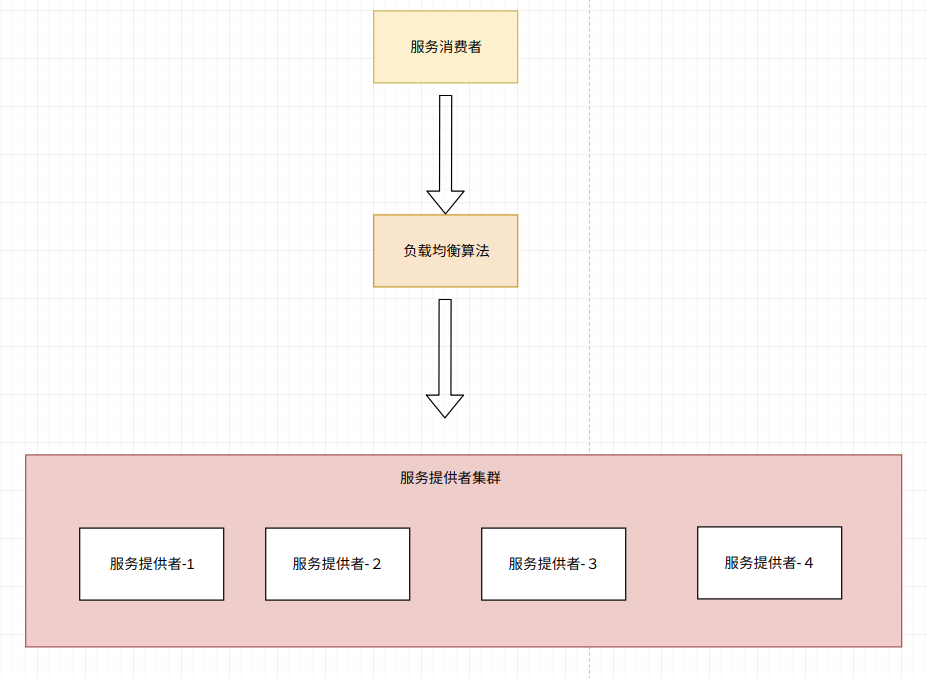
在分散式項目中,為了提高系統的可用性,服務提供者一般都會做集群處理,當其中一個服務出現宕機的時候,集群的其他服務仍然能夠提供服務,從而提高系統的可靠性。 常用的負載均衡演算法有: 隨機演算法 加權隨機演算法 輪詢演算法 加權輪詢演算法 最小時延演算法 一致性hash演算法 負載均衡追求的是每個服務提供者的負載一致 ...
在分散式項目中,為了提高系統的可用性,服務提供者一般都會做集群處理,當其中一個服務出現宕機的時候,集群的其他服務仍然能夠提供服務,從而提高系統的可靠性。
常用的負載均衡演算法有:
- 隨機演算法
- 加權隨機演算法
- 輪詢演算法
- 加權輪詢演算法
- 最小時延演算法
- 一致性hash演算法
負載均衡追求的是每個服務提供者的負載一致,不會出現負載不均衡的情況。
準備
這是一個服務提供者的POJO,包含了服務的host和port等信息
@Slf4j @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class ProviderConfig implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1; //通信host private String host; //通信埠 private Integer port; //請求介面名稱 private String interfaceName; //請求方法 private String[] methods; //應用名稱 private String application; //權重 private int weight; //調用時間 private int callTime; }
定義負載均衡策略介面
public interface LoadbalanceStrategy { //object為擴展參數 public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object); }
隨機演算法
隨機演算法,也就是從服務列表中隨機選擇一個,如果隨機數產生演算法不好,那麼就會導致出現偏向性,導致有些服務命中概率高,有的服務命中概率低,甚至有的服務命中率為0。最後會導致命中率高的時延很嚴重。
隨機演算法的優點是其實現簡單。
實現
也就是產生一個隨機數,從服務List選擇一個,很簡單的演算法。
public class RandomLoadbalanceStrategy implements LoadbalanceStrategy{ @Override public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object) { int index = new Random().nextInt(configs.size()); return configs.get(index); } }
測試
註:後面多處會使用這個方法進行測試
//strategy 負載均衡策略:隨機,加權隨機,輪詢,加權輪詢
//configNum 生產者個數
//testCount 測試次數
public void loadbalace(LoadbalanceStrategy strategy ,int configNum,int testCount ){
List<ProviderConfig> configs = new ArrayList<>();
int[] counts = new int[configNum];
for(int i = 0; i< configNum; i++){
ProviderConfig config = new ProviderConfig();
config.setInterfaceName("com.serviceImpl");
config.setHost("127.0.0.1");
config.setPort(i);
config.setWeight(new Random().nextInt(100));
configs.add(config);
}
//System.out.println(configs);
for(int i = 0; i< testCount ; i++){
ProviderConfig config = strategy.select(configs,null);
// System.out.println("選中的:"+config);
Integer count = counts[config.getPort()];
counts[config.getPort()] = ++count;
}
for(int i = 0; i< configNum; i++){
System.out.println("序號:" + i + " 權重:" + configs.get(i).getWeight() + "--次數:" + counts[i]);
}
}
執行測試
LoadbalanceStrategy strategy1 = new RandomLoadbalanceStrategy(); loadbalace(strategy1,10,1000);
輸出
隨機負載均衡.... 序號:0--次數:98 序號:1--次數:97 序號:2--次數:86 序號:3--次數:99 序號:4--次數:116 序號:5--次數:98 序號:6--次數:96 序號:7--次數:102 序號:8--次數:101 序號:9--次數:107
從測試結果來看,Jdk的隨機演算法還是比較均勻的。
加權隨機演算法
加權隨機就是在隨機演算法的基礎上,給每個服務增加一個權重,權重越大,概率越大。
在應用進行分散式部署時,機器硬體性能和環境的差異會導致服務性能出現不一致。
為瞭解決這個問題,可以給性能差的服務降低權重,給性能好的服務增加權重,以儘可能達到負載均衡的效果。
加權隨機演算法
實現

public class WeightRandomLoadbalanceStrategy implements LoadbalanceStrategy{ @Override public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object) { List<ProviderConfig> newConfigs = new ArrayList<>(); for(ProviderConfig config:configs){ for(int i = 0; i< config.getWeight(); i++){ newConfigs.add(config); } } int index = new Random().nextInt(newConfigs.size()-1); return newConfigs.get(index); } }
還是使用上面的測試代碼loadbalace(LoadbalanceStrategy strategy ,int configNum,int testCount )進行測試。
System.out.println("加權隨機負載均衡....");
LoadbalanceStrategy strategy2 = new WeightRandomLoadbalanceStrategy();
loadbalace(strategy1,10,1000);
測試結果:
加權隨機負載均衡.... 序號:0 權重:44--次數:101 序號:1 權重:27--次數:63 序號:2 權重:22--次數:47 序號:3 權重:61--次數:134 序號:4 權重:97--次數:214 序號:5 權重:38--次數:72 序號:6 權重:42--次數:79 序號:7 權重:51--次數:113 序號:8 權重:16--次數:28 序號:9 權重:67--次數:149
可以看到,權重越大,命中概率頁越大。
輪詢演算法
輪詢演算法就是,輪詢所有的服務,每個服務命中的概率都是一樣的,缺點還是和隨機演算法一樣,還是無法解決機器性能差異的問題。
實現
public class PollingLoadbalanceStrategy implements LoadbalanceStrategy { //使用一個Map來緩存每類應用的輪詢索引 private Map<String,Integer> indexMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object){ Integer index = indexMap.get(getKey(configs.get(0))); if(index == null){ indexMap.put(getKey(configs.get(0)),0); return configs.get(0); } else { index++; if(index >= configs.size()){ index = 0; } indexMap.put(getKey(configs.get(0)),index); return configs.get(index); } } public String getKey(ProviderConfig config){ return config.getInterfaceName(); } }
測試
還是使用上面的方法
System.out.println("\r\n輪詢負載均衡.....");
LoadbalanceStrategy strategy3 = new PollingLoadbalanceStrategy();
loadbalace(strategy3,10,1000);
測試結果
輪詢負載均衡..... 序號:0 權重:88--次數:100 序號:1 權重:82--次數:100 序號:2 權重:58--次數:100 序號:3 權重:68--次數:100 序號:4 權重:67--次數:100 序號:5 權重:57--次數:100 序號:6 權重:19--次數:100 序號:7 權重:43--次數:100 序號:8 權重:4--次數:100 序號:9 權重:35--次數:100
可以看到,測試1000次,每個應用命中的概率都是一樣的。
加權輪詢演算法
原理和上面的加權隨機演算法一樣
實現
public class WeightPollingLoadbalanceStrategy implements LoadbalanceStrategy { private Map<String,Integer> indexMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object){ Integer index = indexMap.get(getKey(configs.get(0))); if(index == null){ indexMap.put(getKey(configs.get(0)),0); return configs.get(0); } else { List<ProviderConfig> newConfigs = new ArrayList<>(); for(ProviderConfig config:configs){ for(int i = 0; i< config.getWeight(); i++){ newConfigs.add(config); } } index++; if(index >= newConfigs.size()){ index = 0; } indexMap.put(getKey(configs.get(0)),index); return newConfigs.get(index); } } public String getKey(ProviderConfig config){ return config.getInterfaceName(); } }
測試
System.out.println("\r\n加權輪詢負載均衡.....");
LoadbalanceStrategy strategy4 = new WeightPollingLoadbalanceStrategy();
loadbalace(strategy4,10,1000);
輸出
加權輪詢負載均衡..... 序號:0 權重:77--次數:182 序號:1 權重:75--次數:150 序號:2 權重:22--次數:44 序號:3 權重:43--次數:86 序號:4 權重:59--次數:118 序號:5 權重:10--次數:20 序號:6 權重:1--次數:2 序號:7 權重:25--次數:50 序號:8 權重:85--次數:170 序號:9 權重:89--次數:178
可以看到,權重越大,命中的概率越大。
最小時延演算法
由於機器性能的差異以及網路傳輸等原因,會導致集群中不同的應用調用時長不一樣。
如果能降低調用耗時長的應用的命中率,提高調用耗時短的命中率,達到動態調整,從而實現最終的負載均衡,那麼便可以解決以上性能差異的問題。
缺點是實現起來比較複雜,因為要計算啟動之後平均調用耗時。
實現
public class LeastActiveLoadbalanceStrategy implements LoadbalanceStrategy{ public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object){ ProviderConfig[] registryConfigs= new ProviderConfig[configs.size()]; configs.toArray(registryConfigs); Arrays.sort(registryConfigs, new Comparator<ProviderConfig>() { @Override public int compare(ProviderConfig o1, ProviderConfig o2) { if(o1.getCallTime() < o2.getCallTime()){ return -1; } else if(o1.getCallTime() == o2.getCallTime()){ return 0; } else { return 1; } } }); return registryConfigs[0]; } }
這裡使用Arrays.sort()來實現耗時排序。
測試
public void leastActiveLoadbalance(LoadbalanceStrategy strategy ,int configNum){ List<ProviderConfig> configs = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i< configNum; i++){ ProviderConfig config = new ProviderConfig(); config.setInterfaceName("com.serviceImpl"); config.setHost("127.0.0.1"); config.setPort(i); config.setWeight(i);
//這裡使用隨機數來模擬調用耗時。 config.setCallTime(new Random().nextInt(100)); configs.add(config); } for(ProviderConfig c:configs){ System.out.println("序號:" + c.getPort() +"--時延:" + c.getCallTime() ); } System.out.println("--------------"); ProviderConfig config = strategy.select(configs,null); System.out.println("最終選擇 序號:" + config.getPort() +"--時延:" + config.getCallTime() ); }
這裡使用隨機數來模擬調用耗時。
System.out.println("\r\n最小時延負載均衡.....");
LoadbalanceStrategy strategy5 = new LeastActiveLoadbalanceStrategy();
leastActiveLoadbalance(strategy5,10);
測試結果
最小時延負載均衡..... 序號:0--時延:83 序號:1--時延:3 序號:2--時延:60 序號:3--時延:52 序號:4--時延:73 序號:5--時延:74 序號:6--時延:37 序號:7--時延:59 序號:8--時延:83 序號:9--時延:2 -------------- 最終選擇 序號:9--時延:2
可以看到命中了耗時最小的應用。
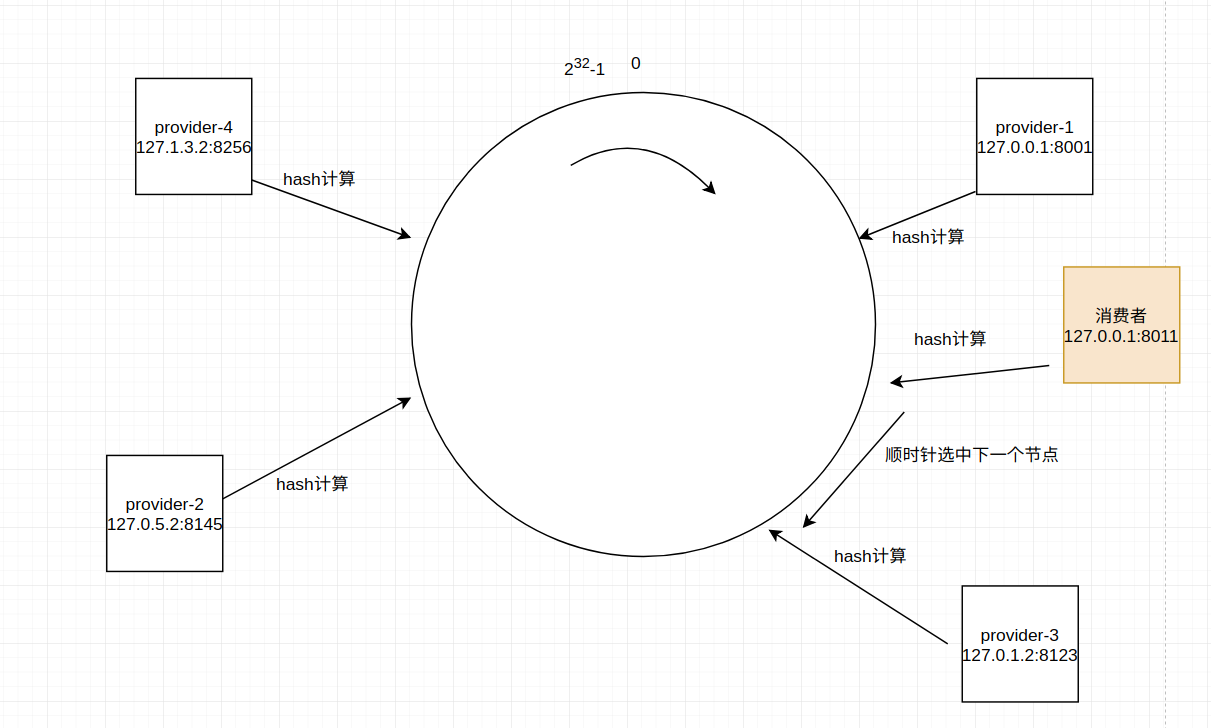
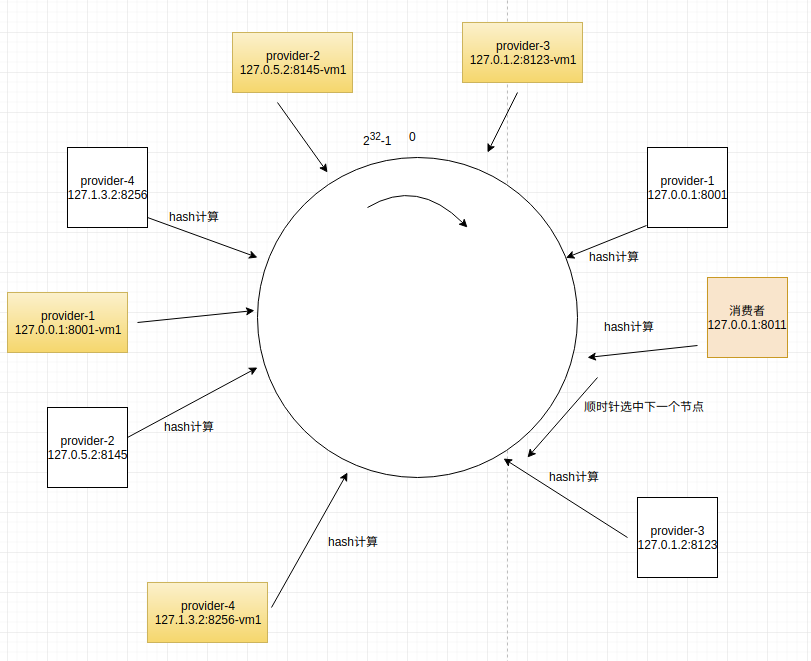
一致性hash演算法
先構造一個長度為232的整數環(這個環被稱為一致性Hash環),根據節點名稱的Hash值(其分佈為[0, 232-1])將伺服器節點放置在這個Hash環上,
然後根據數據的Key值計算得到其Hash值(其分佈也為[0, 232-1]),接著在Hash環上順時針查找距離這個Key值的Hash值最近的伺服器節點,完成Key到伺服器的映射查找。
一致性hash演算法還可以實現一個消費者一直命中一個服務提供者。
如下圖,一共有四個服務提供者
provider-1: 127.0.0.1:8001
provider-2: 127.0.5.2:8145
provider-3: 127.0.1.2:8123
provider-4: 127.1.3.2:8256
通過hash計算後,四個節點分佈在hash環的不同位置上
當有一個消費者(127.0.0.1:8011)通過hash計算後,定位到如圖中所示位置,它會順時針查找下一個節點,選擇第一個查找到的節點。
這裡存在幾個關鍵問題:
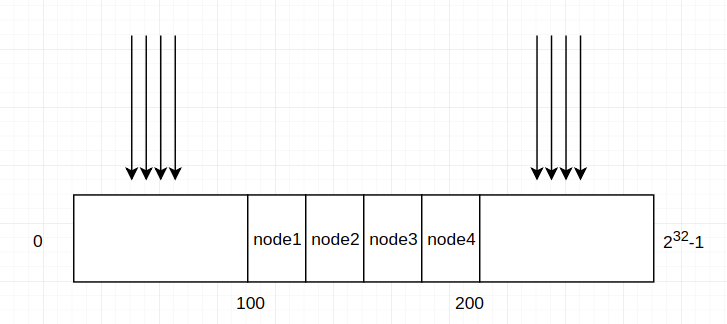
1. hash演算法的影響
如果hash演算法計算結果過於集中,如下圖,節點分佈再很小的範圍內,如果消費者大部分命中範圍之外,就會導致node1負載異常的大,出現負載不均衡的問題。
所以需要一個比較好的hash演算法。
解決這個問題的辦法是需要選擇一個好的hashcode演算法,hash演算法比較
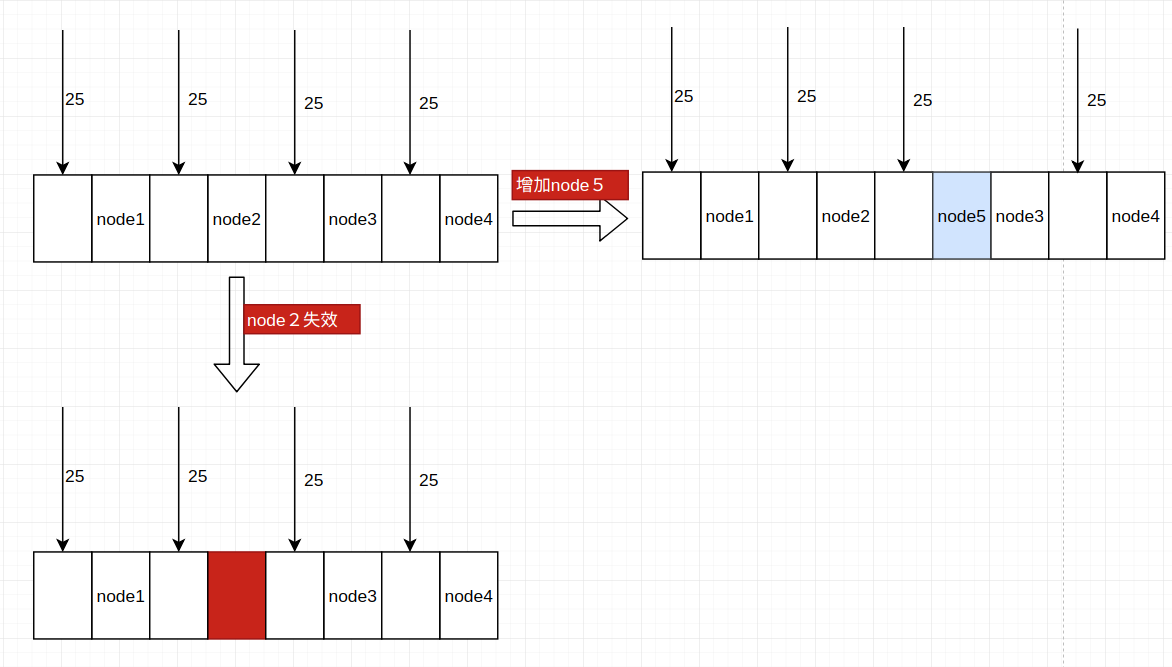
2. 增加或者刪除節點時會導致負載不均衡
如下圖:
正常情況下每個節點都是25%的命中概率
節點node2失效時,之前節點2的所有命中全部加到節點3,導致節點3的負載變大
當增加節點5時,之前節點3的命中全部給了節點5,也還是出現了負載不均衡。
解決這個問題的辦法是增加虛擬節點
如下圖,為每個節點都增加了虛擬節點,增加虛擬節點,可以使整個hash環分佈的更加均勻,但有個問題是,節點越多,維護的性能越大,因此,需要增加多少個虛擬節點,需要根據實際需要進行測試。
實現
虛擬節點的格式為 127.0.0.1:8001&&node1
分別使用jdk 的hashcode演算法和FNV1_32_HASH演算法進行比較。 .
public class UniformityHashLoadbalanceStrategy implements LoadbalanceStrategy{
private static final int VIRTUAL_NODES = 5;
public ProviderConfig select(List<ProviderConfig> configs, Object object){
SortedMap<Integer, ProviderConfig> sortedMap = new TreeMap();
for(ProviderConfig config:configs){
for(int j = 0; j < VIRTUAL_NODES; j++){
sortedMap.put(caculHash(getKey(config.getHost(),config.getPort(),"&&node"+j)),config);
}
}
System.out.println(sortedMap);
Integer requestHashcCode = caculHash((String)object);
SortedMap<Integer, ProviderConfig> subMap = sortedMap.subMap(requestHashcCode,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
ProviderConfig result= null;
if(subMap.size() != 0){
Integer index = subMap.firstKey();
result = subMap.get(index);
}
else{
result = sortedMap.get(0);
}
//// 列印測試數據
new PrintResult(sortedMap,requestHashcCode).print();
/////
return result;
}
private String getKey(String host,int port,String node){
return new StringBuilder().append(host).append(":").append(port).append(node).toString();
}
private int caculHash(String str){
/* int hashCode = str.hashCode();
hashCode = (hashCode<0)?(-hashCode):hashCode;
return hashCode;*/
final int p = 16777619;
int hash = (int)2166136261L;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
hash = (hash ^ str.charAt(i)) * p;
hash += hash << 13;
hash ^= hash >> 7;
hash += hash << 3;
hash ^= hash >> 17;
hash += hash << 5;
// 如果算出來的值為負數則取其絕對值
if (hash < 0)
hash = Math.abs(hash);
return hash;
}
}
//用於列印測試數據
@Data
class PrintResult{
private boolean flag =false;
private SortedMap<Integer, ProviderConfig> sortedMap;
private int requestHashcCode;
public PrintResult(SortedMap<Integer, ProviderConfig> sortedMap, int requestHashcCode) {
this.sortedMap = sortedMap;
this.requestHashcCode = requestHashcCode;
}
public void print(){
sortedMap.forEach((k,v)->{
if( (false == flag) && ( k > requestHashcCode)){
System.out.println("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
}
System.out.println("hashcode: " + k + " " + v.getHost()+":"+v.getPort());
if( (false == flag) && ( k > requestHashcCode)){
System.out.println("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
flag = true;
}
});
System.out.println("------------------請求的hashcode:"+requestHashcCode);
}
}
測試:
public void uniformityHashLoadbalanceStrategyTest(LoadbalanceStrategy strategy ,int configNum){ List<ProviderConfig> configs = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i< configNum; i++){ ProviderConfig config = new ProviderConfig(); config.setInterfaceName("com.serviceImpl"); config.setHost("127.0.0.1"); config.setPort(new Random().nextInt(9999)); config.setWeight(i); config.setCallTime(new Random().nextInt(100)); configs.add(config); } ProviderConfig config = strategy.select(configs,"127.0.0.1:1234"); System.out.println("選擇結果:" + config.getHost() + ":" + config.getPort()); }
System.out.println("\r\n一致性hash負載均衡.....");
uniformityHashLoadbalanceStrategyTest(new UniformityHashLoadbalanceStrategy(),10);
1. jdk 的 hashcode 演算法
hashcode: 441720772 127.0.0.1:1280 hashcode: 441720773 127.0.0.1:1280 hashcode: 441720774 127.0.0.1:1280 hashcode: 441720775 127.0.0.1:1280 hashcode: 441720776 127.0.0.1:1280 hashcode: 1307619854 127.0.0.1:3501 hashcode: 1307619855 127.0.0.1:3501 hashcode: 1307619856 127.0.0.1:3501 hashcode: 1307619857 127.0.0.1:3501 hashcode: 1307619858 127.0.0.1:3501 hashcode: 1363372970 127.0.0.1:779 hashcode: 1363372971 127.0.0.1:779 hashcode: 1363372972 127.0.0.1:779 hashcode: 1363372973 127.0.0.1:779 hashcode: 1363372974 127.0.0.1:779 hashcode: 1397780469 127.0.0.1:5928 hashcode: 1397780470 127.0.0.1:5928 hashcode: 1397780471 127.0.0.1:5928 hashcode: 1397780472 127.0.0.1:5928 hashcode: 1397780473 127.0.0.1:5928 hashcode: 1700521830 127.0.0.1:4065 hashcode: 1700521831 127.0.0.1:4065 hashcode: 1700521832 127.0.0.1:4065 hashcode: 1700521833 127.0.0.1:4065 hashcode: 1700521834 127.0.0.1:4065 hashcode: 1774961903 127.0.0.1:5931 hashcode: 1774961904 127.0.0.1:5931 hashcode: 1774961905 127.0.0.1:5931 hashcode: 1774961906 127.0.0.1:5931 hashcode: 1774961907 127.0.0.1:5931 hashcode: 1814135809 127.0.0.1:5050 hashcode: 1814135810 127.0.0.1:5050 hashcode: 1814135811 127.0.0.1:5050 hashcode: 1814135812 127.0.0.1:5050 hashcode: 1814135813 127.0.0.1:5050 hashcode: 1881959435 127.0.0.1:1991 hashcode: 1881959436 127.0.0.1:1991 hashcode: 1881959437 127.0.0.1:1991 hashcode: 1881959438 127.0.0.1:1991 hashcode: 1881959439 127.0.0.1:1991 hashcode: 1889283041 127.0.0.1:4071 hashcode: 1889283042 127.0.0.1:4071 hashcode: 1889283043 127.0.0.1:4071 hashcode: 1889283044 127.0.0.1:4071 hashcode: 1889283045 127.0.0.1:4071 hashcode: 2118931362 127.0.0.1:7152 hashcode: 2118931363 127.0.0.1:7152 hashcode: 2118931364 127.0.0.1:7152 hashcode: 2118931365 127.0.0.1:7152 hashcode: 2118931366 127.0.0.1:7152 ------------------請求的hashcode:35943393 選擇結果:127.0.0.1:1280
可以看到JDK預設的hashcode方法的問題,各個虛擬節點都是比較集中,會出現很嚴重的負載不均衡問題。
2.使用 FNV1_32_HASH演算法
hashcode: 87760808 127.0.0.1:1926
hashcode: 127858684 127.0.0.1:2285
hashcode: 137207685 127.0.0.1:4429
hashcode: 189558739 127.0.0.1:4429
hashcode: 345597173 127.0.0.1:1926
hashcode: 411873143 127.0.0.1:5844
hashcode: 427733007 127.0.0.1:4429
hashcode: 429935214 127.0.0.1:5844
hashcode: 471059330 127.0.0.1:6013
hashcode: 508134701 127.0.0.1:6141
hashcode: 537200659 127.0.0.1:4429
hashcode: 572740331 127.0.0.1:9615
hashcode: 584730561 127.0.0.1:4429
hashcode: 586630909 127.0.0.1:6013
hashcode: 588198036 127.0.0.1:6297
hashcode: 601750027 127.0.0.1:6013
hashcode: 670864146 127.0.0.1:6297
hashcode: 823792818 127.0.0.1:9615
hashcode: 832758991 127.0.0.1:2285
hashcode: 847195135 127.0.0.1:1926
hashcode: 852642706 127.0.0.1:92
hashcode: 855431312 127.0.0.1:1926
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
hashcode: 1008339891 127.0.0.1:6430
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
hashcode: 1126143483 127.0.0.1:9615
hashcode: 1127241369 127.0.0.1:9615
hashcode: 1169946536 127.0.0.1:6297
hashcode: 1184995718 127.0.0.1:92
hashcode: 1204728048 127.0.0.1:5844
hashcode: 1218277576 127.0.0.1:2285
hashcode: 1253667665 127.0.0.1:92
hashcode: 1294893013 127.0.0.1:9615
hashcode: 1334096245 127.0.0.1:2285
hashcode: 1591823392 127.0.0.1:92
hashcode: 1597482385 127.0.0.1:6141
hashcode: 1647613853 127.0.0.1:6430
hashcode: 1653621871 127.0.0.1:6013
hashcode: 1749432497 127.0.0.1:6297
hashcode: 1765516223 127.0.0.1:92
hashcode: 1860173617 127.0.0.1:6430
hashcode: 1883591368 127.0.0.1:2285
hashcode: 1941022162 127.0.0.1:6430
hashcode: 1952262824 127.0.0.1:6141
hashcode: 1991871891 127.0.0.1:1926
hashcode: 2009814649 127.0.0.1:5844
hashcode: 2011432907 127.0.0.1:6297
hashcode: 2020508878 127.0.0.1:6141
hashcode: 2083262842 127.0.0.1:6013
hashcode: 2086348077 127.0.0.1:6141
hashcode: 2107422149 127.0.0.1:6430
hashcode: 2117355968 127.0.0.1:5844
------------------請求的hashcode:986344464
選擇結果:127.0.0.1:6430
可以看到,各個虛擬節點分佈相對較散,能夠達到較好的效果。
總結
以上給了各個負載均衡演算法的實現思路和代碼實現,測試結果。
現總結如下:
隨機演算法:
好的隨機演算法可以使選擇比較均衡,但還是會出現機器性能差異導致的調用耗時不一樣。優點是實現簡單。
加權隨機演算法:
可以根據不同的機器性能調整不同的權重比,從而降低機器性能差異帶來的問題。
輪詢演算法:
可以使每個節點的選中概率一致,但也會出現隨機演算法的問題。
加權輪詢:
可以根據不同的機器性能調整不同的權重比,從而降低機器性能差異帶來的問題。
最小時延演算法:
根據服務調用耗時動態調整,可以達到比較好的負載均衡。缺點是實現比較複雜。
一致性hash演算法:
可以使消費者始終對應一個服務提供者。缺點是實現相對複雜。同時通過優化hashcode演算法和增加虛擬節點解決分佈不均的問題。
後話
以上的實現僅提供一種思路,實際使用時應該根據實際情況進行性能測試和優化。



