什麼是事件?事件是用戶觸摸手機屏幕,引起的一系列TouchEvent,包括ACTION_DOWN、ACTION_MOVE、ACTION_UP、ACTION_CANCEL等,這些action組合後變成點擊事件、長按事件等。 在這篇文章中,用打Log測試的方法來瞭解Android TouchEvent ...
什麼是事件?事件是用戶觸摸手機屏幕,引起的一系列TouchEvent,包括ACTION_DOWN、ACTION_MOVE、ACTION_UP、ACTION_CANCEL等,這些action組合後變成點擊事件、長按事件等。
在這篇文章中,用打Log測試的方法來瞭解Android TouchEvent 事件分發,攔截,處理過程。雖然看了一些其他的文章和源碼及相關的資料,但是還是覺得需要打下Log和畫圖來瞭解一下,不然很容易忘記了事件傳遞的整個過程。所以寫下這篇文章,達到看完這篇文章基本可以瞭解整個過程,並且可以自己畫圖畫出來給別人看。
先看幾個類,主要是畫出一個3個ViewGroup疊加的界面,併在事件分發、攔截、處理時打下Log.
GitHub地址:https://github.com/libill/TouchEventDemo
一、通過打log分析事件分發
這裡在一個Activity上添加三個ViewGroup來分析,這裡值得註意的是Activity、View是沒有onInterceptTouchEvent方法的。
一、瞭解Activity、ViewGroup1、ViewGroup2、ViewGroup3四個類
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.touchevent.demo.MyActivity"> <com.touchevent.demo.ViewGroup1 android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@color/colorAccent"> <com.touchevent.demo.ViewGroup2 android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="50dp" android:background="@color/colorPrimary"> <com.touchevent.demo.ViewGroup3 android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_margin="50dp" android:background="@color/colorPrimaryDark"> </com.touchevent.demo.ViewGroup3> </com.touchevent.demo.ViewGroup2> </com.touchevent.demo.ViewGroup1> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>主界面:MainActivity.java
public class MyActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private final static String TAG = MyActivity.class.getName(); @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev)); boolean superReturn = super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); Log.d(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + superReturn); return superReturn; } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev)); boolean superReturn = super.onTouchEvent(ev); Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + superReturn); return superReturn; } }三個ViewGroup,裡面的代碼完全一樣:ViewGroup1.java,ViewGroup2.java,ViewGroup3.java。由於代碼一樣所以只貼其中一個類。
public class ViewGroup1 extends LinearLayout { private final static String TAG = ViewGroup1.class.getName(); public ViewGroup1(Context context) { super(context); } public ViewGroup1(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev)); boolean superReturn = super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev); Log.d(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + superReturn); return superReturn; } @Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { Log.i(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev)); boolean superReturn = super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + superReturn); return superReturn; } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev)); boolean superReturn = super.onTouchEvent(ev); Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + superReturn); return superReturn; } }
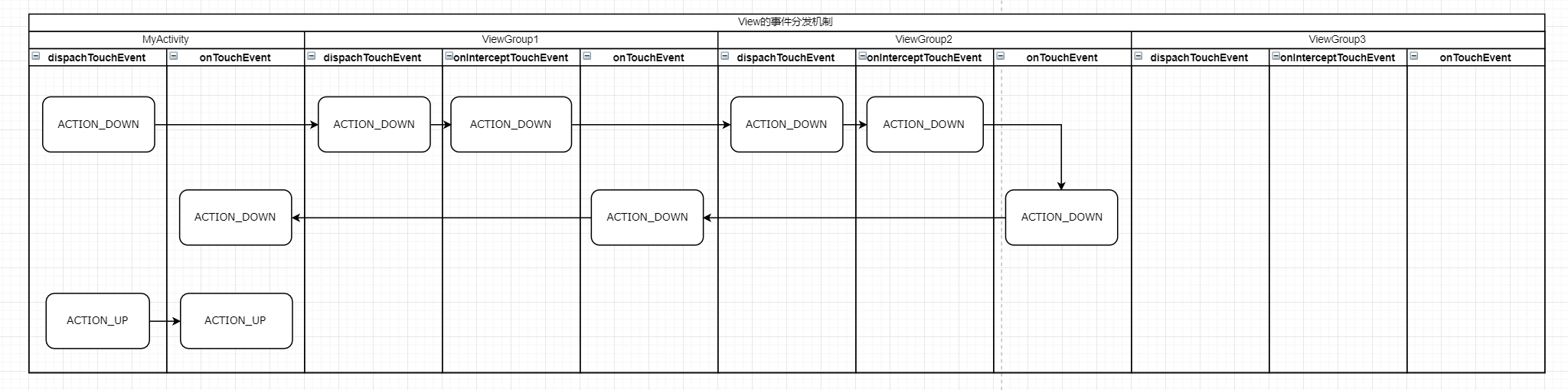
二、不攔截處理任何事件
添加沒有攔截處理任何事件的代碼,看看事件是怎麼傳遞的,選擇Info,查看Log.
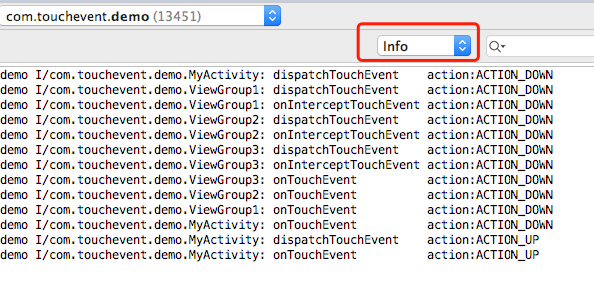
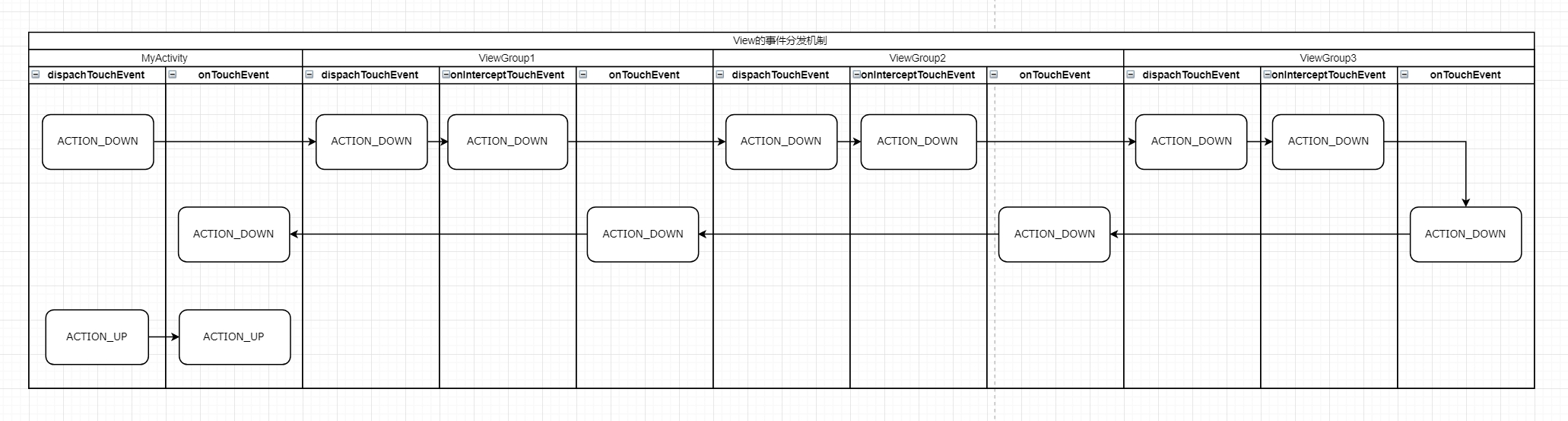
從流程圖可以看出,事件分發從Activity開始,然後分發到ViewGroup,在這個過程中,只要ViewGroup沒有攔截處理,最後還是會回到Activity的onTouchEvent方法。
三、ViewGroup2的dispatchTouchEvent返回true
把ViewGroup2.java的dispatchTouchEvent修改一下,return 返回true使事件不在分發
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev));
Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + true);
return true;
}此時的Log
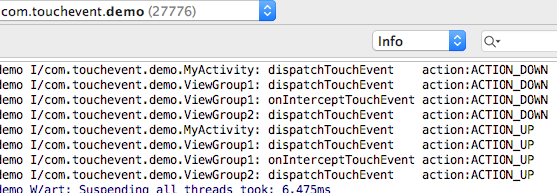
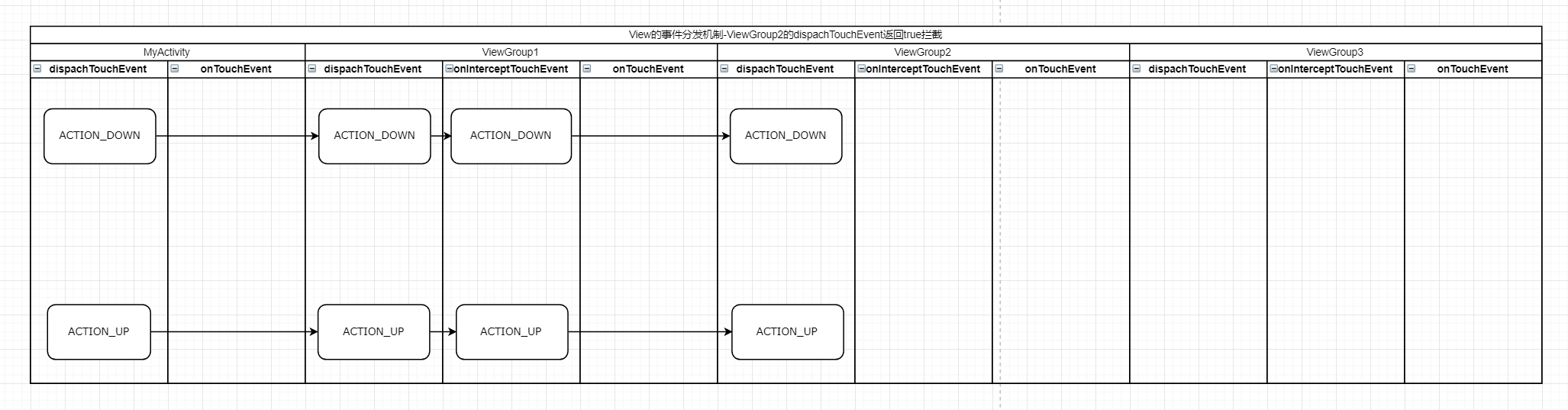
從圖片可以看出,當ViewGroupon2的dispatchTouchEvent返回true後,事件不會再分發傳送到ViewGroup3了,也不會分發到Activity的onTouchEvent了。而是事件到了ViewGroupon2的dispatchTouchEvent後,就停止了。dispatchTouchEvent返回true表示著事件不用再分發下去了。
四、ViewGroup2的onInterceptTouchEvent返回true
把ViewGroup2.java的onInterceptTouchEvent修改一下,return 返回true把事件攔截了
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev));
boolean superReturn = super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
Log.d(TAG, "dispatchTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + superReturn);
return superReturn;
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev));
Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + true);
return true;
}此時的Log
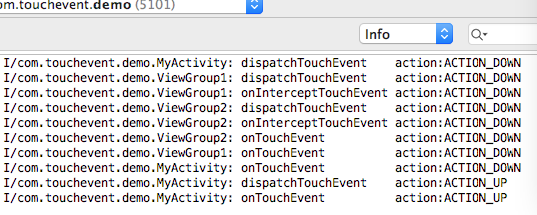
可以看出ViewGroup2攔截了事件,就不會繼續分發到ViewGroup3;而且ViewGroup3攔截了事件又不處理事件,會把事件傳遞到Activity的onTouchEvent方法。
五、ViewGroup2的onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent返回true
把ViewGroup2.java的onTouchEvent修改一下,return 返回true把事件處理了
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev));
Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + true);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev));
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent action:" + StringUtils.getMotionEventName(ev) + " " + true);
return true;
}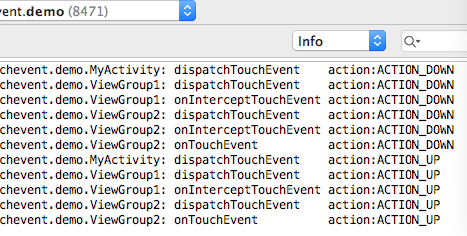
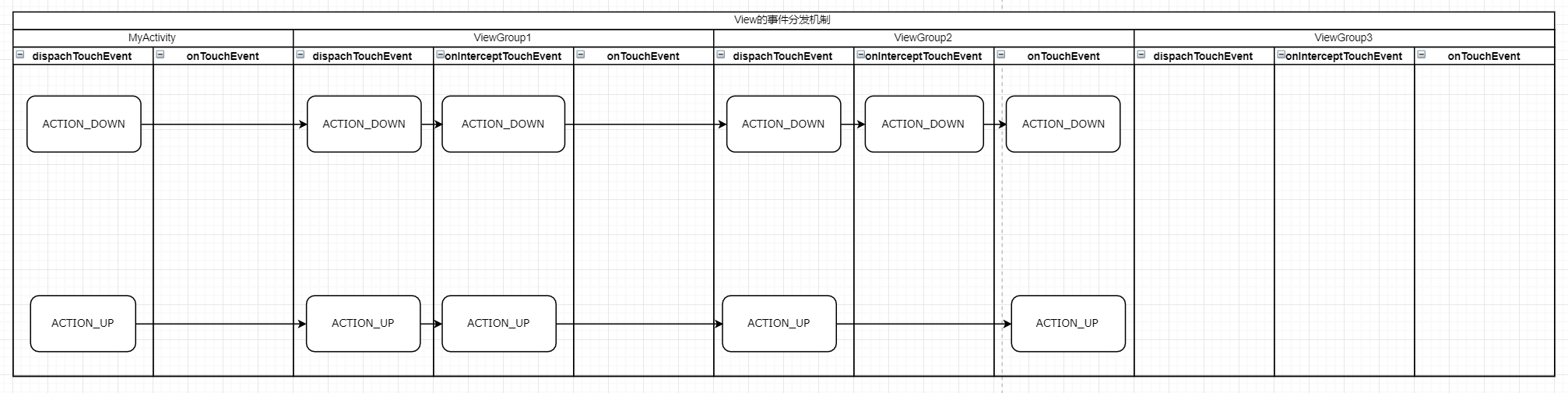
從流程可以總結出,當ViewGroup2的onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent都返回true時,事件最終會走到ViewGroup2的onTouchEvent方法處理事件,後續的事件都會走到這裡來。
上面通過log分析很清楚了,是不是就這樣夠了?其實還不行,還要從源碼的角度去分析下,為什麼事件會這樣分發。
二、通過源碼分析事件分發
一、Activity的dispatchTouchEvent
先看看Activity下的dispatchTouchEvent
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
onUserInteraction();
}
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {
return true;
}
return onTouchEvent(ev);
}onUserInteraction方法
public void onUserInteraction() {
}從代碼可以瞭解
調用Activity的onUserInteraction方法,action為down時會進去onUserInteraction方法,但是這個是空方法不做任何事情,可以忽略。
調用window的superDispatchTouchEvent方法,返回true時事件分發處理結束,否則會調用Activity的onTouchEvent方法。
調用Activity的onTouchEvent方法,進入這個條件的方法是window的superDispatchTouchEvent方法返回false。從上面的分析(二、不攔截處理任何事件)可以知道,所有子View的dispatchTouchEvent、onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent都返回false時會調動Activity的onTouchEvent方法,這個時候也是使window的superDispatchTouchEvent方法返回false成立。
二、window的superDispatchTouchEvent
Activity的getWindow方法
public Window getWindow() {
return mWindow;
}mWindow是如何賦值的?
是在Activity的attach方法賦值的,其實mWindow是PhoneWindow。
Activity的attach方法
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
...
}PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent方法
private DecorView mDecor;
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}DevorView的superDispatchTouchEvent
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}而mDecor是一個繼承FrameLayout的DecorView,就這樣把事件分發到ViewGroup上了。
三、ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent
3.1 ViewGroup攔截事件的情況
// Check for interception.
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}這裡分為2種情況會判斷是否需要攔截,也就是當某一條件成立時,會執行onInterceptTouchEvent判斷是否需要攔截事件。
- 當actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN時。
當mFirstTouchTarget != null時。mFirstTouchTarget是成功處理事件的ViewGroup的子View,也就是ViewGroup的子View在以下情況返回true時,這個在log分析流程圖輕易得到:
2.1 dispatchTouchEvent返回true
2.2 如果子View是ViewGroup時,onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent返回true
另外還有一種情況是disallowIntercept為true時,intercepted直接賦值false不進行攔截。FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT是通過requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent方法來設置的,用於在子View中設置,設置後ViewGroup只能攔截down事件,無法攔截其他move、up、cancel事件。為什麼ViewGroup還能攔截down事件呢?因為ViewGroup在down事件時進行了重置,看看以下代碼
// Handle an initial down.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Throw away all previous state when starting a new touch gesture.
// The framework may have dropped the up or cancel event for the previous gesture
// due to an app switch, ANR, or some other state change.
cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);
resetTouchState();
}
private void resetTouchState() {
clearTouchTargets();
resetCancelNextUpFlag(this);
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;
mNestedScrollAxes = SCROLL_AXIS_NONE;
}通過源碼可以瞭解到,ViewGroup攔截事件後,不再調用onInterceptTouchEvent,而是直接交給mFirstTouchTarget的onTouchEvent處理,如果該onTouchEvent不處理最終會交給Activity的onTouchEvent。
3.2 ViewGroup不攔截事件的情況
ViewGroup不攔截事件時,會遍歷子View,使事件分發到子View進行處理。
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(
childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(
preorderedList, children, childIndex);
// If there is a view that has accessibility focus we want it
// to get the event first and if not handled we will perform a
// normal dispatch. We may do a double iteration but this is
// safer given the timeframe.
if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != null) {
if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != child) {
continue;
}
childWithAccessibilityFocus = null;
i = childrenCount - 1;
}
if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)
|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
continue;
}
newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child);
if (newTouchTarget != null) {
// Child is already receiving touch within its bounds.
// Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling.
newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;
break;
}
resetCancelNextUpFlag(child);
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// Child wants to receive touch within its bounds.
mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime();
if (preorderedList != null) {
// childIndex points into presorted list, find original index
for (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) {
if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) {
mLastTouchDownIndex = j;
break;
}
}
} else {
mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex;
}
mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX();
mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY();
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
break;
}
}3.2.1 尋找可接收事件的子View
通過canViewReceivePointerEvents判斷子View是否能夠接收到點擊事件。必須符合2種情況,缺一不可:1、點擊事件的坐標落在在子View的區域內;2、子View沒有正在播放動畫。滿足條件後,調用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent,其實也是調用子View的dispatchTouchEvent。
private static boolean canViewReceivePointerEvents(@NonNull View child) {
return (child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE
|| child.getAnimation() != null;
}
protected boolean isTransformedTouchPointInView(float x, float y, View child,
PointF outLocalPoint) {
final float[] point = getTempPoint();
point[0] = x;
point[1] = y;
transformPointToViewLocal(point, child);
final boolean isInView = child.pointInView(point[0], point[1]);
if (isInView && outLocalPoint != null) {
outLocalPoint.set(point[0], point[1]);
}
return isInView;
}
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
final boolean handled;
final int oldAction = event.getAction();
if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) {
event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL);
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
event.setAction(oldAction);
return handled;
}
...
// Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch.
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());
}
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
// Done.
transformedEvent.recycle();
return handled;
}當dispatchTransformedTouchEvent返回true時,結束for迴圈遍歷,賦值newTouchTarget,相當於發現了可以接收事件的View,不用再繼續找了。
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
break;在addTouchTarget方法賦值mFirstTouchTarget。
private TouchTarget addTouchTarget(@NonNull View child, int pointerIdBits) {
final TouchTarget target = TouchTarget.obtain(child, pointerIdBits);
target.next = mFirstTouchTarget;
mFirstTouchTarget = target;
return target;
}3.2.2 ViewGroup自己處理事件
另一種情況是mFirstTouchTarget為空時,ViewGroup自己處理事件,這裡註意第三個參數為null,ViewGroup的super.dispatchTouchEvent將調用View的dispatchTouchEvent。
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
}3.3 View處理點擊事件的過程
View的dispatchTouchEvent是怎麼處理事件的呢?
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
boolean result = false;
...
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {
result = true;
}
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
...
return result;
}首先使用onFilterTouchEventForSecurity方法過濾不符合應用安全策略的觸摸事件。
public boolean onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(MotionEvent event) { //noinspection RedundantIfStatement if ((mViewFlags & FILTER_TOUCHES_WHEN_OBSCURED) != 0 && (event.getFlags() & MotionEvent.FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED) != 0) { // Window is obscured, drop this touch. return false; } return true; }mOnTouchListener != null判斷是否設置了OnTouchEvent,設置了就執行mOnTouchListener.onTouch並返回true,不再執行onTouchEvent。這裡得出OnTouchEvent的優先順序高於OnTouchEvent,便於使用setOnTouchListener設置處理點擊事件。
另一種情況是進入onTouchEvent進行處理。
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { final float x = event.getX(); final float y = event.getY(); final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; final int action = event.getAction(); final boolean clickable = ((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE || (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) || (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE; if ((viewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) { if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) { setPressed(false); } mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN; // A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch // events, it just doesn't respond to them. return clickable; } ... }
當View不可用時,依然會處理事件,只是看起來不可用。
接著執行mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}下麵看看up事件是怎麼處理的
/**
* <p>Indicates this view can display a tooltip on hover or long press.</p>
* {@hide}
*/
static final int TOOLTIP = 0x40000000;
if (clickable || (viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
if ((viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
handleTooltipUp();
}
if (!clickable) {
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
mInContextButtonPress = false;
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
}
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (prepressed) {
// The button is being released before we actually
// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed
// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure
// the user sees it.
setPressed(true, x, y);
}
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClickInternal();
}
}
}
if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
}
if (prepressed) {
postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
// If the post failed, unpress right now
mUnsetPressedState.run();
}
removeTapCallback();
}
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
...
}
return true;
}從上面代碼可以瞭解,clickable、TOOLTIP(長按)有一個為true時,就會消耗事件,使onTouchEvent返回true。其中PerformClick內部調用了performClick方法。
public boolean performClick() {
// We still need to call this method to handle the cases where performClick() was called
// externally, instead of through performClickInternal()
notifyAutofillManagerOnClick();
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
return result;
}如果View設置了OnClickListener,那performClick會調用內部的onClick方法。
public void setOnClickListener(@Nullable OnClickListener l) {
if (!isClickable()) {
setClickable(true);
}
getListenerInfo().mOnClickListener = l;
}
public void setOnLongClickListener(@Nullable OnLongClickListener l) {
if (!isLongClickable()) {
setLongClickable(true);
}
getListenerInfo().mOnLongClickListener = l;
}通過setOnClickListener設置clickable,通過setOnLongClickListener設置LONG_CLICKABLE長按事件。設置後使得onTouchEvent返回true。到這裡我們已經分析完成點擊事件的分發過程了。
本文地址:http://libill.github.io/2019/09/09/android-touch-event/
本文參考以下內容:
1、《Android開發藝術探索》



