本文從IO流的繼承體系方面做了簡要的說明,並對常見的IO流進行了介紹並提供了簡單的實例。 ...
IO流位於java.io包中,根據操作數據不同,分為位元組流和字元流;根據數據輸入方面的不同又可分為輸入流和輸出流,無論是何種流,最終都依賴於操作系統。 一、位元組流: 1、位元組流,主要用於圖片、音頻、視頻的傳輸,以二進位的形式進行,分為位元組輸入流和位元組輸出流;位元組流操作的是位元組數組;字元流操作的是字元數組。 2、位元組輸入與位元組輸出流的繼承體系圖
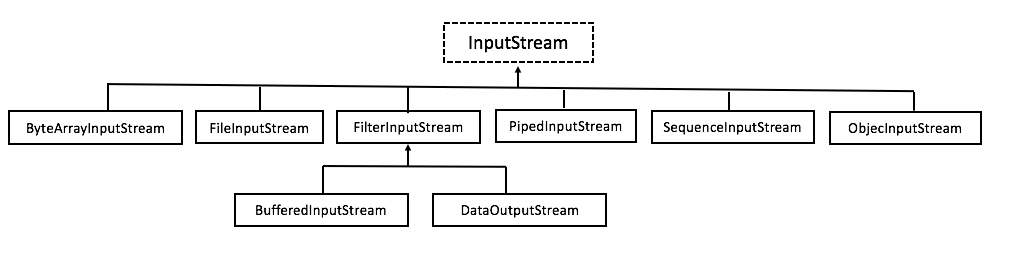
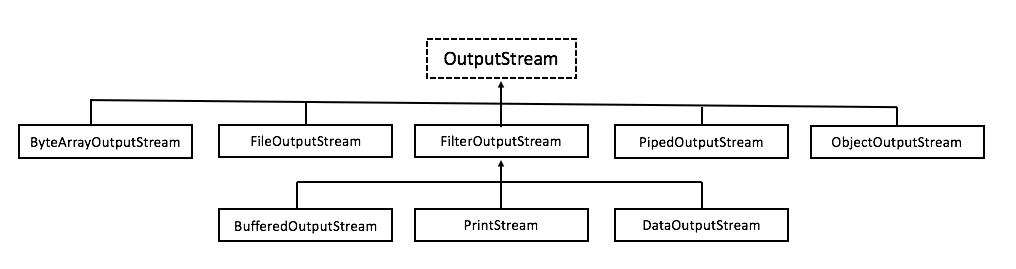
| InputStream 常用方法 | |
| 方法聲明 | 功能描述 |
| int read() | 從輸入流讀取一個8位的位元組,把它轉換為0-255之間的整數,並返回這一整數 |
| int read(byte[] b) | 從輸入流讀取若幹位元組,把它們保存到參數b指定的位元組數組中,返回的整數表示讀取的位元組數 |
| int read(byte[] b,int off,len) | 從輸入流讀取若幹位元組,把它們保存到參數b指定的位元組數組中,off指定位元組數組開始保存數據的起始下標,len表示讀取的位元組 |
| void close() | 關閉此輸入流並釋放與該流關聯的所有系統資源 |
| OutputStream 常用方法 | |
| 方法聲明 | 功能描述 |
| void write(int b) | 向輸出流寫入一個位元組 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 把參數b指定的位元組數組的所有位元組寫到輸出流 |
| void write(byte[] b,int off,len) | 將指定byte數組中從偏移量off開始的len個位元組寫入輸出流 |
| void flush() | 刷新此輸出流並強制寫出所有緩衝的輸出位元組 |
| void close() | 關閉此輸出流並釋放與該流關聯的所有系統資源 |

1 public class Example01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 //創建一個文件位元組型輸入流 4 InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt"); 5 int b = 0; //定義一個int類型的變數b,記住每一次讀取的一個位元組 6 while (true){ 7 b=inputStream.read();//變數b記住讀取的一個位元組 8 if(b==-1){ //如果讀取的位元組為-1,跳出while迴圈 9 break; 10 } 11 System.out.println(b); //否則將b寫出 12 } 13 inputStream.close(); 14 15 //創建一個文件位元組輸出流 16 OutputStream OutputStream= new FileOutputStream("example.txt",true); 17 String string = "人之初"; 18 byte [] bytes= string.getBytes(); 19 for (int i = 0;i<bytes.length;i++){ 20 OutputStream.write(bytes[i]); 21 } 22 OutputStream.close(); 23 } 24 }View Code 文件拷貝:

1 public class Example04 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 //創建一個位元組輸入流,用於讀取當前目錄下source文件中的docx文件 4 InputStream in = new FileInputStream("source/IO工具包.mp4") ; 5 //創建一個文件位元組輸出流,用於將讀取的數據寫入target目錄下的文件中 6 OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("target/IO工具包.mp4"); 7 byte [] buff = new byte[1024]; //定義一個位元組數組,作為緩衝區 8 int len; //定義一個int類型的變數len記住讀取讀入緩衝區的位元組數 9 // int len = 0 ; //定義一個int類型變數,記住每次讀取的一個位元組 10 long begintime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 11 while ((len=in.read(buff))!=-1){ //判斷是否讀到文件末尾 12 out.write(buff,0,len); //從第一位元組開始,向文件寫入len個位元組 13 } 14 long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 15 System.out.println("耗時"+(endtime-begintime)+"毫秒"); 16 in.close(); 17 out.close(); 18 } 19 }View Code 5、裝飾設計模式思想:
TextReader:讀取文本; MediaReader:讀取媒體數據; 抽取共性,形成體系。 Reader |---TextReader read() |---MediaReader 需求1: 提高讀取文本的效率,使用緩衝技術,提供一個讀取文本更高效的讀取方法。 覆蓋TextReader中的方法。建立高效的read方法。所以建立一個TextReader的子類,用於高效的讀取。 Reader |---TextReader read() |--BufferedTextReader |---MediaReader 需求2: 提高讀取媒體數據的效率,派生一個高效的子類,用於高效的讀取。 Reader |---TextReader read() |--BufferedTextReader |---MediaReader |--BufferedMediaReader 發現一個小問題,如果Reader中還有讀取其他數據的子類,如果要高效,那豈不是還要給這個子類添加一個高效子類? 是的,為了給具體的讀取數據的對象增加一些功能,是需要通過子類來完成的。 但是這樣做,會導致這個繼承體系很臃腫!僅僅為了增加一些功能,而進行繼承,不建議的。 這些子類無非就是需要高效,而且這些高效的功能實現是一致的。就是提供一個緩衝區而以。 乾脆,單獨定義一個具備這個緩衝功能的對象,哪個子類需要被緩衝,就將哪個子類傳遞進來。 class BufferedReader extends Reader{ private [];//提供數據 BufferedReader(Reader r){ //對Reader高效就行 } read(){操作的是數組} //高效的讀取動作 } 此時繼承體系: Reader |---TextReader |---MediaReader |---BufferedReader 發現這種設計方式減少了繼承體系的臃腫,增減功能,比繼承更為靈活。 這種設計方式稱為:裝飾設計模式。 解決問題:給一組類增加功能,避免繼承的臃腫,提高靈活。 註意:裝飾類和被裝飾類必須屬於同一體系,通常裝飾類都會提供構造函數接收被裝飾類對象。裝飾類通常不單獨存在。6、位元組緩衝流 使用的是裝飾設計模式 示例:

1 public class Example07 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 //創建一個帶緩衝區的輸入流 4 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream( 5 new FileInputStream("src.txt")); 6 //創建一個帶緩衝區的輸出流 7 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream( 8 new FileOutputStream("des.txt")); 9 int len; 10 while ((len=bis.read())!=-1){ 11 bos.write(len); 12 } 13 bis.close(); 14 bos.close(); 15 } 16 }View Code 二、字元流 1、字元流:為了便於操作數據中的字元數據。原理:位元組流+編碼表。 2、字元流繼承體系
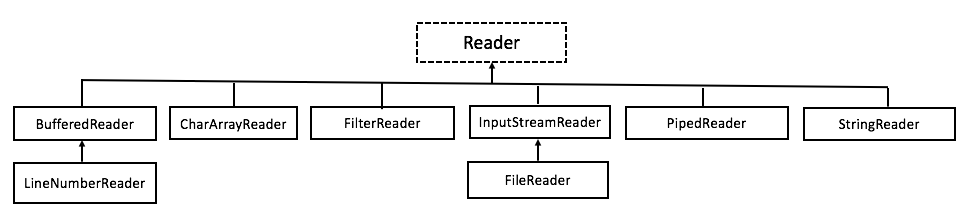
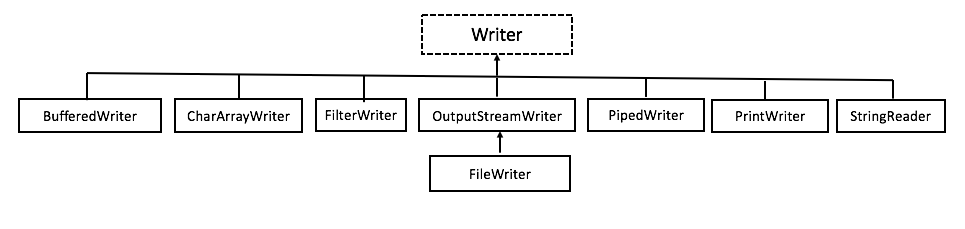
| Reader方法摘要 | |
| abstract void close() | 關閉該流並釋放與之關聯的所有資源。 |
| void mark(int readAheadLimit) | 標記流中的當前位置。 |
| boolean markSupported() | 判斷此流是否支持 mark() 操作。 |
| int read() | 讀取單個字元。 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 將字元讀入數組。 |
| abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 將字元讀入數組的某一部分。 |
| int read(CharBuffer target) | 試圖將字元讀入指定的字元緩衝區。 |
| boolean ready() | 判斷是否準備讀取此流。 |
| void reset() | 重置該流。 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳過字元。 |
| Writer方法摘要 | |
| void close() | 關閉此流,但要先刷新它。 |
| void flush() | 刷新該流的緩衝。 |
| String getEncoding() | 返回此流使用的字元編碼的名稱。 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 寫入字元數組的某一部分。 |
| void write(int c) | 寫入單個字元。 |
| void write(String str, int off, int len) | 寫入字元串的某一部分。 |
flush()和close()的區別? flush();將流中的緩衝區緩衝中的數據刷新到目的地中,刷新後,流還可以繼續使用; close();關閉資源,但在關閉前會將緩衝區中的數據刷新到目的地,否則丟失數據,然後再關閉流,流不可以使用。 如果寫入數據多,一邊寫一邊刷新,最後一次可以不刷新,由close()完成刷新並關閉。4、字元流操作文件 FileReader 和FileWriter 用於讀寫文件;BufferedReader 和BufferdeWriter是具有緩衝功能的流,可以提高讀寫效率。 BufferedReader中有一重要的方法readLind(),該方法用於一次讀取一行文本。

1 public class Example10 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 FileReader reader = new FileReader("src.txt"); 4 //創建一個BufferedReader緩衝對象 5 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 6 FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("des.txt"); 7 //創建一個BufferedWriter緩衝對象 8 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(writer); 9 String string; 10 while ((string=br.readLine())!=null){ 11 bw.write(string); 12 bw.newLine();//寫入一個換行符,該方法會根據不同的操作系統生成相應的換行符 13 } 14 br.close(); 15 bw.close(); 16 } 17 }View Code
BufferedReader一直接子類——LineNumberReader ,一個可以跟蹤行號的輸入流。

1 public class Example11 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 FileReader fr = new FileReader("/Users/Shared/第八章IO練習/exampele09.txt"); //創建字元輸入流 4 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("copy.txt");//創建字元輸出流 5 LineNumberReader lr = new LineNumberReader(fr); //包裝 6 lr.setLineNumber(0); //設置讀取文件的起始行號 7 String line = null; 8 while ((line=lr.readLine())!=null){ 9 fw.write(lr.getLineNumber()+":"+line);//將行號寫入到文件中 10 fw.write("\r\n"); //寫入換行 11 } 12 lr.close(); 13 fw.close(); 14 } 15 }View Code 5、轉換流 轉換流是一種字元流,只能實現位元組流讀寫文本數據的時候,通過轉換流來使用字元高效流的方法。而不能實現圖片、音頻等數據的讀寫。 InputStreamReader:理解上是位元組流通向字元流的橋梁,使用上為:
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));OutputStreamWriter:理解上是字元流通向位元組流的橋梁,使用上還是通過位元組流轉成字元流:
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));

1 public class Example12 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 FileInputStream in= new FileInputStream("src1.txt");//創建位元組輸入流 4 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);//將位元組流輸入轉換成字元輸入流 5 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);//對字元流對象進行包裝 6 FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("des1.txt"); 7 //將位元組流轉換為字元輸出流 8 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(out); 9 //對字元輸出流對象進行包裝 10 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 11 String line; 12 while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){ //判斷是否讀到文件末尾 13 bw.write(line); //輸出讀取到文件 14 } 15 br.close(); 16 bw.close(); 17 } 18 }View Code
三、其他IO流
1、ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream 序列化:把對象按照流一樣的方式傳輸或者存儲。(ObjectOutputStream). 當對象進行序列化時,必須保證該對象實現Serializable介面,否則程式會出現NotSerializableException異常。 反序列號:把網路中的流數據或者文件中的流數據(二進位數據)還原成對象。(ObjectInputStream).
1 public class Example13 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 //序列化對象 4 Person person = new Person("p1","zhangsan",20); 5 //創建文件輸出流對象,將數據寫入objectStream.txt 6 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("objectStream.txt"); 7 //創建對象輸出流對象,用於處理輸出流對象寫入的數據 8 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos); 9 //將Person對象輸出到輸出流中 10 oos.writeObject(person); 11 oos.close(); 12 13 //反序列化對象 14 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("object.txt"); 15 //創建文件輸入流對象,用於讀取指定文件的數據 16 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis); 17 //創建對象輸入流,並且從指定的輸入流中過讀取數據 18 Object p = ois.readObject(); 19 System.out.println(p); 20 ois.close(); 21 } 22 } 23 class Person implements Serializable{ 24 private String id; 25 private String name; 26 private int age; 27 public Person(String id, String name, int age) { 28 super(); 29 this.id = id; 30 this.name = name; 31 this.age = age; 32 } 33 public String getId() { 34 return id; 35 } 36 public String getName() { 37 return name; 38 } 39 public int getAge() { 40 return age; 41 } 42 }View Code 2、DataInputStream,DataOutputStream 有時候並不需要存儲整個對象的信息,而只需要存儲對象的成員數據,這些成員數據的類型又都是基本數據類型,可使用數據操作流:DataInputStream,DataOutputStream 。

1 public class Example15 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream( 4 new FileOutputStream("/Users/Shared/ioexample/dataStream.txt")); 5 DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos); 6 dos.writeByte(12); //寫一個位元組 7 dos.writeChar('1'); //寫一個字元 8 dos.writeBoolean(true); //寫一個布爾值 9 dos.writeUTF("同學,你好"); //寫一個轉換成UTF-8的字元串 10 dos.close(); //關閉流 11 BufferedInputStream bis= new BufferedInputStream( 12 new FileInputStream("/Users/Shared/ioexample/dataStream.txt")); 13 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis); 14 System.out.println(dis.readByte()); //讀取一個位元組 15 System.out.println(dis.readChar()); //讀取一個字元 16 System.out.println(dis.readBoolean()); //讀取一個布爾值 17 System.out.println(dis.readUTF()); //讀一個轉換成UTF-8編碼的字元串 18 dis.close (); //關閉流 19 } 20 }View Code 只有讀取數據的順序與寫數據的順序保持一致,才能保證最終數據的正常性。 3、列印流PrintStream

1 public class Example16 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream( 4 new FileOutputStream("printStream.txt",true)); 5 Student stu = new Student(); 6 ps.print("這是一個數字"); 7 ps.println(19); 8 ps.println(stu); 9 } 10 } 11 class Student { 12 @Override 13 public String toString() { 14 return "我是一個學生"; 15 } 16 }View Code 4、標準輸入輸出流(in、out、err)

1 public class Example17 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 4 int ch; 5 //while迴圈用於讀取鍵盤輸入的數據 6 while ((ch=System.in.read())!=-1){ //判斷是否讀取到數據的末尾 7 //對輸入的字元進行判斷,如果是回車"\r"或者換行"\n",則跳出迴圈 8 if(ch =='\r' || ch=='\n'){ 9 break; 10 } 11 sb.append((char)ch); //將讀取到的數據添加到sb中 12 } 13 System.out.println (sb); //列印鍵盤輸入的數據 14 } 15 }View Code
| 重定向流常用的靜態方法 | |
| 方法聲明 | 功能描述 |
| void setIn(InputStream in) | 對標準輸入流重定向 |
| void setOut(PrintStream out) | 對標準輸出流重定向 |
| void setErr(PrintStream out) | 對標準錯誤輸出流重定向 |

1 public class Example19 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 final PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream();//創建PipedInputStream對象 4 final PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream(); 5 //PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream建立連接,也可寫成pos.connect(pis) 6 pis.connect(pos); 7 new Thread(new Runnable(){ //創立線程 8 public void run(){ 9 //將從鍵盤讀取的數據寫入管道流中 10 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 11 //將從鍵盤讀取的數據寫入管道流中 12 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(pos); 13 while (true){ 14 try{ 15 System.out.println(br.readLine()); 16 Thread.sleep(1000); 17 }catch (Exception e){ 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 },"發送數據的線程").start(); 23 new Thread(new Runnable() { 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 //下麵代碼是從管道流中讀取數據,每讀一行數據輸出一次 27 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(pis)); 28 while (true){ 29 try{ 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"收到的內容:"+br.readLine()); 31 }catch (IOException e){ 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 },"接收數據的線程").start(); 37 } 38 }View Code 6、ByteArrayOutputStream、ByteArrayInputStream 將數據寫入(讀取)到緩衝區,最後一次性寫入(輸出)到文件。 如果讀取的文件非常大,就不能使用這個列,否則會造成記憶體溢出。

1 public class Example20 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 //將數據寫入緩衝區中 4 FileInputStream fs = new FileInputStream("source.txt"); 5 //創建一個字接數據緩衝區 6 ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 7 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("target1.txt"); 8 //下麵的代碼是迴圈讀取緩衝區中的數據,並將數據一次性寫入文件 9 int b1; 10 while ((b1=fs.read())!=-1){ 11 bos.write(b1); 12 } 13 fs.close(); 14 bos.close(); 15 fos.write(bos.toByteArray());//將緩衝區中的數據一次性寫入文件 16 fos.close(); 17 18 //讀取緩衝區中的數據 19 byte[] bufs = new byte[]{97,98,99,100};//創建一個位元組數組 20 ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bufs);//讀取位元組數組中的數據 21 //下麵代碼是迴圈讀取緩衝區中的數據 22 int b2; 23 while ((b2=bis.read())!=-1){ 24 System.out.println((char)b2); 25 } 26 bis.close(); 27 } 28 }View Code 7、CharArrayReader和CharArrayWriter 將字元型數據臨時存入緩衝區。





