概覽 隨著我們的應用程式越來越受歡迎,我們的下一步將要開發多語言功能。方便越來越多的國家使用我們中國的應用程式, 基於 WPF 本地化,我們很多時候使用的是系統資源文件,可是動態切換本地化,就比較麻煩了。 有沒有一種方法既可以適用系統的資源文件,又能方便快捷的切換本地化呢? 實現思路 現在我們將要實 ...
概覽
隨著我們的應用程式越來越受歡迎,我們的下一步將要開發多語言功能。方便越來越多的國家使用我們中國的應用程式,
基於 WPF 本地化,我們很多時候使用的是系統資源文件,可是動態切換本地化,就比較麻煩了。
有沒有一種方法既可以適用系統的資源文件,又能方便快捷的切換本地化呢?
實現思路
現在我們將要實現的是基於 DotNetCore 3.0 以上版本 and WPF 桌面應用程式模塊化的多語言功能。
動態切換多語言思路:
- 把所有模塊的資源文件添加到字典集合。
- 將資源文件里的key,綁定到前臺。
- 通過通知更改
CurrentCulture多語言來使用改變的語言文件里的key。 - 通過綁定
Binding拼接Path 在輸出。
動態切換
我們先來看實現結果

- 第一行是我們的主程式的數據展示,用於業務中的本地化
- 第二行是我們業務模塊A的數據展示
- 第三行是我們業務模塊B的數據展示
來看一下xaml展示

通過ComboBox選擇來切換語言

搭建模擬業務項目
創建一個WPF App(.NET Core)應用程式
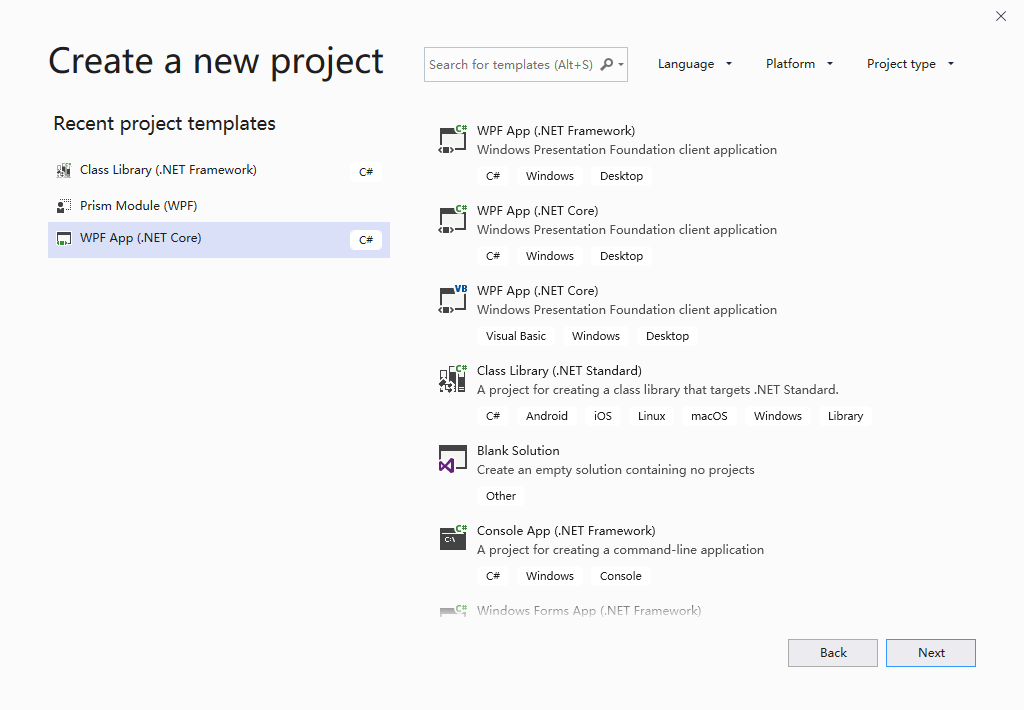
創建完成後,我們需要引入業務A模塊及業務B模塊和業務幫助模塊
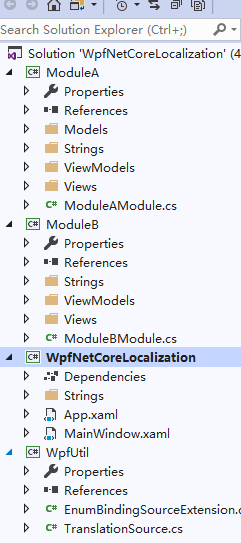
PS:根據自己的業務需要來完成項目的搭建。本教程完全適配多語言功能。
使用ResX資源文件
在各個模塊里添加Strings 文件夾用來包含 各個國家和地區的語言文件。
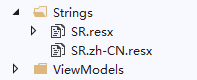
多語言可以參考:https://github.com/UnRunDeaD/WPF---Localization/blob/master/ComboListLanguages.txt
資源文件可以放在任意模塊內,比如業務模塊A ,主程式,底層業務,控制項工具集等
創建各個業務模塊資源文件
Strings文件夾可以任意命名
SR資源文件可以任意命名

幫助類
封裝到底層供各個模塊調用
public class TranslationSource : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public static TranslationSource Instance { get; } = new TranslationSource();
private readonly Dictionary<string, ResourceManager> resourceManagerDictionary = new Dictionary<string, ResourceManager>();
public string this[string key]
{
get
{
Tuple<string, string> tuple = SplitName(key);
string translation = null;
if (resourceManagerDictionary.ContainsKey(tuple.Item1))
translation = resourceManagerDictionary[tuple.Item1].GetString(tuple.Item2, currentCulture);
return translation ?? key;
}
}
private CultureInfo currentCulture = CultureInfo.InstalledUICulture;
public CultureInfo CurrentCulture
{
get { return currentCulture; }
set
{
if (currentCulture != value)
{
currentCulture = value;
// string.Empty/null indicates that all properties have changed
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(string.Empty));
}
}
}
// WPF bindings register PropertyChanged event if the object supports it and update themselves when it is raised
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public void AddResourceManager(ResourceManager resourceManager)
{
if (!resourceManagerDictionary.ContainsKey(resourceManager.BaseName))
{
resourceManagerDictionary.Add(resourceManager.BaseName, resourceManager);
}
}
public static Tuple<string, string> SplitName(string local)
{
int idx = local.ToString().LastIndexOf(".");
var tuple = new Tuple<string, string>(local.Substring(0, idx), local.Substring(idx + 1));
return tuple;
}
}
public class Translation : DependencyObject
{
public static readonly DependencyProperty ResourceManagerProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("ResourceManager", typeof(ResourceManager), typeof(Translation));
public static ResourceManager GetResourceManager(DependencyObject dependencyObject)
{
return (ResourceManager)dependencyObject.GetValue(ResourceManagerProperty);
}
public static void SetResourceManager(DependencyObject dependencyObject, ResourceManager value)
{
dependencyObject.SetValue(ResourceManagerProperty, value);
}
}
public class LocExtension : MarkupExtension
{
public string StringName { get; }
public LocExtension(string stringName)
{
StringName = stringName;
}
private ResourceManager GetResourceManager(object control)
{
if (control is DependencyObject dependencyObject)
{
object localValue = dependencyObject.ReadLocalValue(Translation.ResourceManagerProperty);
// does this control have a "Translation.ResourceManager" attached property with a set value?
if (localValue != DependencyProperty.UnsetValue)
{
if (localValue is ResourceManager resourceManager)
{
TranslationSource.Instance.AddResourceManager(resourceManager);
return resourceManager;
}
}
}
return null;
}
public override object ProvideValue(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
// targetObject is the control that is using the LocExtension
object targetObject = (serviceProvider as IProvideValueTarget)?.TargetObject;
if (targetObject?.GetType().Name == "SharedDp") // is extension used in a control template?
return targetObject; // required for template re-binding
string baseName = GetResourceManager(targetObject)?.BaseName ?? string.Empty;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(baseName))
{
// rootObject is the root control of the visual tree (the top parent of targetObject)
object rootObject = (serviceProvider as IRootObjectProvider)?.RootObject;
baseName = GetResourceManager(rootObject)?.BaseName ?? string.Empty;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(baseName)) // template re-binding
{
if (targetObject is FrameworkElement frameworkElement)
{
baseName = GetResourceManager(frameworkElement.TemplatedParent)?.BaseName ?? string.Empty;
}
}
Binding binding = new Binding
{
Mode = BindingMode.OneWay,
Path = new PropertyPath($"[{baseName}.{StringName}]"),
Source = TranslationSource.Instance,
FallbackValue = StringName
};
return binding.ProvideValue(serviceProvider);
}
}
前臺綁定
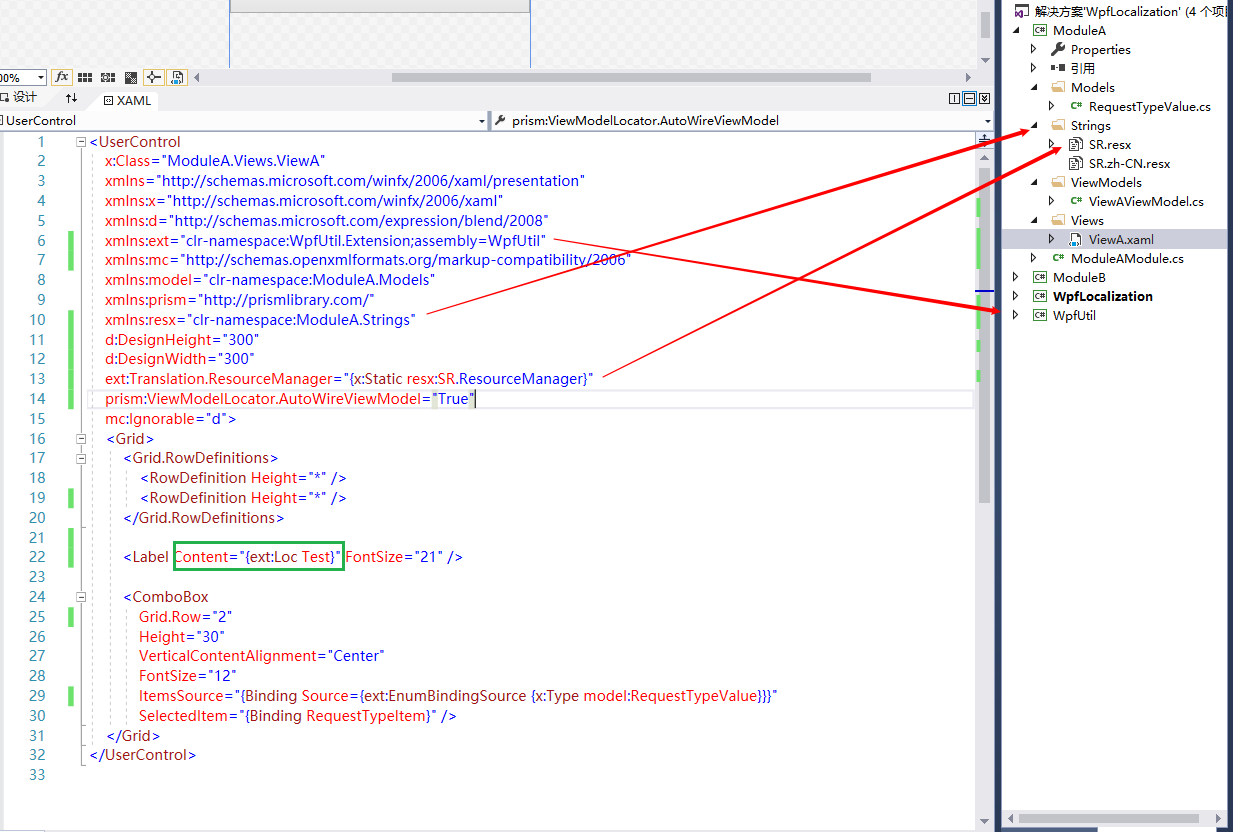
//引用業務模塊
xmlns:ext="clr-namespace:WpfUtil.Extension;assembly=WpfUtil"
// 引用剛纔你命名的文件夾名字
xmlns:resx="clr-namespace:ModuleA.Strings"
// 每個模塊通過幫助類,將當前模塊的資源類,
// 載入到資源管理集合裡面用於分配每個鍵值
// 引用剛纔你命名的資源文件名字 -> SR
ext:Translation.ResourceManager="{x:Static resx:SR.ResourceManager}"顯示文字
//讀取資源文件里的鍵值
<Label Content="{ext:Loc Test}" FontSize="21" />後臺實現
根據業務的需要,我們在界面上無法適用靜態文字顯示的,一般通過後臺代碼來完成,對於 code-behind 的變數使用,同樣可以應用於資源字典。
比如在業餘模塊代碼段里的模擬實現
// SR 是當前業務模塊的資源文件類,管理當前模塊的資源字元串。
// 根據不同的 `CurrentCulture` 選擇相對應的本地化
Message = string.Format(SR.ResourceManager.GetString("Message",Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentUICulture),System.DateTime.Now);PS: 歡迎各位大佬慷慨指點,有不足之處,請指出!有疑問,請指出,喜歡它,請支持!
下載地址
https://github.com/androllen/WpfNetCoreLocalization
相關鏈接
https://github.com/Jinjinov/wpf-localization-multiple-resource-resx-one-language/blob/master/README.md
https://codinginfinity.me/post/2015-05-10/localization_of_a_wpf_app_the_simple_approach


