1. Callable、Future、RunnableFuture、FutureTask的繼承關係 在多線程編程中,我們一般通過一個實現了Runnable介面的對象來創建一個線程,這個線程在內部會執行Runnable對象的run方法。如果說我們創建一個線程來完成某項工作,希望在完成以後該線程能夠返回...
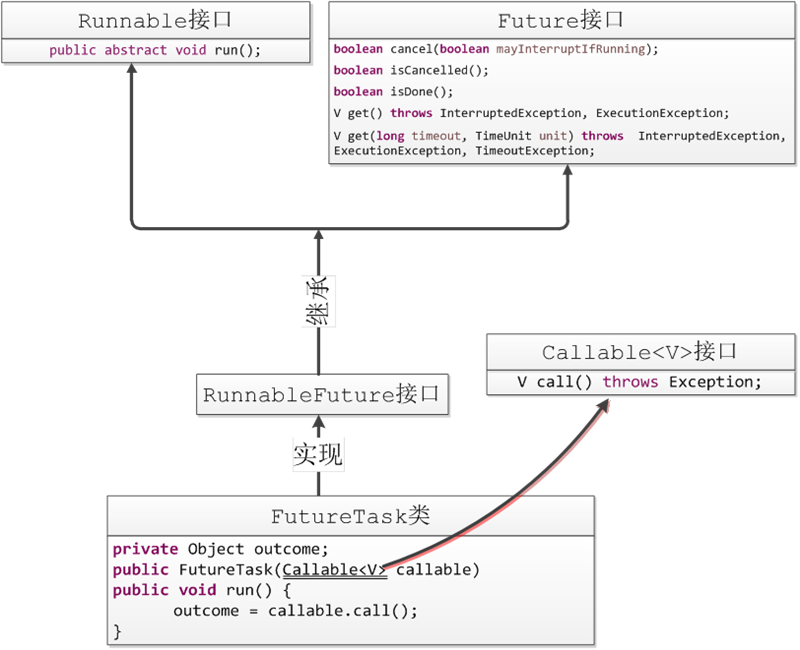
1. Callable、Future、RunnableFuture、FutureTask的繼承關係
在多線程編程中,我們一般通過一個實現了Runnable介面的對象來創建一個線程,這個線程在內部會執行Runnable對象的run方法。如果說我們創建一個線程來完成某項工作,希望在完成以後該線程能夠返回一個結果,但run方法的返回值是void類型,直接實現run方法並不可行,這時我們就要通過FutureTask類來間接實現。
FutureTask實現了RunnableFuture介面,而RunnableFuture介面實際上僅僅是Runnable介面和Future介面的合體。Future介面提供取消任務、檢測任務是否執行完成、等待任務執行完成獲得結果等方法。從圖中可以看出,FutureTask類中的run方法已經實現好了(圖中的代碼僅僅是核心代碼),這個run方法實際上就是調用了由構造函數傳遞進來的call方法,並將返回值存儲在FutureTask的私有數據成員outcome中。這樣一來我們將FutureTask傳遞給一個Thread時,錶面上我們仍然執行的是run,但在run方法的內部實際上執行的是帶有返回值的call方法,這樣即使得java多線程的執行框架保持不變,又實現了線程完成後返回結果的功能。同時FutureTask又將結果存儲在outcome中,我們可以通過調用FutureTask對象的get方法獲取outcome(也就是call方法的返回結果)。
| Future介面功能介紹 | |
| boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); | 功能:設置線程的中斷標誌位 參數:mayInterruptIfRunning為ture,如果線程可以取消則設置線程的中斷標誌位 返回值:若線程已經完成,返回false;否則返回true 註意:要實現取消線程執行的功能,call函數需要在迴圈條件中檢查中斷標誌位,以跳出迴圈 |
| boolean isCancelled(); | 判斷線程是否取消 |
| boolean isDone(); | 線程執行完成,返回true;如果cancel方法返回true,則該方法也返回true |
| V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; | 獲取call方法的返回結果,如果call方法沒有執行完成,則會阻塞當前線程,直到call方法執行完畢,才被喚醒 |
| V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 設置時限的get方法。 |
2. Future及FutureTask的使用
Future以及FutureTask是線程池實現的基礎元素,但不是說Future及FutureTask只能線上程池中才能使用,下麵的例子就說明瞭FutureTask獨立使用的情況。在這個例子中,我們首先隨機產生了2000個整數存於數組中,然後創建了兩個線程,一個線程尋找前1000個數的最大值,另個一線程尋找後1000個數的最大值。主線程比較這兩個線程的返回結果來確定這2000個數的最大值值。
package javaleanning; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class FutureDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException{ int[] a = new int[2000]; Random rd = new Random(); for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++){ a[i] = rd.nextInt(20000); } class FindMax implements Callable<Integer>{ private int begin,end,int a[]; public FindMax(int a[],int begin, int end){ this.a = a;this.begin = begin; this.end = end; } @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int maxInPart = a[begin]; for(int i = begin; i <= end; i++){ if(a[i] > maxInPart){ maxInPart = a[i]; } } return new Integer(maxInPart); } } FutureTask<Integer> findMaxInFirstPart =new FutureTask<Integer>(new FindMax(a,0,999)); FutureTask<Integer> findMaxInSecondPart =new FutureTask<Integer>(new FindMax(a,1000,1999)); new Thread(findMaxInFirstPart).start(); new Thread(findMaxInSecondPart).start(); int maxInFirst = (int) findMaxInFirstPart.get(); int maxInSecond = (int) findMaxInSecondPart.get(); System.out.println("Max is " +(maxInFirst > maxInSecond ? maxInFirst:maxInSecond)); //驗證結果是否正確 int max = a[0]; for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++){ if(a[i] > max){ max = a[i]; } } System.out.println(max); } }
3. FutureTask的實現原理
構造函數
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) { if (callable == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.callable = callable; this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable } public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) { this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result); this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable }
FutureTask有兩個構造函數,通常來說我們使用第一個構造函數。這裡要強調一下第二個構造函數,它有兩個類型參數,分別是Runnable類型和泛型V,然後由這兩個構造一個Callable對象。當線程運行結束以後會返回由構造函數傳遞進來的這個泛型result對象,也就是說返回的值並不是通過運行得到的,而是由構造函數獲取的一個指定的對象。
重要數據成員
private volatile int state; private Object outcome; private volatile Thread runner; private volatile WaitNode waiters;
state表明瞭線程運行call方法的狀態,初始狀態為0,完成後由run方法將其設置為1。通過get方法獲取結果時就必須檢查state的值,如果該值為0,表明需要等待該結果,get方法就會將當前線程阻塞。
outcome表示了call方法的返回結果
runner表示運行FutureTask方法的線程,其值會在run方法中進行初始化
waiters指向了因獲取結果而等待的線程組成的隊列
重要方法
public void run() { if (state != NEW || !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, null, Thread.currentThread())) return; try { Callable<V> c = callable; if (c != null && state == NEW) { V result; boolean ran; try { result = c.call(); ran = true; } catch (Throwable ex) { result = null; ran = false; setException(ex); } if (ran) set(result); } } finally { // runner must be non-null until state is settled to // prevent concurrent calls to run() runner = null; // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent // leaked interrupts int s = state; if (s >= INTERRUPTING) handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); } }
從代碼中可以看出run方法中調用了從構造函數傳遞來的call方法。
protected void set(V v) { if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) { outcome = v; UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state finishCompletion(); } }
當call方法執行完畢後,run方法調用又調用了set方法,它主要實現兩個功能,一個是將結果賦值給outcome,另一個是通過finishCompletion喚醒由調用此FutureTask對象的get方法而阻塞的線程
private void finishCompletion() { // assert state > COMPLETING; for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) { if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) { for (;;) { Thread t = q.thread; if (t != null) { q.thread = null; LockSupport.unpark(t); } WaitNode next = q.next; if (next == null) break; q.next = null; // unlink to help gc q = next; } break; } } done(); callable = null; // to reduce footprint }
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { int s = state; if (s <= COMPLETING) s = awaitDone(false, 0L); return report(s); }
在get方法中首先判斷了state的值,如果call方法還未完成,就會通過awaitDone來阻塞自己。
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException { final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L; WaitNode q = null; boolean queued = false; for (;;) { if (Thread.interrupted()) { removeWaiter(q); throw new InterruptedException(); } int s = state; if (s > COMPLETING) { if (q != null) q.thread = null; return s; } else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet Thread.yield(); else if (q == null) q = new WaitNode(); else if (!queued) queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q.next = waiters, q); else if (timed) { nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime(); if (nanos <= 0L) { removeWaiter(q); return state; } LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos); } else LockSupport.park(this); } }
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { if (!(state == NEW && UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED))) return false; try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception if (mayInterruptIfRunning) { try { Thread t = runner; if (t != null) t.interrupt(); } finally { // final state UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED); } } } finally { finishCompletion(); } return true; }
在cannel方法中,如果允許對線程中斷,則設置該線程的中斷標誌位,並通過finishCompletion方法喚醒因等待結果而阻塞的線程。
參考文章
[1] http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3949310.html
[2] http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1384351141649.html