CSS實現居中對齊的幾種方式 頁面佈局中,居中對齊是我們經常遇到的場景,現在總結幾個常用的方式供大家參考。 場景一:按鈕文字居中對齊,line-height + text-align html代碼: <div class="btn">Hello World</div> CSS代碼: .btn{ wi ...
CSS實現居中對齊的幾種方式
頁面佈局中,居中對齊是我們經常遇到的場景,現在總結幾個常用的方式供大家參考。
場景一:按鈕文字居中對齊,line-height + text-align
html代碼:
<div class="btn">Hello World</div>
CSS代碼:
.btn{
width: 120px;
height: 48px;
border: none;
background: #f8f8f8;
color: #333;
/* 文本水平居中 */
text-align: center;
/* 文本垂直居中 */
ling-height: 48px;
}
效果如圖所示:

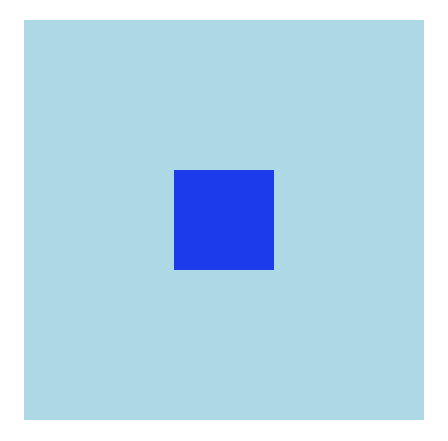
場景二:父元素內部的子元素居中對齊,子元素設置position定位來實現
方式1:position+top/left定位實現
HTML代碼:
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
CSS代碼:
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 100px;
background: lightblue;
/*子元素定位可以是相對定位,也可以是絕對定位,所以父元素最好做定位限制。*/
position: relative;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: none;
background: #1c3beb;
/* 居中代碼,定位可以是相對定位,也可以為絕對定位 */
position: relative;
top: calc(50% - 50px);
left: calc(50% - 50px);
}
方式2:position+top/left+transform來實現居中
上面的子元素的偏移量計算,也可以由CSS3中的新屬性transform來實現:
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: none;
background: #1c3beb;
/* 居中代碼,定位可以是相對定位,也可以為絕對定位 */
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
/*百分比是相對於自身寬高的偏移量計算*/
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
方式3:position+margin來實現居中
上面的子元素也可以利用絕對定位元素的流體特性和margin:auto的自動分配特性來實現居中:
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 100px;
background: lightblue;
position: relative;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: none;
background: #1c3beb;
/* 居中代碼,定位為絕對定位 */
position: absolute;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
}
方式4:彈性佈局實現居中
.father {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 100px;
background: lightblue;
/*啟用彈性佈局,主軸與交叉軸都採用居中對齊*/
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: none;
background: #1c3beb;
}
以上幾種對齊效果都一樣,但是考慮到相容性等問題,推薦方式3。以上幾種方式的對齊效果如下: