的改進演算法,但它是不穩定演算法。先將整個待排序的記錄序列分割成為若幹子序列分別進行直接插入排序,待整個序列中的記錄"基本有序"時,再對全體記錄進行依次直接插入排序。參考:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6104371.html
-
圖片演示

-
代碼實現
//希爾排序
public static int[] shellSort(int[] array){
int current;
for(int step=array.length/2;step>=1;step/=2){
for(int i = step;i<array.length;i++){
current = array[i];
int j = i-step;
while(j>=0&&array[j]>=current){
array[j+step] = array[j];
j -= step;
}
array[j+step] = current;
}
}
return array;
}
5.歸併排序
-
歸併排序(Merge sort)是建立在歸併操作上的一種有效的排序演算法。該演算法是採用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一個非常典型的應用。
-
兩種實現方式
- 自上而下的遞歸
- 自下而上的迭代
-
圖片演示
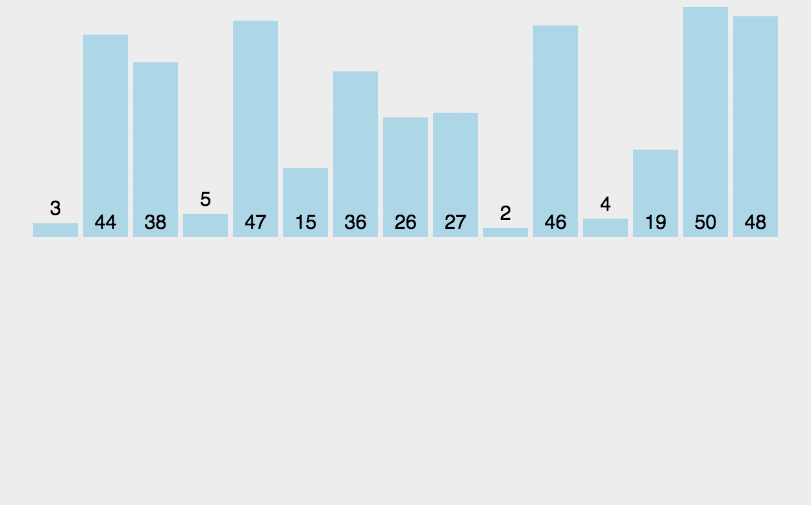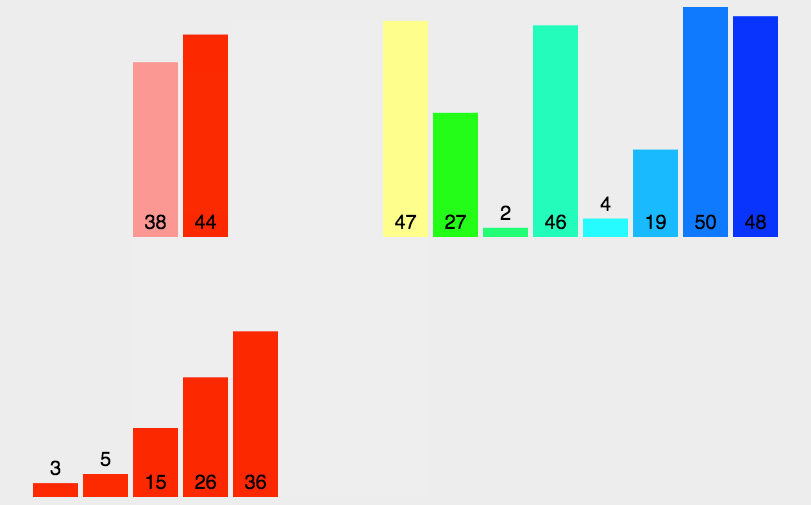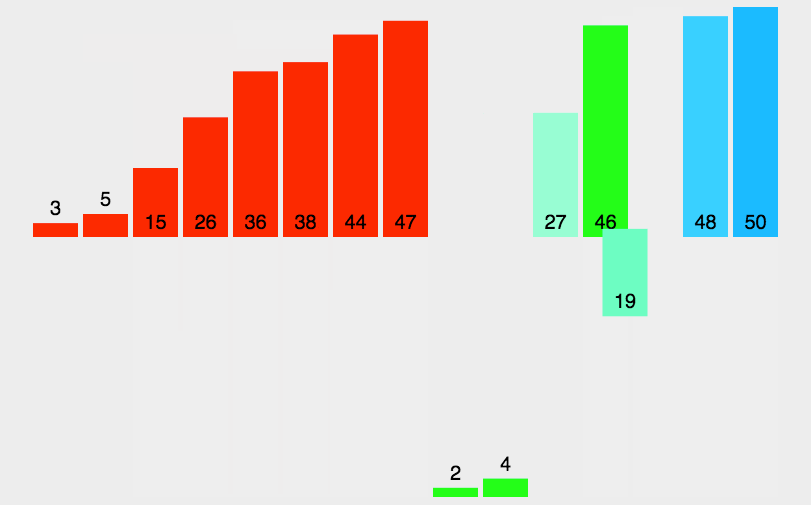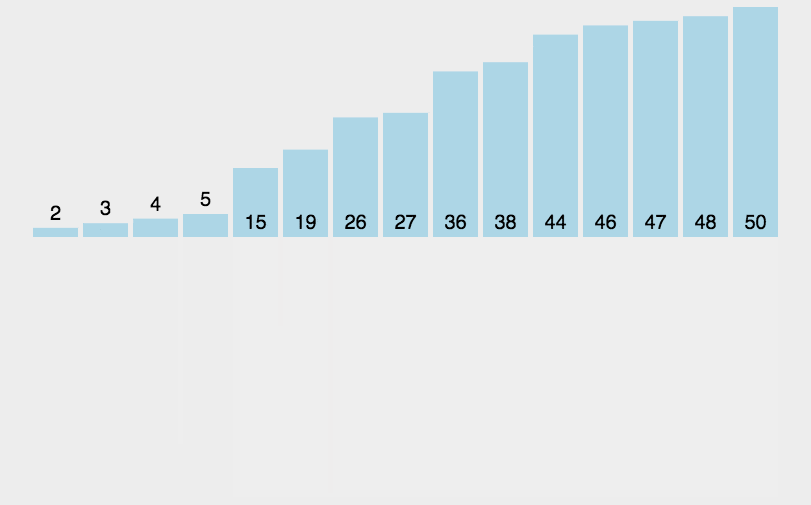
-
代碼實現(java)
public int[] sort(int[] sourceArray) throws Exception { // 對 arr 進行拷貝,不改變參數內容 int[] arr = Arrays.copyOf(sourceArray, sourceArray.length); if (arr.length < 2) { return arr; } int middle = (int) Math.floor(arr.length / 2); int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, middle); int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, middle, arr.length); return merge(sort(left), sort(right)); } protected int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) { int[] result = new int[left.length + right.length]; int i = 0; while (left.length > 0 && right.length > 0) { if (left[0] <= right[0]) { result[i++] = left[0]; left = Arrays.copyOfRange(left, 1, left.length); } else { result[i++] = right[0]; right = Arrays.copyOfRange(right, 1, right.length); } } while (left.length > 0) { result[i++] = left[0]; left = Arrays.copyOfRange(left, 1, left.length); } while (right.length > 0) { result[i++] = right[0]; right = Arrays.copyOfRange(right, 1, right.length); } return result; }



