Python 語音:與機器進行語音交流,讓機器明白你說什麼,這是人們長期以來夢寐以求的事情。 語音識別是一門交叉學科。近二十年來,語音識別技術取得顯著進步,開始從實驗室走向市場。人們預計,未來10年內,語音識別技術將進入工業、家電、通信、汽車電子、醫療、家庭服務、消費電子產品等各個領域。 語音識別... ...
Python 語音
實現語音操控的原理
語音操控分為語音識別和語音朗讀兩部分我們使用speech模塊實現語音模塊(python 2.7)
SAPI是微軟Speech API , 是微軟公司推出的語音介面,而細心的人會發現從WINXP開始,系統上就已經有語音識別的功能了,可是用武之地相當之少,他並沒有給出一些人性化的自定義方案,僅有的語音操控命令顯得相當雞脅。
- Python pywin32,可以使Python調用WIN32COM介面,選擇對應版本下載(區分32位/64位),直接雙擊運行即可
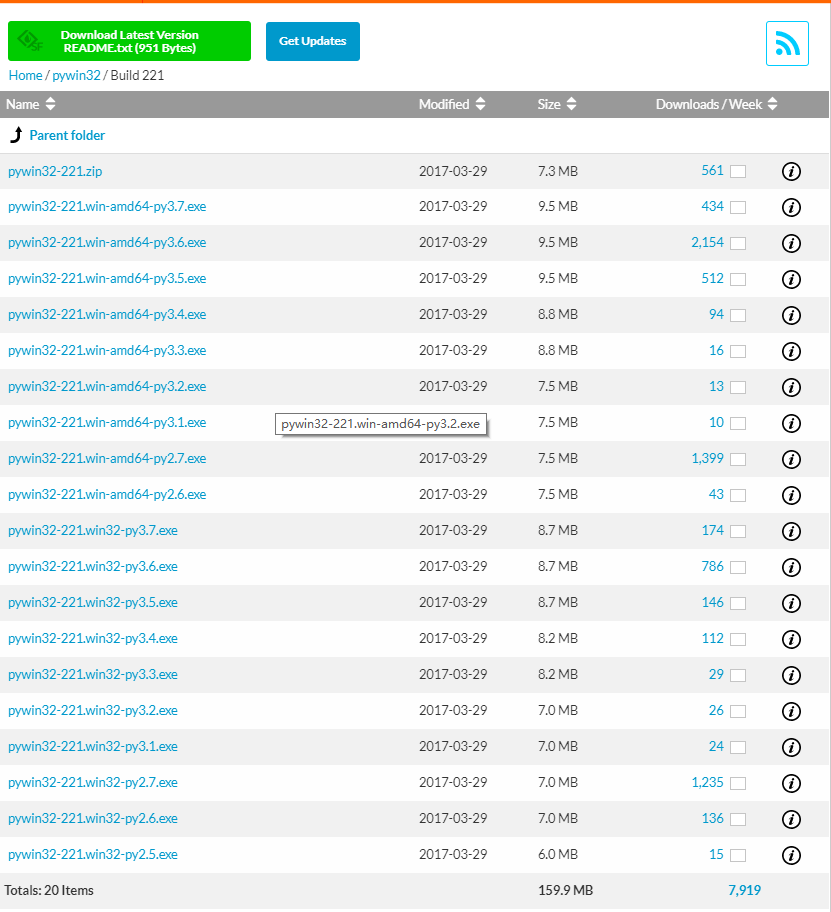
- 安裝speech模塊:
pip install speech
實現個簡易的控制電腦做事情的小程式:
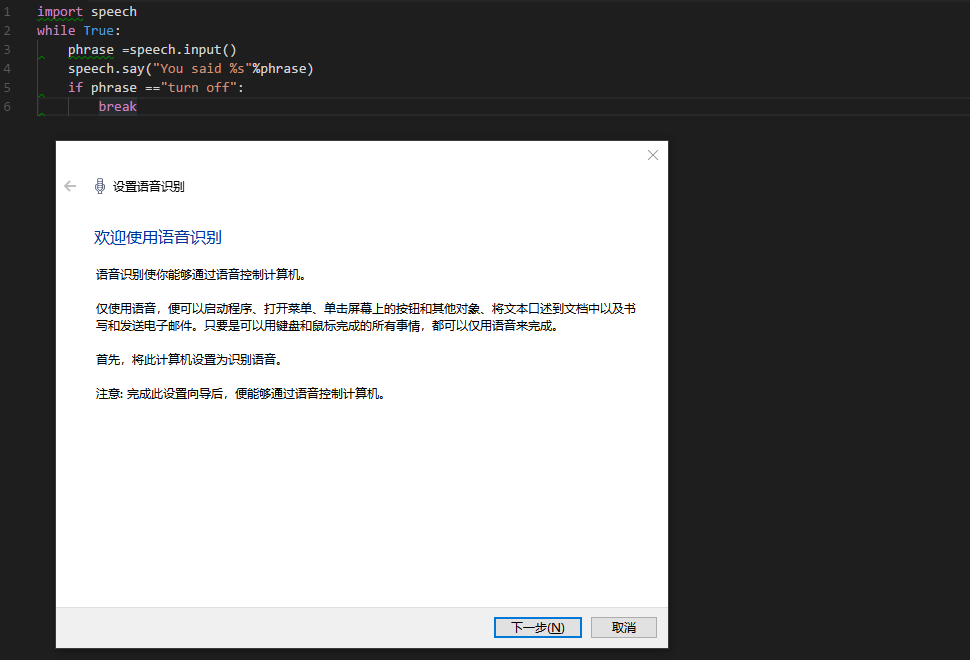
- 首先,來個測試文件
此處僅為啟動和關閉語音系統
import speech
while True:
phrase =speech.input()
speech.say("You said %s"%phrase)
if phrase =="turn off":
break
- 自製個中文庫
phrase = {"closeMainSystem" : "關閉人機交互"
, "film" : "我要看電影"
, "listenMusic" : "我好累啊"
, "blog" : "看博客"
, "cmd" : "cmd" }
- 設計語音對應的電腦操作
def callback(phr, phrase):
if phr == phrase["closeMainSystem"]:
speech.say("Goodbye. 人機交互即將關閉,謝謝使用")
speech.stoplistening()
sys.exit()
elif phr == phrase["film"]:
speech.say("正在為您打開優酷")
webbrowser.open_new("http://www.youku.com/")
elif phr == phrase["listenMusic"]:
speech.say("即將為你啟動豆瓣電臺")
webbrowser.open_new("http://douban.fm/")
elif phr == phrase["blog"]:
speech.say("即將進入Dreamforce.me")
webbrowser.open_new("http://www.cnblogs.com/darksouls/")
elif phr == phrase["cmd"]:
speech.say("即將打開CMD")
os.popen("C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe")
# 可以繼續用 elif 寫對應的自製中文庫中的對應操作
- 主程式
while True:
phr = speech.input()
speech.say("You said %s" % phr)
callback(phr, phrase)
- 完整代碼
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
import os
import sys
import speech
import webbrowser
phrase = {"closeMainSystem" : "關閉人機交互"
, "film" : "我要看電影"
, "listenMusic" : "我好累啊"
, "blog" : "看博客"
, "cmd" : "cmd" }
def callback(phr, phrase):
if phr == phrase["closeMainSystem"]:
speech.say("Goodbye. 人機交互即將關閉,謝謝使用")
speech.stoplistening()
sys.exit()
elif phr == phrase["film"]:
speech.say("正在為您打開優酷")
webbrowser.open_new("http://www.youku.com/")
elif phr == phrase["listenMusic"]:
speech.say("即將為你啟動豆瓣電臺")
webbrowser.open_new("http://douban.fm/")
elif phr == phrase["blog"]:
speech.say("即將進入Dreamforce.me")
webbrowser.open_new("http://www.cnblogs.com/darksouls/")
elif phr == phrase["cmd"]:
speech.say("即將打開CMD")
os.popen("C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe")
# 可以繼續用 elif 寫對應的自製中文庫中的對應操作
while True:
phr = speech.input()
speech.say("You said %s" % phr)
callback(phr, phrase)
發現網上有個語音識別框架:
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
from win32com.client import constants
import os
import win32com.client
import pythoncom
speaker = win32com.client.Dispatch("SAPI.SPVOICE")
class SpeechRecognition:
def __init__(self, wordsToAdd):
self.speaker = win32com.client.Dispatch("SAPI.SpVoice")
self.listener = win32com.client.Dispatch("SAPI.SpSharedRecognizer")
self.context = self.listener.CreateRecoContext()
self.grammar = self.context.CreateGrammar()
self.grammar.DictationSetState(0)
self.wordsRule = self.grammar.Rules.Add("wordsRule", constants.SRATopLevel + constants.SRADynamic, 0)
self.wordsRule.Clear()[self.wordsRule.InitialState.AddWordTransition(None, word) for word in wordsToAdd]
self.grammar.Rules.Commit()
self.grammar.CmdSetRuleState("wordsRule", 1)
self.grammar.Rules.Commit()
self.eventHandler = ContextEvents(self.context)
self.say("Started successfully")
def say(self, phrase):
self.speaker.Speak(phrase)
class ContextEvents(win32com.client.getevents("SAPI.SpSharedRecoContext")):
def OnRecognition(self, StreamNumber, StreamPosition, RecognitionType, Result):
newResult = win32com.client.Dispatch(Result)
print("你在說 ", newResult.PhraseInfo.GetText())
speechstr=newResult.PhraseInfo.GetText()
# 下麵即為語音識別信息對應
if speechstr=="張三":
speaker.Speak("lisi")
elif speechstr=="你好":
speaker.Speak("hello world")
elif speechstr=="國慶快樂":
speaker.Speak("Happy nationalday")
elif speechstr=="新年快樂":
speaker.Speak("happy New Year")
elif speechstr=="李四":
speaker.Speak("a beauty baby")
elif speechstr=="王五":
speaker.Speak("a little boy")
elif speechstr=="趙六":
speaker.Speak("a boy can coding")
else:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
speaker.Speak("語音識別開啟")
wordsToAdd = ["張三",
"你好",
"國慶快樂",
"新年快樂",
"李四",
"王五",
"趙六",]
speechReco = SpeechRecognition(wordsToAdd)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()



