題目描述:這裡 思路: 一、部分分演算法 對於的數據,用暴力解決即可,時間複雜度 對於另外的數據(所有木棍長度相等),考慮用組合數學,答案為 二、正解 我們考慮對整個序列進行桶排序。 我們設每個數出現的次數為。 對於所有≥的數,加上比它小的所有數出現的次數,並加上這個數至這個數中所有數出現的個數。 特 ...
題目描述:這裡
思路:
一、部分分演算法
- 對於
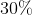 的數據,用暴力解決即可,時間複雜度
的數據,用暴力解決即可,時間複雜度
- 對於另外
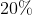 的數據(所有木棍長度相等),考慮用組合數學,答案為
的數據(所有木棍長度相等),考慮用組合數學,答案為
二、正解
我們考慮對整個序列進行桶排序。
我們設每個數出現的次數為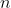 。
。
- 對於所有
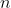 ≥
≥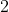 的數,加上比它小的所有數出現的次數,並加上這個數
的數,加上比它小的所有數出現的次數,並加上這個數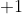 至這個數
至這個數 中所有數出現的個數。
中所有數出現的個數。 - 特別的,對於所有
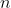 ≥
≥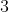 的數,需要再次加上
的數,需要再次加上 。
。
但是,我們會發現這依然過不了(TLE了一個點)。
我們再次仔細觀察正解的統計方式第一條,發現這可以用首碼和優化。
於是,這道題就做完了。
下麵附上代碼:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; template < typename T > void read(T &x) { int f = 1;x = 0;char c = getchar(); for (;!isdigit(c);c = getchar()) if (c == '-') f = -f; for (; isdigit(c);c = getchar()) x = x * 10 + c - '0'; x *= f; } const long long mod = 998244353; int a[200005]; long long bin[200005]; long long sum[200005]; int main() { //freopen(".in", "r", stdin); //freopen(".out", "w", stdout); int n, binmax = INT_MIN; long long ans = 0; read(n); for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { read(a[i]); bin[a[i]]++; binmax = max(binmax, a[i]); } int t = a[1]; int flag = 1; for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++) if(a[i] != t) { flag = 0; break; } if(flag) { long long ans = 1; for(int i = n;i > n - 3;i--) { ans *= i; } cout << (ans / 6) % mod << endl; return 0; } if(n <= 200) { for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) for(int j = i + 1;j <= n;j++) for(int k = j + 1;k <= n;k++) if((a[i] == a[j] || a[i] == a[k] || a[j] == a[k]) && (a[i] + a[j] > a[k]) && a[i] + a[k] > a[j] && a[j] + a[k] > a[i]) ans++; cout << ans % mod << endl; return 0; } sum[0] = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= binmax;i++) sum[i] = bin[i] + sum[i - 1]; long long front = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= binmax;++i) if(bin[i]) { if(bin[i] >= 3) { long long ansj = 1; for(int j = bin[i];j > bin[i] - 3;--j) ansj *= j; ans += ansj / 6; ans %= mod; } if(bin[i] >= 2) { long long tx = bin[i] * (bin[i] - 1) / 2; ans += front * tx; ans %= mod; long long up = min(i * 2, binmax + 1) - 1; long long ty = sum[up] - sum[i]; ans += ty * tx; ans %= mod; } front += bin[i]; } cout << ans << endl; return 0; }


