Spring是以Ioc和Aop為內核,提供了表現層spring MVC 和持久層Spring JDBC等眾多應用技術,還能整合開源世界眾多著名的第三方框架和類庫,成為使用最多的JavaEE企業應用開源框架。 Spring的優勢: Spring的體繫結構:全部基於核心容器Core Container ...
- Spring是以Ioc和Aop為內核,提供了表現層spring MVC 和持久層Spring JDBC等眾多應用技術,還能整合開源世界眾多著名的第三方框架和類庫,成為使用最多的JavaEE企業應用開源框架。
- Spring的優勢:
- 方便解耦,簡化開發;
- Aop編程的支持;
- 聲明式事務的支持;
- 方便程式的測試;
- 方便集成各種優秀框架;
- 降低JavaEE API的使用難度;
- Spring源碼是經典學習的範例;
- Spring的體繫結構:全部基於核心容器Core Container
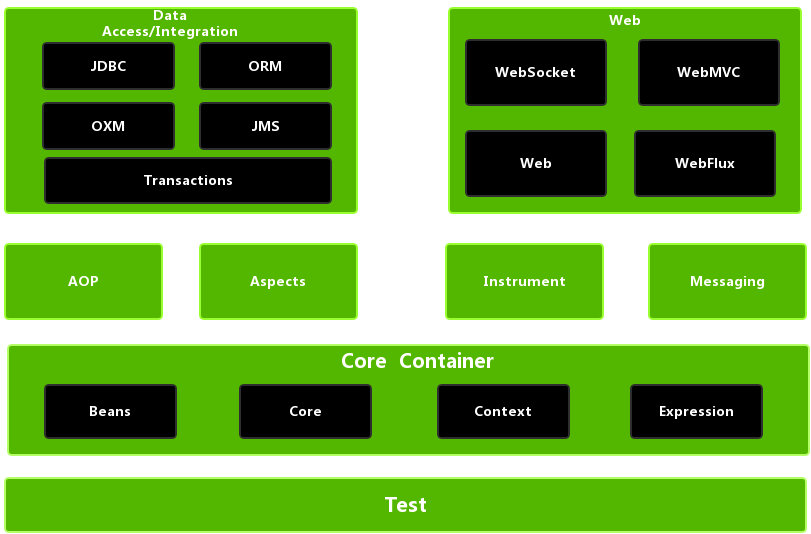
- 編譯時期依賴:JDBC在沒有導依賴包時即mysql驅動時,將無法編譯。即註冊驅動時找不到com.mysql.jdbc.Driver()依賴包;
- 耦合:程式間的依賴關係,其中包括:①類之間的依賴;②方法之間的依賴;
- 解耦:降低程式間的依賴關係,實際開發中應該做到,編譯時期不依賴,運行時才依賴;
- 解耦的思路:
- 使用反射來創建對象,而避免使用new關鍵字,即Class.forName(“全限定類名”)。
- 通過讀取配置文件來獲取要創建對象的全類名,而不是直接寫死,然後再通過反射來創建對象。
- 解耦的方式:
方式一:使用工程模式解耦:(創建Bean對象的工廠,用來創建Service和dao對象的)
1.定義一個配置文件bean.properties配置service和dao層的全類名,
配置的內容:
accountService=com.itheima.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl
accountDao=com.itheima.dao.impl.IAccountImpl
2.通過讀取配置文件的內容,反射創建對象
BeanFactory工廠類:
3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStream; 6 import java.util.Enumeration; 7 import java.util.HashMap; 8 import java.util.Map; 9 import java.util.Properties; 10 11 /** 12 * 創建Bean對象的工廠 13 * Bean:在電腦英語中,有可重用組件的含義 14 * 15 * 它就是創建service和dao對象的 16 * 17 * 1.定義一個配置文件配置service和dao 18 * 配置的內容:唯一標誌=全限定類名(key=value形式) 19 * 2.通過讀取配置文件當中的內容,反射創建對象 20 */ 21 public class BeanFactory { 22 //定義一個properties對象 23 private static Properties properties = new Properties(); 24 25 //定義一個map,用於存儲我們創建的對象,稱之為容器 26 private static Map<String,Object> beans; 27 28 //使用靜態代碼塊為Properties對象賦值 29 static { 30 31 try { 32 //獲取properties文件的流對象 33 InputStream is = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties"); 34 properties.load(is); 35 beans = new HashMap<String, Object>(); 36 //取出配置文件中所有的key 37 Enumeration keys = properties.keys(); 38 //遍歷枚舉 39 while (keys.hasMoreElements()){ 40 //取出每個key 41 String key = keys.nextElement().toString(); 42 //根據key獲取value 43 String beanPath = properties.getProperty(key); 44 //反射創建對象 45 Object value = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance(); 46 //把key和value存入容器之中 47 beans.put(key,value); 48 } 49 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } catch (IOException e) { 52 e.printStackTrace(); 53 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 54 e.printStackTrace(); 55 } catch (InstantiationException e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 58 e.printStackTrace(); 59 } 60 } 61 62 /** 63 * 根據bean的名稱獲取bean對象,此時獲取的對象為單例對象 64 * @param beanName 65 * @return 66 */ 67 public static Object getBean(String beanName){ 68 return beans.get(beanName); 69 } 70 }
*使用工廠模式創建出來的對象,使用Map集合作為容器去存儲之後,創建出來的為單例對象,是我們需要的。(單例對象:只被創建一次,類中的成員只會初始化一次,效率高,而且一般沒有成員變數的定義,如果要定義變數也是在方 法內部。多例對象:每次都是創建一個新的對象,執行效率無單例對象高,從而類中的成員每次都會被初始化)
方式二:使用Spring的Ioc控制反轉(把創建對象的權利交給框架,是框架的重要特征,它包括依賴註入(DI)和依賴查找(DL))
Spring的入門
獲取核心容器對象以及如何根據id獲取bean對象的方式
/** * 模擬一個表現層,用於調用業務層 */ public class Client { /** * 獲取springIoc的核心容器,並且根據id獲取對象 * * ApplicationContext常用的三個實現類 * ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,它可以載入類路徑下的配置文件,要求配置文件必須在類路徑下,不在的話載入不了(更常用) * FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,它可以載入磁碟任意路徑下的配置文件,但要有訪問許可權 * * * * AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,它是用於讀取註解創建容器的 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //1.獲取核心容器對象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); //2.根據id查詢獲取bean對象 IAccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService", IAccountService.class); IAccountDao accountDao = (IAccountDao) ac.getBean("accountDao"); System.out.println(accountService); System.out.println(accountDao); } }
bean.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--把對象的創建交給spring來管理 id為所要創建對象的名稱 class為創建new對象的全限定類名--> <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.IAccountImpl"></bean> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl"></bean> </beans>
- 關於核心容器的兩個介面引發的問題:
ApplicationContetx:在創建核心容器時,創建對象採取的策略是採用立即載入的方式,也就是說,一讀取完配置文件馬上就創建配置文件中配置對象(單例對象)。
BeanFactory:在創建核心容器時,創建對象採取的策略是採用延遲載入的方式,也就是說,什麼時候根據id獲取對象了,什麼時候才真正創建對象(多例對象)。
- 創建bean對象的三種方式:
<!--創建bean的三種方式--> <!-- 第一種方式:使用預設構造函數進行創建,若無預設構造函數,則無法創建 --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl" scope="prototype" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> </bean> <!-- 第二種方式:使用普通工廠中的方法創建對象(使用某個類中的方法創建對象並且存入spring容器) --> <!--<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>--> <!--<bean id="accountService" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>--> <!-- 第三種方式:使用工廠中的靜態方法創建對象(使用某個類中的靜態方法創建對象並且存入spring容器) --> <!--<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getAccountService"></bean>-->
- bean的作用範圍:<bean>的scope屬性取值:singleton-單例(預設值),prototype-多例,request: web中的request請求範圍,session: web中的會話範圍,global-session: 集群環境會話範圍(全局會話)
- bean的生命周期:
- 單例對象生命周期與核心容器相同;
- 多例對象在我們使用對象時被spring框架為我們創建,對象只要在使用過程中就一直活著,當對象長時間不用時由JVM虛擬機垃圾回收。
- Spring中的依賴註入就是為了維護依賴關係,參考bean.xml
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用構造函數註入 --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="test"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="date" ref="now"></constructor-arg> </bean>
<!--配置一個日期對象 Date類型不為基本數據類型,所以要先反射創建Date對象存入Ioc核心容器,之後再用ref屬性接收--> <bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean> <!--使用set方法註入 比較常用的方式--> <bean id="accountService1" class="com.itheima.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl1"> <property name="name" value="test1"></property> <property name="age" value="19"/> <property name="date" ref="now"/> </bean>
<!--複雜類型的註入/集合類型的註入 結構相同標簽可以互換,List結構集合:list,array,set標簽可以通用,Map結構集合:map,props標簽可以通用--> <bean id="accountService2" class="com.itheima.service.impl.IAccountServiceImpl2"> <property name="myStrs"> <array> <value>aaa</value> <value>bbb</value> <value>ccc</value> </array> </property> <property name="myList"> <list> <value>aaa</value> <value>bbb</value> <value>ccc</value> </list> </property> <property name="mySet"> <set> <value>aaa</value> <value>bbb</value> <value>ccc</value> </set> </property> <property name="myMap"> <map> <entry key="testA" value="aaa"></entry> <entry key="testB"> <value>bbb</value> </entry> </map> </property> <property name="myProperties"> <props> <prop key="testC">ccc</prop> <prop key="testD">ddd </prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>



