(一)數組 數組(Array)是一種線性表數據結構。它用一組連續的記憶體空間,來存儲一組具有相同類型的數據。 1、數組支持隨機訪問,根據下標隨機訪問的時間複雜度為 O(1)。 通過 a[i]_address = a[0]_address + i*元素的大小(位元組) ,得到a[i]所在的位置。 2、插入 ...
(一)數組
數組(Array)是一種線性表數據結構。它用一組連續的記憶體空間,來存儲一組具有相同類型的數據。
1、數組支持隨機訪問,根據下標隨機訪問的時間複雜度為 O(1)。
通過 a[i]_address = a[0]_address + i*元素的大小(位元組) ,得到a[i]所在的位置。
2、插入:
數組長度為n,在索引k插入一個元素,k~n的元素都需要向後搬移。時間複雜度為O(n) 。(在末尾插入時間複雜度O(1),首位插入則為O(n),平均時間複雜度為O(n))
如果數組是無序的,可以在末尾插入,再和第k個元素互換,實現O(1)時間複雜度複雜度的插入。
3、刪除
和插入類似。數組長度為n,刪除第k個元素,則k+1~n的元素都需要向前搬移一位,時間複雜度為o(n)。
如果數組是無序的,可以將末尾的元素和第k個元素互換位置,然後再刪除,實現O(1)時間複雜度的刪除。
(二)鏈表
1、數組與鏈表在底層存儲結構上的區別
(1)數組需要一段連續的記憶體空間,鏈表則不需要
(2)鏈表通過“指針”,將一組零散的記憶體空間串聯在一起。
2、常用的鏈表結構
(1)單鏈表
(2)雙向鏈表
(3)迴圈鏈表
3、單鏈表

(1)把記憶體塊(data)稱為鏈表的“結點”,用於存儲數據。next記錄下一個節點的記憶體地址,把這個記錄下個結點地址的指針稱為後繼指針next。
(2)第一個結點稱為頭結點,最後一個結點稱為尾結點。尾結點的指針不是指向下一個結點,而是指向一個空地址NULL,表示這是鏈表的最後一個結點。
(3)鏈表插入、刪除的時間複雜度O(1),只需要修改指針即可。
(4)鏈表隨機訪問的時間複雜度是O(n)。因為鏈表的記憶體空間是零散的,沒法像數組那樣通過簡單的定址公式實現隨機訪問,只能一個一個結點依次遍歷,直到找到相應的結點。
4、迴圈鏈表
和單鏈表唯一的區別就在於尾結點,尾結點的指針指向頭結點,而不是空地址。
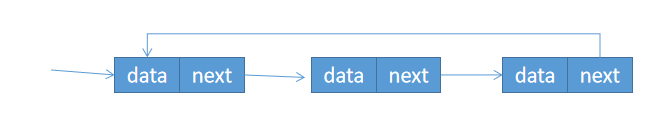
5、雙向鏈表
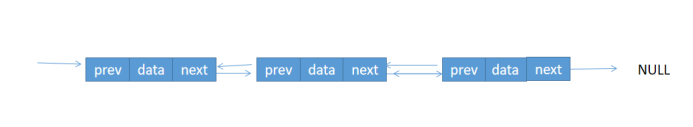
(1)相比單鏈表,多了一個前驅指針,指向前一個結點
(三)練習題
1、單鏈表反轉。 leetcode : 206
1 # 迭代方式 2 class ListNode: 3 def __init__(self, x): 4 self.val = x 5 self.next = None 6 7 class Solution: 8 def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: 9 if head is None or head.next is None: 10 return head 11 prev_node = None 12 while head is not None: 13 next_node = head.next # 備份下一結點的記憶體地址 14 head.next = prev_node # 當前結點的指針指向前一結點(頭結點指向None) 15 prev_node = head # 更新前一結點的值。 16 head = next_node # 設置當前結點為下一結點的地址 17 return prev_node 18 19 if __name__ == "__main__": 20 l1 = ListNode(1) 21 l1.next = ListNode(2) 22 l1.next.next = ListNode(3) 23 l1.next.next.next = ListNode(4) 24 l1.next.next.next.next = ListNode(5) 25 rev_result = Solution().reverseList(l1) 26 for i in range(6): 27 if rev_result is not None: 28 print(rev_result.val) 29 rev_result = rev_result.next 30 else: 31 print(rev_result)
1 # 遞歸方式 2 class ListNode: 3 def __init__(self, x): 4 self.val = x 5 self.next = None 6 7 class Solution: 8 def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: 9 if head is None or head.next is None: 10 return head 11 next_node = self.reverseList(head.next) 12 head.next.next = head 13 head.next = None 14 return next_node 15 """ 16 遞歸和迭代不同的是,遞歸從後向前,迭代從前往後 17 1、 head.val = 4 18 4.next.next = head, 實際就是5的指針指向結點4的記憶體地址 19 4.next = None ,斷開之前 4 -> 5 的指針 20 2、 head.val = 3 21 3.next.next = head, 實際就是4的指針指向結點3的記憶體地址 22 3.next = None , 斷開之前 3 -> 4 的指針 23 ... 24 4: head.val = 1 25 1.next.next = head, 實際就是2的指針指向結點1的記憶體地址 26 1.next = None ,頭結點指向None 27 """ 28 if __name__ == "__main__": 29 l1 = ListNode(1) 30 l1.next = ListNode(2) 31 l1.next.next = ListNode(3) 32 l1.next.next.next = ListNode(4) 33 l1.next.next.next.next = ListNode(5) 34 rev_result = Solution().reverseList(l1) 35 for i in range(6): 36 if rev_result is not None: 37 print(rev_result.val) 38 rev_result = rev_result.next 39 else: 40 print(rev_result)
2、鏈表中環的檢測: leetcode 141
1 # Definition for singly-linked list. 2 # class ListNode: 3 # def __init__(self, x): 4 # self.val = x 5 # self.next = None 6 7 class Solution: 8 def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool: 9 flag = True 10 while head is not None: 11 next_node = head.next 12 if next_node is None: # 如果指針的值為None,表示沒有環 13 return False 14 elif next_node == True: # 如果指針的值為True,表示有環 15 return True 16 head.next = flag # 將結點指針的值設置為True 17 head = next_node # head 設置為下一結點 18 return False
3、兩個有序的鏈表合併,leetcode 21
1 # Definition for singly-linked list. 2 class ListNode: 3 def __init__(self, x): 4 self.val = x 5 self.next = None 6 7 class Solution: 8 def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode: 9 new_node = ListNode("K") 10 move = new_node # 加一個move,是為了讓new_node一直代表頭結點,方便返回數據 11 while l1 and l2: 12 if l1.val > l2.val: 13 move.next = l2 14 l2 = l2.next 15 else: 16 move.next = l1 17 l1 = l1.next 18 move = move.next 19 move.next = l1 if l1 else l2 20 return new_node.next 21 22 23 24 if __name__ == "__main__": 25 l1 = ListNode(1) 26 l1.next = ListNode(2) 27 l1.next.next = ListNode(3) 28 l2 = ListNode(1) 29 l2.next = ListNode(3) 30 l2.next.next = ListNode(4) 31 result = Solution().mergeTwoLists(l1,l2) 32 for i in range(6): 33 print(result.val) 34 result = result.next
4、刪除鏈表倒數第 n 個結點,leetcode 19
1 class ListNode: 2 def __init__(self, x): 3 self.val = x 4 self.next = None 5 6 class Solution: 7 def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode: 8 new_node = ListNode("k") # 加一個哨兵,方便處理頭結點 9 curson = head # 當前結點的指針 10 prev = new_node # 前一結點的指針 11 new_node.next = head 12 num = 0 13 while head: # 得到鏈表的長度 14 num += 1 15 head = head.next 16 for i in range(num): 17 if i == (num - n): # 刪除第n個結點,並返回頭結點 18 prev.next = curson.next 19 return new_node.next 20 prev = curson 21 curson = curson.next 22 return new_node.next 23 24 if __name__ == "__main__": 25 l1 = ListNode(1) 26 l1.next = ListNode(2) 27 l1.next.next = ListNode(3) 28 result = Solution().removeNthFromEnd(l1,3) 29 for i in range(10): 30 try: 31 print(result.val) 32 result = result.next 33 except: 34 pass
5、求鏈表的中間結點 leetcode 876
1 # Definition for singly-linked list. 2 # class ListNode: 3 # def __init__(self, x): 4 # self.val = x 5 # self.next = None 6 7 class Solution: 8 def middleNode(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: 9 curson = head 10 num = 0 11 while head: # 得到鏈表總長度 12 num += 1 13 head = head.next 14 idx = num // 2 # 得到中間結點 15 for i in range(num): # 返回中間結點 16 if i == idx: 17 return curson 18 curson = curson.next



