上一篇講述了solr的安裝啟動過程,這一篇講述如何導入數據到solr里。 一、準備數據 1.1 學生相關表 創建學生表、學生專業關聯表、專業表、學生行業關聯表、行業表、基礎信息表,並創建一條小白的信息。由於navicat收費,所以這裡利用HeidiSQL連接本地的MySql建立表。 1.2查詢數據 ...
上一篇講述了solr的安裝啟動過程,這一篇講述如何導入數據到solr里。
一、準備數據
1.1 學生相關表
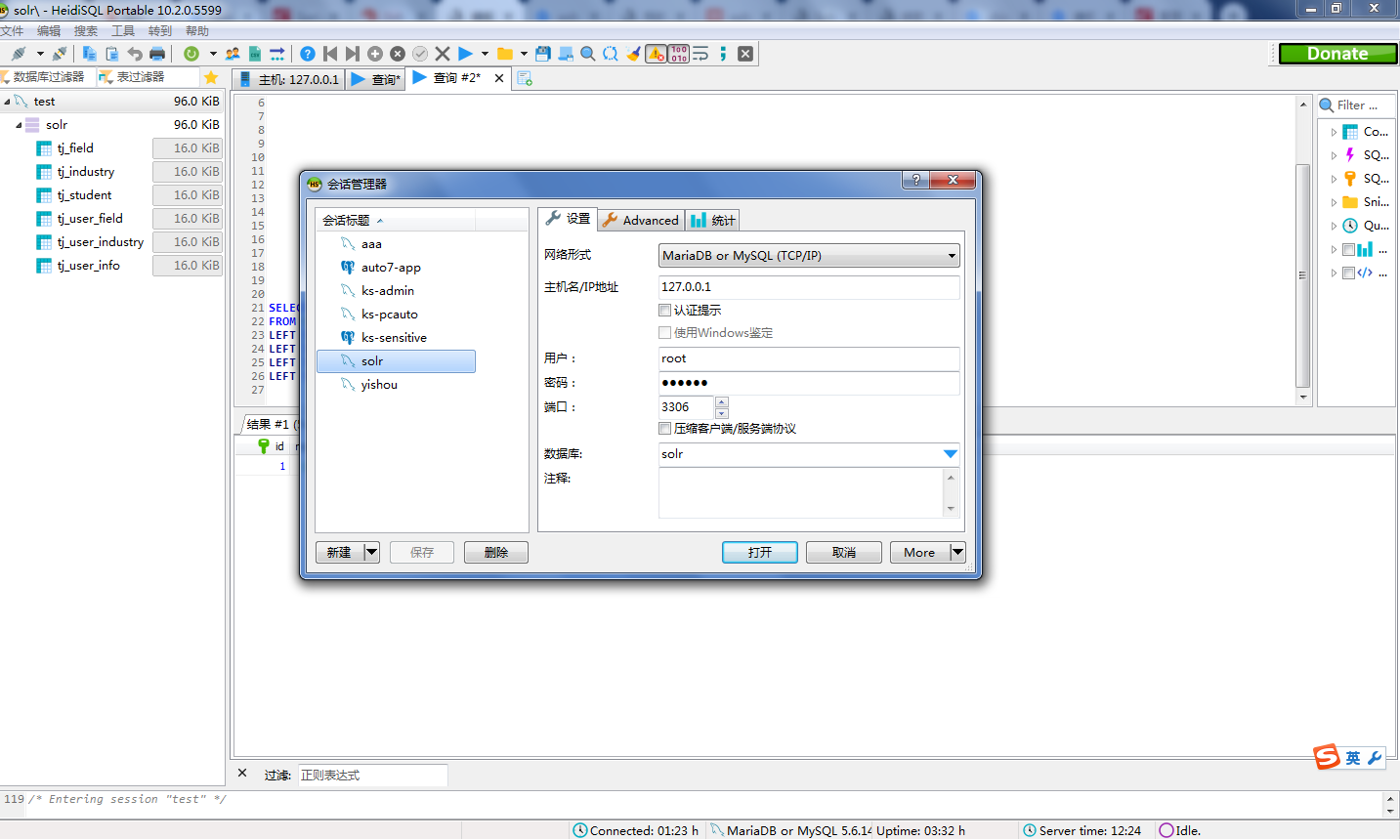
創建學生表、學生專業關聯表、專業表、學生行業關聯表、行業表、基礎信息表,並創建一條小白的信息。由於navicat收費,所以這裡利用HeidiSQL連接本地的MySql建立表。

1.2查詢數據
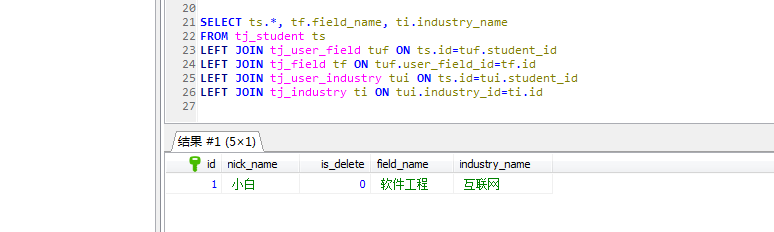
查詢出要導入solr的數據
二、添加jar包
2.1 添加mysql資料庫驅動包
下載jar包,並放入到../solr-7.7.2/server/solr-webapp/webapp/WEB-INF/lib中。
http://central.maven.org/maven2/mysql/mysql-connector-java/5.1.34/
2.2 添加solr索引導入包
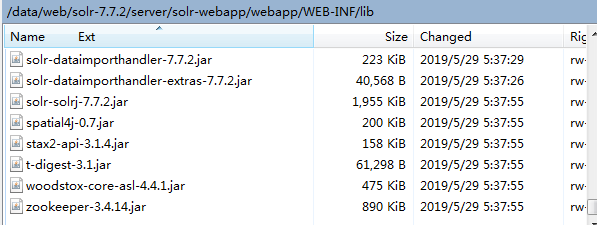
從../dist目錄複製solr-dataimporthandler-7.7.2、solr-dataimporthandler-extras-7.7.2兩個jar包到../solr-7.7.2/server/solr-webapp/webapp/WEB-INF/lib

複製到:
三、修改配置
3.1 添加data-config.xml文件
在core1/conf目錄下添加data-config.xml文件,內容為:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <dataConfig> <dataSource type="JdbcDataSource" driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" url="jdbc:mysql://192.168.33.95:3306/solr" user="root" password="123456" /> <document name="testDoc"> <entity name="tj_student" query="SELECT ts.*, tf.field_name, ti.industry_name FROM tj_student ts LEFT JOIN tj_user_field tuf ON ts.id=tuf.student_id LEFT JOIN tj_field tf ON tuf.user_field_id=tf.id LEFT JOIN tj_user_industry tui ON ts.id=tui.student_id LEFT JOIN tj_industry ti ON tui.industry_id=ti.id"> <entity name="user_info" query="SELECT * FROM tj_user_info WHERE id=${tj_student.id}"> </entity> </entity> </document> </dataConfig>
3.2 修改solrconfig.xml文件
在core1/conf目錄下修改solrconfig.xml文件,添加內容:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. --> <!-- For more details about configurations options that may appear in this file, see http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SolrConfigXml. --> <config> <!-- In all configuration below, a prefix of "solr." for class names is an alias that causes solr to search appropriate packages, including org.apache.solr.(search|update|request|core|analysis) You may also specify a fully qualified Java classname if you have your own custom plugins. --> <!-- Controls what version of Lucene various components of Solr adhere to. Generally, you want to use the latest version to get all bug fixes and improvements. It is highly recommended that you fully re-index after changing this setting as it can affect both how text is indexed and queried. --> <luceneMatchVersion>7.7.2</luceneMatchVersion> <!-- <lib/> directives can be used to instruct Solr to load any Jars identified and use them to resolve any "plugins" specified in your solrconfig.xml or schema.xml (ie: Analyzers, Request Handlers, etc...). All directories and paths are resolved relative to the instanceDir. Please note that <lib/> directives are processed in the order that they appear in your solrconfig.xml file, and are "stacked" on top of each other when building a ClassLoader - so if you have plugin jars with dependencies on other jars, the "lower level" dependency jars should be loaded first. If a "./lib" directory exists in your instanceDir, all files found in it are included as if you had used the following syntax... <lib dir="./lib" /> --> <!-- A 'dir' option by itself adds any files found in the directory to the classpath, this is useful for including all jars in a directory. When a 'regex' is specified in addition to a 'dir', only the files in that directory which completely match the regex (anchored on both ends) will be included. If a 'dir' option (with or without a regex) is used and nothing is found that matches, a warning will be logged. The examples below can be used to load some solr-contribs along with their external dependencies. --> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/contrib/extraction/lib" regex=".*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/dist/" regex="solr-cell-\d.*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/contrib/clustering/lib/" regex=".*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/dist/" regex="solr-clustering-\d.*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/contrib/langid/lib/" regex=".*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/dist/" regex="solr-langid-\d.*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/contrib/velocity/lib" regex=".*\.jar" /> <lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/dist/" regex="solr-velocity-\d.*\.jar" /> <!-- an exact 'path' can be used instead of a 'dir' to specify a specific jar file. This will cause a serious error to be logged if it can't be loaded. --> <!-- <lib path="../a-jar-that-does-not-exist.jar" /> --> <!-- Data Directory Used to specify an alternate directory to hold all index data other than the default ./data under the Solr home. If replication is in use, this should match the replication configuration. --> <dataDir>${solr.data.dir:}</dataDir> <!-- The DirectoryFactory to use for indexes. solr.StandardDirectoryFactory is filesystem based and tries to pick the best implementation for the current JVM and platform. solr.NRTCachingDirectoryFactory, the default, wraps solr.StandardDirectoryFactory and caches small files in memory for better NRT performance. One can force a particular implementation via solr.MMapDirectoryFactory, solr.NIOFSDirectoryFactory, or solr.SimpleFSDirectoryFactory. solr.RAMDirectoryFactory is memory based and not persistent. --> <directoryFactory name="DirectoryFactory" class="${solr.directoryFactory:solr.NRTCachingDirectoryFactory}"/> <!-- The CodecFactory for defining the format of the inverted index. The default implementation is SchemaCodecFactory, which is the official Lucene index format, but hooks into the schema to provide per-field customization of the postings lists and per-document values in the fieldType element (postingsFormat/docValuesFormat). Note that most of the alternative implementations are experimental, so if you choose to customize the index format, it's a good idea to convert back to the official format e.g. via IndexWriter.addIndexes(IndexReader) before upgrading to a newer version to avoid unnecessary reindexing. A "compressionMode" string element can be added to <codecFactory> to choose between the existing compression modes in the default codec: "BEST_SPEED" (default) or "BEST_COMPRESSION". --> <codecFactory class="solr.SchemaCodecFactory"/> <!-- ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Index Config - These settings control low-level behavior of indexing Most example settings here show the default value, but are commented out, to more easily see where customizations have been made. Note: This replaces <indexDefaults> and <mainIndex> from older versions ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ --> <indexConfig> <!-- maxFieldLength was removed in 4.0. To get similar behavior, include a LimitTokenCountFilterFactory in your fieldType definition. E.g. <filter class="solr.LimitTokenCountFilterFactory" maxTokenCount="10000"/> --> <!-- Maximum time to wait for a write lock (ms) for an IndexWriter. Default: 1000 --> <!-- <writeLockTimeout>1000</writeLockTimeout> --> <!-- Expert: Enabling compound file will use less files for the index, using fewer file descriptors on the expense of performance decrease. Default in Lucene is "true". Default in Solr is "false" (since 3.6) --> <!-- <useCompoundFile>false</useCompoundFile> --> <!-- ramBufferSizeMB sets the amount of RAM that may be used by Lucene indexing for buffering added documents and deletions before they are flushed to the Directory. maxBufferedDocs sets a limit on the number of documents buffered before flushing. If both ramBufferSizeMB and maxBufferedDocs is set, then Lucene will flush based on whichever limit is hit first. --> <!-- <ramBufferSizeMB>100</ramBufferSizeMB> --> <!-- <maxBufferedDocs>1000</maxBufferedDocs> --> <!-- Expert: Merge Policy The Merge Policy in Lucene controls how merging of segments is done. The default since Solr/Lucene 3.3 is TieredMergePolicy. The default since Lucene 2.3 was the LogByteSizeMergePolicy, Even older versions of Lucene used LogDocMergePolicy. --> <!-- <mergePolicyFactory class="org.apache.solr.index.TieredMergePolicyFactory"> <int name="maxMergeAtOnce">10</int> <int name="segmentsPerTier">10</int> <double name="noCFSRatio">0.1</double> </mergePolicyFactory> --> <!-- Expert: Merge Scheduler The Merge Scheduler in Lucene controls how merges are performed. The ConcurrentMergeScheduler (Lucene 2.3 default) can perform merges in the background using separate threads. The SerialMergeScheduler (Lucene 2.2 default) does not. --> <!-- <mergeScheduler class="org.apache.lucene.index.ConcurrentMergeScheduler"/> --> <!-- LockFactory This option specifies which Lucene LockFactory implementation to use. single = SingleInstanceLockFactory - suggested for a read-only index or when there is no possibility of another process trying to modify the index. native = NativeFSLockFactory - uses OS native file locking. Do not use when multiple solr webapps in the same JVM are attempting to share a single index. simple = SimpleFSLockFactory - uses a plain file for locking Defaults: 'native' is default for Solr3.6 and later, otherwise 'simple' is the default More details on the nuances of each LockFactory... http://wiki.apache.org/lucene-java/AvailableLockFactories --> <lockType>${solr.lock.type:native}</lockType> <!-- Commit Deletion Policy Custom deletion policies can be specified here. The class must implement org.apache.lucene.index.IndexDeletionPolicy. The default Solr IndexDeletionPolicy implementation supports deleting index commit points on number of commits, age of commit point and optimized status. The latest commit point should always be preserved regardless of the criteria. --> <!-- <deletionPolicy class="solr.SolrDeletionPolicy"> --> <!-- The number of commit points to be kept --> <!-- <str name="maxCommitsToKeep">1</str> --> <!-- The number of optimized commit points to be kept --> <!-- <str name="maxOptimizedCommitsToKeep">0</str> --> <!-- Delete all commit points once they have reached the given age. Supports DateMathParser syntax e.g. --> <!-- <str name="maxCommitAge">30MINUTES</str> <str name="maxCommitAge">1DAY</str> --> <!-- </deletionPolicy> --> <!-- Lucene Infostream To aid in advanced debugging, Lucene provides an "InfoStream" of detailed information when indexing. Setting The value to true will instruct the underlying Lucene IndexWriter to write its debugging info the specified file --> <!-- <infoStream file="INFOSTREAM.txt">false</infoStream> --> </indexConfig> <!-- JMX This example enables JMX if and only if an existing MBeanServer is found, use this if you want to configure JMX through JVM parameters. Remove this to disable exposing Solr configuration and statistics to JMX. For more details see http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SolrJmx --> <jmx /> <!-- If you want to connect to a particular server, specify the agentId --> <!-- <jmx agentId="myAgent" /> --> <!-- If you want to start a new MBeanServer, specify the serviceUrl --> <!-- <jmx serviceUrl="service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://localhost:9999/solr"/> --> <!-- The default high-performance update handler --> <updateHandler class="solr.DirectUpdateHandler2"> <!-- Enables a transaction log, used for real-time get, durability, and and solr cloud replica recovery. The log can grow as big as uncommitted changes to the index, so use of a hard autoCommit is recommended (see below). "dir" - the target directory for transaction logs, defaults to the solr data directory. "numVersionBuckets" - sets the number of buckets used to keep track of max version values when checking for re-ordered updates; increase this value to reduce the cost of synchronizing access to version buckets during high-volume indexing, this requires 8 bytes (long) * numVersionBuckets of heap space per Solr core. --> <updateLog> <str name="dir">${solr.ulog.dir:}</str> <int name="numVersionBuckets">${solr.ulog.numVersionBuckets:65536}</int> </updateLog> <!-- AutoCommit Perform a hard commit automatically under certain conditions. Instead of enabling autoCommit, consider using "commitWithin" when adding documents. http://wiki.apache.org/solr/UpdateXmlMessages maxDocs - Maximum number of documents to add since the last commit before automatically triggering a new commit. maxTime - Maximum amount of time in ms that is allowed to pass since a document was added before automatically triggering a new commit. openSearcher - if false, the commit causes recent index changes to be flushed to stable storage, but does not cause a new searcher to be opened to make those changes visible. If the updateLog is enabled, then it's highly recommended to have some sort of hard autoCommit to limit the log size. --> <autoCommit> <maxTime>${solr.autoCommit.maxTime:15000}</maxTime> <openSearcher>false</openSearcher> </autoCommit> <!-- softAutoCommit is like autoCommit except it causes a 'soft' commit which only ensures that changes are visible but does not ensure that data is synced to disk. This is faster and more near-realtime friendly than a hard commit. --> <autoSoftCommit> <maxTime>${solr.autoSoftCommit.maxTime:-1}</maxTime> </autoSoftCommit> <!-- Update Related Event Listeners Various IndexWriter related events can trigger Listeners to take actions. postCommit - fired after every commit or optimize command postOptimize - fired after every optimize command --> </updateHandler> <!-- IndexReaderFactory Use the following format to specify a custom IndexReaderFactory, which allows for alternate IndexReader implementations. ** Experimental Feature ** Please note - Using a custom IndexReaderFactory may prevent certain other features from working. The API to IndexReaderFactory may change without warning or may even be removed from future releases if the problems cannot be resolved. ** Features that may not work with custom IndexReaderFactory ** The ReplicationHandler assumes a disk-resident index. Using a custom IndexReader implementation may cause incompatibility with ReplicationHandler and may cause replication to not work correctly. See SOLR-1366 for details. --> <!-- <indexReaderFactory name="IndexReaderFactory" class="package.class"> <str name="someArg">Some Value</str> </indexReaderFactory > --> <!-- ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Query section - these settings control query time things like caches ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ --> <query> <!-- Maximum number of clauses in each BooleanQuery, an exception is thrown if exceeded. It is safe to increase or remove this setting, since it is purely an arbitrary limit to try and catch user errors where large boolean queries may not be the best implementation choice. --> <maxBooleanClauses>${solr.max.booleanClauses:1024}</maxBooleanClauses> <!-- Solr Internal Query Caches There are two implementations of cache available for Solr, LRUCache, based on a synchronized LinkedHashMap, and FastLRUCache, based on a ConcurrentHashMap. FastLRUCache has faster gets and slower puts in single threaded operation and thus is generally faster than LRUCache when the hit ratio of the cache is high (> 75%), and may be faster under other scenarios on multi-cpu systems. --> <!-- Filter Cache Cache used by SolrIndexSearcher for filters (DocSets), unordered sets of *all* documents that match a query. When a new searcher is opened, its caches may be prepopulated or "autowarmed" using data from caches in the old searcher. autowarmCount is the number of items to prepopulate. For LRUCache, the autowarmed items will be the most recently accessed items. Parameters: class - the SolrCache implementation LRUCache or (LRUCache or FastLRUCache) size - the maximum number of entries in the cache initialSize - the initial capacity (number of entries) of the cache. (see java.util.HashMap) autowarmCount - the number of entries to prepopulate from and old cache. maxRamMB - the maximum amount of RAM (in MB) that this cache is allowed to occupy. Note that when this option is specified, the size and initialSize parameters are ignored. --> <filterCache class="solr.FastLRUCache" size="512" initialSize="512" autowarmCount="0"/> <!-- Query Result Cache Caches results of searches - ordered lists of document ids (DocList) based on a query, a sort, and the range of documents requested. Additional supported parameter by LRUCache: maxRamMB - the maximum amount of RAM (in MB) that this cache is allowed to occupy --> <queryResultCache class="solr.LRUCache" size="512" initialSize="512" autowarmCount="0"/> <!-- Document Cache Caches Lucene Document objects (the stored fields for each document). Since Lucene internal document ids are transient, this cache will not be autowarmed. --> <documentCache class="solr.LRUCache" size="512" initialSize="512" autowarmCount="0"/> <!-- custom cache currently used by block join --> <cache name="perSegFilter" class="solr.search.LRUCache" size="10" initialSize="0" autowarmCount="10" regenerator="solr.NoOpRegenerator" /> <!-- Field Value Cache Cache used to hold field values that are quickly accessible by document id. The fieldValueCache is created by default even if not configured here. --> <!-- <fieldValueCache class="solr.FastLRUCache" size="512" autowarmCount="128" showItems="32" /> --> <!-- Custom Cache Example of a generic cache. These caches may be accessed by name through SolrIndexSearcher.getCache(),cacheLookup(), and cacheInsert(). The purpose is to enable easy caching of user/application level data. The regenerator argument should be specified as an implementation of solr.CacheRegenerator if autowarming is desired. --> <!-- <cache name="myUserCache" class="solr.LRUCache" size="4096" initialSize="1024" autowarmCount="1024" regenerator="com.mycompany.MyRegenerator" /> --> <!-- Lazy Field Loading If true, stored fields that are not requested will be loaded lazily. This can result in a significant speed improvement if the usual case is to not load all stored fields, especially if the skipped fields are large compressed text fields. --> <enableLazyFieldLoading>true</enableLazyFieldLoading> <!-- Use Filter For Sorted Query A possible optimization that attempts to use a filter to satisfy a search. If the requested sort does not include score, then the filterCache will be checked for a filter matching the query. If found, the filter will be used as the source of document ids, and then the sort will be applied to that. For most situations, this will not be useful unless you frequently get the same search repeatedly with different sort options, and none of them ever use "score" --> <!-- <useFilterForSortedQuery>true</useFilterForSortedQuery> --> <!-- Result Window Size An optimization for use with the queryResultCache. When a search is requested, a superset of the requested number of document ids are collected. For example, if a search for a particular query requests matching documents 10 through 19, and queryWindowSize is 50, then documents 0 through 49 will be collected and cached. Any further requests in that range can be satisfied via the cache. --> <queryResultWindowSize>20</queryResultWindowSize> <!-- Maximum number of documents to cache for any entry in the queryResultCache. --> <queryResultMaxDocsCached>200</queryResultMaxDocsCached> <!-- Query Related Event Listeners Various IndexSearcher related events can trigger Listeners to take actions. newSearcher - fired whenever a new searcher is being prepared and there is a current searcher handling requests (aka registered). It can be used to prime certain caches to prevent long request times for certain requests. firstSearcher - fired whenever a new searcher is being prepared but there is no current registered searcher to handle requests or to gain autowarming data from. --> <!-- QuerySenderListener takes an array of NamedList and executes a local query request for each NamedList in sequence. --> <listener event="newSearcher" class="solr.QuerySenderListener"> <arr name="queries"> <!-- <lst><str name="q">solr</str><str name="sort">price asc</str></lst> <lst><str name="q">rocks</str><str name="sort">weight asc</str></lst> --> </arr> </listener> <listener event="firstSearcher" class="solr.QuerySenderListener"> <arr name="queries"> <!-- <lst> <str name="q">static firstSearcher warming in solrconfig.xml</str> </lst> --> </arr> </listener> <!-- Use Cold Searcher If a search request comes in and there is no current registered searcher, then immediately register the still warming searcher and use it. If "false" then all requests will block until the first searcher is done warming. --> <useColdSearcher>false</useColdSearcher> </query> <!-- Request Dispatcher This section contains instructions for how the SolrDispatchFilter should behave when processing requests for this SolrCore. --> <requestDispatcher> <!-- Request Parsing These settings indicate how Solr Requests may be parsed, and what restrictions may be placed on the ContentStreams from those requests enableRemoteStreaming - enables use of the stream.file and stream.url parameters for specifying remote streams. multipartUploadLimitInKB - specifies the max size (in KiB) of Multipart File Uploads that Solr will allow in a Request. formdataUploadLimitInKB - specifies the max size (in KiB) of form data (application/x-www-form-urlencoded) sent via POST. You can use POST to pass request parameters not fitting into the URL. addHttpRequestToContext - if set to true, it will instruct the requestParsers to include the original HttpServletRequest object in the context map of the SolrQueryRequest under the key "httpRequest". It will not be used by any of the existing Solr components, but may be useful when developing custom plugins. *** WARNING *** Before enabling remote streaming, you should make sure your system has authentication enabled. <requestParsers enableRemoteStreaming="false" multipartUploadLimitInKB="-1" formdataUploadLimitInKB="-1" addHttpRequestToContext="false"/> --> <!-- HTTP Caching Set HTTP caching related parameters (for proxy caches and clients). The options below instruct Solr not to output any HTTP Caching related headers --> <httpCaching never304="true" /> <!-- If you include a <cacheControl> directive, it will be used to generate a Cache-Control header (as well as an Expires header if the value contains "max-age=") By default, no Cache-Control header is generated. You can use the <cacheControl> option even if you have set never304="true" --> <!-- <httpCaching never304="true" > <cacheControl>max-age=30, public</cacheControl> </httpCaching> --> <!-- To enable Solr to respond with automatically generated HTTP Caching headers, and to response to Cache Validation requests correctly, set the value of never304="false" This will cause Solr to generate Last-Modified and ETag headers based on the properties of the Index. The following options can also be specified to affect the values of these headers... lastModFrom - the default value is "openTime" which means the Last-Modified value (and validation against If-Modified-Since requests) will all be relative to when the current Searcher was opened. You can change it to lastModFrom="dirLastMod" if you want the value to exactly correspond to when the physical index was last modified. etagSeed="..." is an option you can change to force the ETag header (and validation against If-None-Match requests) to be different even if the index has not changed (ie: when making significant changes to your config file) (lastModifiedFrom and etagSeed are both ignored if you use the never304="true" option) --> <!-- <httpCaching lastModifiedFrom="openTime" etagSeed="Solr"> <cacheControl>max-age=30, public</cacheControl> </httpCaching> --> </requestDispatcher> <!-- Request Handlers http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SolrRequestHandler Incoming queries will be dispatched to a specific handler by name based on the path specified in the request. If a Request Handler is declared with startup="lazy", then it will not be initialized until the first request that uses it. --> <!-- SearchHandler http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SearchHandler For processing Search Queries, the primary Request Handler provided with Solr is "SearchHandler" It delegates to a sequent of SearchComponents (see below) and supports distributed queries across multiple shards --> <requestHandler name="/dataimport" class="org.apache.solr.handler.dataimport.DataImportHandler"> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="config">data-config.xml</str> </lst> </requestHandler> <requestHandler name="/select" class="solr.SearchHandler"> <!-- default values for query parameters can be specified, these will be overridden by parameters in the request --> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="echoParams">explicit</str> <int name="rows">10</int> <!-- Default search field <str name="df">text</str> --> <!-- Change from JSON to XML format (the default prior to Solr 7.0) <str name="wt">xml</str> --> </lst> <!-- In addition to defaults, "appends" params can be specified to identify values which should be appended to the list of multi-val params from the query (or the existing "defaults"). --> <!-- In this example, the param "fq=instock:true" would be appended to any query time fq params the user may specify, as a mechanism for partitioning the index, independent of any user selected filtering that may also be desired (perhaps as a result of faceted searching). NOTE: there is *absolutely* nothing a client can do to prevent these "appends" values from being used, so don't use this mechanism unless you are sure you always want it. --> <!-- <lst name="appends"> <str name="fq">inStock:true</str> </lst> --> <!-- "invariants" are a way of letting the Solr maintainer lock down the options available to Solr clients. Any params values specified here are used regardless of what values may be specified in either the query, the "defaults", or the "appends" params. In this example, the facet.field and facet.query params would be fixed, limiting the facets clients can use. Faceting is not turned on by default - but if the client does specify facet=true in the request, these are the only facets they will be able to see counts for; regardless of what other facet.field or facet.query params they may specify. NOTE: there is *absolutely* nothing a client can do to prevent these "invariants" values from being used, so don't use this mechanism unless you are sure you always want it. --> <!-- <lst name="invariants"> <str name="facet.field">cat</str> <str name="facet.field">manu_exact</str> <str name="facet.query">price:[* TO 500]</str> <str name="facet.query">price:[500 TO *]</str> </lst> --> <!-- If the default list of SearchComponents is not desired, that list can either be overridden completely, or components can be prepended or appended to the default list. (see below) --> <!-- <arr name="components"> <str>nameOfCustomComponent1</str> <str>nameOfCustomComponent2</str> </arr> --> </requestHandler> <!-- A request handler that returns indented JSON by default --> <requestHandler name="/query" class="solr.SearchHandler"> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="echoParams">explicit</str> <str name="wt">json</str> <str name="indent">true</str> </lst> </requestHandler> <!-- A Robust Example This example SearchHandler declaration shows off usage of the SearchHandler with many defaults declared Note that multiple instances of the same Request Handler (SearchHandler) can be registered multiple times with different names (and different init parameters) --> <requestHandler name="/browse" class="solr.SearchHandler" useParams="query,facets,velocity,browse"> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="echoParams">explicit</str> </lst> </requestHandler> <initParams path="/update/**,/query,/select,/tvrh,/elevate,/spell,/browse"> <




