一、前言 flask中有很多可擴展點(筆者這樣稱呼),其中包含了信號和請求鉤子,這些信號和鉤子有什麼用呢?其主要作用用於幫助我們進行程式的耦合性,當然還可以讓我們自定義一些行為。話不多說,通過閱讀源碼,筆者將這些所有的可擴展點的執行順序進行總結(如下圖),這樣我們更能清楚的知道flask的內部請求流 ...
一、前言
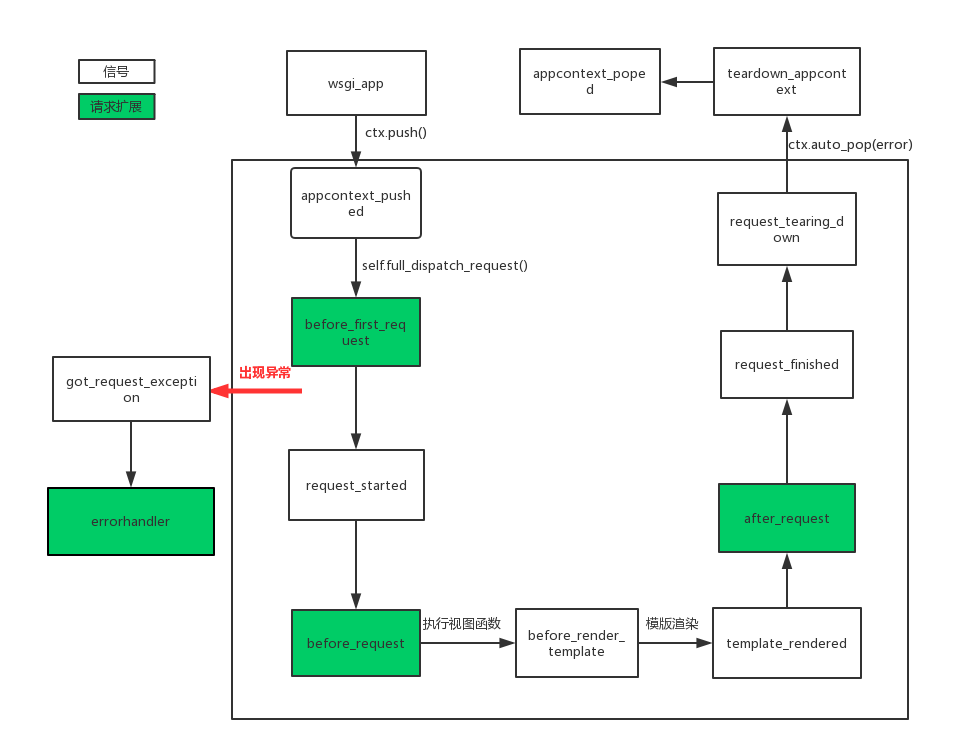
flask中有很多可擴展點(筆者這樣稱呼),其中包含了信號和請求鉤子,這些信號和鉤子有什麼用呢?其主要作用用於幫助我們進行程式的耦合性,當然還可以讓我們自定義一些行為。話不多說,通過閱讀源碼,筆者將這些所有的可擴展點的執行順序進行總結(如下圖),這樣我們更能清楚的知道flask的內部請求流程,後面將對信號以及源碼流程做說明,最後以下所有內容都是基於flask版本為1.0.2。重要:信號的觸發可以在任何時候,以下流程只是源碼的觸發順序。
二、信號
在django中同樣也有信號,但django中是內置的,而Flask框架中的信號基於blinker,所以我們在使用flask信號時候需安裝blinker。
pip3 install blinker
flask中所有的信號在其源碼中都有定義:
request_started = _signals.signal('request-started') # 請求到來前執行 request_finished = _signals.signal('request-finished') # 請求結束後執行 before_render_template = _signals.signal('before-render-template') # 模板渲染前執行 template_rendered = _signals.signal('template-rendered') # 模板渲染後執行 got_request_exception = _signals.signal('got-request-exception') # 請求執行出現異常時執行 request_tearing_down = _signals.signal('request-tearing-down') # 請求執行完畢後自動執行(無論成功與否) appcontext_tearing_down = _signals.signal('appcontext-tearing-down')# 應用上下文執行完畢後自動執行(無論成功與否) appcontext_pushed = _signals.signal('appcontext-pushed') # 應用上下文push時執行 appcontext_popped = _signals.signal('appcontext-popped') # 應用上下文pop時執行 message_flashed = _signals.signal('message-flashed') # 調用消息閃現時,自動觸發
如何使用
使用信號的 connect() 方法訂閱該信號,該方法的第一個參數是當信號發出時所調用的函數。第二個參數是可選參數,定義一個發送者。使用 disconnect() 方法可以退訂信號。
示例:
from flask import Flask, signals, request app = Flask(import_name=__name__) def check_host(app, *args): print(app.config['DEBUG']) print("host is :", request.host) signals.request_started.connect(receiver=check_host) # 請求之前發送信號檢查請求的host @app.route("/") def index(): return 'index' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run() #結果 False host is : 127.0.0.1:5000
在新的版本中還可以使用connect_via信號裝飾器來訂閱信號,以下代碼可以修改為:
from flask import Flask, signals, request app = Flask(import_name=__name__) @signals.request_started.connect_via(app) def check_host(app, *args): print(app.config['DEBUG']) print("host is :", request.host) @app.route("/") def index(): return 'index' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
自定義信號
自定義信號允許我們能跟多進行自定義操作,在自定義信號步驟:
- 定義信號
- 訂閱信號
- 觸發信號
示例:
rom flask import Flask from blinker import Namespace app = Flask(import_name=__name__) model_signals=Namespace() # 定義信號 model_update = model_signals.signal(name='model_update') #觸發信號是對應的操作 def logging(arg): print(arg) print('write log..') #訂閱信號 model_update.connect(logging) @app.route("/") def index(): # 觸發信號 model_update.send('save model') return 'index' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run() 結果: save model write log..
三、源碼流程
在熟悉源碼之前,你需要瞭解下flask的上線文管理,請移步這裡, 之前在請求上下文源碼中就介紹了請求進來會到wsgi_app,以下是源碼定義:
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response): """The actual WSGI application. This is not implemented in :meth:`__call__` so that middlewares can be applied without losing a reference to the app object. Instead of doing this:: app = MyMiddleware(app) It's a better idea to do this instead:: app.wsgi_app = MyMiddleware(app.wsgi_app) Then you still have the original application object around and can continue to call methods on it. .. versionchanged:: 0.7 Teardown events for the request and app contexts are called even if an unhandled error occurs. Other events may not be called depending on when an error occurs during dispatch. See :ref:`callbacks-and-errors`. :param environ: A WSGI environment. :param start_response: A callable accepting a status code, a list of headers, and an optional exception context to start the response. """ ctx = self.request_context(environ) error = None try: try: ctx.push() #存儲請求上下文 response = self.full_dispatch_request() #處理請求,執行視圖函數,返迴響應 except Exception as e: error = e response = self.handle_exception(e) # 處理異常 except: error = sys.exc_info()[1] raise return response(environ, start_response) #返回給客戶端 finally: if self.should_ignore_error(error): error = None ctx.auto_pop(error) #刪除棧中的請求上下文
在wsgi_app中會執行ctx.push方法將上線問push到棧中,此時觸發1.appcontext_pushed,以下是源碼部分:
def push(self): """Binds the app context to the current context.""" self._refcnt += 1 if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'): sys.exc_clear() _app_ctx_stack.push(self) appcontext_pushed.send(self.app) #觸發appcontext_pushed信號
接著執行self.full_dispatch_request(),在改方法中主要是用於請求預處理、以及更具路由匹配執行視圖函數,下麵其源碼:
def full_dispatch_request(self): """Dispatches the request and on top of that performs request pre and postprocessing as well as HTTP exception catching and error handling. .. versionadded:: 0.7 """ self.try_trigger_before_first_request_functions() #執行請求擴展before_first_request try: request_started.send(self) #觸發request_started信號 rv = self.preprocess_request() if rv is None: rv = self.dispatch_request() except Exception as e: rv = self.handle_user_exception(e) #處理異常 return self.finalize_request(rv) #最後對請求進行最後的處理
這裡面執行請求擴展2.before_first_request,然後觸發信號3.request_started信號,接著執行self.preprocess_request()進行請求預處理,源碼:
bp = _request_ctx_stack.top.request.blueprint funcs = self.url_value_preprocessors.get(None, ()) if bp is not None and bp in self.url_value_preprocessors: funcs = chain(funcs, self.url_value_preprocessors[bp]) for func in funcs: func(request.endpoint, request.view_args) funcs = self.before_request_funcs.get(None, ()) #執行請求擴展before_request if bp is not None and bp in self.before_request_funcs: funcs = chain(funcs, self.before_request_funcs[bp]) for func in funcs: rv = func() if rv is not None: return rv
在視圖函數中如果使用了render_template(模版渲染),我們來看下其渲染方法:
def _render(template, context, app): """Renders the template and fires the signal""" before_render_template.send(app, template=template, context=context) # 觸發before_render_template信號 rv = template.render(context) # 模版渲染 template_rendered.send(app, template=template, context=context) ## 觸發template_rendered信號 return rv
渲染模版時候分別觸發5.before_render_template以及6.template_rendered信號,在執行wsgi_app中的self.finalize_request(rv)對請求做最後的處理,源碼:
def finalize_request(self, rv, from_error_handler=False): """Given the return value from a view function this finalizes the request by converting it into a response and invoking the postprocessing functions. This is invoked for both normal request dispatching as well as error handlers. Because this means that it might be called as a result of a failure a special safe mode is available which can be enabled with the `from_error_handler` flag. If enabled, failures in response processing will be logged and otherwise ignored. :internal: """ response = self.make_response(rv) try: response = self.process_response(response) #處理響應 request_finished.send(self, response=response) # 觸發request_finished信號 except Exception: if not from_error_handler: raise self.logger.exception('Request finalizing failed with an ' 'error while handling an error') return response
在觸發request_finished之前會執行self.process_response,源碼:
def process_response(self, response): """Can be overridden in order to modify the response object before it's sent to the WSGI server. By default this will call all the :meth:`after_request` decorated functions. .. versionchanged:: 0.5 As of Flask 0.5 the functions registered for after request execution are called in reverse order of registration. :param response: a :attr:`response_class` object. :return: a new response object or the same, has to be an instance of :attr:`response_class`. """ ctx = _request_ctx_stack.top #獲取請求上下文 bp = ctx.request.blueprint # 獲取藍圖 funcs = ctx._after_request_functions if bp is not None and bp in self.after_request_funcs: funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[bp]))#執行請求擴張after_request if None in self.after_request_funcs: funcs = chain(funcs, reversed(self.after_request_funcs[None])) for handler in funcs: response = handler(response) if not self.session_interface.is_null_session(ctx.session): self.session_interface.save_session(self, ctx.session, response) # 保存session return response
所以這裡先執行了請求擴展7.after_request然後觸發信號8.request_finished信號,當在處理請求時候出現異常則會執行self.handle_exception(e),源碼:
def handle_exception(self, e): """Default exception handling that kicks in when an exception occurs that is not caught. In debug mode the exception will be re-raised immediately, otherwise it is logged and the handler for a 500 internal server error is used. If no such handler exists, a default 500 internal server error message is displayed. .. versionadded:: 0.3 """ exc_type, exc_value, tb = sys.exc_info() got_request_exception.send(self, exception=e) #觸發got_request_exception信號 handler = self._find_error_handler(InternalServerError()) if self.propagate_exceptions: # if we want to repropagate the exception, we can attempt to # raise it with the whole traceback in case we can do that # (the function was actually called from the except part) # otherwise, we just raise the error again if exc_value is e: reraise(exc_type, exc_value, tb) else: raise e self.log_exception((exc_type, exc_value, tb)) if handler is None: return InternalServerError() return self.finalize_request(handler(e), from_error_handler=True)在源碼中我們看到,這裡會觸發got_request_exception信號,當然之後會執行errorhandler請求擴展,最後執行ctx.auto_pop(error)也就是從棧中pop出上下文,源碼:
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel): """Pops the request context and unbinds it by doing that. This will also trigger the execution of functions registered by the :meth:`~flask.Flask.teardown_request` decorator. .. versionchanged:: 0.9 Added the `exc` argument. """ app_ctx = self._implicit_app_ctx_stack.pop() try: clear_request = False if not self._implicit_app_ctx_stack: self.preserved = False self._preserved_exc = None if exc is _sentinel: exc = sys.exc_info()[1] self.app.do_teardown_request(exc) # 觸發request_tearing_down信號 # If this interpreter supports clearing the exception information # we do that now. This will only go into effect on Python 2.x, # on 3.x it disappears automatically at the end of the exception # stack. if hasattr(sys, 'exc_clear'): sys.exc_clear() request_close = getattr(self.request, 'close', None) if request_close is not None: request_close() clear_request = True finally: rv = _request_ctx_stack.pop() # get rid of circular dependencies at the end of the request # so that we don't require the GC to be active. if clear_request: rv.request.environ['werkzeug.request'] = None # Get rid of the app as well if necessary. if app_ctx is not None: app_ctx.pop(exc) #觸發teardown_appcontext信號 assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong request context. ' \ '(%r instead of %r)' % (rv, self)
此時會觸發9.request_tearing_down信號,然後執行到app_ctx.pop(exc):
def pop(self, exc=_sentinel): """Pops the app context.""" try: self._refcnt -= 1 if self._refcnt <= 0: if exc is _sentinel: exc = sys.exc_info()[1] self.app.do_teardown_appcontext(exc) #觸發teardown_appcontext信號 finally: rv = _app_ctx_stack.pop() assert rv is self, 'Popped wrong app context. (%r instead of %r)' \ % (rv, self) appcontext_popped.send(self.app) # 觸發appcontext_poped信號
到pop app_ctx是先觸發了10.teardown_appcontext信號再觸發11.appcontext_poped信號,到此整個flask的所有信號以及所有可擴展點的所有順序執行完畢。
最後,整體的執行順序的流程圖我已經在最開始放上了。



