主要介紹spring mvc控制框架的流程及原理 Spring Web MVC處理請求的流程 具體執行步驟如下: 首先用戶發送請求————>前端控制器,前端控制器根據請求信息(如URL)來決定選擇哪一個頁面控制器進行處理並把請求委托給它,即以前的控制器的控制邏輯部分;圖2-1中的1、2步驟; 頁面控 ...
主要介紹spring mvc控制框架的流程及原理
Spring Web MVC處理請求的流程
具體執行步驟如下:
-
首先用戶發送請求————>前端控制器,前端控制器根據請求信息(如URL)來決定選擇哪一個頁面控制器進行處理並把請求委托給它,即以前的控制器的控制邏輯部分;圖2-1中的1、2步驟;
-
頁面控制器接收到請求後,進行功能處理,首先需要收集和綁定請求參數到一個對象,這個對象在Spring Web MVC中叫命令對象,併進行驗證,然後將命令對象委托給業務對象進行處理;處理完畢後返回一個ModelAndView(模型數據和邏輯視圖名);圖2-1中的3、4、5步驟;
-
前端控制器收回控制權,然後根據返回的邏輯視圖名,選擇相應的視圖進行渲染,並把模型數據傳入以便視圖渲染;圖2-1中的步驟6、7;
-
前端控制器再次收回控制權,將響應返回給用戶,圖2-1中的步驟8;至此整個結束。
Spring Web MVC架構
用戶發送請求到前端控制器
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>spring</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>架構圖對應的DispatcherServlet核心代碼如下:
//前端控制器的分派方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//檢查是否是請求multipart如文件上傳,如果是將通過multipartResolver解析
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//步驟2,請求到處理器(頁面控制器)的映射,通過HanMapping進行映射
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//步驟3,處理適配,即交我們的處理器包裝成相應的適配器,
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
// 304 Not Modified緩存支持
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 執行處理器相關的攔截器的預處理(HandlerInterceptor.preHandle)
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 步驟4、由適配器執行處理器(調用處理器相應功能處理方法)
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 執行處理器相關的攔截器的後處理(HandlerInterceptor.postHandle)
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Error err) {
triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
//....
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
//步驟5 步驟6、解析視圖併進行視圖的渲染
//步驟5 由ViewResolver解析View(viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale))
//步驟6 視圖在渲染時會把Model傳入(view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);)
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
//執行處理器相關的攔截器的完成後處理(HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion)
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}核心架構的具體流程步驟如下:
-
首先用戶發送請求——>DispatcherServlet,前端控制器收到請求後自己不進行處理,而是委托給其他的解析器進行處理,作為統一訪問點,進行全局的流程式控制制;
-
DispatcherServlet——>HandlerMapping, HandlerMapping將會把請求映射為HandlerExecutionChain對象(包含一個Handler處理器(頁面控制器)對象、多個HandlerInterceptor攔截器)對象,通過這種策略模式,很容易添加新的映射策略;
/**
* Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request.
* <p>Tries all handler mappings in order.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
-
DispatcherServlet——>HandlerAdapter,HandlerAdapter將會把處理器包裝為適配器,從而支持多種類型的處理器,即適配器設計模式的應用,從而很容易支持很多類型的處理器;
/**
* Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object.
* @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for
* @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error.
*/
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
-
HandlerAdapter——>處理器功能處理方法的調用,HandlerAdapter將會根據適配的結果調用真正的處理器的功能處理方法,完成功能處理;並返回一個ModelAndView對象(包含模型數據、邏輯視圖名);
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
//...
/**
* Use the given handler to handle this request.
* The workflow that is required may vary widely.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler handler to use. This object must have previously been passed
* to the {@code supports} method of this interface, which must have
* returned {@code true}.
* @throws Exception in case of errors
* @return ModelAndView object with the name of the view and the required
* model data, or {@code null} if the request has been handled directly
*/
ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;
-
ModelAndView的邏輯視圖名——> ViewResolver, ViewResolver將把邏輯視圖名解析為具體的View,通過這種策略模式,很容易更換其他視圖技術;
-
View——>渲染,View會根據傳進來的Model模型數據進行渲染,此處的Model實際是一個Map數據結構,因此很容易支持其他視圖技術;
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
//...
/**
* Render the given ModelAndView.
* <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name.
* @param mv the ModelAndView to render
* @param request current HTTP servlet request
* @param response current HTTP servlet response
* @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved
* @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view
*/
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request);
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
if (mv.isReference()) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" +
getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
//...
/**
* Resolve the given view name into a View object (to be rendered).
* <p>The default implementations asks all ViewResolvers of this dispatcher.
* Can be overridden for custom resolution strategies, potentially based on
* specific model attributes or request parameters.
* @param viewName the name of the view to resolve
* @param model the model to be passed to the view
* @param locale the current locale
* @param request current HTTP servlet request
* @return the View object, or {@code null} if none found
* @throws Exception if the view cannot be resolved
* (typically in case of problems creating an actual View object)
* @see ViewResolver#resolveViewName
*/
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale,
HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
return null;
}-
返回控制權給DispatcherServlet,由DispatcherServlet返迴響應給用戶,到此一個流程結束。
此處我們只是講了核心流程,沒有考慮攔截器、本地解析、文件上傳解析等,後邊再細述。
在此我們可以看出具體的核心開發步驟: 1. DispatcherServlet在web.xml中的部署描述,從而攔截請求到Spring Web MVC 2. HandlerMapping的配置,從而將請求映射到處理器 3. HandlerAdapter的配置,從而支持多種類型的處理器 4. ViewResolver的配置,從而將邏輯視圖名解析為具體視圖技術 5. 處理器(頁面控制器)的配置,從而進行功能處理
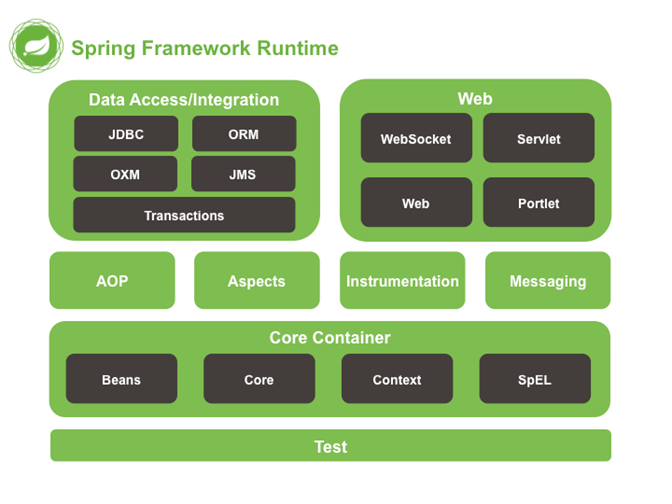
Spring 面向方面編程(AOP)和控制反轉(IOC)容器
-
控制反轉 (Inversion of Control),英文縮寫IoC
應用控制反轉,對象在被創建的時候,由一個調控系統內所有對象的外界實體將其所依賴的對象的引用傳遞給它。 也可以說,依賴被註入到對象中。所以,控制反轉是,關於一個對象如何獲取他所依賴的對象的引用,這個責任的反轉。
控制反轉主要有兩方面:
> 依賴註入 (Dependency Injection),縮寫為DI > 依賴查找 (Dependency Lookup)
其中,依賴註入應用較為廣泛。 依賴註入是一種技術,它是指組件不做定位查詢,只提供普通的Java方法讓容器去決定依賴關係。 容器全權負責的組件的裝配,它會把符合依賴關係的對象通過JavaBean屬性或者構造函數傳遞給需要的對象。
通過JavaBean屬性註射依賴關係的做法稱為設值方法註入(Setter Injection);將依賴關係作為構造函數參數傳入的做法稱為構造器註入(Constructor Injection)。
-
面向切麵編程 (Aspect Oriented Programming),縮寫為AOP
通過預編譯方式和運行期動態代理實現程式功能的統一維護的一種技術。 利用AOP可以對業務邏輯的各個部分進行隔離,從而使得業務邏輯各部分之間的耦合度降低,提高程式的可重用性,同時提高了開發的效率。
主要模塊介紹
核心容器 核心容器提供 Spring 框架的基本功能。核心容器的主要組件是 BeanFactory,它是工廠模式的實現。BeanFactory 使用控制反轉 (IOC) 模式將應用程式的配置和依賴性規範與實際的應用程式代碼分開。
Spring 上下文 Spring 上下文是一個配置文件,向 Spring 框架提供上下文信息。Spring 上下文包括企業服務,例如 JNDI、EJB、電子郵件、國際化、校驗和調度功能。
Spring AOP 通過配置管理特性,Spring AOP 模塊直接將面向方面的編程功能集成到了 Spring 框架中。所以,可以很容易地使 Spring 框架管理的任何對象支持 AOP。Spring AOP 模塊為基於 Spring 的應用程式中的對象提供了事務管理服務。通過使用 Spring AOP,不用依賴 EJB 組件,就可以將聲明性事務管理集成到應用程式中。
Spring DAO JDBC DAO 抽象層提供了有意義的異常層次結構,可用該結構來管理異常處理和不同資料庫供應商拋出的錯誤消息。異常層次結構簡化了錯誤處理,並且極大地降低了需要編寫的異常代碼數量(例如打開和關閉連接)。Spring DAO 的面向 JDBC 的異常遵從通用的 DAO 異常層次結構。
Spring ORM Spring 框架插入了若幹個 ORM 框架,從而提供了 ORM 的對象關係工具,其中包括 JDO、Hibernate 和 iBatis SQL Map。所有這些都遵從 Spring 的通用事務和 DAO 異常層次結構。
Spring Web 模塊 Web 上下文模塊建立在應用程式上下文模塊之上,為基於 Web 的應用程式提供了上下文。所以,Spring 框架支持與 Jakarta Struts 的集成。Web 模塊還簡化了處理多部分請求以及將請求參數綁定到域對象的工作。
Spring MVC 框架 MVC 框架是一個全功能的構建 Web 應用程式的 MVC 實現。通過策略介面,MVC 框架變成為高度可配置的,MVC 容納了大量視圖技術,其中包括 JSP、Velocity、Tiles、iText 和 POI。
Spring 框架的功能可以用在任何 J2EE 伺服器中,大多數功能也適用於不受管理的環境。Spring 的核心要點是:支持不綁定到特定 J2EE 服務的可重用業務和數據訪問對象。毫無疑問,這樣的對象可以在不同 J2EE 環境 (Web 或 EJB)、獨立應用程式、測試環境之間重用。
SpringMVC工作流程描述
-
向伺服器發送HTTP請求,請求被前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 捕獲。
-
DispatcherServlet 根據 <servlet-name>-servlet.xml 中的配置對請求的URL進行解析,得到請求資源標識符(URI)。 然後根據該URI,調用 HandlerMapping 獲得該Handler配置的所有相關的對象(包括Handler對象以及Handler對象對應的攔截器),最後以 HandlerExecutionChain 對象的形式返回。
-
DispatcherServlet 根據獲得的Handler,選擇一個合適的 HandlerAdapter。(附註:如果成功獲得HandlerAdapter後,此時將開始執行攔截器的preHandler(…)方法)。
-
提取Request中的模型數據,填充Handler入參,開始執行Handler(Controller)。 在填充Handler的入參過程中,根據你的配置,Spring將幫你做一些額外的工作:
HttpMessageConveter: 將請求消息(如Json、xml等數據)轉換成一個對象,將對象轉換為指定的響應信息。 數據轉換:對請求消息進行數據轉換。如String轉換成Integer、Double等。 數據根式化:對請求消息進行數據格式化。 如將字元串轉換成格式化數字或格式化日期等。 數據驗證: 驗證數據的有效性(長度、格式等),驗證結果存儲到BindingResult或Error中。
-
Handler(Controller)執行完成後,向 DispatcherServlet 返回一個 ModelAndView 對象;
-
根據返回的ModelAndView,選擇一個適合的 ViewResolver(必須是已經註冊到Spring容器中的ViewResolver)返回給DispatcherServlet。
-
ViewResolver 結合Model和View,來渲染視圖。
-
視圖負責將渲染結果返回給客戶端。
Reference:
-
Spring 系列: Spring 框架簡介 https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/wa-spring1/
源碼閱讀:
https://github.com/tomlxq/best-practice/tree/master/springmvc-introduce


