單列集合框架體系 List 集合體系 主要實現類 依次為 ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector 。 List介面主要特征: 有序,可重覆,有索引,底層容量是動態擴容的。(代碼以JDK 1.8為例) ArrayList:是List介面的主要實現類,底層用數組實現: ,transien ...
單列集合框架體系
List 集合體系 主要實現類 依次為 ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector 。
List介面主要特征:
有序,可重覆,有索引,底層容量是動態擴容的。(代碼以JDK 1.8為例)
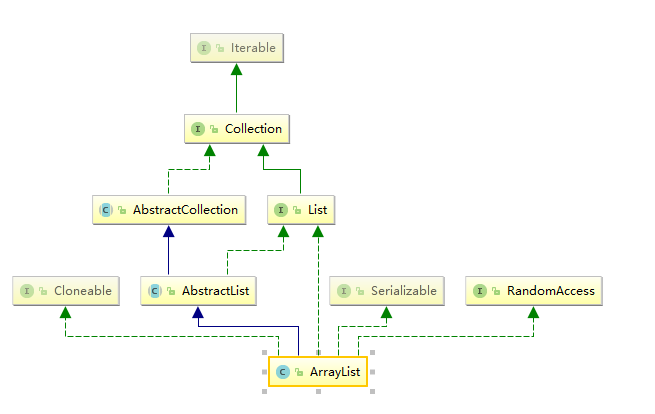
ArrayList:是List介面的主要實現類,底層用數組實現: ,transient Object[] elementData;
線程不安全的,查詢快,增加,刪除 慢(相對於LinkedList)
JDK1.7預設初始長度是10,JDK1.8預設長度是0 ,在調用添加方法之後,才進行長度初始化(值是 10)。
擴容是在當前的數據容量比集合內部數組長度大時,進行擴容,擴容時會先複製原有的數組,然後創建新數組,把原有數組放入新數組中,新數組長度擴圍原有的1.5倍,如果
發現數組長度還是不夠用,那麼直接把當前的實際容量賦值給新數組的容量
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
//如果初始值為10 ,現在集合長度為10 ,在添加低11個元素的時候
//會符合下麵的判斷條件,進入擴容機制
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 先擴大1.5倍,作為新數組的使用長度,通過下麵判斷是否夠用
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
//擴容1.5倍的新數組長度還是不夠用,那麼直接把當前的實際容量賦值給新數組的容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//調用java.util.Arrays 工具包下麵的複製數組方法
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
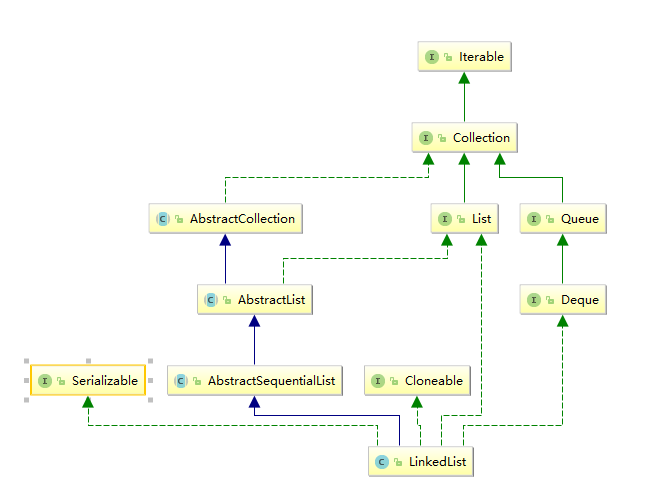
LinkedList:底層是雙向鏈表實現的,有前後元素的地址存儲。
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
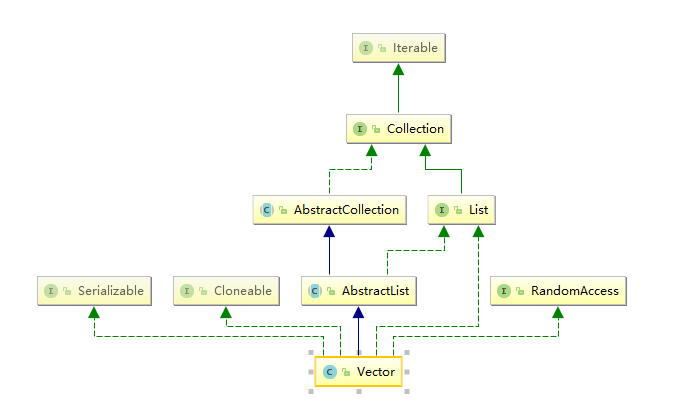
Vector:線程安全的,底層用 Object[] elementData 數組,擴容是原來的2倍長度 這個和ArrayList 是不一樣的
protected Object[] elementData;
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//擴容是原來的2倍長度
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
Set集合體系 主要實現類依次為 HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet;
Set集合的特點:
無序不可重覆,這個不是指存取的順序,指的是數據存放在記憶體中的地址的無序性,簡單點說就是沒有索引排序,是用hash值來進行判斷。
其中HashSet 是Set 的主要實現類,如果沒有特殊情況的話,一般都使用這個類。
無序性:不是指隨機性,底層是數組+鏈表(JDK1.8 會把鏈表轉紅黑樹) 通過hashCode() 計算出對應的hash 值,然後通過hash 值計算出數據存儲在數組 對應的 地址上。
不可重覆性:先計算要存儲值 的hash 值,通過hash 值來計算在容器中數組存放的位置,如果當前數據的hash 值所在容器的位置沒有數據就直接存進去,
如果有,那麼就和容器中的值進行hash 值的比較,如果hash值相同,再計算當前值equals() 容器中該位置的值是否相等,如果相等就代表是同一個元素,就不存進容器中,
如果hash值不同,則直接存進容器中,JDK1.7 是把當前元素存進數組和鏈表的連接處(鏈表前端),JDK1.8是把當前數據存進數據對應數組連接的鏈表的末端。保證元素的不可重覆性。

HashSet:可以存儲null 值,線程不安全的(簡單理解 :就是多線程情況下會不會產生數據不一致的問題,其實安不安全,基本就看是否是 加了鎖,或者是底層是不是用CAS 機制等來進行處理過),
JDK1.7底層是 用數組+鏈表(單向鏈表)初始長度是 16
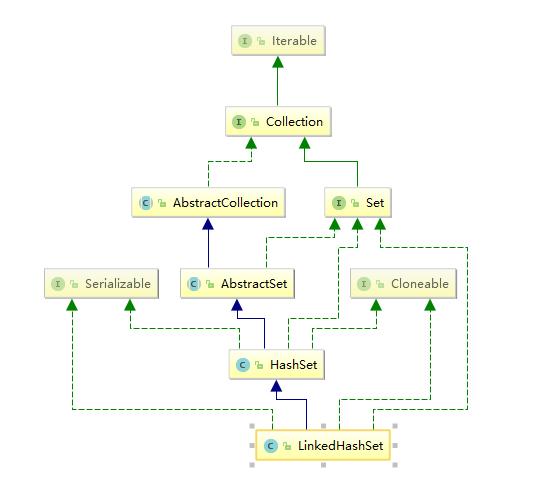
LinkedHashSet:是HashSet 的 子類 通過創建LinkedHashSet 的構造方法,實際是調用的HashSet的私有方法來進行初始化操作,其中的初始化其實直接對應的是LinkedHashMap這個類。
簡單點說,實際上就是用LinkedHashMap 來進行實現的。底層是雙向鏈表
LinkedHashSet:源代碼截取
public class LinkedHashSet<E>
extends HashSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, true);
}
public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity, .75f, true);
}
public LinkedHashSet() {
super(16, .75f, true);
}
}
HashSet 源代碼截取:
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
}
LinkedHashMap 源代碼截取:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
}
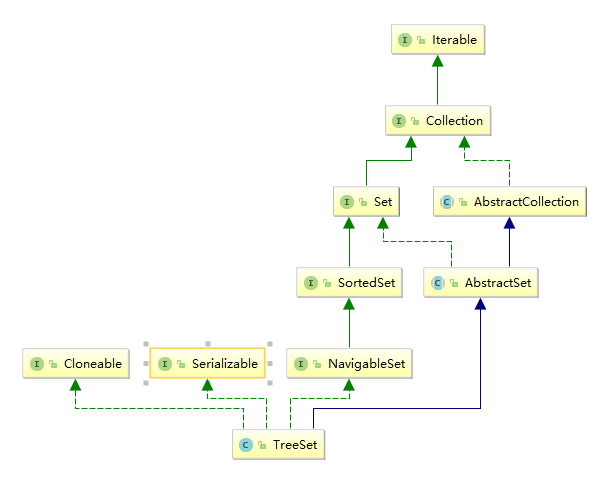
TreeSet:底層使用TreeMap實現,是一個可以排序的set集合。可以定製排序和比較排序,即實現指定泛型類中實體屬性自然排序,也可以通過構造函數來進行指定外部的比較器來進行比較排序。
需要註意的是,向TreeSet中添加的數據要是想同類型的。否則會報錯。
public class CollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add("123");
treeSet.add(123);
}
}
//報錯信息如下
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.String cannot be cast to java.lang.Integer
at java.lang.Integer.compareTo(Integer.java:52)
at java.util.TreeMap.put(TreeMap.java:568)
at java.util.TreeSet.add(TreeSet.java:255)
at CollectionTest.main(CollectionTest.java:10)
如果不實現自然排序介面(Comparable),直接把值放進TreeSet 中還是會報錯:
public class CollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<User> treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",23));
treeSet.add(new User("mikoto",24));
}
}
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: User cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
at java.util.TreeMap.compare(TreeMap.java:1294)
at java.util.TreeMap.put(TreeMap.java:538)
at java.util.TreeSet.add(TreeSet.java:255)
at CollectionTest.main(CollectionTest.java:9)
實現Comparable代碼示例:
public class CollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<User> treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(new User("mikoto",24));
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",23));
Iterator<User> iterator = treeSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
User user = iterator.next();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
//省略 get,set,toString,構造等模板代碼
public class User implements Comparable{
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (o instanceof User){
User user = (User)o;
Integer age = user.getAge();
return this.age.compareTo(age);
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("類型比較錯誤");
}
}
}
測試結果:
User{name='Misaka', age=23}
User{name='mikoto', age=24}
實現Comparator 外部比較器代碼示例:
public class CollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparator<User> comparator = new Comparator<User>() {
public int compare(User o1, User o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.getAge(),o2.getAge());
}
};
TreeSet<User> treeSet = new TreeSet(comparator);
treeSet.add(new User("mikoto",24));
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",23));
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",3));
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",5));
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",6));
treeSet.add(new User("Misaka",1));
Iterator<User> iterator = treeSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
User user = iterator.next();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
輸出結果:
User{name='Misaka', age=1}
User{name='Misaka', age=3}
User{name='Misaka', age=5}
User{name='Misaka', age=6}
User{name='Misaka', age=23}
User{name='mikoto', age=24}



