因為Pthread很少用到,所以對於Pthread的知識沒有摳那麼細緻,所以將Pthread和 NSThread放在了一起。 4.1 Pthread 4.1-1.0 創建線程 - pthread_create 4.1-1.1 __bridge 橋接 <!--?xml version="1.0" en ...
因為Pthread很少用到,所以對於Pthread的知識沒有摳那麼細緻,所以將Pthread和 NSThread放在了一起。
4.1 Pthread
4.1-1.0 創建線程 - pthread_create
1 /* 2 <#pthread_t *restrict#> 線程的id,指向線程標識符的指針,C 語言中類型的結尾通常 _t/Ref,而且不需要使用 * 3 <#const pthread_attr_t *restrict#> 用來設置線程的屬性 (一般為 NULL) 4 <#void *(*)(void *)#> 新建立的線程執行代碼的函數,線程開啟後需要調用的函數或方法 (指向函數的指針) 5 <#void *restrict#> 運行函數的參數,線程的限制 (一般為 NULL) 6 */ 7 8 返回值: 9 - 若線程創建成功,則返回0 10 - 若線程創建失敗,則返回出錯編號 11 12 pthread_create( 13 <#pthread_t *restrict#>, // pthread_t :線程標識符. 14 <#const pthread_attr_t *restrict#>, 15 <#void *(*)(void *)#>, 16 <#void *restrict#> 17 );
4.1-1.1 __bridge 橋接
__bridge 橋接:| 1、在c語言和OC之間,對數據類型進行轉成換 2、通過橋接告訴c語言的函數,name就由C語言去管了 |
| 橋接的目的 : 就是為了告訴編譯器如何管理記憶體,為OC添加自動記憶體管理操作 |
|
|
1 首先導入頭文件 2 3 #import <pthread.h> 4 5 代碼創建: 6 7 // 創建線程,並且線上程中執行 demo 函數 8 - (void)pthreadDemo { 9 10 pthread_t threadId = NULL; 11 NSString *str = @"Hello Pthread"; 12 13 int result = pthread_create(&threadId, NULL, demo, (__bridge void *)(str)); 14 15 if (result == 0) { 16 NSLog(@"創建線程 OK"); 17 } else { 18 NSLog(@"創建線程失敗 %d", result); 19 } 20 } 21 22 // 後臺線程調用函數 23 void *demo(void *params) { 24 NSString *str = (__bridge NSString *)(params); 25 26 NSLog(@"%@ - %@", [NSThread currentThread], str); 27 28 return NULL; 29 }
4.2 NSThread
4.2-1.0 創建線程
|
1 創建方式1 : 通過NSThread的對象方法 (先創建初始化線程alloc/init , 再 start 開啟線程) ——調試方便 2 3 NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:<#(nonnull id)#> 4 selector:<#(nonnull SEL)#> 5 object:<#(nullable id)#> ];
1 #import "ViewController.h" 2 3 @interface ViewController () 4 @end 5 6 @implementation ViewController 7 8 - (void)viewDidLoad { 9 [super viewDidLoad]; 10 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 11 } 12 13 - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { 14 [self threadDemo1]; 15 } 16 17 #pragma mark - 對象方法alloc/init 18 /* 19 - 在 OC 中,任何一個方法的代碼都是從上向下順序執行的 20 - 同一個方法內的代碼,都是在相同線程執行的(block除外) 21 */ 22 - (void)threadDemo1 { 23 NSLog(@"before %@", [NSThread currentThread]); 24 25 // 線程一啟動,就會線上程thread中執行self的run方法 26 NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self 27 selector:@selector(longOperation:) 28 object:@"THREAD"]; 29 30 //開啟線程,通過start方法,就會將我們創建出來的當前線程加入到`可調度線程池`,供CPU調度 31 //[thread start];執行後,會在另外一個線程執行 longOperation: 方法 32 [thread start]; 33 34 NSLog(@"after %@", [NSThread currentThread]); 35 } 36 37 - (void)longOperation:(id)obj { 38 NSLog(@"%@ - %@", [NSThread currentThread], obj); 39 } 40 41 - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { 42 [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; 43 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 44 } 45 46 @end
列印結果:
2016-03-17 18:19:41.878 創建線程1 - 對象方法[2543:387435] before <NSThread: 0x7ffd28c00ca0>{number = 1, name = main}
2016-03-17 18:19:41.880 創建線程1 - 對象方法[2543:387711] <NSThread: 0x7ffd28d77be0>{number = 2, name = (null)} - THREAD
2016-03-17 18:19:41.880 創建線程1 - 對象方法[2543:387435] after <NSThread: 0x7ffd28c00ca0>{number = 1, name = main}
4.2-1.1.1 Target
NSThread 的實例化方法中的 target 指的是開啟線程後,線上程中執行 哪一個對象 的 @selector 方法1 NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self.person 2 selector:@selector(longOperation:) 3 object:@"THREAD"]; 4 5 [thread start];
- 通過指定不同的 target 會在後臺線程執行該對象的 @selector 方法
- 不要看見 target 就寫 self
4.2-1.2 創建線程2 - 類方法
1 創建方式2 : 通過NSThread的類方法 (創建線程後直接自動啟動線程) 2 3 [NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:<#(nonnull SEL)#> 4 toTarget:<#(nonnull id)#> 5 withObject:<#(nullable id)#> ];
1 #import "ViewController.h" 2 3 @interface ViewController () 4 @end 5 6 @implementation ViewController 7 8 - (void)viewDidLoad { 9 [super viewDidLoad]; 10 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 11 } 12 13 - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { 14 [self threadDemo2]; 15 } 16 17 #pragma mark - 類方法 18 - (void)threadDemo2 { 19 NSLog(@"before %@", [NSThread currentThread]); 20 21 // detachNewThreadSelector 類方法不需要啟動,會自動創建線程並執行@selector方法 22 // 它會自動給我們做兩件事 : 1.創建線程對象 2.添加到`可調度線程池` 23 // 通過NSThread的類和NSObject的分類方法直接加入到可調度線程池裡面去,等待CPU調度 24 [NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(longOperation:) 25 toTarget:self 26 withObject:@"DETACH"]; 27 28 NSLog(@"after %@", [NSThread currentThread]); 29 } 30 31 - (void)longOperation:(id)obj { 32 NSLog(@"%@ - %@", [NSThread currentThread], obj); 33 } 34 35 - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { 36 [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; 37 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 38 } 39 40 @end
列印結果:
2016-03-17 18:36:05.339 創建線程2 - 類方法[2647:404930] before <NSThread: 0x7fddf8f01eb0>{number = 1, name = main}
2016-03-17 18:36:05.340 創建線程2 - 類方法[2647:404930] after <NSThread: 0x7fddf8f01eb0>{number = 1, name = main}
2016-03-17 18:36:05.340 創建 線程2 - 類方法[2647:405061] <NSThread: 0x7fddf8e0e7a0>{number = 2, name = (null)} - DETACH
4.2-1.3 創建線程3 - 分類方法(NSObject)
1 創建方式3 : 通過NSObject的分類方法 (隱式創建並直接自動啟動線程) ——推薦,開發常用 2 3 // 此方法在後臺線程中執行 (即是 : 在子線程中執行) 4 [self performSelectorInBackground:<#(nonnull SEL) #> 5 withObject:<#(nullable id) #> per];
1 #import "ViewController.h" 2 3 @interface ViewController () 4 @end 5 6 @implementation ViewController 7 8 - (void)viewDidLoad { 9 [super viewDidLoad]; 10 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 11 } 12 13 - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { 14 [self threadDemo3]; 15 } 16 17 #pragma mark - 分類方法 18 - (void)threadDemo3 { 19 NSLog(@"before %@", [NSThread currentThread]); 20 21 // performSelectorInBackground 是NSObject的分類方法,會自動在後臺線程執行@selector方法 22 // 沒有 thread 字眼,隱式創建並啟動線程 23 // 所有 NSObject 都可以使用此方法,在其他線程執行方法 24 // 通過NSThread的類和NSObject的分類方法直接加入到可調度線程池裡面去,等待CPU調度 25 // PerformSelectorInBackground 可以讓方便地在後臺線程執行任意NSObject對象的方法 26 [self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(longOperation:) 27 withObject:@"PERFORM"]; 28 29 NSLog(@"after %@", [NSThread currentThread]); 30 } 31 32 - (void)longOperation:(id)obj { 33 NSLog(@"%@ - %@", [NSThread currentThread], obj); 34 } 35 36 - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { 37 [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; 38 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 39 } 40 41 @end
列印結果:
2016-03-17 18:41:58.696 創建線程3 - 分類方法[2711:412522] before <NSThread: 0x7ff078c02320>{number = 1, name = main}
2016-03-17 18:41:58.696 創建線程3 - 分類方法[2711:412522] after <NSThread: 0x7ff078c02320>{number = 1, name = main}
2016-03-17 18:41:58.697 創建線程3 - 分類方法[2711:412751] <NSThread: 0x7ff078c0e390>{number = 2, name = (null)} - PERFORM
| 方式2和方式3的優缺點 : |
| 優點:簡單快捷 缺點:無法對線程進行更詳細的設置 |
4.2-2.0 線程屬性
1 主線程相關方法 : 2 3 + (NSThread *)mainThread; // 獲得主線程 4 - (BOOL)isMainThread; // 是否為主線程 5 + (BOOL)isMainThread; // 是否為主線程 6 7 NSThread *main = [NSThread mainThread]; // + (NSThread *)mainThread; 獲得主線程 8 9 [NSThread isMainThread]; // + (BOOL)isMainThread; 類方法判斷,該方法是否為主線程 10 11 [main isMainThread]; // - (BOOL)isMainThread; 對象方法判斷,該對象是否為主線程
1 其他用法: 2 (1) currentThread - 獲得當前線程 : 3 4 舉例 : 5 NSThread *current = [NSThread currentThread]; //獲得當前線程 6 7 (2) threadPriority - 線程的調度優先順序 : 8 9 優先順序,是一個浮點數,取值範圍從 0~1.0 預設優先順序是0.5 值越大,優先順序越高 10 11 優先順序高只是保證 CPU 調度的可能性會高 12 13 建議:在開發的時候,不要修改優先順序 14 多線程的目的:是將耗時的操作放在後臺,不阻塞主線程和用戶的交互! 15 多線程開發的原則:簡單 16 17 //返回當前方法所線上程的優先順序 18 + (double)threadPriority; 19 舉例:[NSThread threadPriority]; 20 21 //設置線程的優先順序 22 + (BOOL)setThreadPriority:(double)p; 23 舉例:self.thread1.threadPriority = 1.0; 24 25 - (double)threadPriority;//返回當前方法所線上程的優先順序 26 - (BOOL)setThreadPriority:(double)p;//設置線程的優先順序 27 28 (3) name - 線程的名字 : 在大的商業項目中,通常需要在程式崩潰時,獲取程式準確執行所在的線程 29 30 - (void)setName:(NSString *)n; //set 方法 31 - (NSString *)name; //get 方法 32 33 舉例: 34 thread.name = @"線程A"; 35 36 (4) stackSize - 棧區大小 37 38 - 預設情況下,無論是主線程還是子線程,棧區大小都是 512K 39 - 棧區大小雖然可以設置,但是我們一般都使用系統預設的大小就行了 40 41 舉例: 42 [NSThread currentThread].stackSize = 1024 * 1024;
代碼示例:
1 // 線程屬性 2 - (void)threadProperty { 3 NSThread *t1 = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self 4 selector:@selector(demo) 5 object:nil]; 6 7 // 1. 線程名稱 8 t1.name = @"Thread AAA"; 9 10 // 2. 優先順序 11 t1.threadPriority = 0; 12 13 [t1 start]; 14 15 NSThread *t2 = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self 16 selector:@selector(demo) 17 object:nil]; 18 // 1. 線程名稱 19 t2.name = @"Thread BBB"; 20 // 2. 優先順序 21 t2.threadPriority = 1; 22 23 [t2 start]; 24 } 25 26 - (void)demo { 27 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { 28 // 堆棧大小 29 NSLog(@"%@ 堆棧大小:%tuK", [NSThread currentThread],[NSThread currentThread].stackSize / 1024); 30 } 31 32 // 模擬崩潰 33 // 判斷是否是主線程 34 if (![NSThread currentThread].isMainThread) { 35 NSMutableArray *a = [NSMutableArray array]; 36 [a addObject:nil]; 37 } 38 }
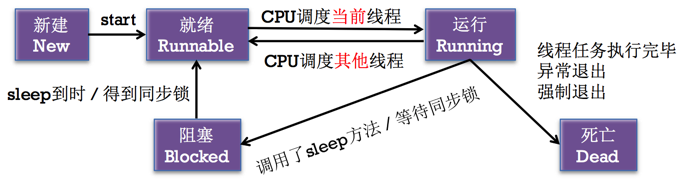
4.2-3.0 線程狀態/線程生命周期
|
線程開啟 : 線程進入可調度線程池
|
|
|
1 方法執行過程,符合某一條件時,可以利用 sleep 方法讓線程進入 阻塞 狀態 2 3 sleepForTimeInterval: //休眠指定時長 (從現在起睡多少秒) 4 sleepUntilDate: //休眠到指定日期 (從現在起睡到指定的日期) 5 @synchronized(self) { } //互斥鎖 6 7 (1)阻塞2秒 8 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2]; // 阻塞狀態 9 10 (2)以當前時間為基準阻塞4秒 11 NSDate *date = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:4.0]; //從現在開始多少秒 12 [NSThread sleepUntilDate:date]; //睡眠多少秒(5)死亡狀態 (一旦線程停止或死亡了,就不能再次開啟任務 , 後續的所有代碼都不會被執行 )
(1) 正常死亡
|
 代碼示例:
代碼示例:
1 #import "ViewController.h" 2 3 @interface ViewController () 4 @end 5 6 @implementation ViewController 7 8 - (void)viewDidLoad { 9 [super viewDidLoad]; 10 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 11 } 12 13 - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { 14 15 // 1.在主線程中創建一個子線程(實例化線程對象) ---> 新建狀態 16 NSThread *Th = 17 [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run) object:nil]; 18 19 // 2.將 Th 線程加入到可調度線程池,等待CPU調度--->就緒狀態 20 [Th start]; 21 22 // 3.讓主線程阻塞,讓當前線程(主線程)休眠 23 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:1.0]; 24 25 // 4.在主線程給 Th 線程打死亡標簽 26 [Th cancel]; //只是打了個標簽,並沒有執行,需要在子線程中 27 } 28 29 // Th 線程---> 運行狀態 30 - (void)run { 31 32 NSThread *huThread = [NSThread currentThread]; 33 34 CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable(); 35 36 for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { 37 if ([huThread isCancelled]) { 38 NSLog(@"good bye1"); 39 return; // --->非正常死亡(被逼著死亡) 40 } 41 42 if (i == 5) { 43 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:3.0]; //--->huThread阻塞狀態3秒 44 // [NSThread sleepUntilDate:[NSDate distantFuture]]; // 睡到遙遠的未來 45 // [NSThread sleepUntilDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:2]]; //線程睡到從現在開始後的2秒為止 46 } 47 48 if ([huThread isCancelled]) { 49 NSLog(@"good bye2"); 50 return; 51 } 52 53 if (i == 20) { 54 //清空資源 55 CGPathRelease(path); 56 57 //在調用下麵方法之前,必須清空資源 非正常死亡--自殺(退出線程) 58 [NSThread exit]; 59 } 60 61 if ([huThread isCancelled]) { 62 NSLog(@"good bye3"); 63 return; 64 } 65 NSLog(@"%d", i); 66 } 67 } //--->huThread死亡狀態 (正常死亡狀態) 68 69 - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { 70 [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; 71 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 72 } 73 74 @end
4.2-4.1 多線程安全隱患 - 資源共用/搶奪
| (1) 起因 : 資源共用概念 : 1塊資源可能會被多個線程共用,也就是多個線程可能會訪問同一塊資源 主要是因為多條線程,對`同一資源同時操作`,導致的問題 |
| (2) 舉例 : 比如多個線程訪問同一個對象、同一個變數、同一個文件 |
| (3) 結果 : 當多個線程訪問同一塊資源時,很容易引發數據錯亂和數據安全問題 (資源強奪) |
| (4) 解決方案 : 互斥鎖 / 同步鎖 |
多線程開發的複雜度相對較高,在開發時可以按照以下套路編寫代碼:
|
1 #import "ViewController.h" 2 3 @interface ViewController () 4 @property(nonatomic, strong) NSThread *thread01; // 售票員01 5 @property(nonatomic, strong) NSThread *thread02; // 售票員02 6 @property(nonatomic, strong) NSThread *thread03; // 售票員03 7 8 @property(nonatomic, assign) NSInteger ticketCount; //票的總數 9 @end 10 11 @implementation ViewController 12 13 - (void)viewDidLoad { 14 [super viewDidLoad]; 15 // Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib. 16 17 self.ticketCount = 10; 18 19 //創建線程 20 self.thread01 = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self 21 selector:@selector(saleTicket) 22 object:nil]; 23 self.thread01.name = @"售票員01"; 24 25 self.thread02 = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self 26 selector:@selector(saleTicket) 27 object:nil]; 28 self.thread02.name = @"售票員02"; 29 30 self.thread03 = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self 31 selector:@selector(saleTicket) 32 object:nil]; 33 self.thread03.name = @"售票員03"; 34 } 35 36 // 開啟線程 37 - (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { 38 [self.thread01 start]; 39 [self.thread02 start]; 40 [self.thread03 start]; 41 } 42 43 // 賣票 44 - (void)saleTicket { 45 46 while (1) { 47 48 @synchronized(self) { //互斥鎖(控制器做鎖對象) 49 // 先取出總數 50 NSInteger count = self.ticketCount; 51 52 // 判斷還有沒有餘票 53 if (count > 0) { 54 self.ticketCount = count - 1; 55 NSLog(@"%@賣了一張票,還剩下%zd張", [NSThread currentThread].name, 56 self.ticketCount); 57 } else { 58 NSLog(@"票已經賣完了"); 59 break; 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 - (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning { 66 [super didReceiveMemoryWarning]; 67 // Dispose of any resources that can be recreated. 68 }


