Spring Security 解析(二) —— 認證過程 在學習Spring Cloud 時,遇到了授權服務oauth 相關內容時,總是一知半解,因此決定先把Spring Security 、Spring Security Oauth2 等許可權、認證相關的內容、原理及設計學 ...
Spring Security 解析(二) —— 認證過程
在學習Spring Cloud 時,遇到了授權服務oauth 相關內容時,總是一知半解,因此決定先把Spring Security 、Spring Security Oauth2 等許可權、認證相關的內容、原理及設計學習並整理一遍。本系列文章就是在學習的過程中加強印象和理解所撰寫的,如有侵權請告知。
項目環境:
- JDK1.8
- Spring boot 2.x
- Spring Security 5.x
一、@EnableGlobalAuthentication 配置 解析
還記得上一篇講解授權過程中提到@EnableWebSecurity 引用了 WebSecurityConfiguration 配置類 和 @EnableGlobalAuthentication 註解嗎? 當時只是講解了下 WebSecurityConfiguration 配置類 ,這次該輪到 @EnableGlobalAuthentication 配置了。
查看 @EnableGlobalAuthentication 註解源碼,我們可以看到其引用了AuthenticationConfiguration 配置類。其中有一個方法值得我們註意,那就是 getAuthenticationManager() (還記得授權過程中調用了 AuthenticationManager().authenticate() 進行認證麽?), 我們來看下其源碼內部大致邏輯:
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
......
// 1 調用 authenticationManagerBuilder 方法獲取 authenticationManagerBuilder 對象,用於 build authenticationManager 對象
AuthenticationManagerBuilder authBuilder = authenticationManagerBuilder(
this.objectPostProcessor, this.applicationContext);
.....
// 2 build 方法調用同授權過程中的 webSecurity.build() 一樣,都是通過父類 AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder.doBuild() 方法中的 performBuild() 方法進行 build, 只是這裡不再是通過其子類 HttpSecurity.performBuild() ,而是通過 AuthenticationManagerBuilder.performBuild()
authenticationManager = authBuilder.build();
.......
return authenticationManager;
}根據源碼我們可以概括其邏輯分2部分:
- 1、 通過調用 authenticationManagerBuilder() 方法獲取 authenticationManagerBuilder 對象
- 2、 調用authenticationManagerBuilder 對象的 build() 創建 authenticationManager 對象並返回
我們再詳細看下這個build的過程,可以發現其 build 調用跟授權過程中build securityFilterChain 一樣 都是通過 AbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder.doBuild() 方法中的 performBuild() 進行構建, 不過這次不再是調用其子類 HttpSecurity.performBuild() 而是 AuthenticationManagerBuilder.performBuild() 。
我們來看下 AuthenticationManagerBuilder.performBuild() 方法內部實現:
protected ProviderManager performBuild() throws Exception {
if (!isConfigured()) {
logger.debug("No authenticationProviders and no parentAuthenticationManager defined. Returning null.");
return null;
}
// 1 創建了一個包含 authenticationProviders 參數 的 ProviderManager 對象
ProviderManager providerManager = new ProviderManager(authenticationProviders,
parentAuthenticationManager);
if (eraseCredentials != null) {
providerManager.setEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication(eraseCredentials);
}
if (eventPublisher != null) {
providerManager.setAuthenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);
}
providerManager = postProcess(providerManager);
return providerManager;
}這裡我們主要關註其內部 創建了一個包含 authenticationProviders 參數 的 ProviderManager (ProviderManager 是 AuthenticationManager 的實現類)對象並返回。
回過頭,我們來看下 AuthenticationManager 介面 源碼:
public interface AuthenticationManager {
// 認證介面
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}可以看到,內部就只有一個我們在授權過程中提到過的 authenticate(),其介面接收一個 Authentication(這個對象我們也不陌生,之前授權過程中提到過的 UsernamePasswordAuthrnticationToken 等都是其實現子類) 對象作為參數。
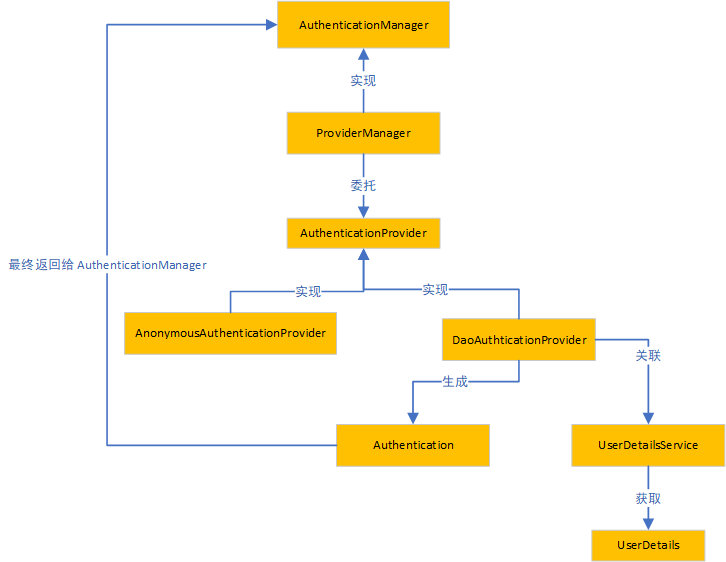
至此認證的部分關鍵類或介面已經浮出水面了,它們分別是 AuthenticationManager 、ProviderManager、AuthenticationProvider、Authentication, 接下來我們就圍繞這幾個類或介面進行剖析。
二、AuthenticationManager
正如我們之前看到的一項,它是整個認證的入口,其定義的認證介面 authenticate() 接收一個 Authentication 對象作為參數。AuthenticationManager 它只是提供了一個認證介面方法,因為在實際使用中,我們不僅有賬戶密碼的登錄方式,還有簡訊驗證碼登錄、郵箱登錄等等,所以它本身不做任何認證,其具體做認證的是 ProviderManager 子類,但正如我們說過的認證方式有很多,如果僅僅依靠 ProviderManager 本身來實現 authenticate() 介面,那我們要支持這麼多認證方式不得寫多少個 if 判斷,而且以後如果我們想要支持指紋登錄,那又不得不在這個方法內部加個if,這種不利於系統擴展的寫法肯定是不可取的,所以 ProviderManager 本身會維護一個List<AuthenticationProvider>列表 ,用於存放多種認證方式,然後通過委托的方式,調用 AuthenticationProvider 來真正實現認證邏輯的 。 而 Authentication 就是我們需要認證的信息(當然不僅僅只包括賬戶信息),通過authenticate() 介面認證成功後返回的 Authentication 就是一個被標識認證成功的對象 。 這裡為什麼要解釋下 AuthenticationManager、ProviderManager、AuthenticationProvider 的關係,主要是一開始容易搞混它們,相信經過這樣一段描述更容易理解了吧。。。
三、Authentication
如果 沒有看過源碼的同學可能會認為 Authentication 是一個類吧,可實際上它是一個 介面,其內部並未存在任何屬性欄位,它僅僅定義了和規範好了認證對象需要的介面方法,我們來看看其定義的介面方法有哪些,分別又什麼作用:
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
// 1 獲取許可權信息(不能僅僅理解未角色許可權,還有菜單許可權等等),預設是GrantedAuthority介面的實現類
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// 2 獲取用戶密碼信息 ,認證成功後會被刪除掉
Object getCredentials();
// 3 主要存放訪問著的ip等信息
Object getDetails();
// 4 重點!! 最重要的身份信息。 大部分情況下是 UserDetails 介面的實現 類,比如 我們 之前配置的 User 對象
Object getPrincipal();
// 5 是否認證(成功)
boolean isAuthenticated();
// 6 設置認證標識
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}既然 Authentication 定義了這些介面方法,那麼其子類實現肯定都按照這個標準或者稱之為規範定製了實現,這裡就不羅列出其子類的具體實現了,有興趣的同學可以去看下 我們最常用的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 實現(包括其 父類 AbstractAuthenticationToken)
四、ProviderManager
它是 AuthenticationManager 的實現子類之一,也是我們最常用的一個實現。正如我們前面提到過的,其內部維護了 一個 List<AuthenticationProvider> 對象, 用於支持和擴展 多種形式的認證方式。我們來看下 其 實現 authenticate() 的源碼:
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
......
// 1 通過 getProviders() 方法獲取到內部維護的 List<AuthenticationProvider> 對象 並 通過遍歷的方式 去 認證,只要認證成功 就 break
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
// 2 正如前面看到的有 很多 AuthenticationProvider 實現,如果每次都是驗證失敗後再掉用下一個 AuthenticationProvider 這種實現是不是很不高效? 所以 這裡通過 supports() 方法來驗證是否可以使用 該 AuthenticationProvider 進行驗證,不可以就直接換下一個
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
try {
// 3 重點,這裡是 調用真實的認證方法
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
if (result == null && parent != null) {
try {
// 4 前面都認證不成功,調用父類(嚴格意思不是調用父類,而是其他的 AuthenticationManager 實現類)認證方法
result = parentResult = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = parentException = e;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication
&& (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// 5 刪除認證成功後的 密碼信息,保證安全
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
if (parentResult == null) {
eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(messages.getMessage(
"ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() },
"No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}梳理下整個方法內部實現邏輯:
- 通過 getProviders() 方法獲取到內部維護的 List
對象 並 通過遍歷的方式 去 認證 - 通過 provider.supports() 方法 來驗證是否可用當前的 AuthenticationProvider 進行驗證,不可以就直接換下一個 ( 其實方法內部就是驗證當前 的 Authentication 對象是不是其某個子類,比如 我們最常用到的 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的 supports 方法就是判斷當前 的 Authentication 是不是 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken )
- 通過 provider.authenticate() 調用 其真正的認證實現
- 如果 前面的所有 AuthenticationProvider 均不能認證成功,嘗試調用 parent.authenticate() 方法 :調用父類(嚴格意思不是調用父類,而是其他的 AuthenticationManager 實現類)認證方法
- 最後 通過 ((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials() 刪除認證成功後的 密碼信息,保證安全
五、AuthenticationProvider(DaoAuthenticationProvider)
正如我們想象的一樣,AuthenticationProvider 是一個介面,本身定義了一個 和 AuthenticationManager 一樣的 authenticate 認證介面方法,外加一個 supports() 用於 判別當前 Authentication 是否可以進行處理。
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
// 定義認證介面方法
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
// 定義判斷是否可以認證處理的介面方法
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}這裡我們就拿我們用得最多的一個 AuthenticationProvider 實現類 DaoAuthenticationProvider(註意,這裡和UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 類似,都是通過父類來實現介面,然後內部處理方法再調用 其 子類進行處理) 來看其內部 這2個抽象方法的實現:
- supports 實現:
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class
.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}可以看到僅僅只是判斷當前的 authentication 是否為 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(或其子類)
- authrnticate 實現
// 1 註意這裡的實現方法是 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的父類 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 實現的
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
// 2 從 authentication 中獲取 用戶名
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
// 3 根據username 從緩存中獲取 認證成功的 UserDetails 信息
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
// 4 如果緩存中沒有用戶信息 需要 獲取用戶信息(由 DaoAuthenticationProvider 實現 )
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
......
}
}
try {
// 5 前置檢查賬戶是否鎖定,過期,凍結(由DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks類實現)
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 6 主要是驗證 獲取到的用戶密碼與傳入的用戶密碼是否一致
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
// 這裡官方發現緩存可能導致了某些問題,又重新去認證一次
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// There was a problem, so try again after checking
// we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache)
cacheWasUsed = false;
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
// 7 後置檢查用戶密碼是否 過期
postAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
// 8 驗證成功後的用戶信息存入緩存
if (!cacheWasUsed) {
this.userCache.putUserInCache(user);
}
Object principalToReturn = user;
if (forcePrincipalAsString) {
principalToReturn = user.getUsername();
}
// 9 重新創建一個 authenticated 為true (即認證成功)的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 對象並返回
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}梳理下authenticate(這裡的方法的實現是由 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 提供的)方法內部實現邏輯:
- 從 入參 authentication 對象中獲取到 username 信息
- (這裡忽略緩存的處理) 調用 retrieveUser() 方法(由 DaoAuthenticationProvider 實現)根據 username 獲取到 系統(一般來說是從資料庫中) 中獲取到 UserDetails** 對象**
- 通過 preAuthenticationChecks.check() 方法檢測 當前獲取到的 UserDetails 是否過期、凍結、鎖定(如果任意一個條件 為 true 將拋出 相應 的異常)
- 通過 additionalAuthenticationChecks() (由 DaoAuthenticationProvider 實現) 判斷 密碼是否一致
- 通過 postAuthenticationChecks.check() 檢測 UserDetails 的密碼是否過期
- 最後通過 createSuccessAuthentication() 重新創建一個 authenticated 為true (即認證成功)的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 對象並返回
雖然我們知道其驗證邏輯, 但其內部很多方法我們不清楚其內部實現,以及這裡新增的一個 關鍵認證類 UserDetails 是怎麼設計的,如何驗證其是否過期等等。
六、 UserDetailsService 和 UserDetails
繼續深入看下 retrieveUser() 方法,首先我們註意到其返回對象是一個 UserDetails,那麼我們先從 UserDetails 入手。
UserDetails:
我們先來看下 UserDetails 源碼:
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
// 1 與 Authentication 的 一樣,都是獲取 許可權信息
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// 2 獲取用戶正確的密碼
String getPassword();
// 3 獲取賬戶名
String getUsername();
// 4 賬戶是否過期
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
// 5 賬戶是否鎖定
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
// 6 密碼是否過期
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
// 7 賬戶是否凍結
boolean isEnabled();
}從上面的 4,5,6,7 介面我們就能夠知道 preAuthenticationChecks.check() 和 postAuthenticationChecks.check() 是如何檢測的了,這裡2個方法的檢測細節就不再深究了,有興趣的同學可以看看源碼,我們只要知道檢測失敗會拋出異常就行了。
咋呼一看,這個UserDetails 和 Authentication 很相似,其實它們之間還真有關係,在createSuccessAuthentication() 傳教Authentication 對象時,它的authorities 就是UserDetails 傳入的。
UserDetailsService:
retrieveUser() 方法是系統通過傳入的賬戶名獲取對應的賬戶信息的唯一方法,我們來看下其內部源碼邏輯:
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
// 通過 UserDetailsService 的loadUserByUsername 方法 獲取用戶信息
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
......
}
}相信看到這裡,一切都關聯上了,這裡的 UserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername() 就是我們在 上一篇 授權過程中 我們自己實現的。 這裡就不再 貼出UserDetailsService 源碼了。
還有additionalAuthenticationChecks() 密碼驗證沒有講到,這裡簡單提下,其內部就是通過 PasswordEncoder.matches() 方法進行密碼匹配的。不過這裡要註意一下,這裡的 PasswordEncoder 在 Security 5 開始預設 替換成了 DelegatingPasswordEncoder 這裡也是和我們之前 討論 loadUserByUsername 方法內部創建User (UserDeatails 實現類之一)是一定要用到 PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder().encode() 加密是相應的。
七、個人總結
認證的頂級管理員 AuthenticationManager 為我們提供了 認證入口( authenticate()介面),但是呢,我們也知道大老闆一般不直接參与實質的工作,所以它把任務安排給它的下屬,也就是我們的 ProviderManager 部門領導 ,部門領導 肩負起 認證的工作(authenticate() 認證的實現),其實呢,我們也知道部門領導也是 直接參數 認證工作的,它都是將實際任務安排給小組長的, 也就是我們的 AuthrnticationProvider ,部門領導 開個會議,聚集了所有小組長 ,讓它們自行判斷(通過
support()) 大老闆交下來的任務 該由誰來完成, 小組長 領到任務後,就把任務 分發給各個小組成員,比如 成員1(UserDetailsService) 只需要 完成 retrieveUser() 的工作,然後成員2 完成 additionalAuthenticationChecks() 的工作,最後由項目經理 ( createSuccessAuthentication() ) 將結果彙報給小組長,然後小組長彙報給部門領導,部門領導 審核一下結果,覺得小組長做得不夠好,然後又做了一些操作 ( eraseCredentials() 擦除密碼信息 ),最後認為 結果 可以了就彙報給老闆,老闆呢,也不多看,直接將結果給了客戶(filter)。
按照慣例,上流程圖:
本文介紹認證過程的代碼可以訪問代碼倉庫中的 security 模塊 ,項目的github 地址 : https://github.com/BUG9/spring-security
如果您對這些感興趣,歡迎star、follow、收藏、轉發給予支持!



