嵌套:將一系列字典存儲在列表中,或將列表作為值存儲在字典中,這稱為嵌套。既可以在列表中嵌套字典,也可以在字典中嵌套列表,甚至在字典中嵌套字典。 一、列表中嵌套字典 1)一般創建方式: student_A ={'name':'Allen','age':'14','grade':'8'} student ...
嵌套:將一系列字典存儲在列表中,或將列表作為值存儲在字典中,這稱為嵌套。既可以在列表中嵌套字典,也可以在字典中嵌套列表,甚至在字典中嵌套字典。
一、列表中嵌套字典
1)一般創建方式:
student_A ={'name':'Allen','age':'14','grade':'8'}
student_B ={'name':'Jack','age':'12','grade':'6'}
student_C ={'name':'Lucy','age':'13','grade':'7'}
student_D ={'name':'polo','age':'14','grade':'8'}
#上述四行,創建了4個字典,每個字典代表一個學生
students=[student_A,student_B,student_C,student_D]#將上述4個學生放名為students的列表中
for student in students: #遍歷students列表
print(student) #列印每個學生
print("\n")
2)批量創建同類型的字典,比如游戲中很多同類型小兵
#創建更多的同類型的字典 ghosts=[] #創建一個空ghosts列表 for ghost_number in range(10): #創建10個ghost,註意range(10)是從0-9 new_ghost={'name':'rubbish','life':'10','speed':'1'} #同類型的名字rubbish,顏色為green,生命力為10,速度為1 ghosts.append(new_ghost) #append()是將創建的new_ghost放到列表ghosts最後 for ghost in ghosts: #遍歷創建的ghosts列表 print(ghost) #列印ghosts中的每個元素,即10個同類型的ghost print("Total number of ghosts:"+str(len(ghosts))) #列印ghosts列表中元素的個數,len()求元素個數,str()轉為字元串
3)同類型的字典,可通過迴圈,及切片進行增、刪、改等操作。
for ghost in ghosts[0:3]: if ghost['color'] == 'green': ghost['color'] = 'yellow' ghost['speed'] = 2 ghost['life'] = 5 for ghost in ghosts: print(ghost)
運行如果:

二、字典中嵌套列表
比如在實際生活中,描述菜單,如果使用列表,只能存儲菜餚的配料;但如果使用字典,就不僅可在其中包含配料列表,還可包含其他有關描述。
如下示例,存儲了菜單的兩方面信息:菜餚類型和配料列表。
其中的配料列表是一個與鍵 'toppings' (佐料)相關聯的值。
要訪問該列表,使用字典名和鍵 'toppings' ,就像訪問字典中的其他值一樣,這將返回一個配料列表,而不是單個值
1)嵌套一個列表
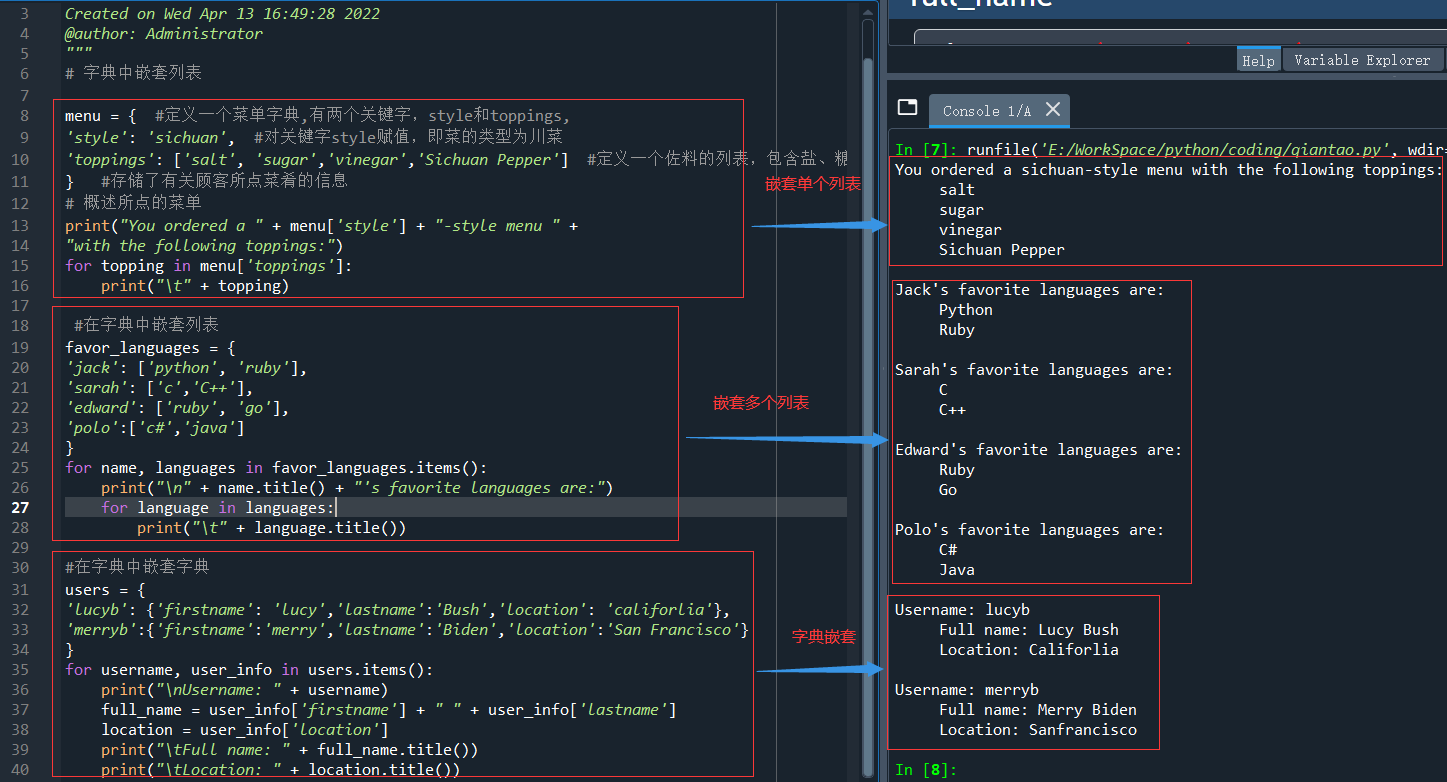
# 存儲所點菜單的信息 menu = { # 定義一個菜單字典 'style': 'sichuan', #定義菜單的類型,四川菜 'toppings': ['salt', 'sugar','vinegar','Sichuan Pepper'] # 定義一個佐料的列表,包含鹽、糖、醋、花椒 } #存儲了有關顧客所點菜餚的信息 # 概述所點的菜單 print("You ordered a " + menu['style'] + "-style menu " + "with the following toppings:") for topping in menu['toppings']: print("\t" + topping)
2)嵌套多個列表
favor_languages = { 'jack': ['python', 'ruby'], 'sarah': ['c','C++'], 'edward': ['ruby', 'go'], 'polo':['c#','java'] } for name, languages in favor_languages.items(): print("\n" + name.title() + "'s favorite languages are:") for language in languages: print("\t" + language.title())
三、在字典中存儲字典
網站有多個用戶,每個都有獨特ID(或用戶名),可以在字典中將用戶名作為鍵,再將每位用戶的信息存儲在一個字典中,並將該字典作為與用戶名相關聯的值。對於每位用戶,都存儲了其三項信息:名、姓和居住地;為訪問這些信息,遍歷所有的用戶名,並訪問與每個用戶名相關聯的信息字典
#在字典中嵌套字典 users = { #創建一個users的字典,字典中有兩個關鍵字(id)lucyb和merryb, 'lucyb': {'firstname': 'lucy','lastname':'Bush','location': 'califorlia'}, 'merryb':{'firstname':'merry','lastname':'Biden','location':'San Francisco'} } # lucyb和merryb又分別為兩字典,各自有三個關鍵字,firstname,lastname和location for username, user_info in users.items(): #遍歷字典uers的每一項 print("\nUsername: " + username) full_name = user_info['firstname'] + " " + user_info['lastname'] location = user_info['location'] print("\tFull name: " + full_name.title()) print("\tLocation: " + location.title())
運行結果: