寫在前面 整個項目都托管在了 Github 上: 查找更方便的版本見: 這一節內容可能會用到的庫文件有 SymbolTable,同樣在 Github 上可以找到。 善用 Ctrl + F 查找題目。 習題&題解 3.1.1 題目 編寫一段程式,創建一張符號表並建立字母成績和數值分數的對應關係,如下表 ...
寫在前面
整個項目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp
查找更方便的版本見:https://alg4.ikesnowy.com/
這一節內容可能會用到的庫文件有 SymbolTable,同樣在 Github 上可以找到。
善用 Ctrl + F 查找題目。
習題&題解
3.1.1
題目
編寫一段程式,創建一張符號表並建立字母成績和數值分數的對應關係,如下表所示。從標準輸入讀取一系列字母成績,計算並列印 GPA(字母成績對應的分數的平均值)。
| A+ | A | A- | B+ | B | B- | C+ | C | C- | D | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.33 | 4.00 | 3.67 | 3.33 | 3.00 | 2.67 | 2.33 | 2.00 | 1.67 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/GPA.java.html
ST.java:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/edu/princeton/cs/algs4/ST.java.html
建立一個符號表,然後把鍵值放進去,讀取計算即可。
和上一章節用過的方法類似,先定義了一個介面 IST<Key, Value> ,包含書中提到的基本 API。
然後定義類 ST ,用標準庫裡面的 Dictionary 實現了 IST 。
代碼
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SymbolTable
{
/// <summary> 利用庫函數實現的標準符號表。 </summary>
public class ST<Key, Value> : IST<Key, Value>, IEnumerable<Key>
{
private Dictionary<Key, Value> st;
/// <summary> 新建一個符號表。 </summary>
public ST() => this.st = new Dictionary<Key, Value>();
/// <summary> 檢查符號表中是否存在與鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 對應的值。 </summary>
public virtual bool Contains(Key key) => this.st.ContainsKey(key);
/// <summary> 從符號表中刪除鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 及對應的值。 </summary>
public virtual void Delete(Key key) => this.st.Remove(key);
/// <summary> 獲取鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 對應的值,不存在時返回 null。 </summary>
public virtual Value Get(Key key) => this.st[key];
/// <summary> 獲取枚舉器。 </summary>
public IEnumerator<Key> GetEnumerator() => this.st.Keys.GetEnumerator();
/// <summary> 檢查符號表是否為空。 </summary>
public virtual bool IsEmpty() => this.st.Count == 0;
/// <summary> 獲得符號表中所有鍵的集合。 </summary>
public virtual IEnumerable<Key> Keys() => this.st.Keys;
/// <summary> 向符號表中插入新的鍵值對。 </summary>
public virtual void Put(Key key, Value value) => this.st.Add(key, value);
/// <summary> 獲取符號表中鍵值對的數量。 </summary>
public virtual int Size() => this.st.Count;
/// <summary> 獲取枚舉器。 </summary>
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() => GetEnumerator();
}
}另請參閱
3.1.2
題目
開發一個符號表的實現 ArrayST,使用(無序)數組來實現我們的基本 API。
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/ArrayST.java.html
建立兩個數組,分別存放鍵和值,一一對應。
添加時直接將新鍵值對放到數組最後即可。
刪除時將待刪除的鍵值對和位於最後的鍵值對交換,然後將其置空即可。
代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SymbolTable
{
/// <summary>
/// 符號表(數組實現)。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="Key">鍵類型。</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="Value">值類型。</typeparam>
public class ArrayST<Key, Value> : IST<Key, Value>
{
private Key[] keys; // 鍵數組
private Value[] values; // 值數組
private int n = 0; // 鍵值對數目
/// <summary>
/// 建立基於數組實現的符號表。
/// </summary>
public ArrayST() : this(8) { }
/// <summary>
/// 建立基於數組實現的符號表。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="initCapacity">初始大小。</param>
public ArrayST(int initCapacity)
{
this.keys = new Key[initCapacity];
this.values = new Value[initCapacity];
}
/// <summary>
/// 檢查鍵 <typeparamref name="Key"/> 是否存在。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">需要檢查是否存在的鍵。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(Key key) => Get(key).Equals(default(Key));
/// <summary>
/// 刪除鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 及對應的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">需要刪除的鍵。</param>
public void Delete(Key key)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
{
if (key.Equals(this.keys[i]))
{
this.keys[i] = this.keys[this.n - 1];
this.values[i] = this.values[this.n - 1];
this.keys[this.n - 1] = default(Key);
this.values[this.n - 1] = default(Value);
this.n--;
if (this.n > 0 && this.n == this.keys.Length / 4)
Resize(this.keys.Length / 2);
return;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲取鍵對應的值,若鍵不存在則返回 null。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">需要查找的鍵。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Value Get(Key key)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
if (this.keys[i].Equals(key))
return this.values[i];
return default(Value);
}
/// <summary>
/// 檢查符號表是否為空。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool IsEmpty() => this.n == 0;
/// <summary>
/// 獲得包含全部鍵的集合。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys()
{
Key[] result = new Key[this.n];
Array.Copy(this.keys, result, this.n);
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// 向符號表中插入新元素,若鍵存在將被替換。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">鍵。</param>
/// <param name="value">值。</param>
public void Put(Key key, Value value)
{
Delete(key);
if (this.n >= this.values.Length)
Resize(this.n * 2);
this.keys[this.n] = key;
this.values[this.n] = value;
this.n++;
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回符號表中鍵值對的數量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>鍵值對數量。</returns>
public int Size() => this.n;
/// <summary>
/// 為符號表重新分配空間。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="capacity">新分配的空間大小。</param>
private void Resize(int capacity)
{
Key[] tempKey = new Key[capacity];
Value[] tempValue = new Value[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
tempKey[i] = this.keys[i];
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
tempValue[i] = this.values[i];
this.keys = tempKey;
this.values = tempValue;
}
}
}另請參閱
3.1.3
題目
開發一個符號表的實現 OrderedSequentialSearchST,
使用有序鏈表來實現我們的有序符號表 API。
解答
基於無序鏈表的官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/SequentialSearchST.java.html
有序符號表的 API 見書中表 3.1.4(中文版 P230,英文版 P366)。
在官方實現的基礎上修改 Put 方法,先找到合適位置再插入新的鍵值對,保證鏈表有序。
為方便插入操作,可以使用雙向鏈表作為基礎進行實現。
表中同時維護開頭和末尾引用,加快獲得最值的速度。
代碼
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SymbolTable
{
/// <summary>
/// 基於有序鏈表的有序符號表實現。
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="Key">符號表鍵類型。</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="Value">符號表值類型。</typeparam>
public class OrderedSequentialSearchST<Key, Value> : IST<Key, Value>, IOrderedST<Key, Value>
where Key : IComparable<Key>
{
/// <summary>
/// 符號表結點。
/// </summary>
private class Node
{
public Key Key { get; set; } // 鍵。
public Value Value { get; set; } // 值。
public Node Next { get; set; } // 後繼。
public Node Prev { get; set; } // 前驅。
}
private Node first = null; // 起始結點。
private Node tail = null; // 末尾結點。
private int n = 0; // 鍵值對數量。
/// <summary>
/// 構造基於有序鏈表的有序符號表。
/// </summary>
public OrderedSequentialSearchST() { }
/// <summary>
/// 大於等於 key 的最小值。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Ceiling(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.tail;
while (pointer != null && Greater(key, pointer.Key))
pointer = pointer.Prev;
return pointer == null ? default(Key) : pointer.Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 在表中是否存在對應的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">鍵。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(Key key) => Floor(key).Equals(key);
/// <summary>
/// 從表中刪去鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 對應的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">鍵。</param>
public void Delete(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && !pointer.Key.Equals(key))
pointer = pointer.Next;
if (pointer == null)
return;
Delete(pointer);
}
/// <summary>
/// 從鏈表中刪除結點 <paramref name="node"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="node">待刪除的結點。</param>
private void Delete(Node node)
{
Node prev = node.Prev;
Node next = node.Next;
if (prev == null)
this.first = next;
else
prev.Next = next;
if (next == null)
this.tail = prev;
this.n--;
}
/// <summary>
/// 刪除最大的鍵。
/// </summary>
public void DeleteMax()
{
if (this.n == 0)
throw new Exception("ST Underflow");
Delete(this.tail);
}
/// <summary>
/// 刪除最小的鍵。
/// </summary>
public void DeleteMin()
{
if (this.n == 0)
throw new Exception("ST Underflow");
Delete(this.first);
}
/// <summary>
/// 小於等於 Key 的最大值。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Floor(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(key, pointer.Key))
pointer = pointer.Next;
return pointer == null ? default(Key) : pointer.Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲取鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 對應的值,不存在則返回 null。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">鍵。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Value Get(Key key)
{
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Greater(key, pointer.Key))
pointer = pointer.Next;
if (pointer == null)
return default(Value);
else if (pointer.Key.Equals(key))
return pointer.Value;
else
return default(Value);
}
/// <summary>
/// 符號表是否為空。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool IsEmpty() => this.n == 0;
/// <summary>
/// 獲得符號表中所有鍵的集合。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys() => this.n == 0 ? new List<Key>() : Keys(this.first.Key, this.tail.Key);
/// <summary>
/// 獲得符號表中 [<paramref name="lo"/>, <paramref name="hi"/>] 之間的鍵。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="lo">範圍起點。</param>
/// <param name="hi">範圍終點。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys(Key lo, Key hi)
{
List<Key> list = new List<Key>();
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, lo))
pointer = pointer.Next;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, hi))
{
list.Add(pointer.Key);
pointer = pointer.Next;
}
if (pointer.Key.Equals(hi))
list.Add(pointer.Key);
return list;
}
/// <summary>
/// 最大的鍵。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Max() => this.tail == null ? default(Key) : this.tail.Key;
/// <summary>
/// 最小的鍵。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Min() => this.first == null ? default(Key) : this.first.Key;
/// <summary>
/// 向符號表插入鍵值對,重覆值將被替換。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">鍵。</param>
/// <param name="value">值。</param>
public void Put(Key key, Value value)
{
Delete(key);
Node temp = new Node()
{
Key = key,
Value = value,
Prev = null,
Next = null
};
Node left = null, right = this.first;
while (right != null && Less(right.Key, temp.Key))
{
left = right;
right = right.Next;
}
Insert(left, right, temp);
if (left == null)
this.first = temp;
if (right == null)
this.tail = temp;
this.n++;
}
/// <summary>
/// 小於 Key 的鍵的數量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Rank(Key key)
{
int counter = 0;
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, key))
{
pointer = pointer.Next;
counter++;
}
return counter;
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲得排名為 k 的鍵(從 0 開始)。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="k">排名</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public Key Select(int k)
{
if (k >= this.n)
throw new Exception("k must less than ST size!");
Node pointer = this.first;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
pointer = pointer.Next;
return pointer.Key;
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲得符號表中鍵值對的數量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Size() => this.n;
/// <summary>
/// [<paramref name="lo"/>, <paramref name="hi"/>] 之間鍵的數量。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="lo">範圍起點。</param>
/// <param name="hi">範圍終點。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int Size(Key lo, Key hi)
{
int counter = 0;
Node pointer = this.first;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, lo))
pointer = pointer.Next;
while (pointer != null && Less(pointer.Key, hi))
{
pointer = pointer.Next;
counter++;
}
return counter;
}
/// <summary>
/// 鍵 <paramref name="a"/> 是否小於 <paramref name="b"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">檢查是否較小的鍵。</param>
/// <param name="b">檢查是否較大的鍵。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool Less(Key a, Key b) => a.CompareTo(b) < 0;
/// <summary>
/// 鍵 <paramref name="a"/> 是否大於 <paramref name="b"/>。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a">檢查是否較大的鍵。</param>
/// <param name="b">檢查是否較小的鍵。</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool Greater(Key a, Key b) => a.CompareTo(b) > 0;
/// <summary>
/// 將結點 <paramref name="k"/> 插入到 <paramref name="left"/> 和 <paramref name="right"/> 之間。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left">作為前驅的結點。</param>
/// <param name="right">作為後繼的結點。</param>
/// <param name="insert">待插入的結點。</param>
private void Insert(Node left, Node right, Node k)
{
k.Prev = left;
k.Next = right;
if (left != null)
left.Next = k;
if (right != null)
right.Prev = k;
}
}
}另請參閱
3.1.4
題目
開發抽象數據類型 Time 和 Event 來處理表 3.1.5 中的例子中的數據。
解答
利用 Time 類型記錄時間,用 Event 來記錄事件內容。
Time 類型包含時分秒三個 int 變數,同時實現 IComparable 介面。
Event 類型只包含事件的名稱,相當於對 string 做了一個封裝。
隨後以 Time 為鍵類型,Event 為值類型,利用上一題編寫的有序符號表進行操作。
代碼
Time 類
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace _3._1._4
{
/// <summary>
/// 時間類。
/// </summary>
public class Time : IComparable<Time>
{
public int Hour { get; set; }
public int Minute { get; set; }
public int Second { get; set; }
public Time() : this(0, 0, 0) { }
public Time(int hour, int minute, int second)
{
this.Hour = hour;
this.Minute = minute;
this.Second = second;
}
public int CompareTo(Time other)
{
int result = this.Hour.CompareTo(other.Hour);
if (result == 0)
result = this.Minute.CompareTo(other.Minute);
if (result == 0)
result = this.Second.CompareTo(other.Second);
return result;
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (this == obj)
return true;
return CompareTo((Time)obj) == 0;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
int result = 1;
result += this.Hour;
result *= 31;
result += this.Minute;
result *= 31;
result += this.Second;
return result;
}
public override string ToString()
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.Append(this.Hour < 10 ? "0" + this.Hour : this.Hour.ToString());
sb.Append(":");
sb.Append(this.Minute < 10 ? "0" + this.Minute : this.Minute.ToString());
sb.Append(":");
sb.Append(this.Second < 10 ? "0" + this.Second : this.Second.ToString());
return sb.ToString();
}
}
}Event 類
namespace _3._1._4
{
public class Event
{
public string EventMessage { get; set; }
public Event() : this(null) { }
public Event(string message)
{
this.EventMessage = message;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return this.EventMessage;
}
}
}另請參閱
3.1.5
題目
實現 SequentialSearchST 中的 size()、delete() 和 keys() 方法。
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/SequentialSearchST.java.html
size() 方法只需要直接返回當前的 n 值即可。
delete() 方法需要遍歷鏈表,找到對應結點並刪除。
keys() 方法只需要根據當前的 n 新建一個數組,把鏈表中的鍵值存入即可。
代碼
/// <summary>
/// 從表中刪去鍵 <paramref name="key"/> 及其對應的值。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">要刪除的鍵。</param>
public void Delete(Key key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key can't be null");
Node before = null, target = this.first;
while (target != null && !target.Key.Equals(key))
{
before = target;
target = target.Next;
}
if (target != null)
Delete(before, target);
}
/// <summary>
/// 從鏈表中刪除指定的結點。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="before"><paramref name="target"/> 的前驅。</param>
/// <param name="target">準備刪除的結點。</param>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">當 <paramref name="target"/> 為 <c>null</c> 時拋出此異常。</exception>
private void Delete(Node before, Node target)
{
if (target == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("target can't be null");
if (before == null)
this.first = target.Next;
else
before.Next = target.Next;
this.n--;
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲得所有的鍵。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>包含所有鍵的集合。</returns>
public IEnumerable<Key> Keys()
{
Key[] keys = new Key[this.n];
Node pointer = this.first;
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
{
keys[i] = pointer.Key;
pointer = pointer.Next;
}
return keys;
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲取符號表中的鍵值對數量。
/// </summary>
/// <returns>當前符號表中的鍵值對數量。</returns>
public int Size() => this.n;另請參閱
3.1.6
題目
用輸入中的單詞總數 W 和不同單詞總數 D 的函數給出 FrequencyCounter 調用的 put() 和 get() 方法的次數。
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
每個單詞都會被放進符號表一次,
因此 Put 的調用次數就等於單詞總數 W +1(註意尋找最大值的時候有一次 Put 調用)
對於重覆的單詞,輸入時會先調用 Get 獲得當前計數之後再 Put 回去。
尋找最大值時,對於符號表中的每個鍵值都會調用兩次 Get。
重覆的單詞數量 = (W - D)。
因此 Get 方法的調用次數 = (W - D) + 2D
3.1.7
題目
對於 N=10、10^2、10^3、10^4、10^5 和 10^6,
在 N 個小於 1000 的隨機非負整數中 FrequencyCounter 平均能夠找到多少個不同的鍵?
解答
在 FrequencyCounter 中添加一個 CountDistinct 方法,計算不重覆的鍵數。
public static int CountDistinct<TKey>(TKey[] keys, IST<TKey, int> st)
{
int distinct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < keys.Length; i++)
{
if (!st.Contains(keys[i]))
st.Put(keys[i], distinct++);
}
return distinct;
}結果如下:
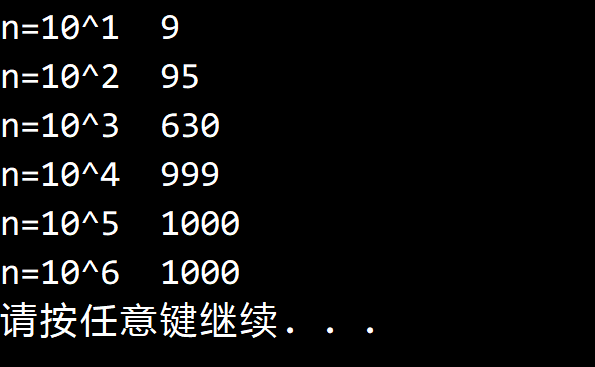
另請參閱
3.1.8
題目
在《雙城記》中,使用頻率最高的長度大於等於 10 的單詞是什麼?
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
《雙城記》:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
官網給出的數據末尾有完整的版權說明,因此使用頻率最高的單詞變成了版權方的名字 Gutenberg-tm。
去掉末尾的版權聲明之後,獲得的單詞是:Monseigneur
另請參閱
3.1.9
題目
在 FrequencyCounter 中添加追蹤 put() 方法的最後一次調用的代碼。
列印出最後插入的那個單詞以及在此之前總共從輸入中處理了多少個單詞。
用你的程式處理 tale.txt 中長度分別大於等於 1、8 和 10 的單詞。
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
《雙城記》:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
對 FrequencyCounter 做修改,在調用 Put 方法之前,將單詞記錄在字元串變數 lastPut 中。
在讀入單詞結束之後輸出 lastPut 和 words 變數。
將末尾的版權信息刪除後,得到的結果如下:
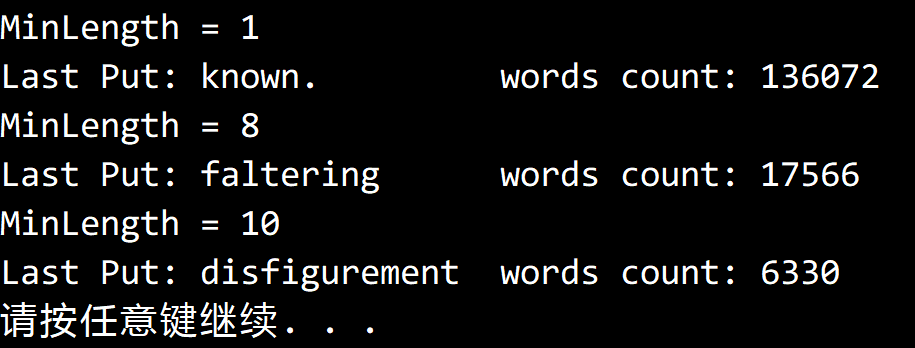
代碼
public static string MostFrequentlyWord(string filename, int minLength, IST<string, int> st)
{
int distinct = 0, words = 0;
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(filename));
string[] inputs =
sr
.ReadToEnd()
.Split(new char[] { ' ', '\r', '\n' },
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string lastPut = "";
foreach (string s in inputs)
{
if (s.Length < minLength)
continue;
words++;
if (st.Contains(s))
{
lastPut = s;
st.Put(s, st.Get(s) + 1);
}
else
{
lastPut = s;
st.Put(s, 1);
distinct++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Last Put: " + lastPut + "\t words count: " + words);
string max = "";
st.Put(max, 0);
foreach (string s in st.Keys())
if (st.Get(s) > st.Get(max))
max = s;
return max;
}另請參閱
3.1.10
題目
給出用 SequentialSearchST 將
鍵 E A S Y Q U E S T I O N 插入一個空符號表的過程的軌跡。
一共進行了多少次比較?
解答
如圖所示:

插入新的鍵值對需要遍歷整個鏈表,比較次數等於鏈表在插入前的鍵值對數目。
修改已有的鍵值對則需要遍歷鏈表直到找到該鍵值對,比較次數等於該鍵值對以及它之前所有鍵值對的數目。
共比較 0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 4 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 = 55 次。
3.1.11
題目
給出用 BinarySearchST 將鍵 E A S Y Q U E S T I O N 插入一個空符號表的過程的軌跡。
一共進行了多少次比較?
解答
鍵的軌跡如下圖所示:
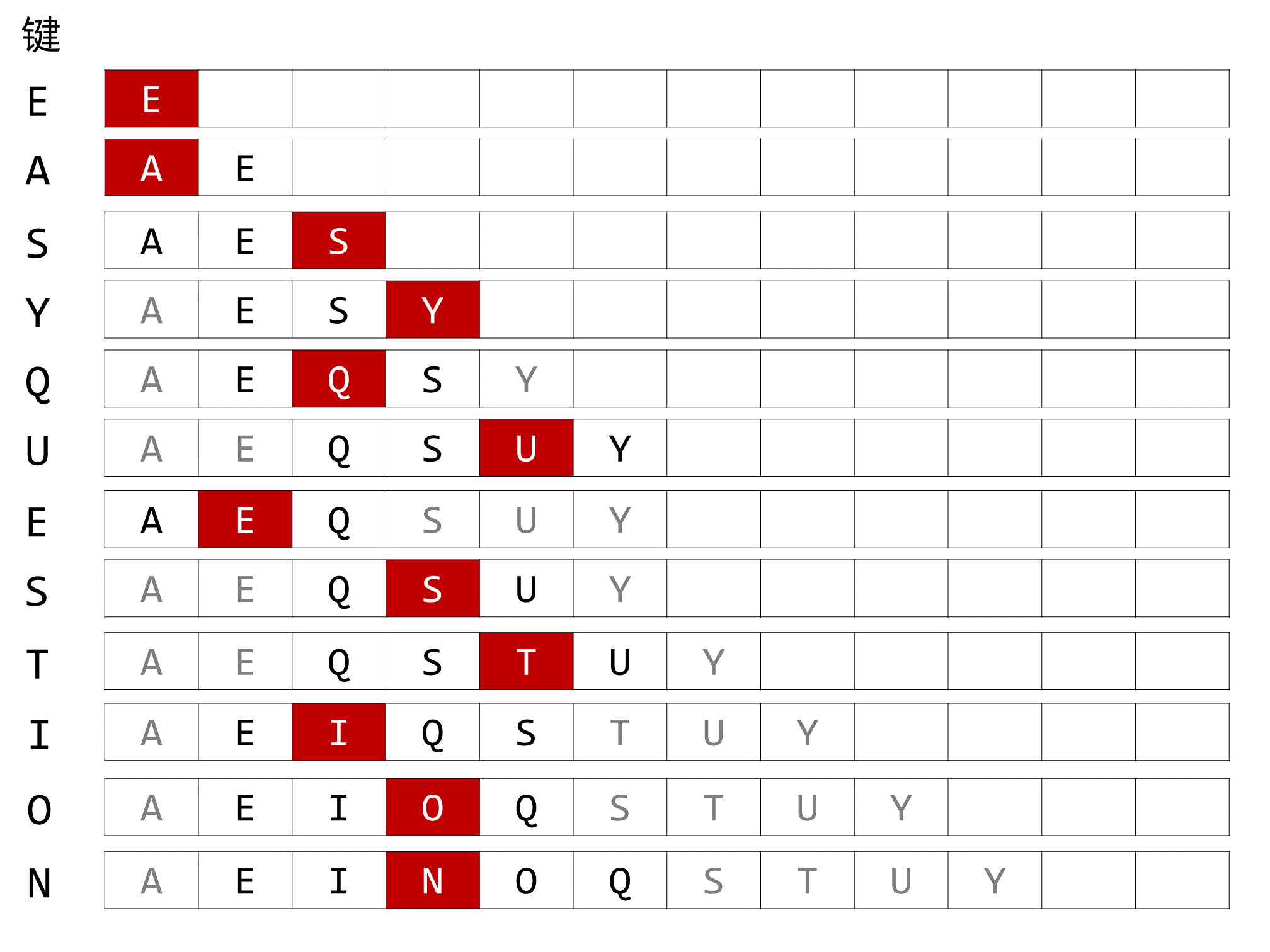
鍵查找使用二分查找優化,插入新的鍵時不必與每個鍵都進行比較。
共進行了 0 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 29 次比較。
3.1.12
題目
修改 BinarySearchST,用一個 Item 對象的數組而非兩個平行數組來保存鍵和值。
添加一個構造函數,接受一個 Item 的數組為參數並將其歸併排序。
解答
建立類 Item:
public class Item<TKey, TValue> : IComparable<Item<TKey, TValue>>
where TKey : IComparable<TKey>
{
public TKey Key { get; set; }
public TValue Value { get; set; }
public int CompareTo(Item<TKey, TValue> other)
{
return this.Key.CompareTo(other.Key);
}
}之後修改 BinarySearchST,將其中的 TKey[] keys 和 TValue[] values 數組用 Item[] items 數組代替。
例如 keys[i] 變為 items[i].Key,values[i] 變為 items[i].Value。
添加一個構造函數,調用之前編寫的歸併排序實現。
/// <summary>
/// 根據已有的鍵值對構造一個符號表。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="items">已有的鍵值對。</param>
public ItemBinarySearchST(Item<TKey, TValue>[] items)
{
this.items = new Item<TKey, TValue>[items.Length];
Array.Copy(items, this.items, items.Length);
this.n = items.Length;
MergeSort merge = new MergeSort();
merge.Sort(this.items);
}另請參閱
3.1.13
題目
對於一個會隨機混合進行 10^3 次 put() 和 10^6 次 get() 操作的應用程式,
你會使用本節中的哪種符號表的實現?說明理由。
解答
Get() 調用次數比 Put() 調用次數多了三個數量級,
BinarySearchST 和 SequentialSearchST 的平均 Put() 開銷是一樣的,
因此選擇平均 Get() 開銷更小的 BinarySearchST。
3.1.14
題目
對於一個會隨機混合進行 10^6 次 put() 和 10^3 次 get() 操作的應用程式,
你會使用本節中的哪種符號表實現?說明理由。
解答
根據上題給出的結論,選擇 BinarySearchST。
由於 BinarySearchST 和 SequentialSearchST 執行 Put() 的開銷相同
因此選擇 Get() 開銷更低的 BinarySearchST。
3.1.15
題目
假設在一個 BinarySearchST 的用常式序中,查找操作的次數是插入操作的 1000 倍。
當分別進行 10^3、10^6 和 10^9 次查找時,請估計插入操作在總耗時中的比例。
解答
假設先全部 Put(),再進行查找操作。
即分別進行 $ 1 $, $ 10 ^ 3 $, $ 10 ^ 6 $ 次插入
$ N = 1 $ 時,可以直接得出比例 $ 0.1 % $。
$ N = 10 ^ 3 $ 時,
插入耗時 $ = 1 + 2 + ... + 10 ^ 3 = 500500 $,
查詢耗時 $ = 10 ^ 6 * \lg(10 ^ 3) = 9965784 $,
比例為 $ 4.782 % $。
$ N = 10 ^ 6 $ 時
插入耗時 $ = 1 + 2 + ... + 10 ^ 6 = 500000500000 $,
查詢耗時 $ = 10 ^ 9 * \lg(10 ^ 6) = 19931568569 $,
比例為 $ 96.17 % $。
3.1.16
題目
為 BinarySearchST 實現 delete() 方法。
解答
官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/BinarySearchST.java.html
先通過二分查找獲得下標,然後後面的元素依次向前移動一位。
public void Delete(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("argument to Delete() is null");
if (IsEmpty())
return;
int i = Rank(key);
if (i == this.n && this.keys[i].CompareTo(key) != 0)
return;
for (int j = i; j < this.n - 1; j++)
{
this.keys[j] = this.keys[j + 1];
this.values[j] = this.values[j + 1];
}
this.n--;
this.keys[this.n] = default(TKey);
this.values[this.n] = default(TValue);
if (this.n > 0 && this.n == this.keys.Length / 4)
Resize(this.n / 2);
}另請參閱
3.1.17
題目
為 BinarySearchST 實現 floor() 方法。
解答
官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/BinarySearchST.java.html
先通過二分查找大於等於 key 的鍵下標 i,
如果 keys[i] 和 key 相等則直接返回 keys[i],
否則返回 keys[i-1]。
public TKey Floor(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("argument to Floor() is null");
int i = Rank(key);
if (i < this.n && this.keys[i].CompareTo(key) == 0)
return this.keys[i];
if (i == 0)
return default(TKey);
else
return this.keys[i - 1];
}另請參閱
3.1.18
題目
證明 BinarySearchST 中 rank() 方法的實現的正確性。
解答
設 key 為目標鍵。
演算法初始時 lo = 0, hi = n - 1,數組已排序。
當找到目標鍵時,返回的下標 mid 顯然是正確的。
(0...a[mid - 1] 都小於 a[mid],同時 a[mid] = key)
接下來證明:當目標鍵不存在時,lo 可以代表小於 key 的鍵的個數。
由演算法內容,當迴圈退出時,一定有 lo 和 hi 交叉,即 lo > hi。
考慮最後一次迴圈,必然執行了 lo = mid + 1 或者 hi = mid - 1。
即最後一次迴圈之後 lo = mid + 1 > hi 或 hi = mid - 1 < lo。
又由於 mid = (lo + hi) / 2,代入有:
即(lo + hi) / 2 + 1 > hi 或(lo + hi) / 2 - 1 < lo
(lo - hi) / 2 + 1 > 0 或(hi - lo) / 2 - 1 < 0
(hi - lo) / 2 < 1
hi - lo < 2
由於 hi 和 lo 都是整數,故有 hi -lo <= 1
由演算法的內容可以得出,最後一次迴圈時,
下標小於 lo 的元素都小於 key,下標大於 hi 的元素都大於 key
且下標小於 lo 的元素正好有 lo 個 (0...lo - 1)。
當 lo = hi 時,mid = lo
若 key > lo,則 lo = lo + 1,即 a[lo] 本身也小於 key。
若 key < lo,lo 不變,即 a[lo] 就是大於 key 的第一個元素。
當 lo = hi - 1 時,mid = lo
若 key > lo,則 lo = lo + 1 = hi,變為上一種情況。
若 key < lo,則 hi = lo - 1,a[lo] 是大於 key 的第一個元素。
綜上,Rank() 是正確的。
3.1.19
題目
修改 FrequencyCounter,列印出現頻率最高的所有單詞,而非之一。
提示:請用 Queue。
解答
將頻率和當前最大頻率相同的單詞都放到一個隊列里即可。
string max = "";
Queue<string> queue = new Queue<string>();
st.Put(max, 0);
foreach (string s in st.Keys())
{
if (st.Get(s) > st.Get(max))
{
max = s;
queue.Clear();
queue.Enqueue(s);
}
else if (st.Get(s) == st.Get(max))
{
queue.Enqueue(s);
}
}另請參閱
3.1.20
題目
補全命題 B 的證明(證明 N 的一般情況)。
提示:先證明 C(N) 的單調性,即對於所有的 N>0,C(N)<=C(N+1)。
解答
國內的書中關於命題 B 的證明有錯誤,新版的證明如下:

雖然新版還是有個小錯誤,$ n-2 $ 應該改為 $ k-2 $。
勘誤見:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/errata/errata-printing11.php。
先證單調性,利用數學歸納法:
已知對於 $ N=0 $,滿足 $ C(0) \le C(1) $。
假設對於 $ N=n $,滿足 $ C(n) \le C(n+1) $。
根據遞歸式,有:
\[
\begin{eqnarray*}
& C(n) & \le C(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor) + 1 \\
\\
& C(n+1) & \le
\begin{cases}
C(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor) +1 & \text{$ n $ 是偶數} \\
C(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor + 1) + 1 & \text{$ n $ 是奇數}
\end{cases}\\
\\
& C(n+2) & \le C(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor + 1) + 1
\end{eqnarray*}
\]
又 $ C(n) \le C(n+1) $ ,推出 $ C(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor) + 1 \le C(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor + 1) + 1 $。
故 $ C(n+1) \le C(n+2) \(,由數學歸納法,\) C(n) \le C(n+1) $ 成立。
已知當 $ N = 2^k - 1 $ 時,有 $ C(N) \le k = \lg(N+1) \le \lg N + 1$。
接下來證明在 $ (2^k - 1, 2^{k + 1} -1) $ 範圍內上式仍然成立。
不妨設 $ 0 < M < 2^k $ ,則有 $ 2^k - 1 < N + M < 2^{k + 1} -1 \(。 轉變為證:\) C(N+M) \le \lg (N+M) + 1 $ 。
由於 $ C(N+M) $ 是一個整數,則 $ \lfloor \lg(N+M) +1\rfloor = k+1 $。
即求證: $ C(N+M) \le k+1 $。
由單調性可得 $ C(N+M) \le C(2^{k+1} - 1) \le k+1 $,得證。
3.1.21
題目
記憶體使用。
基於 1.4 節中的假設,
對於 N 對鍵值比較 BinarySearchST 和 SequentialSearchST 的記憶體使用情況。
不需要記錄鍵值本身占用的記憶體,只統計它們的引用。
對於BinarySearchST,假設數組大小可以動態調整,
數組中被占用的空間比例為 25%~100%。
解答
BinarySearchST
包含一個鍵數組和一個值數組,以及一個 int 變數。
數組長度變化範圍為 N~4N ,故總大小:
從 2 × (24 + 8N) +4 = 52 + 16N 位元組 (100 %),
到 2 × (24 + 32N) +4 = 52 + 64N 位元組(25 %)之間變動。
SequentialSearchST
包含 N 個結點以及一個 int 變數
(16 + 8 + 8 + 8)N + 4 = 4 + 40N 位元組
3.1.22
題目
自組織查找。
自組織查找指的是一種能夠將數組元素重新排序
使得被訪問頻率較高的元素更容易被找到的查找演算法。
請修改你為習題 3.1.2 給出的答案,在每次查找命中時:
將被找到的鍵值對移動到數組的開頭,將所有中間的鍵值對向右移動一格。
這個啟髮式的過程被稱為前移編碼。
解答
對 Get() 做修改,得到 MoveToFrontArrayST。
public TValue Get(TKey key)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < this.n; i++)
if (this.keys[i].Equals(key))
break;
if (i == this.n)
return default(TValue);
TKey toFrontKey = this.keys[i];
TValue toFrontValue = this.values[i];
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
this.keys[j] = this.keys[j - 1];
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
this.values[j] = this.values[j - 1];
this.keys[0] = toFrontKey;
this.values[0] = toFrontValue;
return this.values[0];
}另請參閱
3.1.23
題目
二分查找的分析。
請證明對於大小為 N 的符號表,
一次二分查找所需的最大比較次數正好是 N 的二進位表示的位數,
因為右移一位的操作會將二進位的 N 變為二進位的 [N/2]。
解答
這裡的右移操作可以理解為 「小數點前移一位」
即數字依次向右退一位,個位上的數字被捨棄。
對於十進位,小數點前移一位會使 $ n $ 變為 $ \lfloor n / 10 \rfloor $。
同樣對於二進位就會使 $ n $ 變為 $ \lfloor n / 2 \rfloor $。
當需要除以 $ 2 $ 的 $ k $ 次冪的時候,可以用右移 $ k $ 位代替並減少時間開銷。
同理可以用左移 $ k $ 位來代替乘以 $ 2 $ 的 $ k $ 次冪。
註:
這樣會降低程式可讀性,
並且某些語言(C / C++)的編譯器已經可以自動執行這項優化了。
請充分考慮你的代碼受眾之後再決定是否採用這種寫法。
二分查找的最大查找次數 = $ \lg N + 1$ (見 3.1.20 的證明)
一個數最多被左移的次數也正好等於 $ \lfloor \lg N \rfloor + 1 $
(任意正整數都能被表示為 $ 2 ^ k + m $ 的形式,即 $ k +1 $ 位二進位數)
因此一次二分查找所需的最大比較次數正好是 $ N $ 的二進位表示的位數。
3.1.24
題目
插值法查找。
假設符號表的鍵支持算術操作(例如,它們可能是 Double 或者 Integer 類型的值)。
編寫一個二分查找來模擬查字典的行為,
例如當單詞的首字母在字母表的開頭時我們也會在字典的前半部分進行查找。
具體來說,設 klo 為符號表的第一個鍵,khi 為符號表的最後一個鍵,
當要查找 kx 時,先和 [(kx-klo)/(khi-klo)] 進行比較,而非取中間元素。
用 SearchCompare 調用 FrequencyCounter 來比較你的實現和 BinarySearchST 的性能。
解答
FrequencyCounter 的官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
二分查找總是與中間值進行比較,現在改為與數組中第 x% 位置上的元素比較。
具體而言,$ \frac{k_x-k_{lo}}{k_{hi}-k_{lo}} $ 代表數組在均勻情況下目標值 $ k_x $ 的相對位置(一個比率,在數組第 x% 的位置上)。
那麼相對應的下標就等於 $ lo+\frac{k_x-k_{lo}}{k_{hi}-k_{lo}} \times (hi - lo) $。
用這個式子代替原來的 $ mid=lo + (hi-lo)/2 $ 即可。
不難看出這種方法對於分佈相對均勻的數組比較有利,相對於二分查找而言迭代次數會少很多。
但如果數組分佈不夠均勻,也可能表現出不如二分查找的性能。
實驗結果也證實了這一判斷,就隨機數組而言,插值查找相對於二分查找只有 1% 左右的性能提升。

代碼
SearchCompare 在書中沒有出現,但可以簡單的實現為調用 FrequencyCounter 並計時的方法:
public static long Time<TKey>(IST<TKey, int> st, TKey[] keys)
{
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
FrequencyCounter.MostFrequentlyKey(st, keys);
sw.Stop();
return sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}由於這裡需要使用數字而非字元串作為鍵值,需要對官方給出的 FrequencyCounter 做一些修改:
public static TKey MostFrequentlyKey<TKey> (IST<TKey, int> st, TKey[] keys)
{
foreach (TKey s in keys)
{
if (st.Contains(s))
st.Put(s, st.Get(s) + 1);
else
st.Put(s, 1);
}
TKey max = keys[0];
foreach (TKey s in st.Keys())
if (st.Get(s) > st.Get(max))
max = s;
return max;
}另請參閱
3.1.25
題目
緩存。因為預設的 contains() 的實現中調用了 get(),
所以 FrequencyCounter 的內迴圈會將同一個鍵查找兩三遍:
if (!st.contains(word)) st.put(word, 1);
else st.put(word, st.get(word) + 1);為了能夠提高這樣的用例代碼的效率,我們可以用一種叫做緩存的技術手段,
即將訪問最頻繁的鍵的位置保存在一個變數中。
修改 SequentialSearchST 和 BinarySearchST 來實現這個點子。
解答
英文原文指的是 most recently accessed key,因此指的是最近訪問的鍵。
實現比較簡單,先在類中定義一個新的成員 cache 作為緩存,
然後修改 Get 方法,在實際查找之前先檢查緩存,如果緩存未命中則在查找之後更新它。
要註意的是緩存指向內容的有效性,在數組中指的是下標是否有效,在鏈表中指的是結點是否為空。
利用《雙城記》測試的結果:

代碼
BinarySearchST
cache 是一個 int 類型的變數,代表下標。
在二分查找前先檢查緩存,要註意cache超出數組大小的情況。
如果緩存未命中,則進行二分查找,併在返回結果前更新緩存。
public TValue Get(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("argument to Get() is null");
if (IsEmpty())
return default(TValue);
if (this.cache < this.n && this.keys[this.cache].Equals(key)) // 緩存檢查
return this.values[this.cache];
int rank = Rank(key);
if (rank < this.n && this.keys[rank].Equals(key))
{
this.cache = rank; // 更新緩存
return this.values[rank];
}
return default(TValue);
}SequentialSearchST
cache 是一個結點類型的變數,代表一個鍵值對。
類似的,在順序查找前先檢查緩存,如果緩存未命中則更新緩存。
要註意的是如果緩存的結點被刪除,需要將緩存置為 null。
Get() 方法
public TValue Get(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key can't be null");
if (this.cache != null && this.cache.Key.Equals(key)) // 檢查緩存
return this.cache.Value;
for (Node pointer = this.first; pointer != null; pointer = pointer.Next)
{
if (pointer.Key.Equals(key))
{
this.cache = pointer; // 更新緩存
return pointer.Value;
}
}
return default(TValue);
}Delete() 方法
public void Delete(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("key can't be null");
Node before = null, target = this.first;
while (target != null && !target.Key.Equals(key))
{
before = target;
target = target.Next;
}
if (target == this.cache) // 刪除緩存
this.cache = null;
if (target != null)
Delete(before, target);
}另請參閱
3.1.26
題目
基於字典的頻率統計。
修改 FrequencyCounter,接受一個字典文件作為參數,
統計標準輸入中出現在字典中的單詞的頻率,並將單詞和頻率列印為兩張表格,
一張按照頻率高低排序,一張按照字典順序排序。
解答
字典文件:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/web2.txt
《雙城記》:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
瀏覽器可能會直接打開 txt,此時右鍵鏈接-目標另存為即可下載。
FrequencyCounter 的官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/FrequencyCounter.java.html
我們利用 BinarySearchST 會自動對鍵排序的性質來實現字典序排序。
首先將字典存到一個符號表中,按照 “單詞-序號” 的形式保存。
然後讀入文件,如果讀入的單詞存在於字典中,
則將其以 “序號-單詞” 的形式存到 BinarySearchST 中去。
讀入完畢後,遍歷 BinarySearchST 即可獲得字典序的單詞列表。
對於按頻率排序,我們基於已有的實現修改。
在每次取得最大值之後,輸出並刪除最大值,如此迴圈即可獲得頻率排序的單詞序列。
也可以將單詞-頻率序列全部讀出來存放到數組之中,然後用第二章的排序演算法排序。
測試結果,取 minLength = 13,只截取了部分。
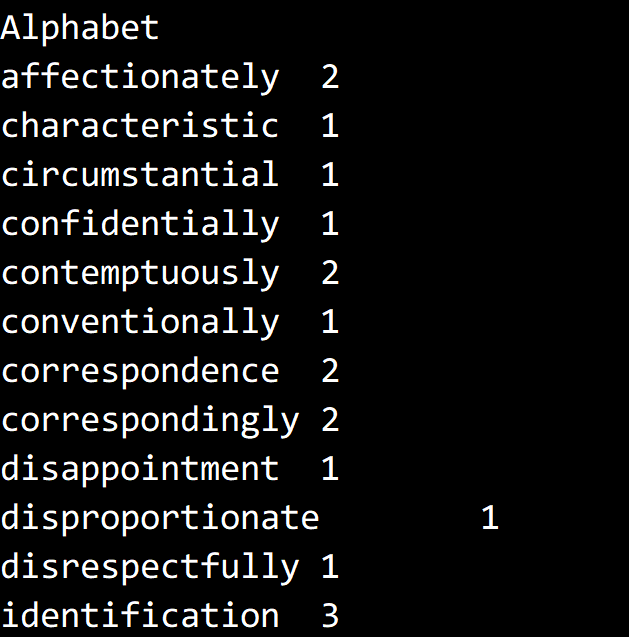
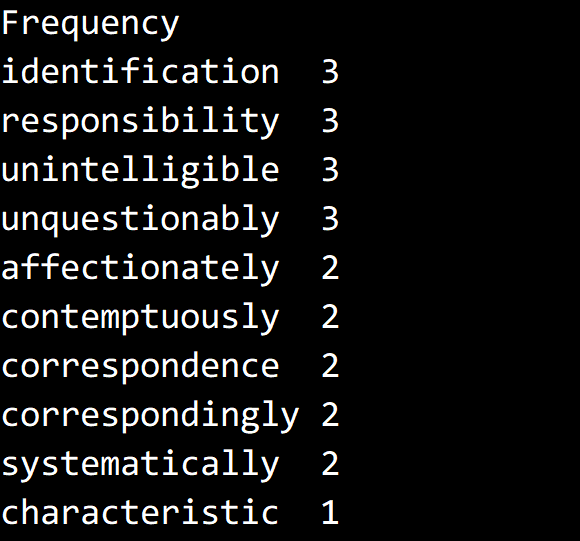
代碼
public static void LookUpDictionary(string filename, string dictionaryFile, int minLength)
{
// 初始化字典
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(dictionaryFile));
string[] words = sr.ReadToEnd().Split(new char[] { ' ', '\r', '\n' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
BinarySearchST<string, int> dictionary = new BinarySearchST<string, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.Length; i++)
{
if (words[i].Length > minLength)
dictionary.Put(words[i], i);
}
sr.Close();
// 讀入單詞
StreamReader srFile = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(filename));
string[] inputs = srFile.ReadToEnd().Split(new char[] { ' ', '\r', '\n' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
srFile.Close();
BinarySearchST<int, string> stDictionary = new BinarySearchST<int, string>();
BinarySearchST<string, int> stFrequency = new BinarySearchST<string, int>();
foreach (string s in inputs)
{
if (stFrequency.Contains(s))
stFrequency.Put(s, stFrequency.Get(s) + 1);
else if (dictionary.Contains(s))
{
stFrequency.Put(s, 1);
stDictionary.Put(dictionary.Get(s), s);
}
}
// 輸出字典序
Console.WriteLine("Alphabet");
foreach (int i in stDictionary.Keys())
{
string s = stDictionary.Get(i);
Console.WriteLine(s + "\t" + stFrequency.Get(s));
}
// 頻率序
Console.WriteLine("Frequency");
int n = stFrequency.Size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string max = "";
stFrequency.Put(max, 0);
foreach (string s in stFrequency.Keys())
if (stFrequency.Get(s) > stFrequency.Get(max))
max = s;
Console.WriteLine(max + "\t" + stFrequency.Get(max));
stFrequency.Delete(max);
}
}另請參閱
3.1.27
題目
小符號表。
假設一段 BinarySearchST 的用例插入了 N 個不同的鍵並會進行 S 次查找。
當構造表的成本和所有查找的總成本相同時,給出 S 的增長數量級。
解答
事實上就是說,先構造一個包含 N 個不重覆鍵的符號表,然後進行 S 次查找。
給出 S 的增長數量級,使得構造符號表的成本和查找的成本相同。
這裡假設一次數組交換和一次比較的成本是相同的。
先考慮構造符號表的成本,一次 Put() 需要調用一次 Rank() 和一次插入操作。
2.1 節插入排序的命題 B 給出了每次插入平均需要移動一半的數組元素的結論。
於是構造符號表所需的成本約為:$n\lg n + \frac{1}{2}\sum_{k=1}^{n} k=n\lg n + \frac{n(n-1)}{4} $ 。
這裡查找的成本是這麼計算的:$ \lg0+\lg1+\cdots+\lg n < n\lg n $
查找所需的成本比較簡單,一次二分查找的比較次數約為 $ \lg n $,總成本就是 $ S\lg n $ 。
令兩邊相等,解方程即可得到 $ S=n+\frac{n(n-1)}{4\lg n} $ 。
如果用大 O 記法,也可以記為 $ O(n^2 / \lg n) $,如果要選擇一個比較常用的上界則可以選擇 $ O(n^2) $。
實驗結果,兩邊的成本是很接近的:

另請參閱
3.1.28
題目
有序的插入。
修改 BinarySearchST,使得插入一個比當前所有鍵都大的鍵只需要常數時間
(這樣在構造符號表時有序的使用 put() 插入鍵值對就只需要線性時間了)。
解答
將重新分配數組空間的代碼提前,然後添加判斷語句即可。
BinarySearchSTOrderedInsertion:
/* 省略 */
if (this.n == this.keys.Length)
Resize(this.n * 2);
// 如果插入的鍵比所有鍵都大則直接插入末尾。
if (this.n == 0 || this.keys[this.n - 1].CompareTo(key) < 0)
{
this.keys[this.n] = key;
this.values[this.n] = value;
this.n++;
return;
}
int i = Rank(key);
/* 省略 */另請參閱
3.1.29
題目
測試用例。
編寫一段測試代碼 TestBinarySearch.java
用來測試正文中
min()、max()、floor()、ceiling()、select()、rank()、deleteMin()、deleteMax() 和 keys() 的實現。
可以參考 3.1.3.1 節的索引用例,添加代碼使其在適當的情況下接受更多的命令行參數。
解答
官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/TestBinarySearchST.java.html
官方實現中有幾處錯誤,需要做一些修改。
/* 省略 */
Console.WriteLine("Testing Select()");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < st.Size(); i++) // 迴圈條件不能有 '='
Console.WriteLine(i + " " + st.Select(i));
Console.WriteLine();
/* 省略 */
while (!st.IsEmpty())
st.Delete(st.Select(st.Size() / 2));
Console.WriteLine("After deleting the remaining keys");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------");
// 異常處理
try
{
foreach (string s in st.Keys())
Console.WriteLine(s + " " + st.Get(s));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception: " + ex.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine();
/* 省略 */結果如下:
size = 10
min = A
max = X
Testing Keys()
-----------------------------------
A 8
C 4
E 12
H 5
L 11
M 9
P 10
R 3
S 0
X 7
Testing Select()
-----------------------------------
0 A
1 C
2 E
3 H
4 L
5 M
6 P
7 R
8 S
9 X
key Rank Floor Ceil
-----------------------------------
A 0 A A
B 1 A C
C 1 C C
D 2 C E
E 2 E E
F 3 E H
G 3 E H
H 3 H H
I 4 H L
J 4 H L
K 4 H L
L 4 L L
M 5 M M
N 6 M P
O 6 M P
P 6 P P
Q 7 P R
R 7 R R
S 8 S S
T 9 S X
U 9 S X
V 9 S X
W 9 S X
X 9 X X
Y 10 X
Z 10 X
After deleting the smallest 3 keys
-----------------------------------
H 5
L 11
M 9
P 10
R 3
S 0
X 7
After deleting the remaining keys
-----------------------------------
Exception: called Min() with empty table
After adding back N keys
-----------------------------------
A 8
C 4
E 12
H 5
L 11
M 9
P 10
R 3
S 0
X 7另請參閱
3.1.30
題目
驗證。
向 BinarySearchST 加入斷言(assert)語句,
在每次插入和刪除數據後檢查演算法的有效性和數據結構的完整性。
例如,對於每個索引必有 i==rank(select(i)) 且數組應該總是有序的。
解答
官方實現:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/31elementary/BinarySearchST.java.html。
首先在 BinarySearchST



