第一、基本概念 棧中的元素遵守“先進後出”的原則(LIFO,Last In First Out) 只能在棧頂進行插入和刪除操作 壓棧(或推入、進棧)即push,將數據放入棧頂並將棧頂指針加一 出棧(或彈出)即pop,將數據從棧頂刪除並將棧頂指針減一 棧的基本操作有:pop,push,判斷空,獲取棧頂 ...
第一、基本概念
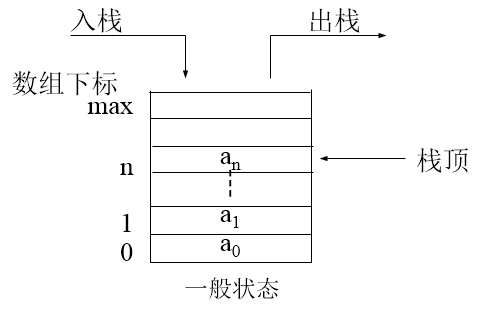
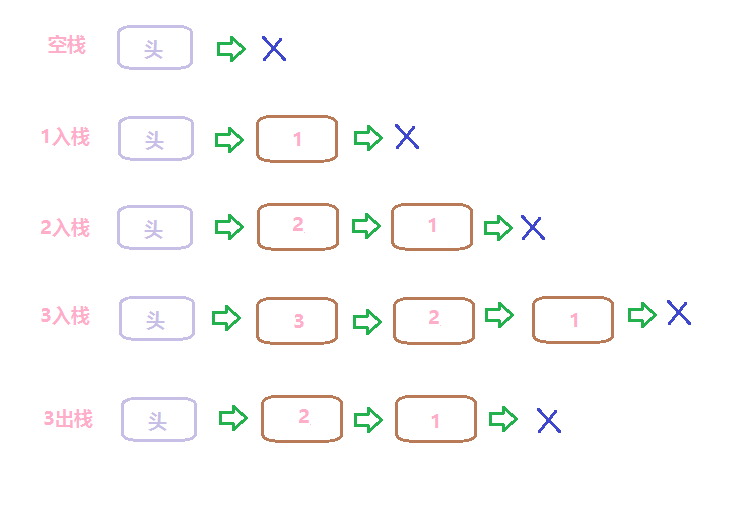
棧中的元素遵守“先進後出”的原則(LIFO,Last In First Out)
只能在棧頂進行插入和刪除操作
壓棧(或推入、進棧)即push,將數據放入棧頂並將棧頂指針加一
出棧(或彈出)即pop,將數據從棧頂刪除並將棧頂指針減一
棧的基本操作有:pop,push,判斷空,獲取棧頂元素,求棧大小
第二、實現方式
棧一般 採用數組或者鏈表2中方式實現,各有各的特點,我這裡採用倒插法鏈表實現
第三、代碼實現

#pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> struct node { T value; //儲存的值 node<T>* next; node() :next(nullptr) {}; node(T t) : value(t), next(nullptr) {} }; template <typename T> class Stack { int length; //入棧數量 node<T> *head; //棧的頭部 public: Stack() { length = 0; head = new node<T>; } void push(T arg); //入棧 T pop(); //出棧 T top(); //獲取棧頂元素 void print(); //列印棧 int size(); //獲取棧內元素個數 bool isEmpty(); //判斷空 }; template<typename T> void Stack<T>::push(T arg) { node<T>* pnode = new node<T>(arg); pnode->next = head->next; head->next = pnode; length++; } template<typename T> T Stack<T>::pop() { if (head->next!=NULL) { node<T>* pnode = head->next; T pdata = pnode->value; head->next = head->next->next; delete pnode; return pdata; } } template<typename T> T Stack<T>::top() { while (head->next!=NULL) { return head->next->value; } } template<typename T> void Stack<T>::print() { while (head->next != NULL) { head = head->next; cout << head->value << endl; } } template<typename T> int Stack<T>::size() { return length; } template<typename T> bool Stack<T>::isEmpty() { return length == 0; }View Code
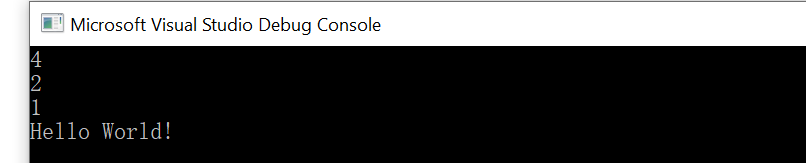
測試
#include "pch.h" #include "Stack.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { Stack<int> st; st.push(1); st.push(2); st.push(4); st.print(); std::cout << "Hello World!\n"; }