多線程基本概念 多線程實現方案 1.pthread 2.NSThread (1)基本使用 (2)設置線程屬性 (3)線程的狀態 (4)線程安全 (5)線程間通信 (6)如何計算代碼段的執行時間 3.GCD (1)GCD基本知識 兩個核心概念 隊列和任務 同步函數和非同步函數 (2)GCD基本使用【重點 ...
多線程基本概念
01 進程
進程是指在系統中正在運行的一個應用程式。每個進程之間是獨立的,每個進程均運行在其專用且受保護的記憶體空間內。
02 線程
2-1 基本概念
1個進程要想執行任務,必須得有線程(每1個進程至少要有1條線程),線程是進程的基本執行單元,一個進程(程式)的所有任務都線上程中執行。
2-2 線程的串列
1個線程中任務的執行是串列的,如果要在1個線程中執行多個任務,那麼只能一個一個地按順序執行這些任務。也就是說,在同一時間內,1個線程只能執行1個任務。
03 多線程
3-1 基本概念
即1個進程中可以開啟多條線程,每條線程可以並行(同時)執行不同的任務。
3-2 線程的並行
並行即同時執行。比如同時開啟3條線程分別下載3個文件(分別是文件A、文件B、文件C。
3-3 多線程併發執行的原理
在同一時間里,CPU只能處理1條線程,只有1條線程在工作(執行)。多線程併發(同時)執行,其實是CPU快速地在多條線程之間調度(切換),如果CPU調度線程的時間足夠快,就造成了多線程併發執行的假象
3-4 多線程優缺點
優點
1)能適當提高程式的執行效率。
2)能適當提高資源利用率(CPU、記憶體利用率)
缺點
1)開啟線程需要占用一定的記憶體空間(預設情況下,主線程占用1M,子線程占用512KB),如果開啟大量的線程,會占用大量的記憶體空間,降低程式的性能。
2)線程越多,CPU在調度線程上的開銷就越大。
3)程式設計更加複雜:比如線程之間的通信、多線程的數據共用
04 多線程在iOS開發中的應用
4-1 主線程
1)一個iOS程式運行後,預設會開啟1條線程,稱為“主線程”或“UI線程”。
2)作用。刷新顯示UI,處理UI事件。
4-2 使用註意
1)不要將耗時操作放到主線程中去處理,會卡住線程。
2)和UI相關的刷新操作必須放到主線程中進行處理。
多線程實現方案
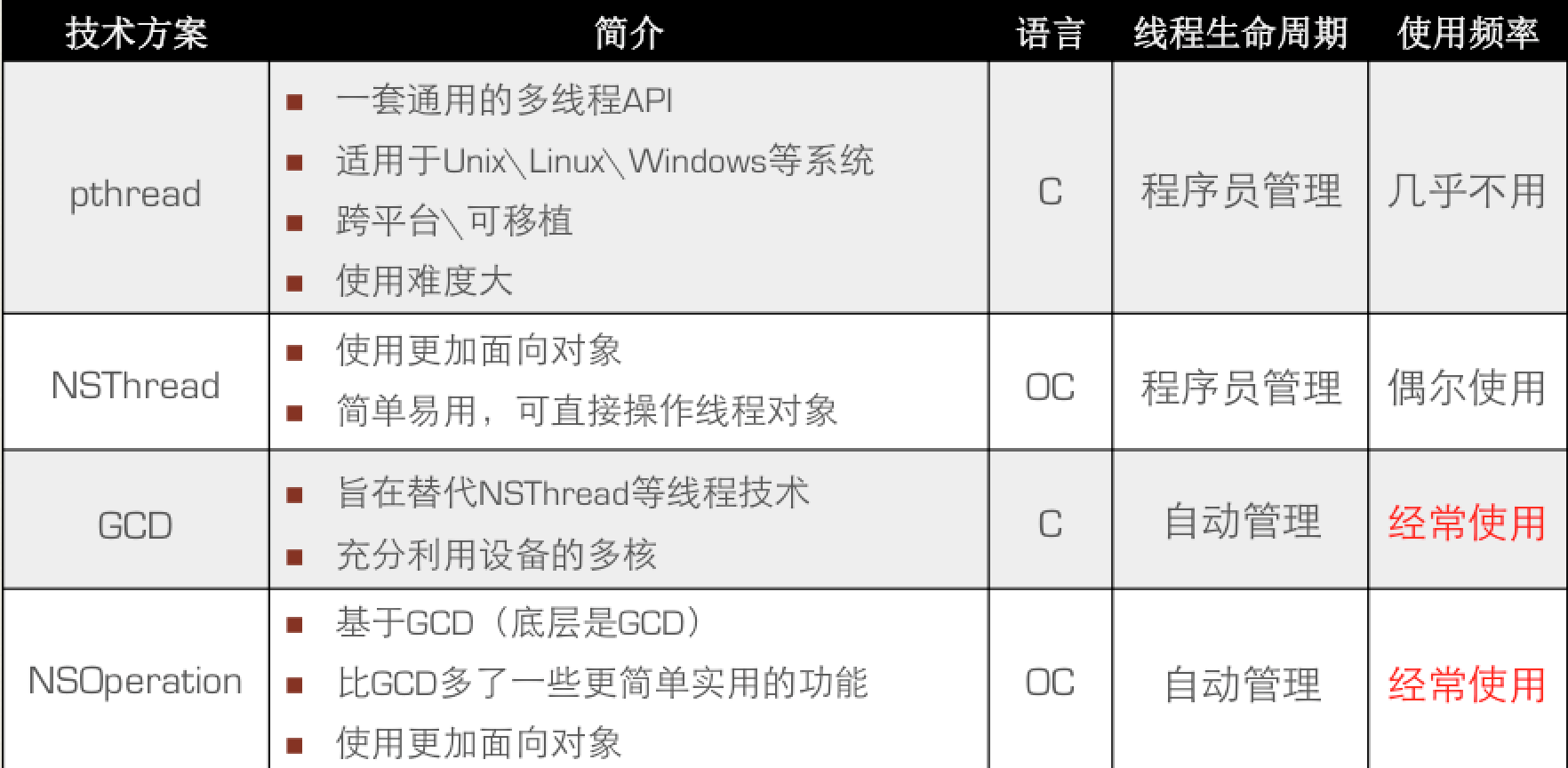
1.pthread
//pthread需要包含頭文件
//1.創建線程對象
pthread_t thread;
NSString *name = @"線程";
//2.使用pthread創建線程
//第一個參數:線程對象地址
//第二個參數:線程屬性
//第三個參數:指向函數的指針
//第四個參數:傳遞給該函數的參數
pthread_create(&thread, NULL, run, (__bridge void *)(name));2.NSThread
(1)基本使用
**第一種:alloc init**
需要手動開啟線程,可以拿到線程對象進行詳細設置
//1.創建線程
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run:) object:@"線程"];
//2.啟動線程
[thread start];
**第二種:分離(detach)出一條子線程**
自動啟動線程,無法對線程進行更詳細的設置
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(run:) toTarget:self withObject:@"分離出的子線程"];
**第三種:後臺線程**
自啟動,不能詳細設置
[self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(run:) withObject:@"後臺線程"];(2)設置線程屬性
//線程名稱
thread.name = @"線程A";
//線程的優先順序,取值範圍0.0~1.0,1.0的優先順序最高,預設0.5
thread.threadPriority = 1.0;(3)線程的狀態
//線程的各種狀態:新建-就緒-運行-阻塞-死亡
//常用的控制線程狀態的方法
[NSThread exit];//退出當前線程
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2.0];//阻塞線程
[NSThread sleepUntilDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:2.0]];//阻塞線程
//註意:線程死了不能復生(4)線程安全
01 前提:多個線程訪問同一塊資源會發生數據安全問題
02 解決方案:加互斥鎖
03 相關代碼:@synchronized(self){}
04 專業術語-線程同步
05 原子和非原子屬性(是否對setter方法加鎖)
(5)線程間通信
-(void)touchesBegan:(nonnull NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event
{
//開啟子線程下載圖片
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(downloadImage) toTarget:self withObject:nil];
}
-(void)downloadImage
{
//1.確定圖片url
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://p6.qhimg.com/t01d2954e2799c461ab.jpg"];
//2.根據url地址下載圖片數據到本地(二進位數據)
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
//3.把下載到本地的二進位數據轉換成圖片
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
//4.回到主線程刷新UI
//4.1 第一種方式
// [self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(showImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:YES];
//4.2 第二種方式
[self.imageView performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(setImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:YES];
//4.3 第三種方式
// [self.imageView performSelector:@selector(setImage:) onThread:[NSThread mainThread] withObject:image waitUntilDone:YES];
}(6)如何計算代碼段的執行時間
//第一種方法
NSDate *start = [NSDate date];
//2.根據url地址下載圖片數據到本地(二進位數據)
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
NSDate *end = [NSDate date];
NSLog(@"第二步操作花費的時間為%f",[end timeIntervalSinceDate:start]);
//第二種方法
CFTimeInterval start = CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
CFTimeInterval end = CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();
NSLog(@"第二步操作花費的時間為%f",end - start);3.GCD
(1)GCD基本知識
- 兩個核心概念 隊列和任務
- 同步函數和非同步函數
(2)GCD基本使用【重點】

(3)GCD線程間通信
//0.獲取一個全局的隊列
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0);
//1.先開啟一個線程,把下載圖片的操作放在子線程中處理
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
//2.下載圖片
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://h.hiphotos.baidu.com/zhidao/pic/item/6a63f6246b600c3320b14bb3184c510fd8f9a185.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
NSLog(@"下載操作所在的線程--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
//3.回到主線程刷新UI
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
self.imageView.image = image;
//列印查看當前線程
NSLog(@"刷新UI---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
});
});(4)GCD其它常用函數
01 柵欄函數(控制任務的執行順序)
dispatch_barrier_async(queue, ^{
NSLog(@"--dispatch_barrier_async-");
});
02 延遲執行(延遲·控制在哪個線程執行)
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(2.0 * NSEC_PER_SEC)), dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^{
NSLog(@"---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
});
03 一次性代碼(註意不能放到懶載入)
-(void)once
{
//整個程式運行過程中只會執行一次
//onceToken用來記錄該部分的代碼是否被執行過
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
NSLog(@"-----");
});
}
04 快速迭代(開多個線程併發完成迭代操作)
dispatch_apply(subpaths.count, queue, ^(size_t index) {
});
05 隊列組(同柵欄函數)
//創建隊列組
dispatch_group_t group = dispatch_group_create();
//隊列組中的任務執行完畢之後,執行該函數
dispatch_group_notify(dispatch_group_t group,
dispatch_queue_t queue,
dispatch_block_t block);4.NSOperation
(1)概念
- NSOperation是對GCD的包裝
- 兩個核心概念【隊列+操作】
(2)使用
- NSOperation本身是抽象類,只能只有它的子類
- 三個子類分別是:NSBlockOperation、NSInvocationOperation以及自定義繼承自NSOperation的類
- NSOperation和NSOperationQueue結合使用實現多線程併發
(3)代碼
// 1.NSInvocationOperation
//1.封裝操作
NSInvocationOperation *operation = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run) object:nil];
//2.啟動操作
[operation start];
-------------------------------------------------
// 2.NSBlockOperation
//1.封裝操作
/*
NSBlockOperation提供了一個類方法,在該類方法中封裝操作
*/
NSBlockOperation *operation = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
//在主線程中執行
NSLog(@"---download1--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
//2.追加操作,追加的操作在子線程中執行
[operation addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"---download2--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
[operation addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"---download3--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
//3.啟動執行操作
[operation start];
----------------------------------------------
// 3.自定義NSOperation
//如何封裝操作?
//自定義的NSOperation,通過重寫內部的main方法實現封裝操作
-(void)main
{
NSLog(@"--main--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}
//如何使用?
//1.實例化一個自定義操作對象
ZCOperation *op = [[ZCOperation alloc]init];
//2.執行操作
[op start];NSOperationQueue
(1)NSOperation中的兩種隊列
- 主隊列 通過mainQueue獲得,凡是放到主隊列中的任務都將在主線程執行
- 非主隊列 直接alloc init出來的隊列。非主隊列同時具備了併發和串列的功能,通過設置最大併發數屬性來控制任務是併發執行還是串列執行
(2)代碼
//自定義NSOperation
-(void)customOperation
{
//1.創建隊列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封裝操作
//好處:1.信息隱蔽
//2.代碼復用
ZCOperation *op1 = [[ZCOperation alloc]init];
ZCOperation *op2 = [[ZCOperation alloc]init];
//3.添加操作到隊列中
[queue addOperation:op1];
[queue addOperation:op2];
}
//NSBlockOperation
- (void)block
{
//1.創建隊列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封裝操作
NSBlockOperation *op1 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"1----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
NSBlockOperation *op2 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"2----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
[op2 addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"3----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
[op2 addExecutionBlock:^{
NSLog(@"4----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
//3.添加操作到隊列中
[queue addOperation:op1];
[queue addOperation:op2];
//補充:簡便方法
[queue addOperationWithBlock:^{
NSLog(@"5----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
}
//NSInvocationOperation
- (void)invocation
{
/*
GCD中的隊列:
串列隊列:自己創建的,主隊列
併發隊列:自己創建的,全局併發隊列
NSOperationQueue
主隊列:[NSOperationQueue mainqueue];凡事放在主隊列中的操作都在主線程中執行
非主隊列:[[NSOperationQueue alloc]init],併發和串列,預設是併發執行的
*/
//1.創建隊列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封裝操作
NSInvocationOperation *op1 = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(download1) object:nil];
NSInvocationOperation *op2 = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(download2) object:nil];
NSInvocationOperation *op3 = [[NSInvocationOperation alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(download3) object:nil];
//3.把封裝好的操作添加到隊列中
[queue addOperation:op1];//[op1 start]
[queue addOperation:op2];
[queue addOperation:op3];
}
(3)NSOperation其它用法
設置最大併發數【控制任務併發和串列】
//1.創建隊列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.設置最大併發數
//註意點:該屬性需要在任務添加到隊列中之前進行設置
//該屬性控制隊列是串列執行還是併發執行
//如果最大併發數等於1,那麼該隊列是串列的,如果大於1那麼是並行的
//系統的最大併發數有個預設的值,為-1,如果該屬性設置為0,那麼不會執行任何任務
queue.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 2;暫停和恢復以及取消
//設置暫停和恢復
//suspended設置為YES表示暫停,suspended設置為NO表示恢復
//暫停表示不繼續執行隊列中的下一個任務,暫停操作是可以恢復的
if (self.queue.isSuspended) {
self.queue.suspended = NO;
}else
{
self.queue.suspended = YES;
}
//取消隊列裡面的所有操作
//取消之後,當前正在執行的操作的下一個操作將不再執行,而且永遠都不在執行,就像後面的所有任務都從隊列裡面移除了一樣
//取消操作是不可以恢復的
[self.queue cancelAllOperations];
---------自定義NSOperation取消操作--------------------------
-(void)main
{
//耗時操作1
for (int i = 0; i<1000; i++) {
NSLog(@"任務1-%d--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
NSLog(@"+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
//蘋果官方建議,每當執行完一次耗時操作之後,就查看一下當前隊列是否為取消狀態,如果是,那麼就直接退出
//好處是可以提高程式的性能
if (self.isCancelled) {
return;
}
//耗時操作2
for (int i = 0; i<1000; i++) {
NSLog(@"任務1-%d--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
NSLog(@"+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
}(3)NSOperation實現線程間通信
開子線程下載圖片
//1.創建隊列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.使用簡便方法封裝操作並添加到隊列中
[queue addOperationWithBlock:^{
//3.在該block中下載圖片
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://news.51sheyuan.com/uploads/allimg/111001/133442IB-2.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
NSLog(@"下載圖片操作--%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
//4.回到主線程刷新UI
[[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] addOperationWithBlock:^{
self.imageView.image = image;
NSLog(@"刷新UI操作---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
}];
下載多張圖片合成綜合案例(設置操作依賴)
//02 綜合案例
- (void)download2
{
NSLog(@"----");
//1.創建隊列
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
//2.封裝操作下載圖片1
NSBlockOperation *op1 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://h.hiphotos.baidu.com/zhidao/pic/item/6a63f6246b600c3320b14bb3184c510fd8f9a185.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
//拿到圖片數據
self.image1 = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
}];
//3.封裝操作下載圖片2
NSBlockOperation *op2 = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://pic.58pic.com/58pic/13/87/82/27Q58PICYje_1024.jpg"];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
//拿到圖片數據
self.image2 = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
}];
//4.合成圖片
NSBlockOperation *combine = [NSBlockOperation blockOperationWithBlock:^{
//4.1 開啟圖形上下文
UIGraphicsBeginImageContext(CGSizeMake(200, 200));
//4.2 畫image1
[self.image1 drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 0, 200, 100)];
//4.3 畫image2
[self.image2 drawInRect:CGRectMake(0, 100, 200, 100)];
//4.4 根據圖形上下文拿到圖片數據
UIImage *image = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext();
// NSLog(@"%@",image);
//4.5 關閉圖形上下文
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
//7.回到主線程刷新UI
[[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]addOperationWithBlock:^{
self.imageView.image = image;
NSLog(@"刷新UI---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}];
}];
//5.設置操作依賴
[combine addDependency:op1];
[combine addDependency:op2];
//6.添加操作到隊列中執行
[queue addOperation:op1];
[queue addOperation:op2];
[queue addOperation:combine];
}補充
使用create函數創建的併發隊列和全局併發隊列的主要區別:
1.全局併發隊列在整個應用程式中本身是預設存在的,並且對應有高優先順序、預設優先順序、低優先順序和後臺優先順序一共四個併發隊列,我們只是選擇其中的一個直接拿來用。而create函數是實打實的從頭開始去創建一個隊列。
2.在iOS6.0之前,在GCD中凡是使用了帶create和retain的函數在最後都需要做一次release操作。而主隊列和全局併發隊列不需要我們手動release。當然了,在iOS6.0之後GCD已經被納入到了ARC的記憶體管理範疇中,即便是使用retain或者create函數創建的對象也不再需要開發人員手動釋放,我們像對待普通OC對象一樣對待GCD就OK。
3.在使用柵欄函數的時候,蘋果官方明確規定柵欄函數只有在和使用create函數自己的創建的併發隊列一起使用的時候才有效(沒有給出具體原因)
4.其它區別涉及到XNU內核的系統級線程編程,不一一列舉。
5.給出一些參考資料(可以自行研究):
GCDAPI:https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/Performance/Reference/GCD_libdispatch_Ref/index.html#//apple_ref/c/func/dispatch_queue_create
Libdispatch版本源碼:http://www.opensource.apple.com/source/libdispatch/libdispatch-187.5/

